Abstract
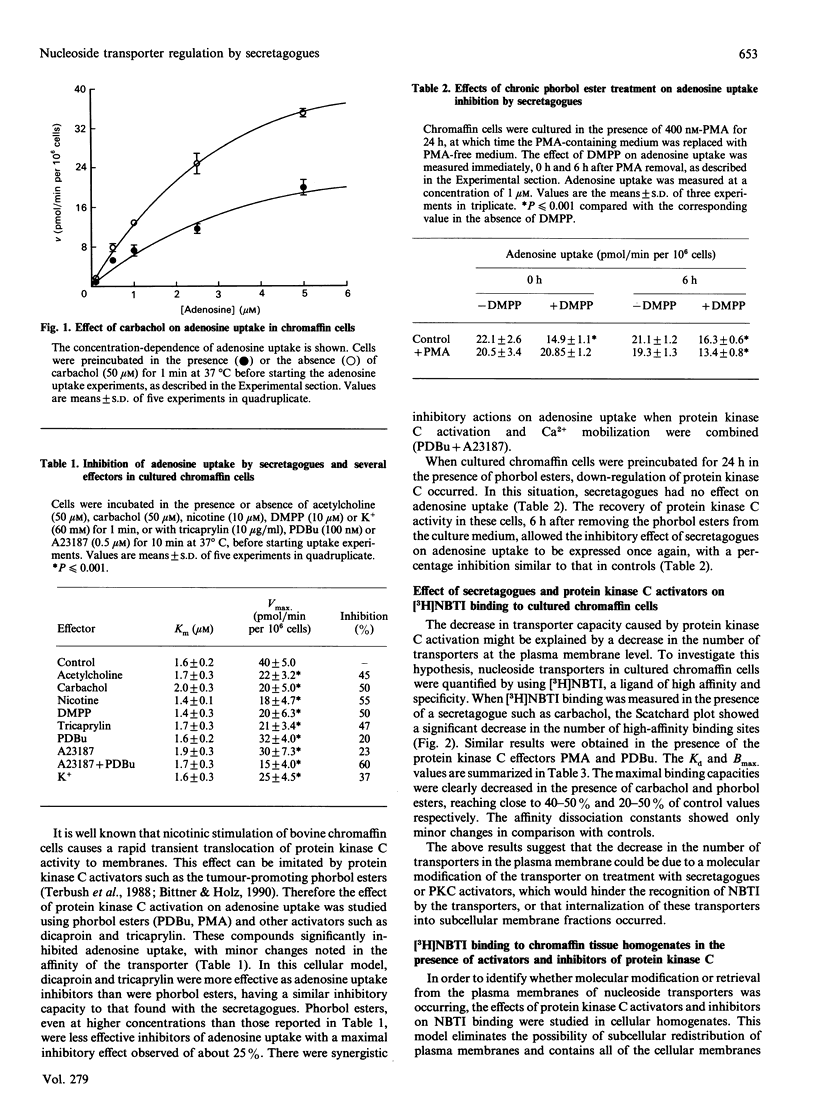
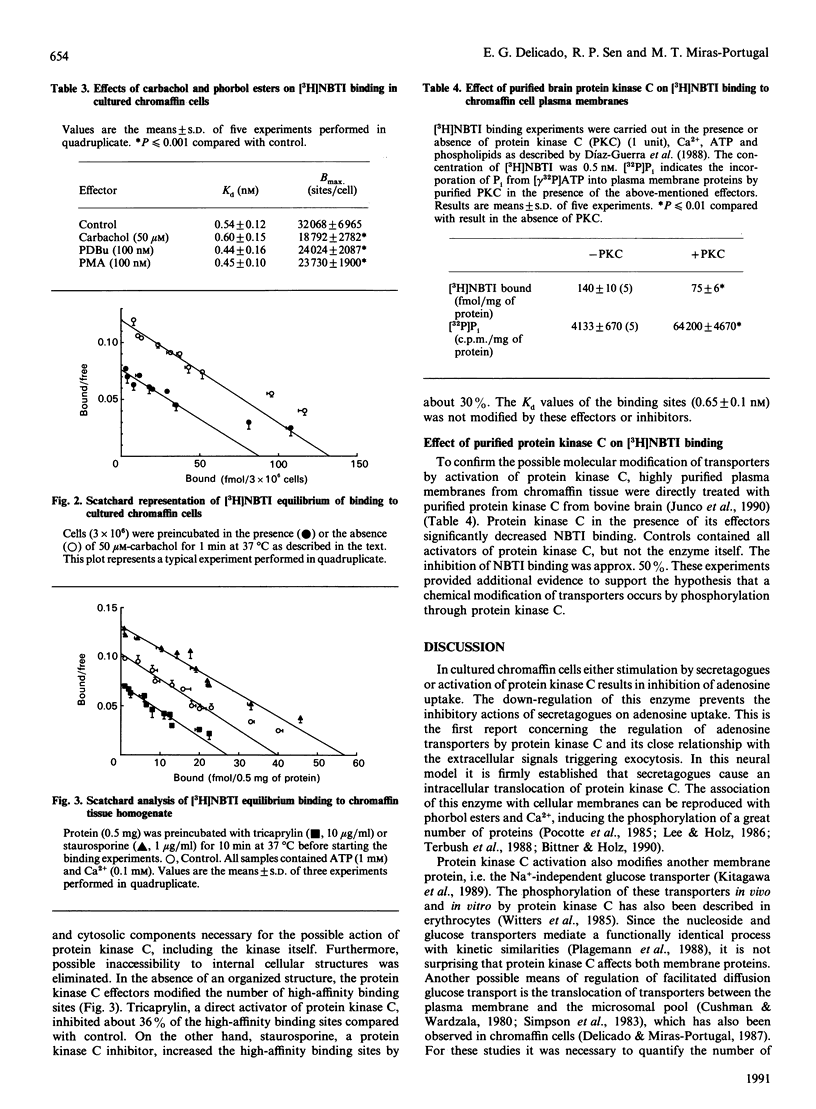
Secretagogues inhibited adenosine uptake in chromaffin cells without causing apparent changes in the uptake affinity. The inhibition caused by carbachol, nicotine and acetylcholine reached 50%. This inhibition was reproduced by the action of protein kinase C activators such as phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA; 100 nM), phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate (PDBu; 100 nM), dicaproin (10 micrograms/ml) and tricaprylin (10 micrograms/ml), with inhibitions of Vmax. of 18, 20, 37 and 47% respectively. No changes in the affinity of uptake were observed with these effectors. Down-regulation of protein kinase C by phorbol esters decreased the inhibitory effects of carbachol on adenosine uptake. Binding studies with nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBTI) showed a similar decrease in the number of transporters when chromaffin cells were treated with the same effectors used for the uptake studies. The high-affinity dissociation constants showed minor changes with respect to the control. The ratio between maximal uptake capacity and the transporter number per cell was not significantly modified by the action of secretagogues or direct effectors of protein kinase C. The number of high-affinity binding sites for NBTI was decreased in cellular homogenates by the direct action of protein kinase C activators, with staurosporine able to reverse this action. Protein kinase C from bovine brain in the presence of ATP and effectors, decreased the number of high-affinity NBTI-binding sites in purified chromaffin cell plasma membranes. These data suggest the possibility of a molecular modification at the transporter level.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bader M. F., Hikita T., Trifaró J. M. Calcium-dependent calmodulin binding to chromaffin granule membranes: presence of a 65-kilodalton calmodulin-binding protein. J Neurochem. 1985 Feb;44(2):526–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb05445.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner M. A., Holz R. W. Phorbol esters enhance exocytosis from chromaffin cells by two mechanisms. J Neurochem. 1990 Jan;54(1):205–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb13302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D. Mechanisms of secretion from adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 25;779(2):201–216. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(84)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Wardzala L. J. Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport systems to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4758–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delicado E. G., Miras Portugal M. T. Glucose transporters in isolated chromaffin cells. Effects of insulin and secretagogues. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 15;243(2):541–547. doi: 10.1042/bj2430541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delicado E. G., Rodrigues A., Sen R. P., Sebastiao A. M., Ribeiro J. A., Miras-Portugal M. T. Effect of 5'-(N-ethylcarboxamido)adenosine on adenosine transport in cultured chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1990 Jun;54(6):1941–1946. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04895.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delicado E. G., Torres M., Miras-Portugal M. T. Glucose transporters in chromaffin cells: subcellular distribution and characterization. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 29;229(1):35–39. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80792-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Guerra M. J., Sánchez-Prieto J., Bosca L., Pocock J., Barrie A., Nicholls D. Phorbol ester translocation of protein kinase C in guinea-pig synaptosomes and the potentiation of calcium-dependent glutamate release. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jun 30;970(2):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90174-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon E. L., Pearson J. D., Slakey L. L. The hydrolysis of extracellular adenine nucleotides by cultured endothelial cells from pig aorta. Feed-forward inhibition of adenosine production at the cell surface. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15496–15507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins L. S., Berg D. K. Cyclic AMP-dependent mechanism regulates acetylcholine receptor function on bovine adrenal chromaffin cells and discriminates between new and old receptors. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1157–1165. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junco M., Díaz-Guerra M. J., Boscá L. Substrate-dependent inhibition of protein kinase C by specific inhibitors. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 9;263(1):169–171. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80731-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa T., Tanaka M., Akamatsu Y. Regulation of glucose transport activity and expression of glucose transporter mRNA by serum, growth factors and phorbol ester in quiescent mouse fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Mar 27;980(1):100–108. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90205-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. W., Jarvis S. M. Nucleoside transport in rat cerebral-cortical synaptosomes. Evidence for two types of nucleoside transporters. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 15;249(2):557–564. doi: 10.1042/bj2490557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. A., Holz R. W. Protein phosphorylation and secretion in digitonin-permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells. Effects of micromolar Ca2+, phorbol esters, and diacylglycerol. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):17089–17098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marangos P. J., Deckert J. [3H]dipyridamole binding to guinea pig brain membranes: possible heterogeneity of central adenosine uptake sites. J Neurochem. 1987 Apr;48(4):1231–1236. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb05651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marangos P. J., Patel J., Clark-Rosenberg R., Martino A. M. [3H]nitrobenzylthioinosine binding as a probe for the study of adenosine uptake sites in brain. J Neurochem. 1982 Jul;39(1):184–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb04717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miras-Portugal M. T., Torres M., Rotllan P., Aunis D. Adenosine transport in bovine chromaffin cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1712–1719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin D., Aunis D. Reorganization of alpha-fodrin induced by stimulation in secretory cells. Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):589–592. doi: 10.1038/315589a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintor J., Torres M., Castro E., Miras-Portugal M. T. Characterization of diadenosine tetraphosphate (Ap4A) binding sites in cultured chromaffin cells: evidence for a P2y site. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;103(4):1980–1984. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintor J., Torres M., Miras-Portugal M. T. Carbachol induced release of diadenosine polyphosphates--Ap4A and Ap5A--from perfused bovine adrenal medulla and isolated chromaffin cells. Life Sci. 1991;48(24):2317–2324. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90268-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G., Wohlhueter R. M., Woffendin C. Nucleoside and nucleobase transport in animal cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Oct 11;947(3):405–443. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocotte S. L., Frye R. A., Senter R. A., TerBush D. R., Lee S. A., Holz R. W. Effects of phorbol ester on catecholamine secretion and protein phosphorylation in adrenal medullary cell cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):930–934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson P. J., Brown S. J., Bailyes E. M., Luzio J. P. Ectoenzymes control adenosine modulation of immunoisolated cholinergic synapses. Nature. 1987 May 21;327(6119):232–234. doi: 10.1038/327232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotllán P., Miras-Portugal M. T. Purine nucleotide synthesis in adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1985 Apr;44(4):1029–1036. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb08721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Yver D. R., Hissin P. J., Wardzala L. J., Karnieli E., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transporters in the isolated rat adipose cells: characterization of subcellular fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 19;763(4):393–407. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TerBush D. R., Bittner M. A., Holz R. W. Ca2+ influx causes rapid translocation of protein kinase C to membranes. Studies of the effects of secretagogues in adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18873–18879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres M., Bader M. F., Aunis D., Miras-Portugal M. T. Nerve growth factor effect on adenosine transport in cultured chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1987 Jan;48(1):233–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb13152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres M., Delicado E. G., Miras-Portugal M. T. Adenosine transporters in chromaffin cells: subcellular distribution and characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 25;969(2):111–120. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres M., Fideu M. D., Miras-Portugal M. T. All nucleoside transporters in bovine chromaffin cells are nitrobenzylthioinosine sensitive. Neurosci Lett. 1990 May 4;112(2-3):343–347. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres M., Pintor J., Miras-Portugal M. T. Presence of ectonucleotidases in cultured chromaffin cells: hydrolysis of extracellular adenine nucleotides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 May 15;279(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90460-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. Purine receptors in mammalian tissues: pharmacology and functional significance. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1987;27:315–345. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.27.040187.001531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witters L. A., Vater C. A., Lienhard G. E. Phosphorylation of the glucose transporter in vitro and in vivo by protein kinase C. 1985 Jun 27-Jul 3Nature. 315(6022):777–778. doi: 10.1038/315777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


