Abstract
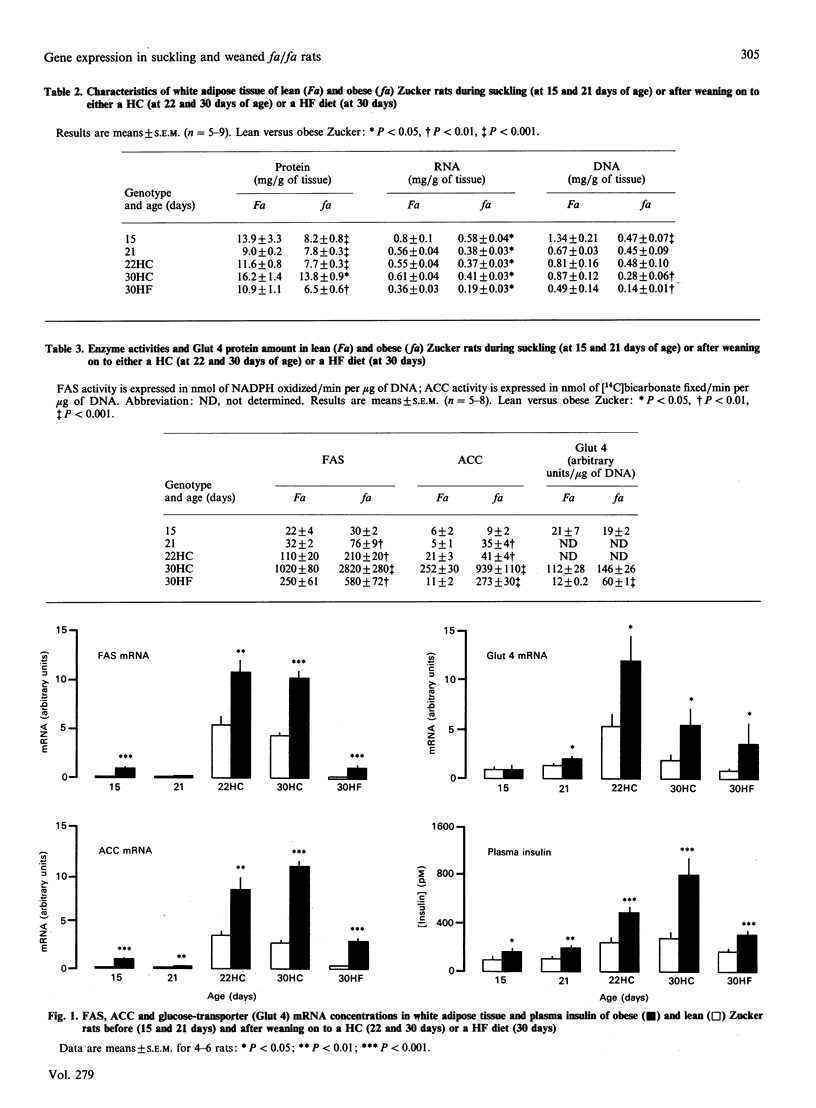
Previous experiments have shown that insulin-induced glucose utilization is increased in white adipose tissue of young obese Zucker rats. We have investigated the possible role of over-expression of the muscle/fat glucose transporter (Glut 4) and key lipogenic enzymes in this increased insulin-responsiveness. The amount or activity and the mRNA concentrations of Glut 4, fatty acid synthase (FAS) and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) were measured before and after weaning in white adipose tissue of obese and lean Zucker rats. Comparison of the levels of Glut 4 and lipogenic-enzyme expression in 15-day-old suckling and 30-day-old weaned rats on a high-carbohydrate diet shows a marked increase in the latter group. The increase was, in lean and obese rats respectively, 6- and 7-fold for the amount of Glut 4 and 2- and 3-fold for its mRNA concentrations, 40- and 100-fold for the activity of lipogenic enzymes (FAS and ACC) and 30- and 10-fold for their mRNA concentrations. Furthermore, all these parameters, except the amount of Glut 4, were 2-5-fold higher in obese rats, both before and after weaning. Changes at weaning were largely blunted when rats were weaned on to a high-fat diet, although the differences between lean and obese rats persisted, and even became significant for the amount of Glut 4. Whatever the experimental conditions, plasma insulin levels were significantly higher in obese than in lean rats. These results indicate the existence of an enhanced expression of Glut 4, FAS and ACC in white adipose tissue of young obese fa/fa rats which could be related to the increased plasma insulin levels.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazin R., Lavau M. Development of hepatic and adipose tissue lipogenic enzymes and insulinemia during suckling and weaning on to a high-fat diet in Zucker rats. J Lipid Res. 1982 Aug;23(6):839–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Biswas C., Vicario P. P., Strout H. V., Saperstein R., Pilch P. F. Decreased expression of the insulin-responsive glucose transporter in diabetes and fasting. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):70–72. doi: 10.1038/340070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J. Identification of a novel gene encoding an insulin-responsive glucose transporter protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90968-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bougnères P. F., Artavia-Loria E., Henry S., Basdevant A., Castaño L. Increased basal glucose production and utilization in children with recent obesity versus adults with long-term obesity. Diabetes. 1989 Apr;38(4):477–483. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.4.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulangé A., Planche E., de Gasquet P. Onset of genetic obesity in the absence of hyperphagia during the first week of life in the Zucker rat (fa/fa). J Lipid Res. 1979 Sep;20(7):857–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron M. J., Brosius F. C., 3rd, Alper S. L., Lodish H. F. A glucose transport protein expressed predominately in insulin-responsive tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2535–2539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S. D., Armstrong M. K., Jump D. B. Dietary polyunsaturated fats uniquely suppress rat liver fatty acid synthase and S14 mRNA content. J Nutr. 1990 Feb;120(2):225–231. doi: 10.1093/jn/120.2.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupe C., Perdereau D., Ferre P., Hitier Y., Narkewicz M., Girard J. Lipogenic enzyme activities and mRNA in rat adipose tissue at weaning. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 1):E126–E133. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.258.1.E126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilettuso B. A., Wandsness P. J. Effect of age on hyperphagia in the genetically obese Zucker rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Jan;154(1):1–5. doi: 10.3181/00379727-154-39589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto H., Kayano T., Buse J. B., Edwards Y., Pilch P. F., Bell G. I., Seino S. Cloning and characterization of the major insulin-responsive glucose transporter expressed in human skeletal muscle and other insulin-responsive tissues. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7776–7779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey W. T., Huecksteadt T. P., Birnbaum M. J. Pretranslational suppression of an insulin-responsive glucose transporter in rats with diabetes mellitus. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):60–63. doi: 10.1126/science.2662408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godbole V. Y., Grundleger M. L., Pasquine T. A., Thenen S. W. Composition of rat milk from day 5 to 20 of lactation and milk intake of lean and preobese Zucker pups. J Nutr. 1981 Mar;111(3):480–487. doi: 10.1093/jn/111.3.480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godbole V., York D. A., Bloxham D. P. Developmental changes in the fatty (fafa) rat: evidence for defective thermogenesis preceding the hyperlipogenesis and hyperinsulinaemia. Diabetologia. 1978 Jul;15(1):41–44. doi: 10.1007/BF01219327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodridge A. G. Dietary regulation of gene expression: enzymes involved in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr. 1987;7:157–185. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.07.070187.001105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., Bell G. I. Facilitative glucose transporters: an expanding family. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jan;15(1):18–23. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90125-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerre-Millo M., Lavau M., Horne J. S., Wardzala L. J. Proposed mechanism for increased insulin-mediated glucose transport in adipose cells from young, obese Zucker rats. Large intracellular pool of glucose transporters. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2197–2201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainault I., Guerre-Millo M., Guichard C., Lavau M. Differential regulation of adipose tissue glucose transporters in genetic obesity (fatty rat). Selective increase in the adipose cell/muscle glucose transporter (GLUT 4) expression. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):1127–1131. doi: 10.1172/JCI115077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issad T., Ferré P., Pastor-Anglada M., Baudon M. A., Girard J. Development of insulin sensitivity in white adipose tissue during the suckling-weaning transition in the rat. Involvement of glucose transport and lipogenesis. Biochem J. 1989 Nov 15;264(1):217–222. doi: 10.1042/bj2640217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Brown R., Navarro J., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulatable tissues express a unique insulin-sensitive glucose transport protein. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):183–185. doi: 10.1038/333183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Strube M., Mueckler M. Molecular cloning and characterization of an insulin-regulatable glucose transporter. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):83–87. doi: 10.1038/338083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeanrenaud B. An hypothesis on the aetiology of obesity: dysfunction of the central nervous system as a primary cause. Diabetologia. 1985 Aug;28(8):502–513. doi: 10.1007/BF00281984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenness R. Proceedings: Biosynthesis and composition of milk. J Invest Dermatol. 1974 Jul;63(1):109–118. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12678111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. R., Stern J. S., Greenwood M. R., Hirsch J. Adipose tissue hyperplasia and hyperinsulinemia on Zucker obese female rats: a developmental study. Metabolism. 1978 Dec;27(12 Suppl 2):1941–1954. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(78)80011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Charron M. J., Lodish H. F., Cushman S. W., Flier J. S. Differential regulation of two glucose transporters in adipose cells from diabetic and insulin-treated diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):404–411. doi: 10.1172/JCI114180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Divergent mechanisms for the insulin resistant and hyperresponsive glucose transport in adipose cells from fasted and refed rats. Alterations in both glucose transporter number and intrinsic activity. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):691–699. doi: 10.1172/JCI113649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsurada A., Iritani N., Fukuda H., Matsumura Y., Nishimoto N., Noguchi T., Tanaka T. Effects of nutrients and hormones on transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase in rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jun 20;190(2):435–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsurada A., Iritani N., Fukuda H., Matsumura Y., Nishimoto N., Noguchi T., Tanaka T. Effects of nutrients and hormones on transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of fatty acid synthase in rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jun 20;190(2):427–433. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koranyi L., James D., Mueckler M., Permutt M. A. Glucose transporter levels in spontaneously obese (db/db) insulin-resistant mice. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):962–967. doi: 10.1172/JCI114526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krief S., Bazin R., Dupuy F., Lavau M. Increased in vivo glucose utilization in 30-day-old obese Zucker rat: role of white adipose tissue. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 1):E342–E348. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.3.E342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavau M., Bazin R., Guerre-Millo M. Increased capacity for fatty acid synthesis in white and brown adipose tissues from 7-day-old obese Zucker pups. Int J Obes. 1985;9 (Suppl 1):61–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavau M., Bazin R. Inguinal fat pad weight plotted versus body weight as a method of genotype identification in 16-day-old Zucker rats. J Lipid Res. 1982 Aug;23(6):941–943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leturque A., Postic C., Ferre P., Girard J. Nutritional regulation of glucose transporter in muscle and adipose tissue of weaned rats. Am J Physiol. 1991 Apr;260(4 Pt 1):E588–E593. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.260.4.E588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. C. Purification and crystallization of rat liver fatty acid synthetase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Jul;209(2):613–619. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90320-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Jacobs R., Smith M. B., Morris H. P. The regulation of fatty acid biosynthesis in rat hepatomas. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3588–3595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape M. E., Lopez-Casillas F., Kim K. H. Physiological regulation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase gene expression: effects of diet, diabetes, and lactation on acetyl-CoA carboxylase mRNA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Nov 15;267(1):104–109. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Planche E., Joliff M., de Gasquet P., Leliepvre X. Evidence of a defect in energy expenditure in 7-day-old Zucker rat (fa/fa). Am J Physiol. 1983 Aug;245(2):E107–E113. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.245.2.E107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pénicaud L., Ferré P., Terretaz J., Kinebanyan M. F., Leturque A., Doré E., Girard J., Jeanrenaud B., Picon L. Development of obesity in Zucker rats. Early insulin resistance in muscles but normal sensitivity in white adipose tissue. Diabetes. 1987 May;36(5):626–631. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.5.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pénicaud L., Kinebanyan M. F., Ferré P., Morin J., Kandé J., Smadja C., Marfaing-Jallat P., Picon L. Development of VMH obesity: in vivo insulin secretion and tissue insulin sensitivity. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 1):E255–E260. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.257.2.E255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohner-Jeanrenaud F., Hochstrasser A. C., Jeanrenaud B. Hyperinsulinemia of preobese and obese fa/fa rats is partly vagus nerve mediated. Am J Physiol. 1983 Apr;244(4):E317–E322. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.4.E317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHERRER K., DARNELL J. E. Sedimentation characteristics of rapidly labelled RNA from HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Jun 4;7:486–490. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90341-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivitz W. I., DeSautel S. L., Kayano T., Bell G. I., Pessin J. E. Regulation of glucose transporter messenger RNA levels in rat adipose tissue by insulin. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Apr;4(4):583–588. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-4-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujikawa M., Kimura S. Changes in lipid synthesis in rat adipose tissue during development. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 1980;26(4):367–374. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.26.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- York D. A., Shargill N. S., Godbole V. Serum insulin and lipogenesis in the suckling 'fatty' fa/fa rat. Diabetologia. 1981 Aug;21(2):143–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00251282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


