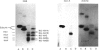Abstract
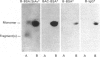
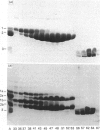
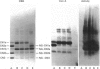
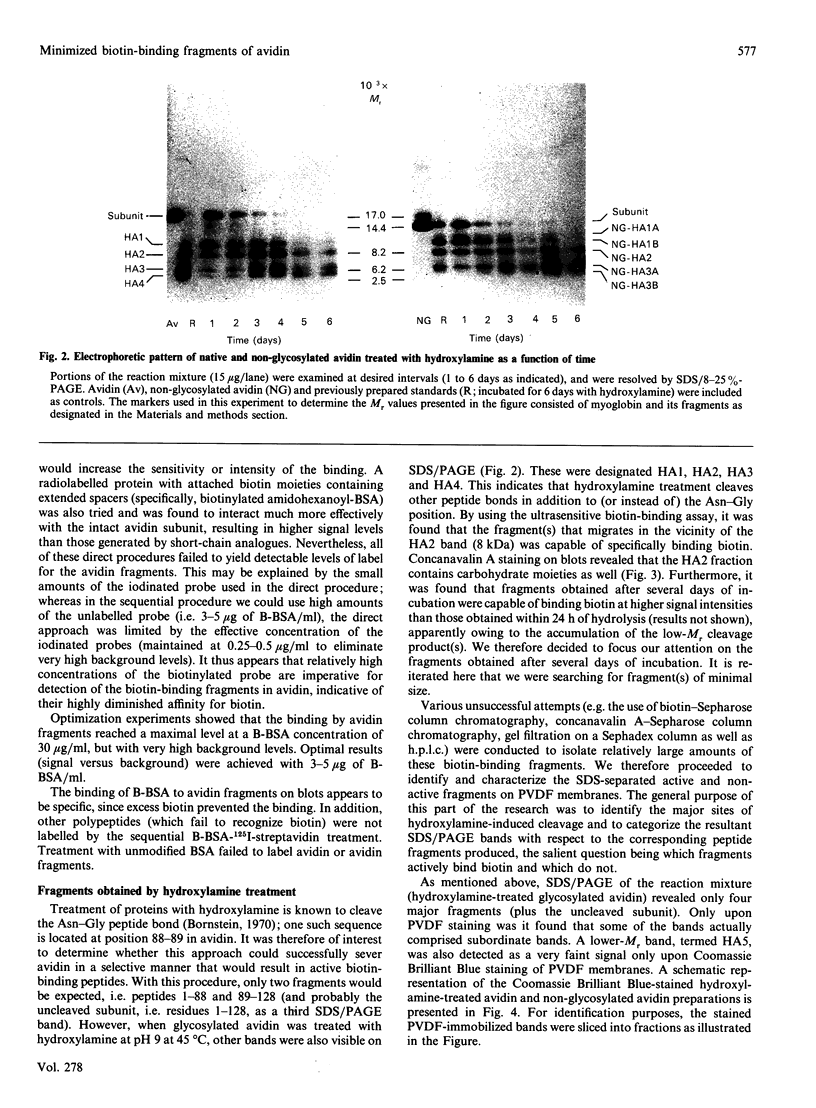
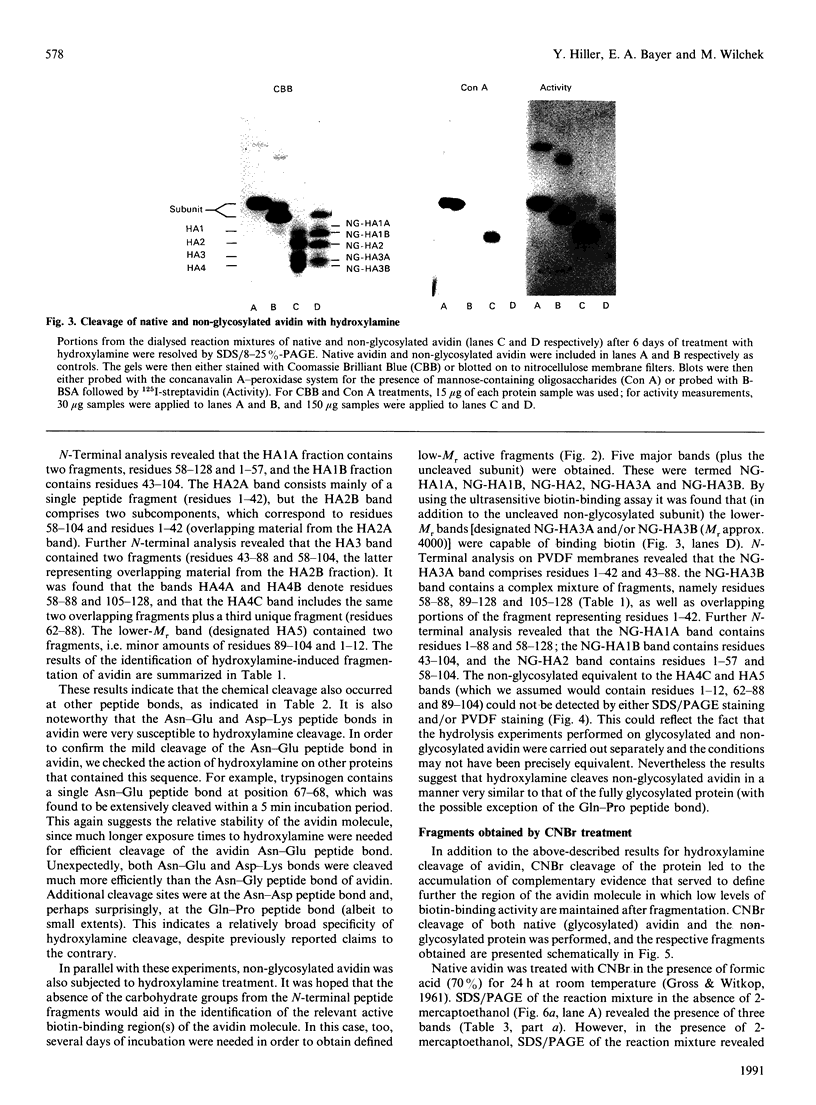
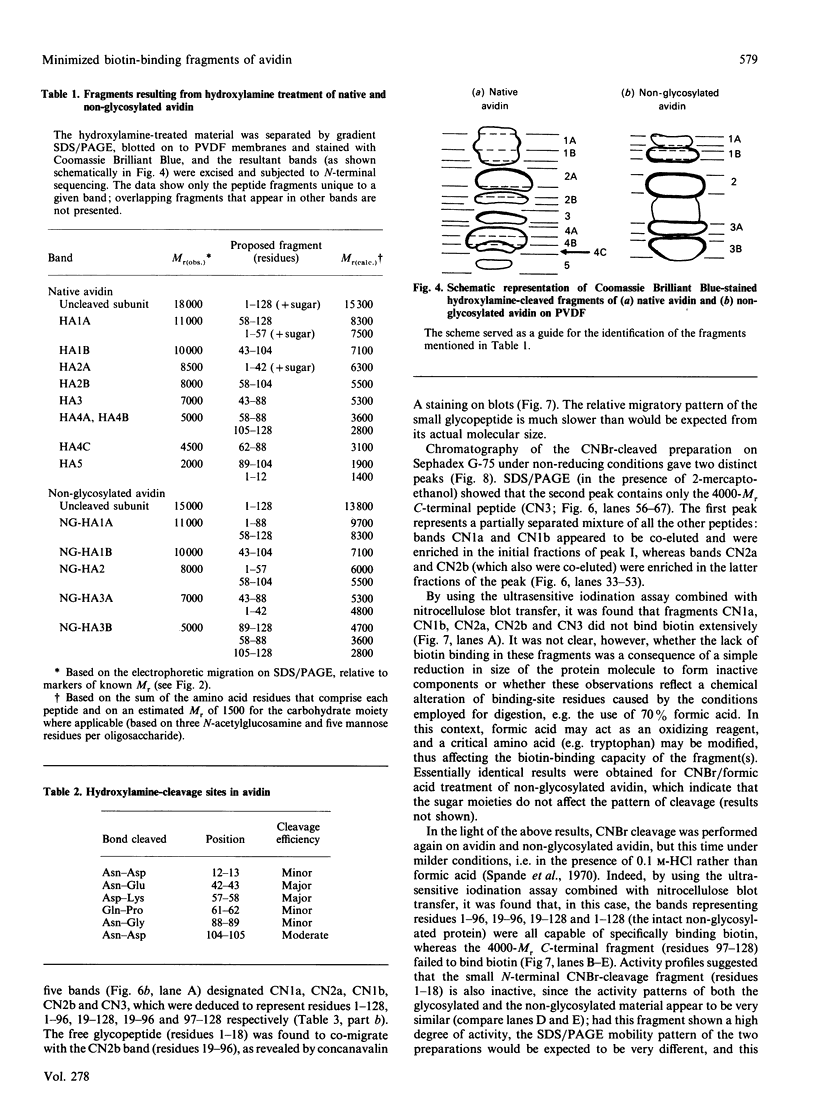
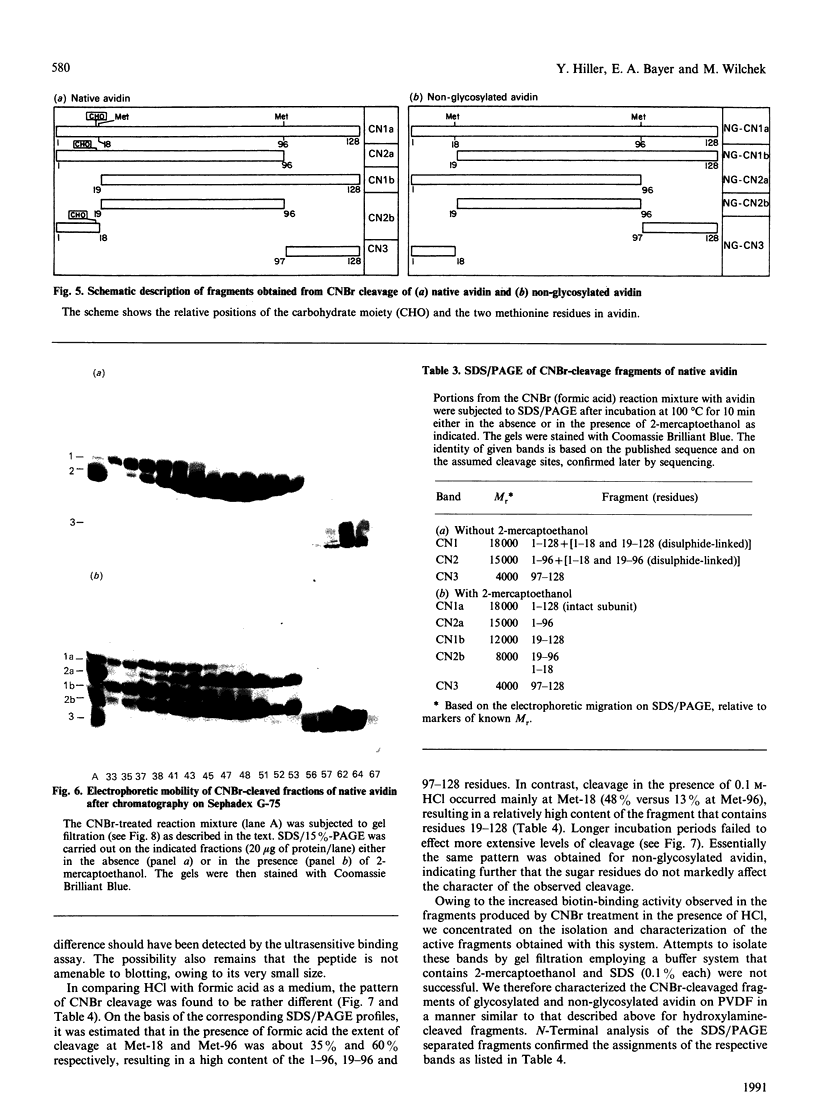
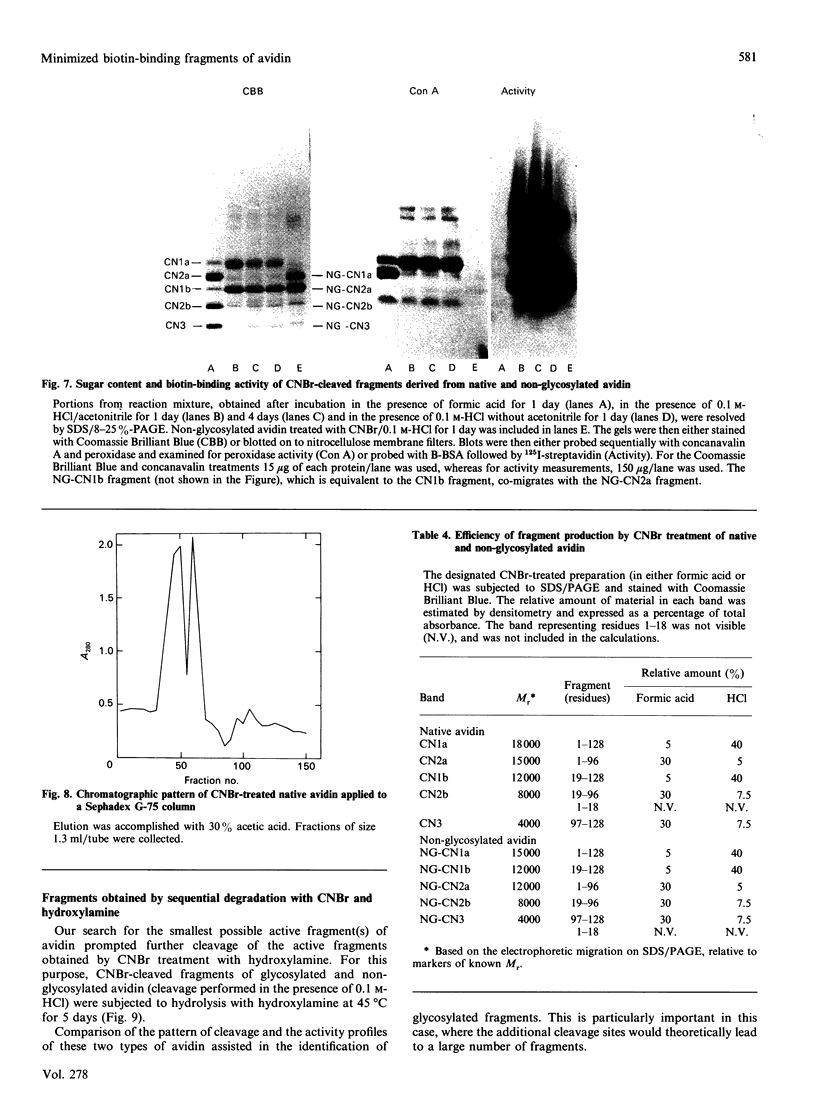
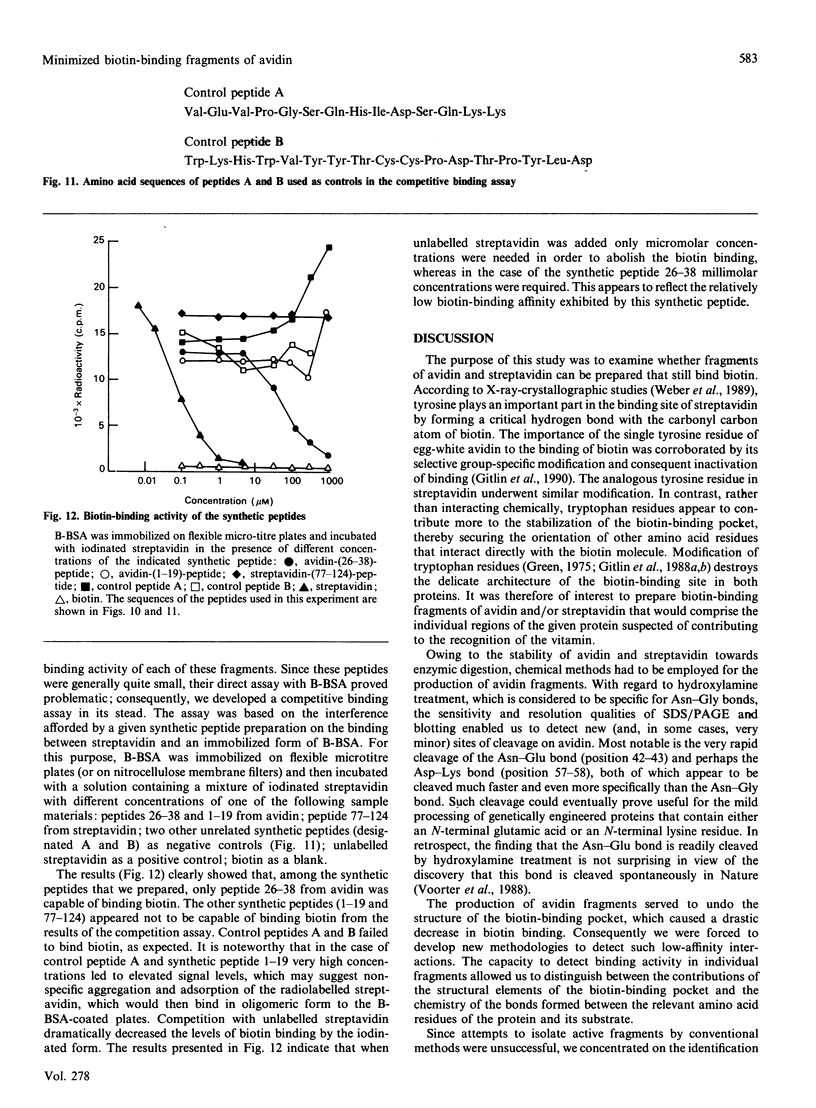
The object of this study was to define minimized biotin-binding fragments, or 'prorecognition sites', of either the egg-white glycoprotein avidin or its bacterial analogue streptavidin. Because of the extreme stability to enzymic hydrolysis, fragments of avidin were prepared by chemical means and examined for their individual biotin-binding capacity. Treatment of avidin with hydroxylamine was shown to result in new cleavage sites in addition to the known Asn-Gly cleavage site (position 88-89 in avidin). Notably, the Asn-Glu and Asp-Lys peptide bonds (positions 42-43 and 57-58 respectively) were readily cleaved; in addition, lesser levels of hydrolysis of the Gln-Pro (61-62) and Asn-Asp (12-13 and 104-105) bonds could be detected. The smallest biotin-binding peptide fragment, derived from hydroxylamine cleavage of either native or non-glycosylated avidin, was identified to comprise residues 1-42. CNBr cleavage resulted in a 78-amino acid-residue fragment (residues 19-96) that still retained activity. The data ascribe an important biotin-binding function to the overlapping region (residues 19-42) of avidin, which bears the single tyrosine moiety. This contention was corroborated by synthesizing a tridecapeptide corresponding to residues 26-38 of avidin; this peptide was shown to recognize biotin. Streptavidin was not susceptible to either enzymic or chemical cleavage methods used in this work. The approach taken in this study enabled the experimental distinction between the chemical and structural elements of the binding site. The capacity to assign biotin-binding activity to the tyrosine-containing domain of avidin underscores its primary chemical contribution to the binding of biotin by avidin.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argaraña C. E., Kuntz I. D., Birken S., Axel R., Cantor C. R. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the streptavidin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1871–1882. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Ben-Hur H., Gitlin G., Wilchek M. An improved method for the single-step purification of streptavidin. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1986 Sep;13(2):103–112. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(86)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Ben-Hur H., Hiller Y., Wilchek M. Postsecretory modifications of streptavidin. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 15;259(2):369–376. doi: 10.1042/bj2590369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. Application of avidin-biotin technology to affinity-based separations. J Chromatogr. 1990 Jun 27;510:3–11. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)93733-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. Protein biotinylation. Methods Enzymol. 1990;184:138–160. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)84268-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Balian G. Cleavage at Asn-Gly bonds with hydroxylamine. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:132–145. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P. Structure of alpha-1-CB8, a large cyanogen bromide produced fragment from the alpha-1 chain of rat collagen. The nature of a hydroxylamine-sensitive bond and composition of tryptic peptides. Biochemistry. 1970 Jun 9;9(12):2408–2421. doi: 10.1021/bi00814a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. C. Glycoprotein detection in nitrocellulose transfers of electrophoretically separated protein mixtures using concanavalin A and peroxidase: application to arenavirus and flavivirus proteins. Anal Biochem. 1982 Dec;127(2):389–394. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fling S. P., Gregerson D. S. Peptide and protein molecular weight determination by electrophoresis using a high-molarity tris buffer system without urea. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 15;155(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS E., WITKOP B. Nonenzymatic cleavage of peptide bonds: the methionine residues in bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1856–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Davis F. E., Palade G. E. Protein blotting in uniform or gradient electric fields. Anal Biochem. 1985 Jan;144(1):32–40. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90080-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Palade G. E. Protein blotting: principles and applications. Anal Biochem. 1983 May;131(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin G., Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. Studies on the biotin-binding site of avidin. Tryptophan residues involved in the active site. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 15;250(1):291–294. doi: 10.1042/bj2500291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin G., Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. Studies on the biotin-binding site of streptavidin. Tryptophan residues involved in the active site. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):279–282. doi: 10.1042/bj2560279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin G., Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. Studies on the biotin-binding sites of avidin and streptavidin. Tyrosine residues are involved in the binding site. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):527–530. doi: 10.1042/bj2690527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. Avidin and streptavidin. Methods Enzymol. 1990;184:51–67. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)84259-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. Avidin. Adv Protein Chem. 1975;29:85–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60411-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M., Toms E. J. The properties of subunits of avidin coupled to sepharose. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;133(4):687–700. doi: 10.1042/bj1330687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groman E. V., Rothenberg J. M., Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. Enzymatic and radioactive assays for biotin, avidin, and streptavidin. Methods Enzymol. 1990;184:208–217. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)84276-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi R. Carboxypeptidase Y in sequence determination of peptides. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:84–93. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrikson K. P., Allen S. H., Maloy W. L. An avidin monomer affinity column for the purification of biotin-containing enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1979 Apr 15;94(2):366–370. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90374-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiller Y., Gershoni J. M., Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. Biotin binding to avidin. Oligosaccharide side chain not required for ligand association. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):167–171. doi: 10.1042/bj2480167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohanski R. A., Lane M. D. Monovalent avidin affinity columns. Methods Enzymol. 1990;184:194–200. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)84274-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzban G. P., Gitlin G., Bayer E. A., Wilchek M., Horowitz P. M. Biotin binding changes the conformation and decreases tryptophan accessibility of streptavidin. J Protein Chem. 1990 Dec;9(6):673–682. doi: 10.1007/BF01024762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzban G. P., Gitlin G., Bayer E. A., Wilchek M., Horowitz P. M. Shielding of tryptophan residues of avidin by the binding of biotin. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8537–8542. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERRIFIELD R. B. SOLID-PHASE PEPTIDE SYNTHESIS. 3. AN IMPROVED SYNTHESIS OF BRADYKININ. Biochemistry. 1964 Sep;3:1385–1390. doi: 10.1021/bi00897a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pähler A., Hendrickson W. A., Kolks M. A., Argaraña C. E., Cantor C. R. Characterization and crystallization of core streptavidin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):13933–13937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEERS E., Jr, CRAVEN G. R., ANFINSEN C. B., BETHUNE J. L. EVIDENCE FOR NONIDENTICAL CHAINS IN THE BETA-GALACTOSIDASE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2478–2484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I. Quantitation: first check what you are measuring. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Oct;15(10):376–376. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90232-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spande T. F., Witkop B., Degani Y., Patchornik A. Selective cleavage and modification of peptides and proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1970;24:97–260. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60242-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorter C. E., de Haard-Hoekman W. A., van den Oetelaar P. J., Bloemendal H., de Jong W. W. Spontaneous peptide bond cleavage in aging alpha-crystallin through a succinimide intermediate. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19020–19023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P. C., Ohlendorf D. H., Wendoloski J. J., Salemme F. R. Structural origins of high-affinity biotin binding to streptavidin. Science. 1989 Jan 6;243(4887):85–88. doi: 10.1126/science.2911722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilchek M., Bayer E. A. Avidin-biotin technology ten years on: has it lived up to its expectations? Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Oct;14(10):408–412. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90289-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]