Abstract
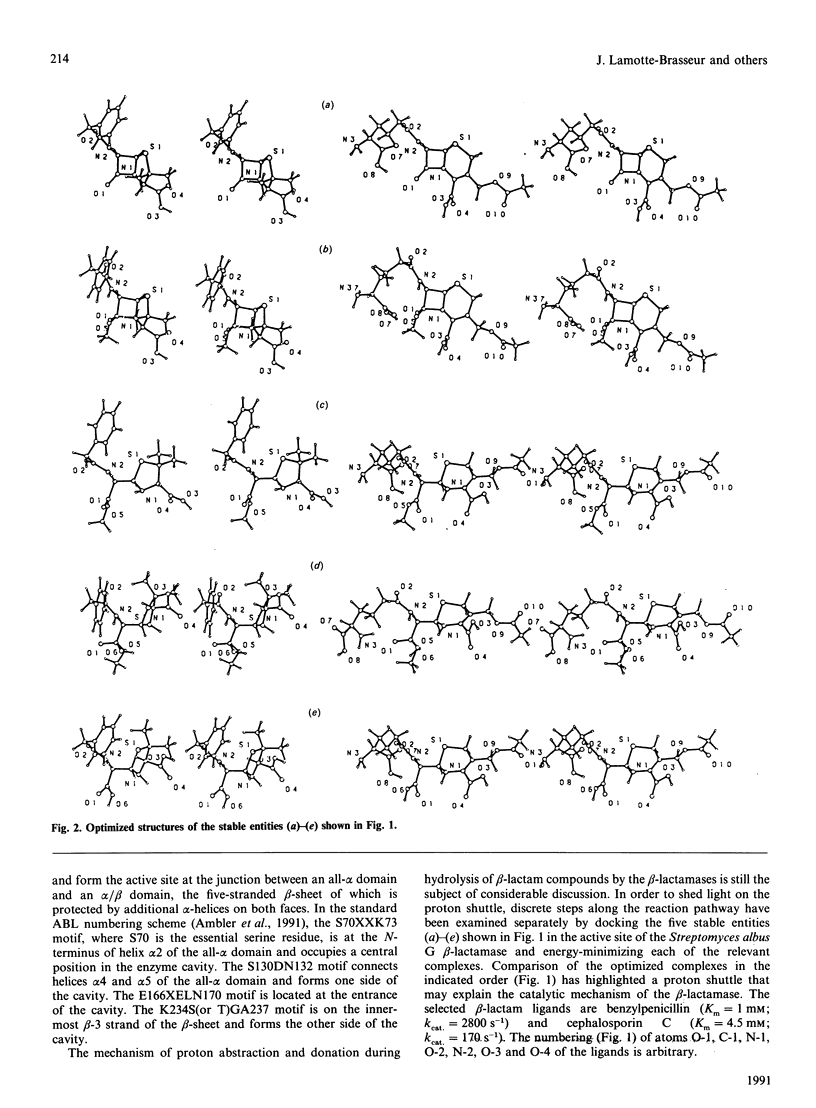
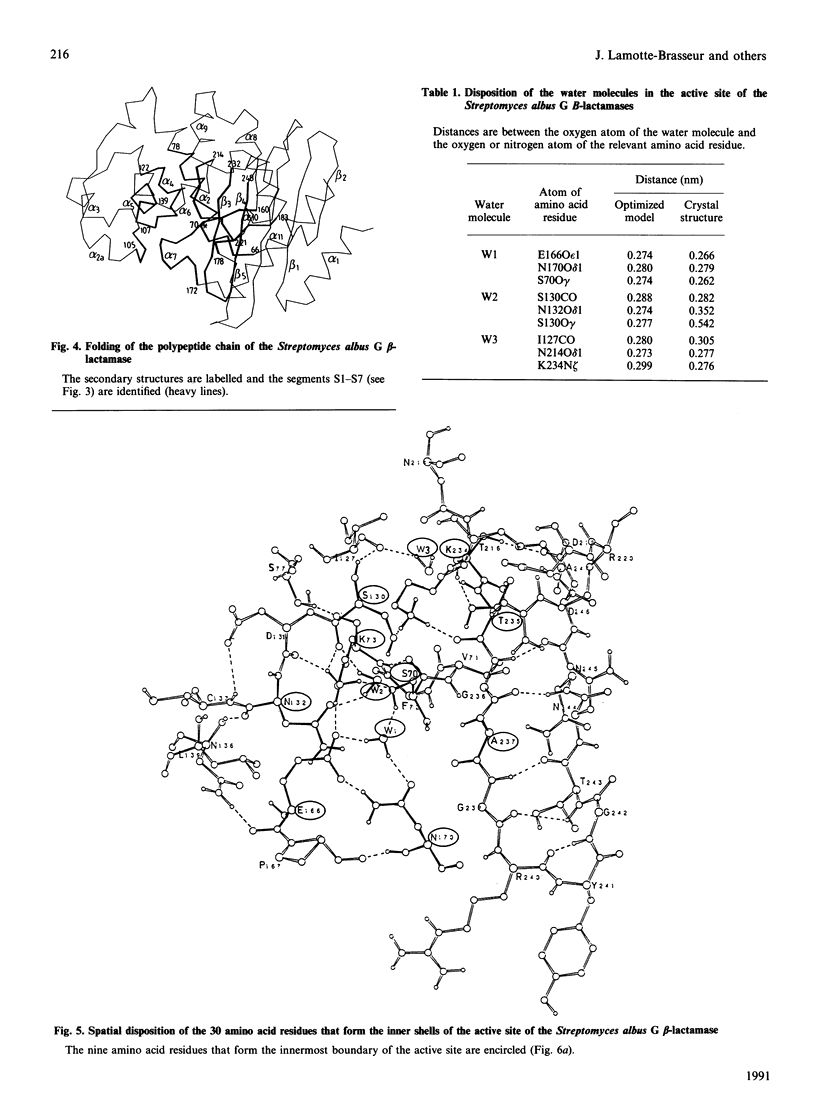
Optimization by energy minimization of stable complexes occurring along the pathway of hydrolysis of benzylpenicillin and cephalosporin C by the Streptomyces albus G beta-lactamase has highlighted a proton shuttle that may explain the catalytic mechanism of the beta-lactamases of class A. Five residues, S70, S130, N132, T235 and A237, are involved in ligand binding. The gamma-OH group of T235 and, in the case of benzylpenicillin, the gamma-OH group of S130 interact with the carboxylate group, on one side of the ligand molecule. The side-chain NH2 group of N132 and the carbonyl backbone of A237 interact with the exocyclic CONH amide bond, on the other side of the ligand. The backbone NH groups of S70 and A237 polarize the carbonyl group of the scissile beta-lactam amide bond. Four residues, S70, K73, S130 and E166, and two water molecules, W1 and W2, perform hydrolysis of the bound beta-lactam compound. E166, via W1, abstracts the proton from the gamma-OH group of S70. While losing its proton, the O-gamma atom of S70 attacks the carbonyl carbon atom of the beta-lactam ring and, concomitantly, the proton is delivered back to the adjacent nitrogen atom via W2, K73 and S130, thus achieving formation of the acyl-enzyme. Subsequently, E166 abstracts a proton from W1. While losing its proton, W1 attacks the carbonyl carbon atom of the S70 ester-linked acyl-enzyme and, concomitantly, re-entry of a water molecule W'1 replacing W1 allows E166 to deliver the proton back to the same carbonyl carbon atom, thus achieving hydrolysis of the beta-lactam compound and enzyme recovery. The model well explains the differences found in the kcat. values for hydrolysis of benzylpenicillin and cephalosporin C by the Streptomyces albus G beta-lactamase. It also explains the effects caused by site-directed mutagenesis of the Bacillus cereus beta-lactamase I [Gibson, Christensen & Waley (1990) Biochem J. 272, 613-619].
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P., Coulson A. F., Frère J. M., Ghuysen J. M., Joris B., Forsman M., Levesque R. C., Tiraby G., Waley S. G. A standard numbering scheme for the class A beta-lactamases. Biochem J. 1991 May 15;276(Pt 1):269–270. doi: 10.1042/bj2760269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collatz E., Labia R., Gutmann L. Molecular evolution of ubiquitous beta-lactamases towards extended-spectrum enzymes active against newer beta-lactam antibiotics. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1615–1620. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00537.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehottay P., Dusart J., De Meester F., Joris B., Van Beeumen J., Erpicum T., Frère J. M., Ghuysen J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the Streptomyces albus G beta-lactamase precursor. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jul 15;166(2):345–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghuysen J. M. Serine beta-lactamases and penicillin-binding proteins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:37–67. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.000345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson R. M., Christensen H., Waley S. G. Site-directed mutagenesis of beta-lactamase I. Single and double mutants of Glu-166 and Lys-73. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 15;272(3):613–619. doi: 10.1042/bj2720613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg O., Moult J. Bacterial resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics: crystal structure of beta-lactamase from Staphylococcus aureus PC1 at 2.5 A resolution. Science. 1987 May 8;236(4802):694–701. doi: 10.1126/science.3107125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig B., Kabat E. A., Katz L., Levinthal C., Wu T. T. Model-building of neurohypophyseal hormones. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 25;80(2):277–295. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90173-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob F., Joris B., Lepage S., Dusart J., Frère J. M. Role of the conserved amino acids of the 'SDN' loop (Ser130, Asp131 and Asn132) in a class A beta-lactamase studied by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 15;271(2):399–406. doi: 10.1042/bj2710399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris B., Ghuysen J. M., Dive G., Renard A., Dideberg O., Charlier P., Frère J. M., Kelly J. A., Boyington J. C., Moews P. C. The active-site-serine penicillin-recognizing enzymes as members of the Streptomyces R61 DD-peptidase family. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 1;250(2):313–324. doi: 10.1042/bj2500313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matagne A., Misselyn-Bauduin A. M., Joris B., Erpicum T., Granier B., Frère J. M. The diversity of the catalytic properties of class A beta-lactamases. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 1;265(1):131–146. doi: 10.1042/bj2650131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moews P. C., Knox J. R., Dideberg O., Charlier P., Frère J. M. Beta-lactamase of Bacillus licheniformis 749/C at 2 A resolution. Proteins. 1990;7(2):156–171. doi: 10.1002/prot.340070205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oefner C., D'Arcy A., Daly J. J., Gubernator K., Charnas R. L., Heinze I., Hubschwerlen C., Winkler F. K. Refined crystal structure of beta-lactamase from Citrobacter freundii indicates a mechanism for beta-lactam hydrolysis. Nature. 1990 Jan 18;343(6255):284–288. doi: 10.1038/343284a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sougakoff W., Petit A., Goussard S., Sirot D., Bure A., Courvalin P. Characterization of the plasmid genes blaT-4 and blaT-5 which encode the broad-spectrum beta-lactamases TEM-4 and TEM-5 in enterobacteriaceae. Gene. 1989 May 30;78(2):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90236-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


