Abstract
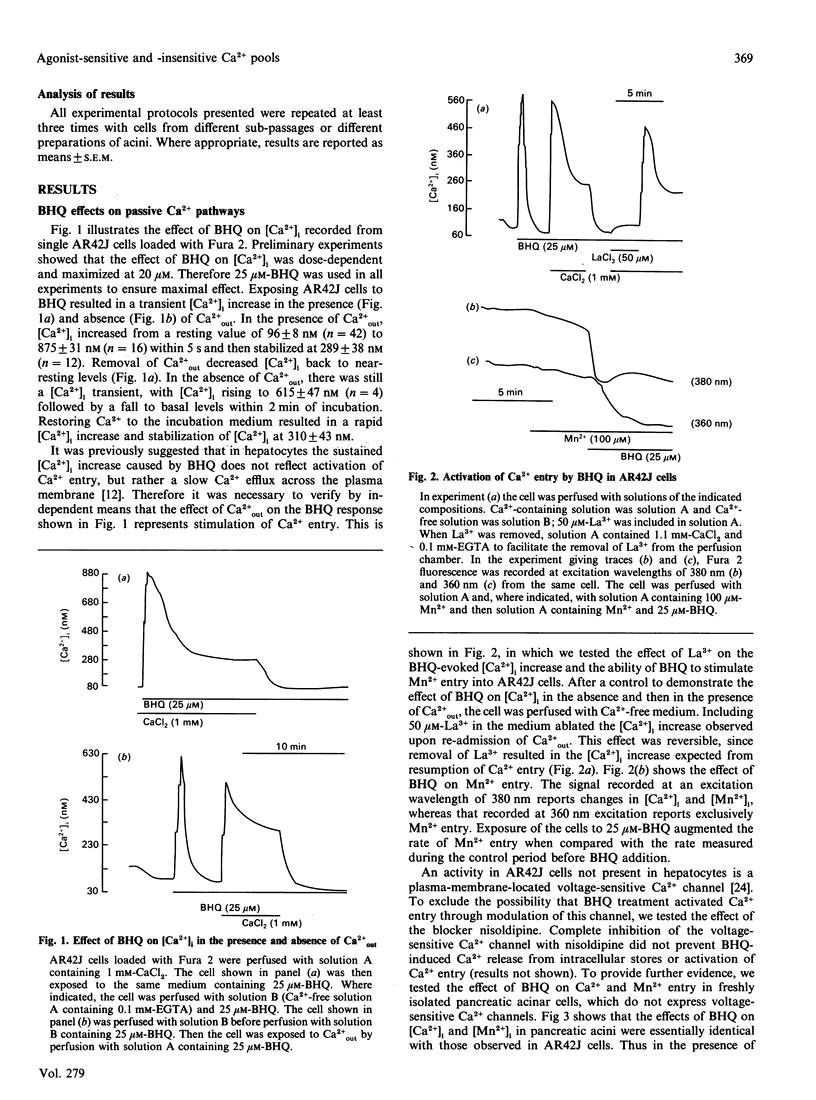
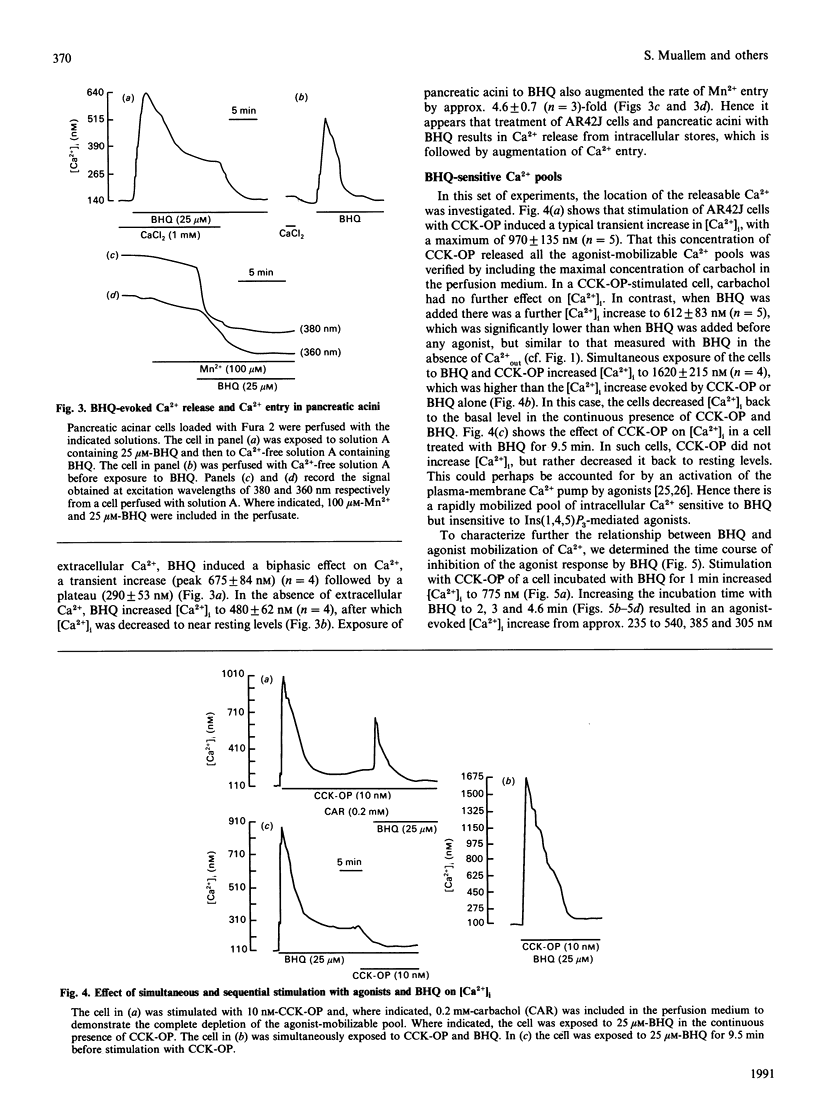
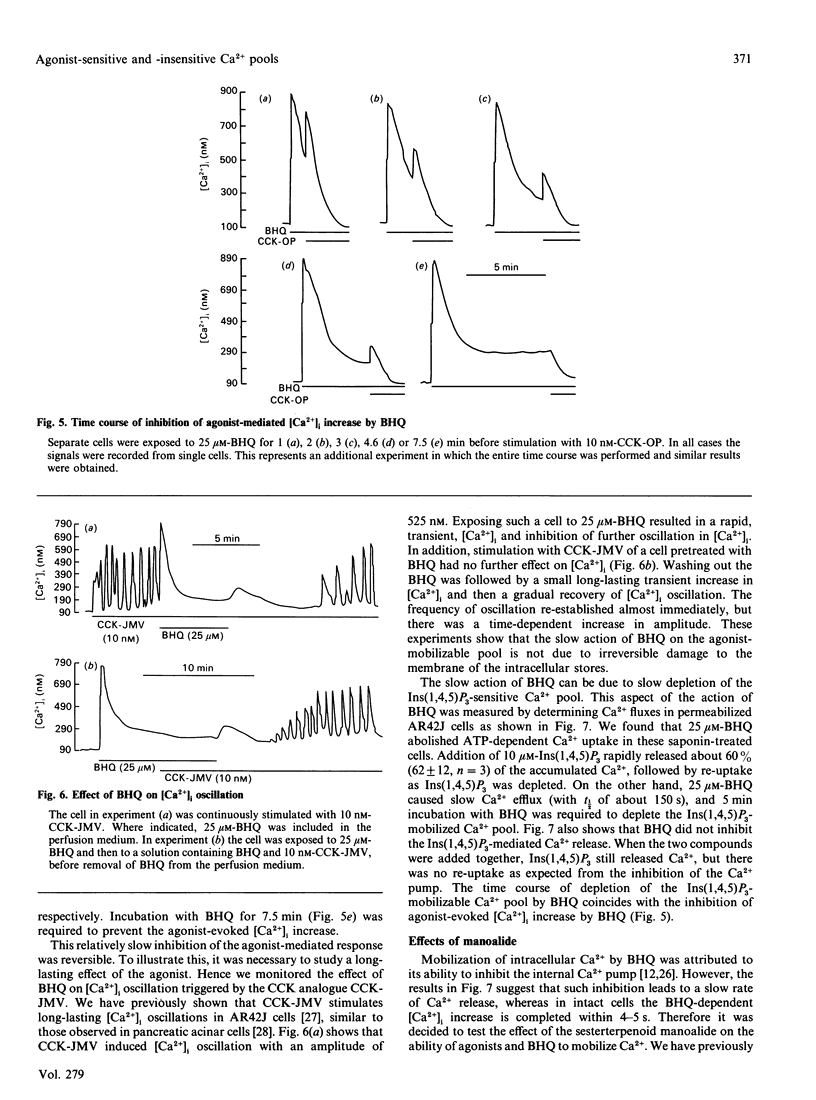
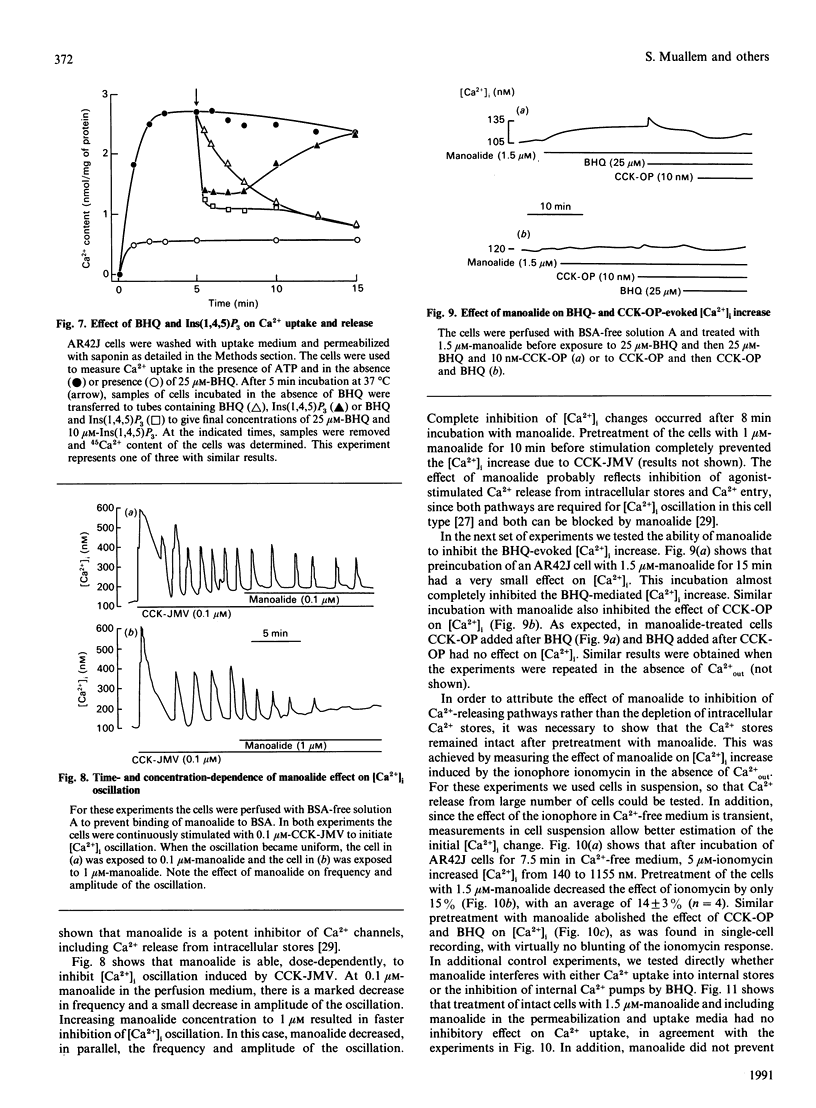
The mechanism of action of a novel compound, 2,5-di-(t-butyl)-1,4-benzohydroquinone (BHQ), used to modulate cell free cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) was studied in AR42J cells and pancreatic acini by using single-cell fluorescence techniques applied to Fura-2-loaded cells. In the presence of extracellular Ca2+ (Ca(2+)out), BHQ induced a biphasic [Ca2+]i increase, an initial and rapid transient followed by a sustained increase. The initial increase was due to Ca2+ release from intracellular stores, being independent of Ca(2+)out. The sustained response was due to Ca2+ entry, being dependent on Ca(2+)out, blocked by La3+ and correlated with an increased rate of Mn2+ entry, all indicative of increased plasma-membrane permeability to Ca2+. Treatment of AR42J cells with BHQ for about 5 min reversibly blocked agonist-dependent Ca2+ release and oscillations, whereas agonist pretreatment decreased, but did not prevent, the effects of BHQ on [Ca2+]i. Accordingly, depletion of the Ins(1,4,5)P3-mobilizable pool in permeabilized AR42J cells by BHQ required 5 min of incubation, although inhibition of the internal Ca2+ pump by BHQ was rapid. These observations suggest that BHQ mobilized an additional intracellular Ca2+ pool that did not respond to changes in Ins(1,4,5)P3. Manoalide, an inhibitor of Ca2+ channels, inhibited agonist-evoked [Ca2+]i oscillation and [Ca2+]i increase in a dose- and time-dependent manner without significant effect on internal Ca2+ pumps and Ca2+ content of the internal stores. Manoalide also inhibited the BHQ-evoked [Ca2+]i increase in the absence and presence of Ca(2+)out. Neither BHQ nor manoalide affected Ins(1,4,5)P3 levels in resting or stimulated cells. Therefore, the effect of BHQ appears to involve unmasking of passive Ca(2+)-permeation pathways in the plasma and intracellular membranes that do not respond to cholecystokinin octapeptide, following its described inhibition of the internal-store Ca2+ pumps responsible for accumulating Ca2+ in these pools.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bastié M. J., Williams J. A. Gastrointestinal peptides activate Na(+)-H+ exchanger in AR42J cells by increasing its affinity for intracellular H+. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):G958–G966. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.258.6.G958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Calcium oscillations. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9583–9586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruzzone R., Halban P. A., Gjinovci A., Trimble E. R. A new, rapid, method for preparation of dispersed pancreatic acini. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 1;226(2):621–624. doi: 10.1042/bj2260621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Cheek T. R., Morgan A., O'Sullivan A. J., Moreton R. B., Berridge M. J., Mata A. M., Colyer J., Lee A. G., East J. M. Distribution of two distinct Ca2+-ATPase-like proteins and their relationships to the agonist-sensitive calcium store in adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):72–74. doi: 10.1038/342072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burk S. E., Lytton J., MacLennan D. H., Shull G. E. cDNA cloning, functional expression, and mRNA tissue distribution of a third organellar Ca2+ pump. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18561–18568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Chilvers E. R., Willcocks A. L., Nahorski S. R. Heterogeneity of [3H]inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate binding sites in adrenal-cortical membranes. Characterization and validation of a radioreceptor assay. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):421–427. doi: 10.1042/bj2650421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek T. R., Thastrup O. Internal Ca2+ mobilization and secretion in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Cell Calcium. 1989 May-Jun;10(4):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(89)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duddy S. K., Kass G. E., Orrenius S. Ca2(+)-mobilizing hormones stimulate Ca2+ efflux from hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20863–20866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Mechanisms of action of calcium-mobilizing agonists: some variations on a young theme. FASEB J. 1988 Aug;2(11):2670–2676. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.11.2456243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallam T. J., Jacob R., Merritt J. E. Influx of bivalent cations can be independent of receptor stimulation in human endothelial cells. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 1;259(1):125–129. doi: 10.1042/bj2590125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. R., Takemura H., Putney J. W., Jr Kinetics of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol cyclic 1:2,4,5-trisphosphate metabolism in intact rat parotid acinar cells. Relationship to calcium signalling. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10314–10319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. 'Quantal' Ca2+ release and the control of Ca2+ entry by inositol phosphates--a possible mechanism. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 9;263(1):5–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80692-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson T. R., Patterson S. I., Thastrup O., Hanley M. R. A novel tumour promoter, thapsigargin, transiently increases cytoplasmic free Ca2+ without generation of inositol phosphates in NG115-401L neuronal cells. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 1;253(1):81–86. doi: 10.1042/bj2530081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass G. E., Duddy S. K., Moore G. A., Orrenius S. 2,5-Di-(tert-butyl)-1,4-benzohydroquinone rapidly elevates cytosolic Ca2+ concentration by mobilizing the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ pool. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15192–15198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass G. E., Llopis J., Chow S. C., Duddy S. K., Orrenius S. Receptor-operated calcium influx in rat hepatocytes. Identification and characterization using manganese. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17486–17492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matozaki T., Göke B., Tsunoda Y., Rodriguez M., Martinez J., Williams J. A. Two functionally distinct cholecystokinin receptors show different modes of action on Ca2+ mobilization and phospholipid hydrolysis in isolated rat pancreatic acini. Studies using a new cholecystokinin analog, JMV-180. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6247–6254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Hallam T. J. Platelets and parotid acinar cells have different mechanisms for agonist-stimulated divalent cation entry. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6161–6164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Rink T. J. Regulation of cytosolic free calcium in fura-2-loaded rat parotid acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17362–17369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. A., McConkey D. J., Kass G. E., O'Brien P. J., Orrenius S. 2,5-Di(tert-butyl)-1,4-benzohydroquinone--a novel inhibitor of liver microsomal Ca2+ sequestration. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 30;224(2):331–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80479-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muallem S., Beeker T. G. Relationship between hormonal, GTP and Ins(1,4,5)P3-stimulated Ca2+ uptake and release in pancreatic acinar cells. Biochem J. 1989 Oct 15;263(2):333–339. doi: 10.1042/bj2630333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muallem S., Beeker T., Pandol S. J. Role of Na+/Ca2+ exchange and the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump in hormone-mediated Ca2+ efflux from pancreatic acini. J Membr Biol. 1988 May;102(2):153–162. doi: 10.1007/BF01870453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muallem S. Calcium transport pathways of pancreatic acinar cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:83–105. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.000503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muallem S., Khademazad M., Sachs G. The route of Ca2+ entry during reloading of the intracellular Ca2+ pool in pancreatic acini. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2011–2016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muallem S., Pandol S. J., Beeker T. G. Calcium mobilizing hormones activate the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump of pancreatic acinar cells. J Membr Biol. 1988 Nov;106(1):57–69. doi: 10.1007/BF01871767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osipchuk Y. V., Wakui M., Yule D. I., Gallacher D. V., Petersen O. H. Cytoplasmic Ca2+ oscillations evoked by receptor stimulation, G-protein activation, internal application of inositol trisphosphate or Ca2+: simultaneous microfluorimetry and Ca2+ dependent Cl- current recording in single pancreatic acinar cells. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):697–704. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08162.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandol S. J., Schoeffield M. S., Fimmel C. J., Muallem S. The agonist-sensitive calcium pool in the pancreatic acinar cell. Activation of plasma membrane Ca2+ influx mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):16963–16968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney T. A., Sass E. J., Thomas A. P. Characterization of cytosolic calcium oscillations induced by phenylephrine and vasopressin in single fura-2-loaded hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17131–17141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharff O., Foder B., Thastrup O., Hofmann B., Møller J., Ryder L. P., Jacobsen K. D., Langhoff E., Dickmeiss E., Christensen S. B. Effect of thapsigargin on cytoplasmic Ca2+ and proliferation of human lymphocytes in relation to AIDS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Dec 9;972(3):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90200-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura H., Hughes A. R., Thastrup O., Putney J. W., Jr Activation of calcium entry by the tumor promoter thapsigargin in parotid acinar cells. Evidence that an intracellular calcium pool and not an inositol phosphate regulates calcium fluxes at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12266–12271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thastrup O., Dawson A. P., Scharff O., Foder B., Cullen P. J., Drøbak B. K., Bjerrum P. J., Christensen S. B., Hanley M. R. Thapsigargin, a novel molecular probe for studying intracellular calcium release and storage. Agents Actions. 1989 Apr;27(1-2):17–23. doi: 10.1007/BF02222186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thastrup O., Foder B., Scharff O. The calcium mobilizing tumor promoting agent, thapsigargin elevates the platelet cytoplasmic free calcium concentration to a higher steady state level. A possible mechanism of action for the tumor promotion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 13;142(3):654–660. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91464-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakui M., Petersen O. H. Cytoplasmic Ca2+ oscillations evoked by acetylcholine or intracellular infusion of inositol trisphosphate or Ca2+ can be inhibited by internal Ca2+. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 24;263(2):206–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81374-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler L. A., Sachs G., De Vries G., Goodrum D., Woldemussie E., Muallem S. Manoalide, a natural sesterterpenoid that inhibits calcium channels. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6531–6538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Monck J. R. Hormone effects on cellular Ca2+ fluxes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:107–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.000543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods N. M., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Agonist-induced oscillations in cytoplasmic free calcium concentration in single rat hepatocytes. Cell Calcium. 1987 Feb;8(1):79–100. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(87)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao H., Khademazad M., Muallem S. Agonist-mediated Ca2+ release in permeabilized UMR-106-01 cells. Transport properties and generation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14822–14827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao H., Loessberg P. A., Sachs G., Muallem S. Regulation of intracellular Ca2+ oscillation in AR42J cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):20856–20862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


