Abstract
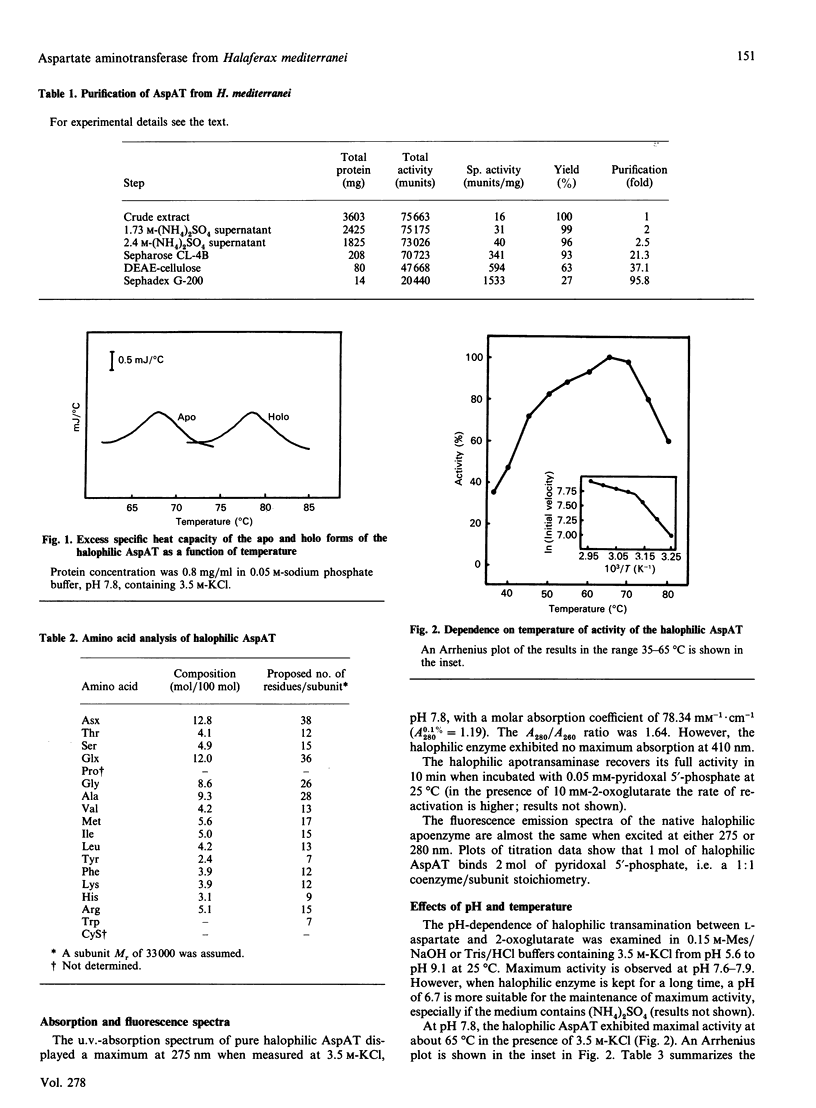
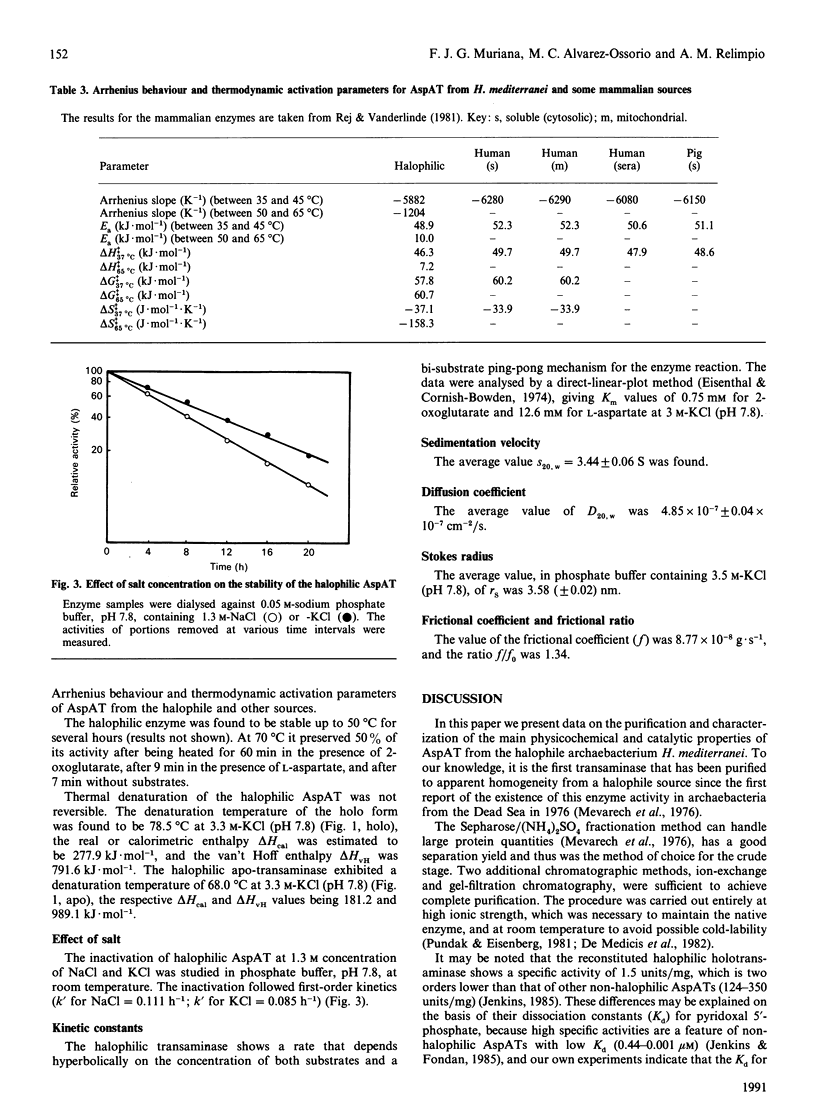
Aspartate aminotransferase from the archaebacterium Haloferax mediterranei was purified and found to be homogeneous. An average Mr of 66,000 was estimated. The native halophilic transaminase exhibited no maximum absorption at 410 nm, which indicates that the apo form is obtained by our purification procedure, and the molar absorption coefficient at 275 nm in 3.5 M-KCl (pH 7.8) was found to be 78.34 mM-1.cm-1. Plots of titration data show that 1 mol of halophilic aspartate aminotransferase binds 2 mol of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. The halophilic transaminase behaved as a dimer with two similar subunits and had a maximum activity in the pH range 7.6-7.9 and at 65 degrees C in 3.5 M-KCl. By differential scanning calorimetry, the denaturation temperature of the halophilic holo- and apo-transaminase was determined to be 78.5 and 68.0 degrees C respectively at 3.3 M-KCl (pH 7.8). At low salt concentration the halophilic transaminase was inactivated, following first-order kinetics. The Km values for 2-oxoglutarate and L-aspartate, in 3 M-KCl (pH 7.8), were 0.75 mM and 12.6 mM respectively.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEAVEN G. H., HOLIDAY E. R. Ultraviolet absorption spectra of proteins and amino acids. Adv Protein Chem. 1952;7:319–386. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belew M., Fohlman J. Gel filtration of proteins on Sephacryl S-200 superfine in 6 M guanidine-HCl. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jul 15;91(2):302–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81197-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg H., Wachtel E. J. Structural studies of halophilic proteins, ribosomes, and organelles of bacteria adapted to extreme salt concentrations. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1987;16:69–92. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.16.060187.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenthal R., Cornish-Bowden A. The direct linear plot. A new graphical procedure for estimating enzyme kinetic parameters. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):715–720. doi: 10.1042/bj1390715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOVIN T., CHRAMBACH A., NAUGHTON M. A. AN APPARATUS FOR PREPARATIVE TEMPERATURE-REGULATED POLYACRYLAMIDE GEL ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1964 Nov;9:351–369. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90192-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John R. A., Fowler L. J. Kinetic and spectral properties of rabbit brain 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase. Biochem J. 1976 Jun 1;155(3):645–651. doi: 10.1042/bj1550645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keradjopoulos D., Holldorf A. W. Purification and properties of alanine dehydrogenase from Halobacterium salinarium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Sep 12;570(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90195-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu S., Inoue K., Kondo K., Aki K., Kagamiyama H. Aspartate aminotransferase isozymes from rabbit liver. Purification and properties. J Biochem. 1985 May;97(5):1337–1345. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laidler K. J., Peterman B. F. Temperature effects in enzyme kinetics. Methods Enzymol. 1979;63:234–257. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)63012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lain-Guelbenzu B., Muñoz-Blanco J., Cárdenas J. Purification and properties of L-aspartate aminotransferase of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Mar 30;188(3):529–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15432.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leicht W., Werber M. M., Eisenberg H. Purification and characterization of glutamate dehydrogenase from Halobacterium of the Dead Sea. Biochemistry. 1978 Sep 19;17(19):4004–4010. doi: 10.1021/bi00612a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. S., Bada J. L., Somero G. N. Temperature adaptation of enzymes: roles of the free energy, the enthalpy, and the entropy of activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):430–432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marino G., Nitti G., Arnone M. I., Sannia G., Gambacorta A., De Rosa M. Purification and characterization of aspartate aminotransferase from the thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus solfataricus. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12305–12309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mevarech M., Leicht W., Werber M. M. Hydrophobic chromatography and fractionation of enzymes from extremely halophilic bacteria using decreasing concentration gradients of ammonium sulfate. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 1;15(11):2383–2387. doi: 10.1021/bi00656a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muriana F. J., Sánchez M. C., Rodulfo J. D., Alvarez-Ossorio M. C., Relimpio A. M. Optimization of the cell envelope disruption of extremely halophilic bacteria. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1987 Jan;14(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(87)90003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pundak S., Eisenberg H. Structure and activity of malate dehydrogenase from the extreme halophilic bacteria of the Dead Sea. 1. Conformation and interaction with water and salt between 5 M and 1 M NaCl concentration. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep 1;118(3):463–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05542.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rej R., Vanderlinde R. E. Effects of temperature on the steady-state kinetics and measurement of aspartate aminotransferases. Clin Chem. 1981 Feb;27(2):213–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P. H., Boland M. J., Farnden K. J. Enzymes of nitrogen metabolism in legume nodules: partial purification and properties of the aspartate aminotransferases from lupine nodules. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Jul;209(2):524–533. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi T., Kagamiyama H., Nozaki M. Aspartate: 2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase from bakers' yeast: crystallization and characterization. J Biochem. 1982 Jul;92(1):35–43. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi T., Toyosato M., Soda K. Crystalline aspartate aminotransferase from Pseudomonas striata. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jan 1;61(1):34–37. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80165-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


