Abstract
Detection of the resistance mediated by class C β-lactamases remains a challenging issue, considering that transferable plasmid-mediated class C β-lactamases are of worldwide concern. Methods for the identification of strains that produce extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) or metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs) have been developed and applied for routine use in clinical microbiology laboratories, but no practical methods for identification of plasmid-mediated class C producers have been established to date. We therefore developed three simple methods for clinical microbiology laboratories that allow identification of plasmid-mediated class C β-lactamase-producing bacteria using a boronic acid derivative, 3-aminophenylboronic acid (APB), one of the specific inhibitors of class C β-lactamases. Detection by the disk potentiation test was based on the enlargement of the growth-inhibitory zone diameter (by greater than or equal to 5 mm) around a Kirby-Bauer disk containing a ceftazidime (CAZ) or a cefotaxime (CTX) disk in combination with APB. In a double-disk synergy test, the discernible expansion of the growth-inhibitory zone around the CAZ or the CTX disk toward a disk containing APB was indicative of class C β-lactamase production. A greater than or equal to eightfold decrease in the MIC of CAZ or CTX in the presence of APB was the criterion for detection in the microdilution test. By using these methods, Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates producing plasmid-mediated class C β-lactamases, ACT-1, CMY-2, CMY-9, FOX-5, LAT-1, and MOX-1, were successfully distinguished from those producing other classes of β-lactamases, such as ESBLs and MBLs. These methods will provide useful information needed for targeted antimicrobial therapy and better infection control.
The production of β-lactamases is the major mechanism of resistance to β-lactams, which are most frequently used for the treatment of various infectious diseases. Class C β-lactamases, which belong to group 1 according to the classification of Bush et al. (7), are cephalosporinases, which are poorly inhibited by β-lactamase inhibitors, such as clavulanic acid (CLA) and sulbactam. Class C β-lactamases are clinically important because they usually confer resistance to a variety of β-lactams, including oxyiminocephalosporins and some cephamycins, as well as penicillins and monobactam, when they are produced in large amounts (14, 21, 32). They are usually chromosomally encoded AmpC enzymes in several bacterial species belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae, including Enterobacter cloacae, Enterobacter aerogenes, Citrobacter freundii, Morganella morganii, Serratia marcescens, and Escherichia coli, which are frequently encountered as nosocomial pathogens. Moreover, since the first report of transferable plasmid-mediated class C β-lactamases, such as MIR-1, in the late 1980s (3, 30), their increasing presence worldwide is becoming of great concern (9, 13, 22, 24). In Japan, MOX-1 (15), CMY-9 (10), and CMY-2 and DHA-1 (unpublished data) have been identified so far. Although simple methods for the identification of extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) and metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs) have been established and are already in laboratory use (1, 29), detection of the resistance mediated by class C β-lactamases still remains a challenging issue. Several methods that use the Kirby-Bauer (KB) disk potentiation method (20, 21, 34, 35, 45) with some β-lactamase inhibitors (2, 5) or the three-dimensional method (9, 22, 39) have been developed; and a cefoxitin agar medium-based assay that uses preparations of bacterial cell extracts has been reported (26). However, these methods are technically intricate, and interpretation of their results is not sufficiently simple for routine use in clinical microbiology laboratories. PCR or multiplex PCR analyses are able to provide satisfactory results in the identification and classification of genes for β-lactamases (25, 31, 38, 44), but equipment availability is limited to medical institutions, such as university hospitals. They are also costly and require time-consuming techniques. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay has also been developed and has known sensitivity and specificity for the detection of certain class C β-lactamases. This technique is less costly than genetic methods, but it is not sensitive for the detection of class C β-lactamases that possess less than 70% homology to CMY-2 (16). Thus, practical and simple methods for detection of the resistance mediated by plasmid-mediated class C β-lactamases are urgently needed for enhanced infection control.
In 1982, boronic acids were reported as reversible inhibitors of AmpC enzymes belonging to the class C β-lactamases (4). Serial studies revealed the structure-based mechanism of inhibition of AmpC β-lactamases by boronic acids (34, 37, 41), and novel compounds that inhibit AmpC β-lactamases with nanomolar Ki values were prepared by stereoselective organic synthesis (23). However, there are only a few reports of studies that applied boronic acids to the identification of class C β-lactamase-producing bacteria (19, 34). In the present study we used one of the boronic acids, 3-aminophenylboronic acid (APB), and here we propose simple and practical methods for the identification of class C β-lactamase-producing bacteria showing resistance to broad-spectrum β-lactams, including cephamycins. The methods constructed in the present study promise to be very helpful for the screening of plasmid-mediated class C β-lactamase-producing bacteria in clinical microbiology laboratories.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains, chemicals, and antibiotics.
The bacterial strains used in this study and the β-lactamases that they produce are shown in Table 1. The types of β-lactamase genes were previously confirmed by PCR analyses, cloning and sequencing experiments, as well as isoelectric focusing, as described elsewhere (6, 10, 15, 25, 36, 40, 42, 43, 44). APB, 3-nitrophenylboronic acid (NPB), and 2-thiopheneboronic acid (TPB) were purchased from Tokyo Kasei Kogyo Co., Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan). Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was purchased from Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd. (Osaka, Japan). Mueller-Hinton (MH) agar and MH broth were obtained from Becton Dickinson and Company (Paramus, N.J.). KB disks were commercially supplied by Eiken Chemical Co., Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan).
TABLE 1.
Bacterial strains used in this study and MICs of CAZ and CTX with or without β-lactamase inhibitors
| Strain | β-Lactamase | MIC (μg/ml)
|
Reference | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAZ | CAZ + CLA | CAZ + SMA | CAZ + APB | CTX | CTX + CLA | CTX + SMA | CTX + APB | |||
| E. coli NS12 | CMY-2 | 128 | 64 | 128 | 4 | 64 | 32 | 64 | 2 | This study |
| E. coli HKY515 | CMY-2 | 256 | 128 | 256 | 4 | 64 | 32 | 64 | 4 | This study |
| E. coli HKY701 | CMY-2 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 2 | 32 | 32 | 64 | 4 | This study |
| E. coli MRY041197 | CMY-2 | >256 | 256 | >256 | 8 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 8 | This study |
| E. coli HKY581 | CMY-2 | 256 | 128 | 256 | 8 | 128 | 128 | 256 | 4 | This study |
| E. coli C502 | CMY-2 | 256 | 256 | 256 | 16 | 16 | 32 | 32 | 2 | This study |
| E. coli KG2 | CMY-2 | 128 | 128 | 64 | 4 | 64 | 32 | 64 | 8 | This study |
| E. coli MRY041243 | CMY-8 | 256 | 256 | >256 | 4 | 64 | 32 | 64 | 0.5 | This study |
| E. coli M68 | CMY-9 | 256 | 256 | 256 | 1 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 16 | 10 |
| E. coli Coral Gables 66040 | FOX-5 | >128 | >128 | >128 | 4 | 64 | 64 | 64 | 1 | G. A. Jacoby |
| E. coli Coral J53 (a trans- formant) | ACT-1 | 8 | 4 | 4 | ≤0.25 | 2 | 2 | 2 | ≤0.25 | G. A. Jacoby |
| E. coli HKY28 | Mutant AmpC | 64 | 32 | 64 | 4 | 16 | 4 | 8 | 1 | 11 |
| K. pneumoniae NU2936 | MOX-1 | 64 | 32 | 32 | 0.5 | 256 | 256 | 256 | 8 | 15 |
| K. pneumoniae HKY-L1 | MOX-1 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 1 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 4 | This study |
| K. pneumoniae KPW142 | CMY-8 | 32 | 32 | 64 | 1 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 4 | This study |
| K. pneumoniae HKY209 | CMY-9 | >128 | >128 | >128 | 2 | >128 | >128 | >128 | 2 | This study |
| K. pneumoniae HKY327 | CMY-19 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 16 | 64 | 64 | 64 | 1 | This study |
| K. pneumoniae 5064 | FOX-5 | 64 | 64 | 64 | 2 | 8 | 16 | 16 | 0.5 | 36 |
| K. pneumoniae Bronx Lebanon 18 | ACT-1 | 64 | 64 | 128 | 64 | 8 | 16 | 8 | 0.5 | G. A. Jacoby |
| K. pneumoniae P20 | LAT-1 | 64 | 64 | 64 | 2 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 1 | 40 |
| Hafnia alvei EE47a | AmpC | 64 | 128 | 64 | 2 | 32 | 64 | 32 | 2 | This study |
| E. coli NCB03522b | CMY-2 + CTX-M-9 | 64 | 16 | 64 | 16 | 256 | 8 | 256 | 256 | This study |
| K. pneumoniae NCB02189a | DHA-1 + CTX-M-9 | 16 | 128 | 16 | 1 | 32 | 8 | 32 | 2 | This study |
| E. coli AYW-1 | TEM-26 | >128 | 0.5 | >128 | >128 | 2 | <0.06 | 2 | 2 | 44 |
| E. coli HKY322 | TEM-91 | 128 | 0.5 | 128 | >128 | 1 | <0.06 | 1 | 1 | 18 |
| E. coli MRY041435 | TEM-132 | 64 | 1 | 64 | 64 | 8 | ≤0.25 | 4 | 4 | This study |
| E. coli HKY453 | SHV-24 | >128 | 2 | >128 | >128 | 2 | 0.13 | 2 | 2 | 17 |
| E. coli NCB03515 | CTX-M-3 | 32 | ≤0.25 | 16 | 16 | >256 | ≤0.25 | 256 | 256 | This study |
| E. coli MRY04718 | CTX-M-3 | 64 | 1 | 128 | 32 | >256 | ≤0.25 | >256 | >256 | This study |
| E. coli AYW-2 | CTX-M-2 | 8 | 0.13 | 8 | 4 | >128 | <0.06 | >128 | >128 | This study |
| E. coli NCB03490 | CTX-M-2 | 4 | ≤0.25 | 4 | 1 | 128 | ≤0.25 | 256 | 64 | This study |
| E. coli NCB03520 | CTX-M-14 | 2 | 0.25 | 4 | 1 | 128 | 0.13 | >128 | 128 | This study |
| E. coli AYW-3 | CTX-M-9 | 0.5 | <0.06 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 32 | <0.06 | 64 | 16 | This study |
| K. pneumoniae HKY402 | SHV-12 | >128 | 1 | >128 | >128 | 32 | <0.06 | 32 | 32 | 44 |
| K. pneumoniae MRY041410 | TEM-132 | 64 | 1 | 64 | 64 | 4 | ≤0.25 | 4 | 8 | This study |
| K. pneumoniae K108 | CTX-M-1 | 2 | 0.25 | 1 | 2 | 64 | <0.06 | 64 | 64 | This study |
| K. pneumoniae MRY04332 | CTX-M-3 | 16 | 1 | 8 | 8 | 128 | ≤0.25 | 128 | 128 | This study |
| K. pneumoniae HKY495 | CTX-M-2 | 16 | 1 | 16 | 16 | 128 | 0.13 | >128 | >128 | This study |
| K. pneumoniae MRY04504 | CTX-M-2 | 2 | ≤0.25 | 2 | 4 | 64 | ≤0.25 | 128 | 64 | This study |
| K. pneumoniae NCB03502 | CTX-M-9 | 0.5 | 0.06 | 1 | 1 | 32 | <0.06 | 64 | 32 | This study |
| K. pneumoniae NCB03081 | CTX-M-9 | 4 | ≤0.25 | 4 | 4 | 32 | ≤0.25 | 32 | 32 | This study |
| K. pneumoniae KG525 | GES-3J | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | 64 | 8 | 64 | 32 | 42 |
| K. pneumoniae KG502 | GES-4J | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | 32 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 43 |
| E. coli NCB03426 | IMP-1 | 64 | 64 | ≤0.25 | 64 | 16 | 16 | ≤0.25 | 16 | This study |
| E. coli NCB02465 | IMP-1 | 128 | 128 | ≤0.25 | 128 | 32 | 64 | ≤0.25 | 64 | This study |
| K. pneumoniae KP115 | IMP-1 | >128 | 128 | 1 | >128 | 64 | 64 | 0.25 | 64 | This study |
| K. pneumoniae NCB03034 | IMP-1 | 64 | 64 | ≤0.25 | 64 | 128 | 128 | ≤0.25 | 128 | This study |
| E. coli EE61 | OXA-30 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | This study |
Production of AmpC or DHA-1 might be augmented in the presence of clavulanic acid.
E. coli strain NCB03522 also produces the TEM-1 penicillinase.
Susceptibility test.
The MICs of ceftazidime (CAZ) and cefotaxime (CTX) with or without β-lactamase inhibitors were determined by the agar dilution method with MH agar, according to the recommendations of CLSI (formerly the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards) in document M2-A8 (28). Clavulanic acid (GlaxoSmithKline K.K., Tokyo, Japan) was added at a concentration of 4 μg/ml, and both sodium mercaptoacetic acid (SMA) and APB were added at a concentration of 300 μg/ml. The MIC of APB was generally above 2,400 μg/ml, so the concentration of APB employed in this study did not show any detectable effect on bacterial growth or susceptibilities to antimicrobial agents.
Detection of class C β-lactamase production.
Class C β-lactamase production was determined by the following three methods. Clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae or E. coli producing the following plasmid-mediated class C β-lactamases were used as positive controls: ACT-1 (6), CMY-2 and CMY-9 (10), FOX-5 (36), LAT-1 (40), and MOX-1 (15). Because of the similarity of its chromosomal enzyme to one of the plasmid-mediated β-lactamases, ACC-1, an isolate of Hafnia alvei was added to the positive controls (24). As negative controls, we used clinical isolates of K. pneumoniae or E. coli producing other plasmid-mediated β-lactamases: TEM-26 (44); TEM-91 (17); SHV-12 (44); SHV-24 (18); CTX-M-1, CTX-M-2, CTX-M-9, and GES-3 (42); GES-4 (43); and IMP-1 (Table 1). The boronic acids APB, NPB, and TPB were dissolved in DMSO at a concentration of 100 mg/ml and used for the following tests.
Disk potentiation test.
A colony of a test strain which was suspected of being a class C β-lactamase producer was suspended in and diluted with MH broth medium to 108 CFU/ml and spread on an MH agar plate with a cotton swab, according to the protocol recommended by CLSI in document M2-A8 (28). Three hundred micrograms of one of the boronic acids, APB, NPB, or TPB, was added to a commercially available KB disk containing 30 μg of CAZ or CTX. These disks were placed on the MH agar plate described above in pairs with a KB disk containing 30 μg of CAZ or CTX with a center-to-center distance of 30 mm (Fig. 1A). The agar plates were incubated at 37°C overnight. The diameter of the growth-inhibitory zone around a CAZ disk with APB was compared with that around a CAZ disk without APB for the detection of class C β-lactamase production.
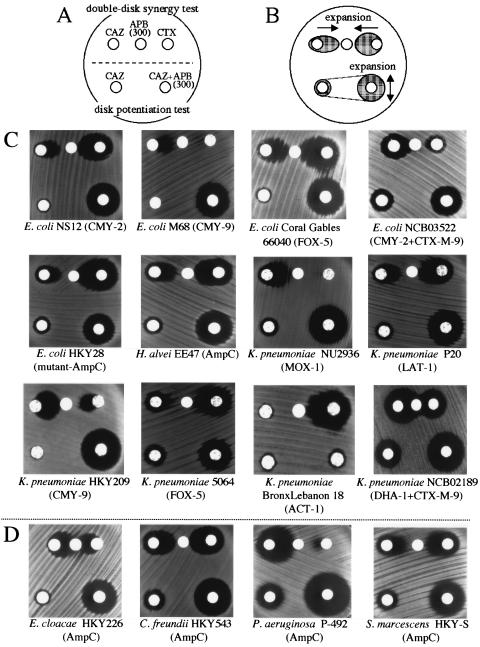
FIG. 1.
DDST and disk potentiation test for class C β-lactamase producers. (A) Scheme of disk arrangement for the two tests. The upper three disks are for DDST, and the lower two are for the disk potentiation test. The amount of APB added to the disk was 300 μg. (B) Typical observations of the growth-inhibitory zones among class C β-lactamase producers. The growth-inhibitory zones are expanded toward the APB disk in DDST. In the disk potentiating test, the diameter of the growth-inhibitory zone is expanded around the disk containing both CAZ and APB compared with that around the disk containing solely CAZ. (C) Practical changes in the morphologies or the diameters of the growth-inhibitory zones among the class C β-lactamase-producing strains. Expansion of the growth-inhibitory zone toward the APB disk is observed around the disks containing CAZ or CTX in DDST (upper) among the class C β-lactamase producers. In the disk potentiation test (lower), enlargement of the diameter of the growth-inhibitory zone of greater than or equal to 5 mm is seen among all class C β-lactamase producers except K. pneumoniae BronxLebanon 18. (D) DDST and disk potentiation test against chromosomal AmpC producers. Similar findings are observed among gram-negative rods that produce chromosomally encoded inducible AmpC type β-lactamases, suggesting that the new identification method described in the present study can also be applied to chromosomal AmpC producers, as well as plasmid-mediated class C β-lactamase producers.
Double-disk synergy test (DDST).
Three hundred micrograms of APB was added to a disk that contained no antibiotics and that was the same size as the KB disk. This APB-containing disk was placed on an MH agar plate on which the bacterial suspension to be examined had been spread. Two other KB disks containing 30 μg of CAZ and CTX were also placed on the MH agar plate, with a center-to-center distance to the boronic acid-containing disk of 18 mm (Fig. 1A). The plate was incubated at 37°C overnight, and the change in the shape of the growth-inhibitory zone around the CAZ or the CTX disk through the interaction with the boronic acid-containing disk was observed for the detection of class C β-lactamase production (Fig. 1B).
Microdilution test.
MH broth containing serial dilutions of CAZ or CTX at concentrations ranging from 0.125 to 256 μg/ml and containing 300 μg (1.9 mM) of APB with the same serial dilution of CAZ or CTX was prepared and placed in a 96-well plate. A bacterial suspension was inoculated into each well, according to the recommendation of CLSI in document M7-A6 (27). The plate was incubated at 37°C overnight. The decrease in the MIC of CAZ or CTX in combination with APB was used for the identification of a class C β-lactamase producer.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Plasmid-mediated class C β-lactamases have been identified worldwide since the late 1980s, and they are emerging threats to antibiotic therapy for various infectious diseases because they confer to pathogenic bacteria, especially E. coli and K. pneumoniae, resistance to broad-spectrum β-lactams (9, 10, 13, 15, 22, 24, 32). Boronic acids have been recognized as specific inhibitors of AmpC β-lactamases since 1982 (4, 8, 34, 37, 41). Using three commercially available boronic acids, APB, NPB, and TPB, in the present study, we evaluated three different methods for the identification of bacteria producing class C β-lactamases which would be simple enough for routine use in a clinical microbiology laboratory.
First, we developed the disk potentiation test, which is similar to the confirmation test for ESBL production recommended by CLSI in document M100-S14 (29). We selected three commercially available boronic acids, APB, NPB, and TPB, as the specific inhibitors of class C β-lactamases and observed the enlargement of the growth-inhibitory zone diameter around the disk containing CAZ in combination with these inhibitors. The boronic acids were dissolved in DMSO and added to the KB disk containing 30 μg of CAZ. DMSO itself had no apparent effect on the growth of the isolates tested when it was added to the disk at a volume up to 10 μl (data not shown). Both NPB and TPB were found to have antibacterial activity by themselves at concentrations of about 300 μg/ml, leading to a misinterpretation of the changes in the diameter of the growth-inhibitory zone (data not shown). Therefore, we chose APB as the most practical candidate among the specific inhibitors of class C β-lactamases for further examination. Among the four drugs that we tested, CAZ, CTX, cefmetazole, and moxalactam, CAZ showed the best performance in combination with APB. When a cutoff value of a 5-mm enlargement of the growth-inhibitory zone diameter or greater was set, all K. pneumoniae and E. coli isolates producing the plasmid-mediated class C β-lactamases, except for ACT-1-producing K. pneumoniae BronxLebanon 18, could be detected (Fig. 1C); and the specificity of the test was nearly 100% for the negative controls of producers of other classes of β-lactamases (Fig. 2). The exception, K. pneumoniae BronxLebanon 18, was less inhibited by APB when CAZ was used. However, a successful test result was obtained with the combination of CTX and APB (data not shown). This strain was supposed to produce another ESBL or to have an alteration in the permeability of the outer membrane, and the test reported by Pitout et al. (33) might be useful for this kind of strain. H. alvei was also found to be positive as an AmpC β-lactamase producer. Also, this method could detect E. coli HKY28, a mutant AmpC producer which was moderately susceptible to β-lactamase inhibitors such as tazobactam and sulbactam (11). Two well-characterized isolates, E. coli NCB03522 and K. pneumoniae NCB02189, which produce plasmid-mediated CMY-2 and DHA-1, respectively, together with CTX-M-9, were examined with this disk potentiation test. Using the drug-inhibitor combinations of CAZ plus APB and CTX plus clavulanic acid, we could detect class C β-lactamases and CTX-M-9 separately, with no apparent interaction of these two different classes of β-lactamases.
FIG. 2.
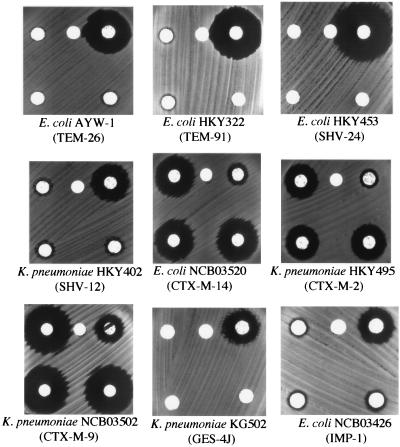
DDST (upper) and disk potentiation test (lower) for non-class C β-lactamase producers. No apparent changes in the shapes or the diameters of the growth-inhibitory zones around the disks containing CAZ or CTX are observed in the presence of APB (300 μg per disk). The arrangement of the disks was as described for Fig. 1.
Second, we applied DDST to the identification of class C β-lactamase producers. Powers et al. (34) first described the potentiation effect of a boronic acid, benzo(b)thiophene-2-boronic acid, to the antimicrobial activity of CAZ; and Liebana et al. (19) used this synergism test for confirmation of the presence of an AmpC-like enzyme. This method, similar to the simple test which we described earlier (1) for the detection of metallo-β-lactamases by the use of thiol compounds, was based on the interpretation of the change in morphology in the growth-inhibitory zone in order to detect class C β-lactamases. An APB-containing disk and a disk containing a test drug, CAZ or CTX, were placed on an MH agar plate which had been inoculated with a test isolate, with the center-to-center distance of 18 mm. After overnight incubation, expansion of the growth-inhibitory zone toward the APB-containing disk was interpreted to be a positive result for class C β-lactamase production. With the combination of APB and CAZ or CTX, all plasmid-mediated class C β-lactamases of the positive controls were detected (Fig. 1C), and no apparent changes in the morphology of the growth-inhibitory zone were observed for the negative controls producing other classes of β-lactamases (Fig. 2). For E. coli NCB03522 and K. pneumoniae NCB02189, which produce plasmid-mediated CMY-2 or DHA-1 together with CTX-M-9, the center-to-center distance between the CAZ and the APB disks should be shortened to 12 mm in order to detect a more discernible expansion of the growth-inhibitory zone around the CAZ disk toward the APB disk.
The microdilution method is one of the most familiar methods for the determination of MICs in clinical laboratories due to the recent introduction of rapid automated bacterial identification and antimicrobial susceptibility test systems. Three hundred micrograms of APB was added to the serial dilution of CAZ, and the MICs of CAZ determined with and without APB were compared according to the methods recommended by CLSI (27). The MICs appeared to be similar to those shown in Table 1, which were determined by the agar dilution method, according to the recommendations of CLSI (28). More than or equal to an eightfold decrease in the MIC of CAZ in combination with APB was indicative of the production of plasmid-mediated class C β-lactamases in E. coli and K. pneumoniae. Most of the isolates showed more than or equal to an eightfold reduction in the MIC of CAZ in the presence of APB, while only a fourfold reduction of MIC was observed in E. coli NCB03522 (Fig. 3). For ACT-1-producing K. pneumoniae BronxLebanon 18, this test was positive, with a 16-fold reduction in the MIC of CTX in combination with APB (Fig. 3). As shown in Fig. 4, the classes of β-lactamases produced by clinical isolates can be easily distinguished from each other by using three kinds of inhibitors, especially when a strain chiefly produces a single type of β-lactamase.
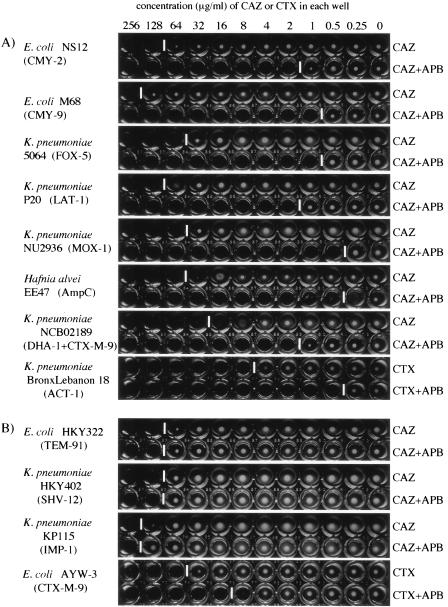
FIG. 3.
Microdilution test with APB for detection of class C β-lactamases. APB was added to serial dilutions of CAZ or CTX, and the concentration of ABP in each well is 300 μg/ml. (A) Detection of plasmid-mediated class C β-lactamases in representative E. coli and K. pneumoniae isolates and chromosomal AmpC β-lactamase in H. alvei EE47. An eightfold or greater decrease in the MIC of CAZ or CTX with the addition of APB is indicative of the production of class C β-lactamases. (B) Negative results of microdilution test by using APB for E. coli and K. pneumoniae isolates producing class A ESBLs or a class B MBL, IMP-1. Among the strains tested, the level of resistance to cefotaxime was reduced in the presence of APB in a few strains, such as CTX-M-9-producing E. coli AYW-3; and the coproduction of chromosomal AmpC was suspected in this strain. It may even be possible to distinguish strains that chiefly produce a class A or a class B enzyme, together with a small amount of a class C enzyme, from those that mainly produce class C enzymes when the breakpoint was set at a decrease in the MIC of greater than or equal to eightfold (three tubes) in the presence of APB. White vertical bars between the wells indicate the upper limit of bacterial growth in each line.
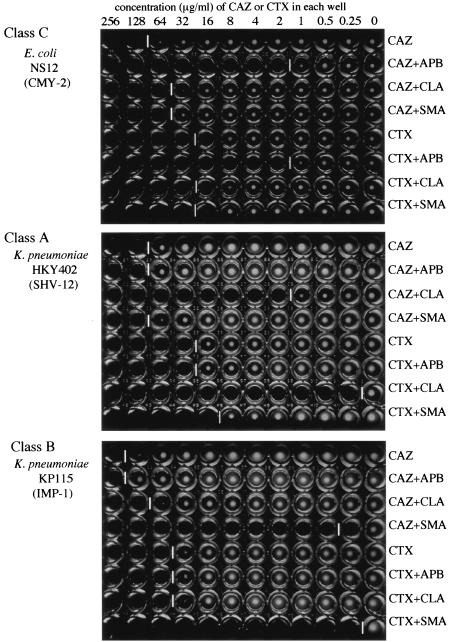
FIG. 4.
Microdilution test using three inhibitors for detection of presumptive β-lactamase types. Three inhibitors, APB (300 μg/ml), CLA (4 μg/ml), and SMA (300 μg/ml), were added in each line of the wells. The inhibition patterns of each inhibitor for strains producing class A, class B, and class C β-lactamases are demonstrated by using cefotaxime and ceftazidime as indicators. White vertical bars between the wells indicate the upper limit of bacterial growth in each line.
Moreover, we applied the former two methods to several CAZ-resistant clinical isolates of E. cloacae, C. freundii, S. marcescens, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa for the detection of their chromosomal AmpC β-lactamases. Most of these isolates showed positive results, suggesting that they are probably hyperproducers of chromosomal AmpC β-lactamases. The results of both tests for the representative strains, E. cloacae HKY226, C. freundii HKY543, S. marscecens HKY-S, and P. aeruginosa P-492, are shown in Fig. 1D. For the E. cloacae isolates, successful detection was achieved by shortening the center-to-center distance of the two disks containing CAZ and APB from 18 mm to 12 mm in DDST. A few isolates of S. marcescens and P. aeruginosa were less inhibited by APB, so they could not be detected by either method (data not shown). They might produce additional unknown β-lactamases other than the AmpC type or overexpress their multidrug efflux systems (12).
According to these results, all three tests, the disk potentiation test, the double-disk synergy test, and the microdilution test with APB, were very simple, highly sensitive, and specific for the identification of bacteria producing class C β-lactamases. Thus, they are fully applicable for routine use in clinical microbiology laboratories. Although the results for the production of class C enzymes obtained by these methods is sometimes ambiguous when the strains also coproduce a large amount of ESBLs or MBLs, the methods provide useful information on the mechanism of drug resistance mediated by class C β-lactamases for enhanced infection control and effective antimicrobial therapy.
Acknowledgments
We thank Kumiko Kai for technical assistance. K. pneumoniae P20 producing LAT-1 was a kind gift from E. Tzelepi; and K. pneumoniae BronxLebanon 18 producing ACT-1, E. coli Coral Gables 66040 producing FOX-5, and E. coli Coral J53 (a transformant) producing ACT-1 were graciously provided by G. A. Jacoby. K. pneumoniae 5064 producing FOX-5 was the kind gift of A. M. Queenan.
This research was supported by grants from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan (grants Shinkou-H15-09 and Shinkou-H15-10).
REFERENCES
- 1.Arakawa, Y., N. Shibata, K Shibayama, H. Kurokawa, T. Yagi, H. Fujiwara, and M. Goto. 2000. Convenient test for screening metallo-β-lactamase-producing gram-negative bacteria by using thiol compounds. J. Clin. Microbiol. 38:40-43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Barnaud, G., G. Arlet, C. Verdet, O. Gaillot, P. H. Lagrange, and A. Philippon. 1998. Salmonella enteritidis: AmpC plasmid-mediated inducible β-lactamase (DHA-1) with an ampR gene from Morganella morganii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 42:2352-2358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bauernfeind, A., Y. Chong, and S. Schweighart. 1989. Extended broad-spectrum β-lactamase in Klebsiella pneumoniae including resistance to cephamycins. Infection 17:316-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Beesley, T., N. Gascoyne, V. Knott-Hunziker, S. Petursson, S. G. Waley, B. Jaurin, and T. Grundstrom. 1982. The inhibition of class C β-lactamases by boronic acids. Biochem. J. 209:229-233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Black, J. A., K. S. Thomson, and J. D. D. Pitout. 2004. Use of β-lactamase inhibitors in disk tests to detect plasmid-mediated AmpC β-lactamases. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42:2203-2206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bradford, P. A., C. Urban, N. Mariano, S. A. Projan, J. J. Rahal, and K. Bush. 1997. Imipenem resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae is associated with the combination of ACT-1, a plasmid-mediated AmpC β-lactamase, and the loss of an outer membrane protein. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 41:563-569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bush, K., G. A. Jacoby, and A. A. Medeiros. 1995. A functional classification scheme for β-lactamases and its correlation with molecular structure. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 39:1211-1233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Buzzoni, V., J. Blazquez, S. Ferrari, S. Calo, A. Venturelli, and M. P. Costi. 2004. Aza-boronic acids as non-β-lactam inhibitors of AmpC-β-lactamase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 14:3979-3983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Coudron, P. E., E. S. Moland, and K. S. Thomson. 2000. Occurrence and detection of AmpC β-lactamases among Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Proteus mirabilis isolates at a veterans medical center. J. Clin. Microbiol. 38:1791-1796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Doi, Y., N. Shibata, K. Shibayama, K. Kamachi, H. Kurokawa, K. Yokoyama, T. Yagi, and Y. Arakawa. 2002. Characterization of a novel plasmid-mediated cephalosporinase (CMY-9) and its genetic environment in an Escherichia coli clinical isolate. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 46:2427-2434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Doi, Y., J. Wachino, M. Ishiguro, H. Kurokawa, K. Yamane, N. Shibata, K. Shibayama, K. Yokoyama, H. Kato, T. Yagi, and Y. Arakawa. 2004. Inhibitor-sensitive AmpC β-lactamase variant produced by an Escherichia coli clinical isolate resistant to oxyiminocephalosporins and cephamycins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 48:2652-2658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dubois, V., C. Arpin, M. Melon, B. Melon, C. Andre, C. Frigo, and C. Quentin. 2001. Nosocomial outbreak due to a multiresistant strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa P12: efficacy of cefepime-amikacin therapy and analysis of β-lactam resistance. J. Clin. Microbiol. 39:2072-2078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fey, P. D., T. J. Safranek, M. E. Rupp, E. F. Dunne, E. Ribot, P. C. Iwen, P. A. Bradford, F. J. Angulo, and S. H. Hinrichs. 2000. Ceftriaxone-resistant Salmonella infection acquired by a child from cattle. N. Engl. J. Med. 27:1242-1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hansen, N. D. 2003. AmpC β-lactamases: what do we need to know for the future? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 52:2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Horii, T., Y. Arakawa, M. Ohta, S. Ichiyama, R. Wacharotayankun, and N. Kato. 1993. Plasmid-mediated AmpC-type β-lactamase isolated from Klebsiella pneumoniae confers resistance to broad-spectrum β-lactams, including moxalactam. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 37:984-990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hujer, A. M., M. G. Page, M. S. Helfand, B. Yeiser, and R. A. Bonomo. 2002. Development of a sensitive and specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detecting and quantifying CMY-2 and SHV β-lactamases. J. Clin. Microbiol. 40:1947-1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kurokawa, H., T. Yagi, N. Shibata, K. Shibayama, K. Kamachi, and Y. Arakawa. 2000. A new SHV-derived extended-spectrum β-lactamase (SHV-24) that hydrolyzes ceftazidime through a single-amino-acid substitution (D179G) in the omega-loop. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 44:1725-1727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kurokawa, H., N. Shibata, Y. Doi, K. Shibayama, K. Kamachi, T. Yagi, and Y. Arakawa. 2003. A new TEM-derived extended-spectrum β-lactamase (TEM-91) with an R164C substitution at the omega-loop confers ceftazidime resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47:2981-2983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Liebana, E., M. Gibbs, C. Clouting, L. Barker, F. A. Crifton-Hardley, E. Pleydell, B. Abdalhamid, N. D. Hanson, L. Martin, C. Poppe, and R. H. Davies. 2004. Characterization of β-lactamases responsible for resistance to extended-spectrum cephalosporins in Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica strains from food-producing animals in the United Kingdom. Microb. Drug Resist. 10:1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Livermore, D., and D. F. J. Brown. 2001. Detection of β-lactamase-mediated resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 48(Suppl. 1):59-64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Livermore, D. M. 1995. β-Lactamases in laboratory and clinical resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 8:557-584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Manchanda, V., and N. P. Singh. 2003. Occurrence and detection of AmpC β-lactamases among gram-negative clinical isolates using a modified three-dimensional test at Guru Tegh Bahadur Hospital, Deli, India. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 51:415-418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Morandi, F., E. Caselli, S. Morandi, P. J. Focia, J. Blazquez, B. K. Shoichet, and F. Prati. 2003. Nanomolar inhibitors of AmpC β-lactamase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125:685-695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nadjar, D., M. Rouveau, C. Verdet, J. Donay, P. H. Herrmann, A. Lagrange, A. Philippon, and G. Arlet. 2000. Outbreak of Klebsiella pneumoniae producing transferable AmpC-type β-lactamase (ACC-1) originating from Hafnia alvei. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 187:35-40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nagano, N., N. Shibata, Y. Saito, Y. Nagano, and Y. Arakawa. 2003. Nosocomial outbreak of infection by Proteus mirabilis that produces extended-spectrum CTX-M-2 type β-lactamase. J. Clin. Microbiol. 41:5530-5536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nasim, K., S. Elsayed, J. D. D. Pitout, J. Conly, D. L. Church, and D. B. Gregson. 2004. New method for laboratory detection of AmpC β-lactamases in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42:4799-4802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. 2003. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically, 6th ed. Approved standard M7-A6. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Wayne, Pa.
- 28.National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. 2003. Performance standards for antimicrobial disk susceptibility tests, 8th ed. Approved standard M2-A8. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Wayne, Pa.
- 29.National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. 2004. Performance standards for antimicrobial and susceptibility testing: 14th informational supplement (M100-S14). National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Wayne, Pa.
- 30.Papanicolaou, G. A., A. A. Medeiros, and G. A. Jacoby. 1990. Novel plasmid-mediated β-lactamase (MIR-1) conferring resistance to oxyimino- and α-methoxy β-lactams in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 34:2200-2209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Perez-Perez, F. J., and N. D. Hanson. 2002. Detection of plasmid-mediated AmpC-type β-lactamase genes in clinical isolates by using multiplex PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 40:2153-2162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Philippon, A., G. Arlet, G. A. Jacoby. 2002. Plasmid-determined AmpC-type β-lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 46:1-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pitout, J. D., M. D. Reisbig, E. C. Venter, D. L. Church, and N. D. Hanson. 2003. Modification of the double-disk test for detection of Enterobacteriaceae producing extended-spectrum and AmpC β-lactamases. J. Clin. Microbiol. 41:3933-3935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Powers, R. A., J. Blazquez, G. Scott Weston, M. Morosini, F. Baquero, and B. K. Shoichet. 1999. The complexed structure and antimicrobial activity of a non-β-lactam inhibitor of AmpC β-lactamase. Protein Sci. 8:2330-2337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Qin, X., S. J. Weissman, M. F. Chesnut, B. Zhang, and L. Shen. 2004. Kirby-Bauer disk approximation to detect inducible third-generation cephalosporin resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 3:13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Queenan, A. M., S. Jenkins, and K. Bush. 2001. Cloning and biochemical characterization of FOX-5, an AmpC-type plasmid-encoded β-lactamase from a New York City Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolate. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 45:3189-3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Scott Weston, G., J. Blazquez, F. Baquero, and B. K. Shoichet. 1998. Structure-based enchancement of boronic acid-based inhibitors of AmpC β-lactamase. J. Med. Chem. 41:4577-4586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Shibata, N., Y. Doi, K. Yamane, T. Yagi, H. Kurokawa, K. Shibayama, H. Kato, K. Kai, and Y. Arakawa. 2003. PCR typing of genetic determinants for metallo-β-lactamases and integrases carried by gram-negative bacteria isolated in Japan, with focus on the class 3 integron. J. Clin. Microbiol. 41:5407-5413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Thomson, K. S., and C. C. Sanders. 1992. Detection of extended-spectrum β-lactamases in members of the family Enterobacteriaceae: comparison of the double-disk test and three-dimensional tests. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 36:1877-1882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tzouvelekis, L. S., E. Tzelepi, A. F. Mentis, and A. Tsakris. 1993. Identification of a novel plasmid-mediated β-lactamase with chromosomal cephalosporinase characteristics in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 31:645-654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Usher, K. C., L. C. Blaszczak, G. Scott Weston, B. K. Shoichet, and S. J. Remington. 1998. Three-dimensional structure of AmpC β-lactamase from Escherichia coli bound to a transition-state analogue: possible implications for the oxyanion hypothesis and inhibitor design. Biochemistry 37:16082-16092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wachino, J., Y. Doi, K. Yamane, N. Shibata, T. Yagi, T. Kubota, H. Ito, and Y. Arakawa. 2004. Nosocomial spread of ceftazidime-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strains producing a novel class A β-lactamase, GES-3, in a neonatal intensive care unit in Japan. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 48:1960-1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Wachino, J., Y. Doi, K. Yamane, N. Shibata, T. Yagi, T. Kubota, and Y. Arakawa. 2004. Molecular characterization of a cephamycin-hydrolyzing and inhibitor-resistant class A β-lactamase, GES-4, possessing a single G170S substitution in the omega-loop. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 48:2905-2910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yagi, T., H. Kurokawa, N. Shibata, K. Shibayama, and Y. Arakawa. 2000. A preliminary survey of extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli in Japan. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 184:112-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Yong, D., R. Park, J. H. Yum, K. Lee, E. C. Choi, and Y. Chong. 2002. Further modification of the Hodge test to screen AmpC β-lactamase (CMY-1)-producing strains of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Microbiol. Methods 51:407-410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]