Abstract
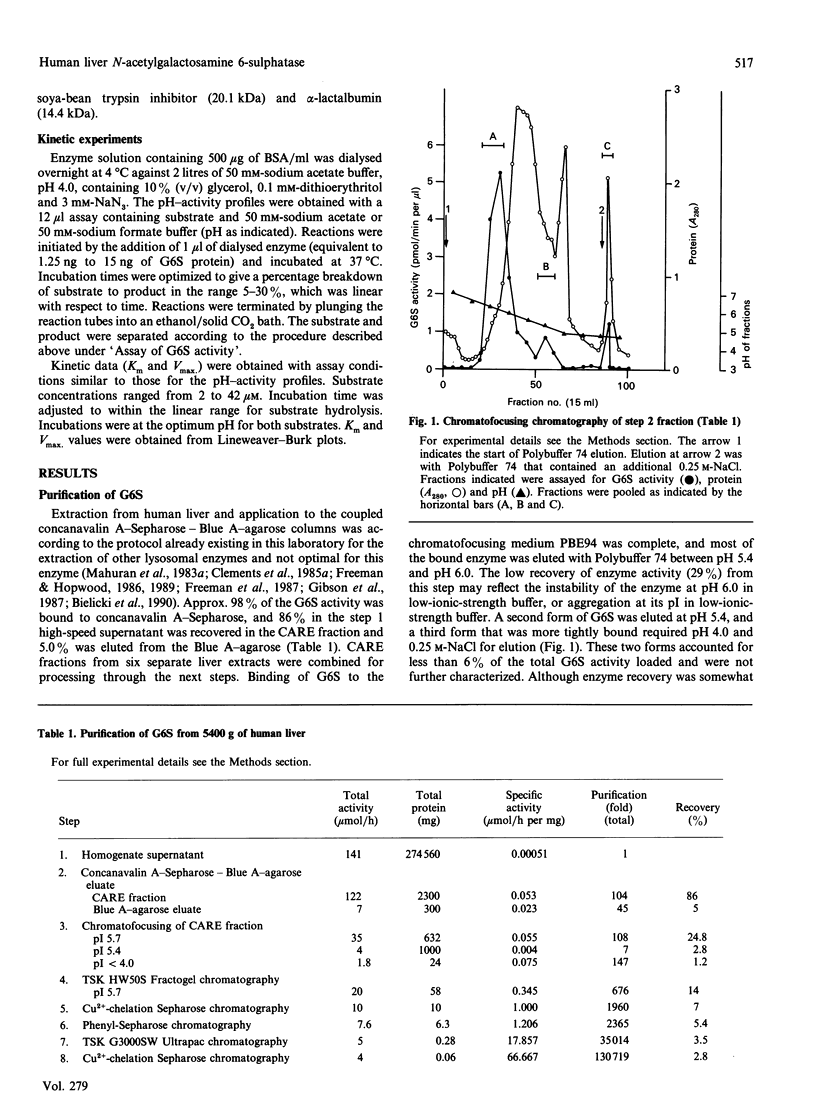
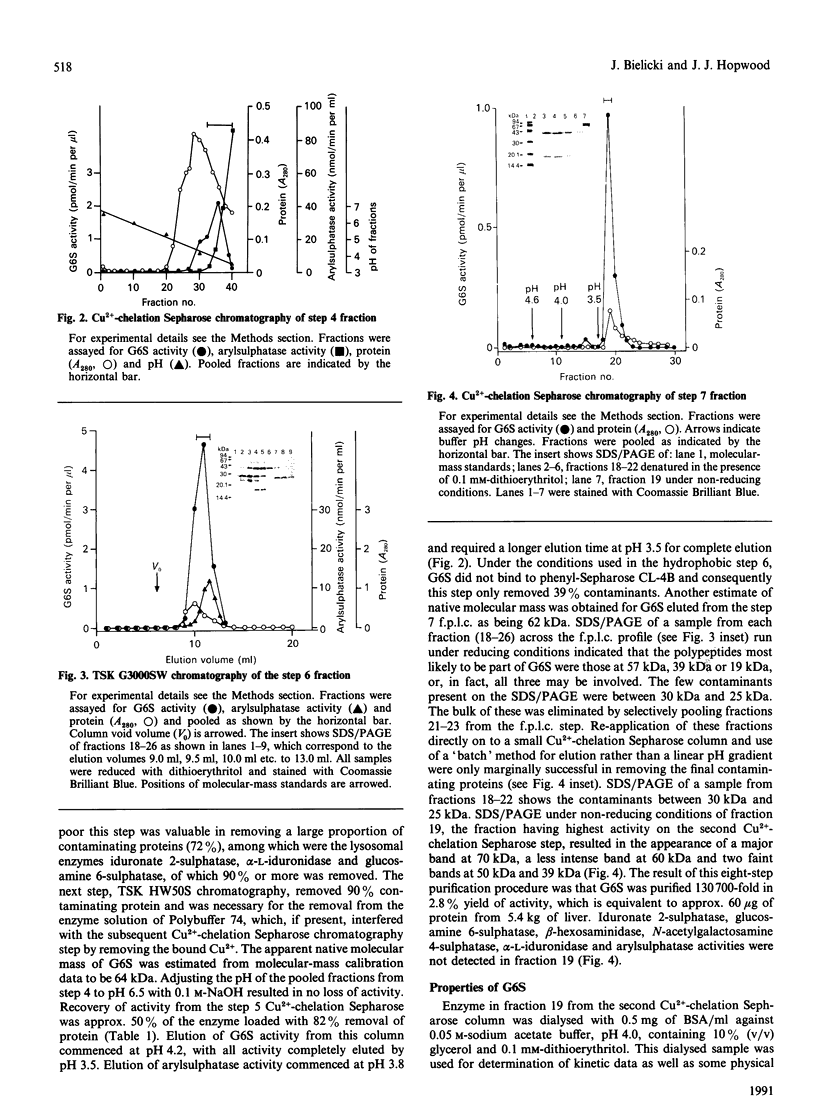
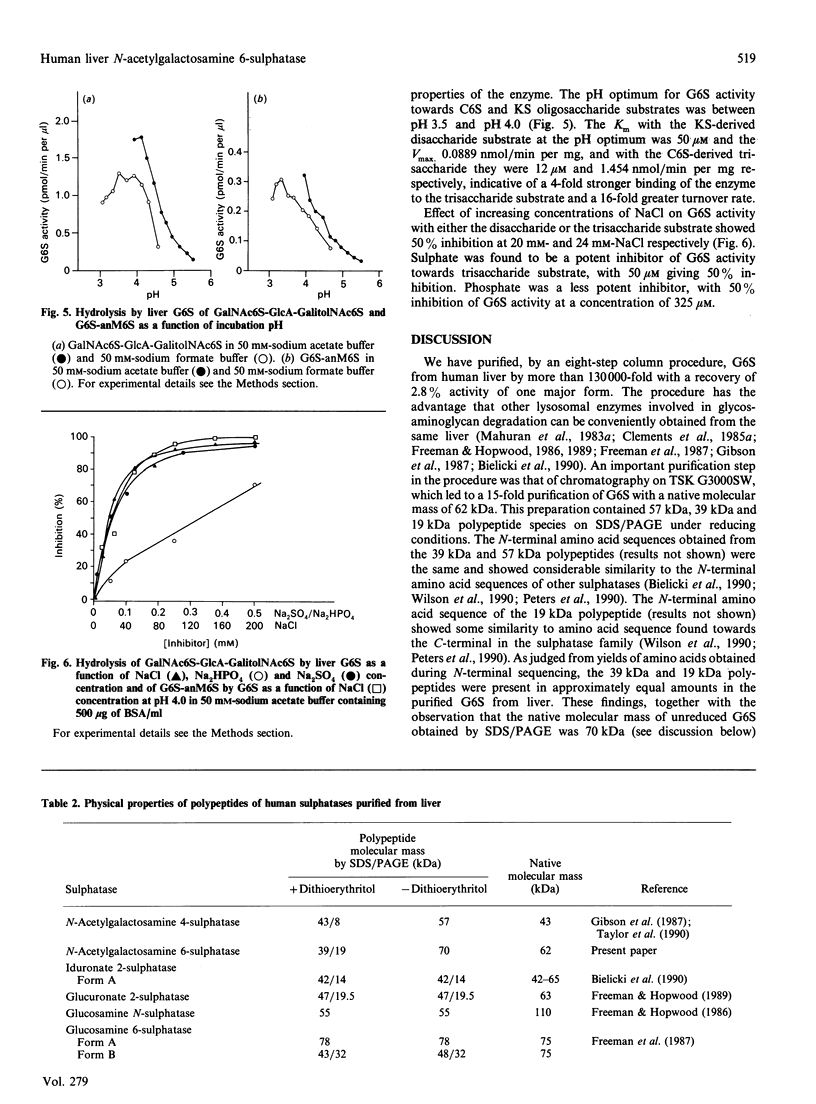
Human N-acetylgalactosamine 6-sulphatase (EC 3.1.6.14), which is involved in the lysosomal degradation of the glycosaminoglycans keratan sulphate and chondroitin 6-sulphate, was purified more than 130,000-fold in 2.8% yield from liver by an eight-step column procedure. One major form was identified with a pI of 5.7 and a native molecular mass of 62 kDa by gel filtration. When analysed by SDS/PAGE, dithioerythritol-reduced enzyme contained polypeptides of molecular masses 57 kDa, 39 kDa and 19 kDa, whereas non-reduced enzyme contained a major polypeptide of molecular mass 70 kDa. It is proposed that active enzyme contains either the 57 kDa polypeptide or disulphide-linked 39 kDa and 19 kDa polypeptides. Minor amounts of other enzyme forms separated during the chromatofocusing step and the Blue A-agarose step were not further characterized. Purified N-acetylgalactosamine 6-sulphatase was inactive towards 4-methylumbelliferyl sulphate, but was active, with pH optima of 3.5-4.0, towards 6-sulphated oligosaccharide substrates. Km values of 12.5 and 50 microM and Vmax. values of 1.5 and 0.09 mumol/min per mg were determined with oligosaccharide substrates derived from chondroitin 6-sulphate and keratan sulphate respectively. Sulphate, phosphate and chloride ions were inhibitors of enzyme activity towards both substrates, with 50 microM-Na2SO4 giving 50% inhibition towards the chondroitin 6-sulphate trisaccharide substrate.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bielicki J., Freeman C., Clements P. R., Hopwood J. J. Human liver iduronate-2-sulphatase. Purification, characterization and catalytic properties. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 1;271(1):75–86. doi: 10.1042/bj2710075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang P. L., Rosa N. E., Davidson R. G. Differential assay of arylsulfatase A and B activities: a sensitive method for cultured human cells. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):382–389. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90795-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements P. R., Brooks D. A., McCourt P. A., Hopwood J. J. Immunopurification and characterization of human alpha-L-iduronidase with the use of monoclonal antibodies. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 1;259(1):199–208. doi: 10.1042/bj2590199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements P. R., Brooks D. A., Saccone G. T., Hopwood J. J. Human alpha-L-iduronidase. 1. Purification, monoclonal antibody production, native and subunit molecular mass. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 1;152(1):21–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements P. R., Mahuran D. J., Hopwood J. J. Improved concanavalin A-Sepharose elution by specific readsorption of glycoproteins. J Chromatogr. 1983 May 20;261(1):77–82. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)87920-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements P. R., Muller V., Hopwood J. J. Human alpha-L-iduronidase. 2. Catalytic properties. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 1;152(1):29–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman C., Clements P. R., Hopwood J. J. Human liver N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulphate sulphatase. Purification and characterization. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):347–354. doi: 10.1042/bj2460347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman C., Hopwood J. J. Human liver glucuronate 2-sulphatase. Purification, characterization and catalytic properties. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 1;259(1):209–216. doi: 10.1042/bj2590209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman C., Hopwood J. J. Human liver sulphamate sulphohydrolase. Determinations of native protein and subunit Mr values and influence of substrate agylcone structure on catalytic properties. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 15;234(1):83–92. doi: 10.1042/bj2340083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson G. J., Saccone G. T., Brooks D. A., Clements P. R., Hopwood J. J. Human N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulphate sulphatase. Purification, monoclonal antibody production and native and subunit Mr values. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 15;248(3):755–764. doi: 10.1042/bj2480755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glössl J., Truppe W., Kresse H. Purification and properties of N-acetylgalactosamine 6-sulphate sulphatase from human placenta. Biochem J. 1979 Jul 1;181(1):37–46. doi: 10.1042/bj1810037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood J. J., Elliott H. Detection of Morquio A syndrome using radiolabelled substrates derived from keratan sulphate for the estimation of galactose 6-sulphate sulphatase. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Sep;65(3):325–331. doi: 10.1042/cs0650325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood J. J., Elliott H., Muller V. J., Saccone G. T. Diagnosis of Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome by the use of radiolabelled oligosaccharides as substrates for the determination of arylsulphatase B activity. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 15;234(3):507–514. doi: 10.1042/bj2340507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood J. J., Elliott H. Selective depolymerisation of keratan sulfate: production of radiolabelled substrates for 6-O-sulfogalactose sulfatase and beta-D-galactosidase. Carbohydr Res. 1983 Jun 16;117:263–274. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(83)88092-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim C. T., Horwitz A. L. Purification and properties of human N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 13;657(2):344–355. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahuran D., Clements P., Carrella M., Strasberg P. M. A high recovery method for concentrating microgram quantities of protein from large volumes of solution. Anal Biochem. 1983 Mar;129(2):513–516. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90585-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahuran D., Clements P., Hopwood J. A rapid four column purification of 2-deoxy-D-glucoside-2-sulphamate sulphohydrolase from human liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jun 9;757(3):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters C., Schmidt B., Rommerskirch W., Rupp K., Zühlsdorf M., Vingron M., Meyer H. E., Pohlmann R., von Figura K. Phylogenetic conservation of arylsulfatases. cDNA cloning and expression of human arylsulfatase B. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3374–3381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. A., Gibson G. J., Brooks D. A., Hopwood J. J. Human N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulphatase biosynthesis and maturation in normal, Maroteaux-Lamy and multiple-sulphatase-deficient fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 1;268(2):379–386. doi: 10.1042/bj2680379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. J., Morris C. P., Anson D. S., Occhiodoro T., Bielicki J., Clements P. R., Hopwood J. J. Hunter syndrome: isolation of an iduronate-2-sulfatase cDNA clone and analysis of patient DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8531–8535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]