Abstract
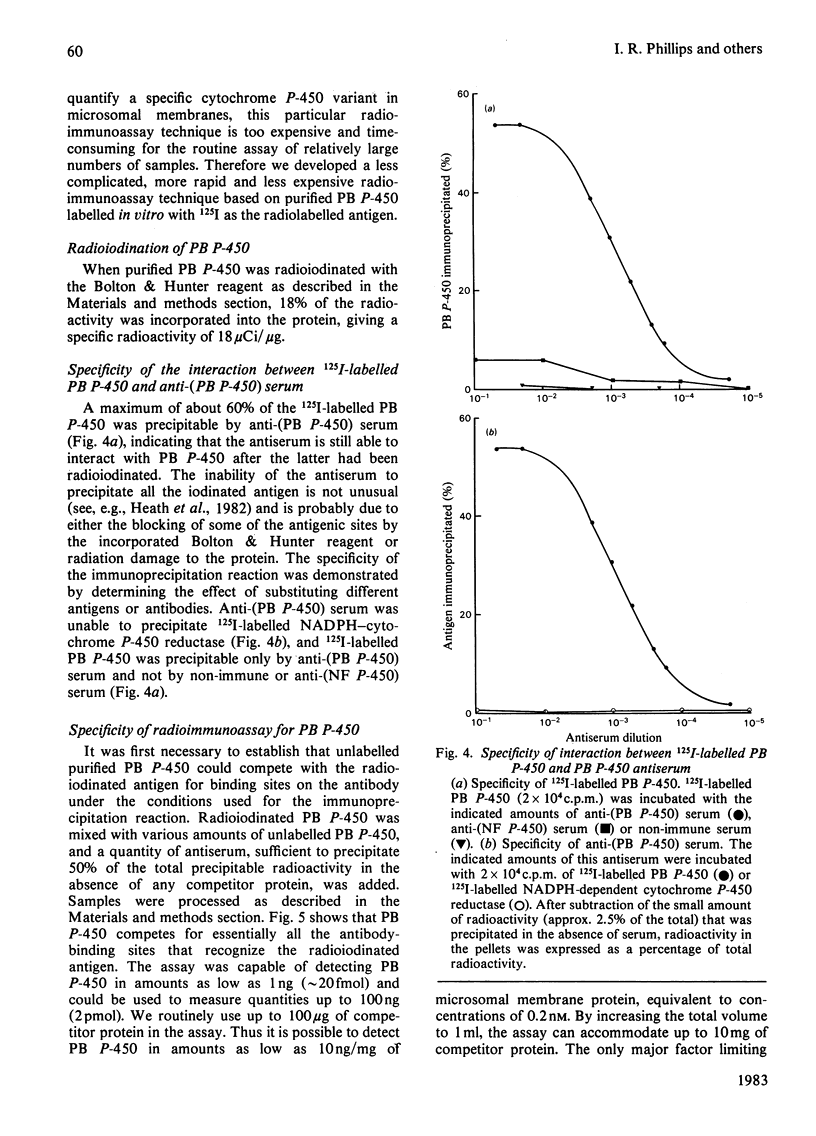
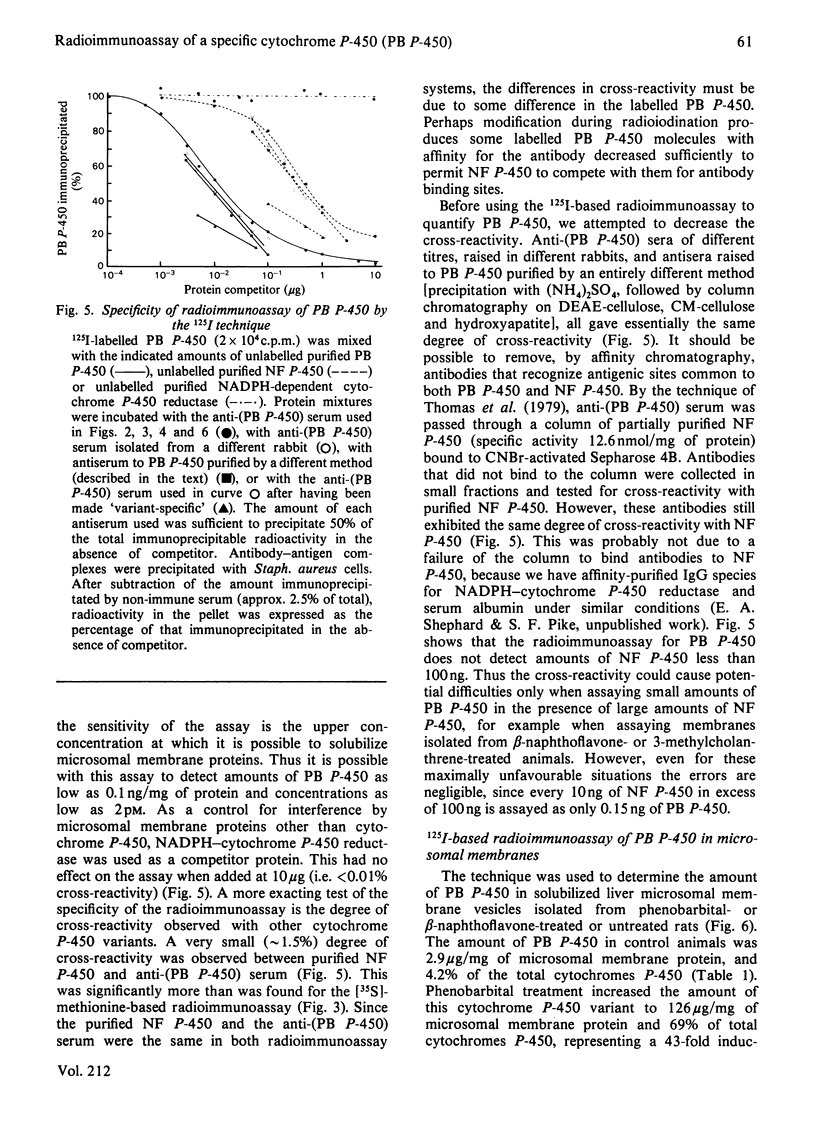
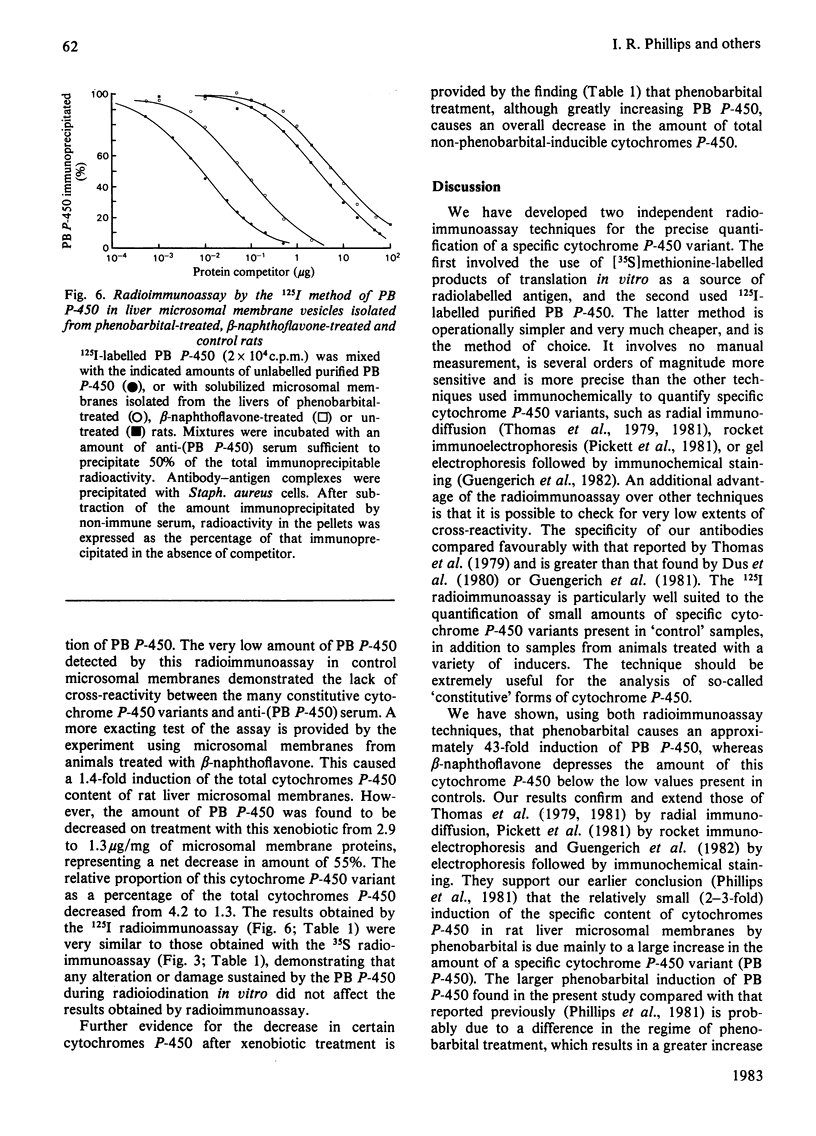
Two independent radioimmunoassay techniques for the major phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 (PB P-450) of rat liver microsomal membranes are described. The first technique employs as the source of radiolabelled antigen the products of translation in vitro labelled with [35S]methionine. The second technique employs purified antigen labelled with 125I and is quicker, less expensive and more precise. Both assays are highly specific for PB P-450 and can detect quantities of this variant as small as 1 ng. This is several orders of magnitude more sensitive than any method described previously for the quantification of cytochromes P-450, and consequently the technique is particularly well suited for the quantification of so-called constitutive cytochrome P-450 variants that are present in very low amounts. The results of the radioimmunoassays demonstrate that the apparent 2.6-fold induction of total cytochromes P-450 after phenobarbital treatment is due to a 43-fold increase in Pb P-450. Although beta-naphthoflavone increases the total content of cytochrome P-450 of microsomal membranes 1.4-fold, it actually causes a 55% decrease in the amount of PB P-450. Thus different xenobiotics can have differential effects on the expression of the genes for specific cytochrome P-450 variants.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adesnik M., Bar-Nun S., Maschio F., Zunich M., Lippman A., Bard E. Mechanism of induction of cytochrome P-450 by phenobarbital. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10340–10345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botelho L. H., Ryan D. E., Levin W. Amino acid compositions and partial amino acid sequences of three highly purified forms of liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 from rats treated with polychlorinated biphenyls, phenobarbital, or 3-methylcholanthrene. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5635–5640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botelho L. H., Ryan D. E., Yuan P. M., Kutny R., Shively J. E., Levin W. Amino-terminal and carboxy-terminal sequence of hepatic microsomal cytochrome P-450d, a unique hemoprotein from rats treated with isosafrole. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 16;21(6):1152–1155. doi: 10.1021/bi00535a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnick E., Brosseau M., Levin W., Reik L., Ryan D. E., Thomas P. E. Administration of 3-methylcholanthrene to rats increases the specific hybridizable mRNA coding for cytochrome P-450c. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4083–4087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbert R. A., Bresnick E., Levin W., Ryan D. E., Thomas P. E. Synthesis of liver cytochrome P-450b in a cell-free protein synthesizing system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Dec 14;91(3):886–891. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91962-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conney A. H. Pharmacological implications of microsomal enzyme induction. Pharmacol Rev. 1967 Sep;19(3):317–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois R. N., Waterman M. R. Effect of phenobarbital administration to rats on the level of the in vitro synthesis of cytochrome P-450 directed by total rat liver RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 12;90(1):150–157. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91602-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dus K. M., Litchfield W. J., Hippenmeyer P. J., Bumpus J. A., Obidoa O., Spitsberg V., Jefcoate C. R. Comparative immunochemical studies of cytochrome P-450CAM of Pseudomonas putida and of cytochrome P-450SCC of bovine adrenocortical mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(2):307–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernster L., Orrenius S. Substrate-induced synthesis of the hydroxylating enzyme system of liver microsomes. Fed Proc. 1965 Sep-Oct;24(5):1190–1199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOUTS J. R., ROGERS L. A. MORPHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE LIVER ACCOMPANYING STIMULATION OF MICROSOMAL DRUG METABOLIZING ENZYME ACTIVITY BY PHENOBARBITAL, CHLORDANE, BENZPYRENE OR METHYL-CHOLANTHRENE IN RATS. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Jan;147:112–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelboin H. V. Carcinogens, enzyme induction, and gene action. Adv Cancer Res. 1967;10:1–81. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P. Isolation and purification of cytochrome P-450, and the existence of multiple forms. Pharmacol Ther. 1979;6(1):99–121. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(79)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Martin M. V. Purification of cytochrome P-450, NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase, and epoxide hydratase from a single preparation of rat liver microsomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Dec;205(2):365–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P. Separation and purification of multiple forms of microsomal cytochrome P-450. Partial characterization of three apparently homogeneous cytochromes P-450 prepared from livers of phenobarbital- and 3-methylcholanthrene-treated rats. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 10;253(21):7931–7939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Wang P., Davidson N. K. Estimation of isozymes of microsomal cytochrome P-450 in rats, rabbits, and humans using immunochemical staining coupled with sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 30;21(7):1698–1706. doi: 10.1021/bi00536a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Wang P., Mason P. S., Mitchell M. B. Immunological comparison of rat, rabbit, and human microsomal cytochromes P-450. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2370–2378. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe N., Ingild A. Immunization, isolation of immunoglobulins, estimation of antibody titre. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:161–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath R., Jeffery S., Carter N. Radioimmunoassay of human muscle carbonic anhydrase III in dystrophic states. Clin Chim Acta. 1982 Mar 12;119(3):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90343-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai Y. The use of 8-aminooctyl sepharose for the separation of some components of the hepatic microsomal electron transfer system. J Biochem. 1976 Aug;80(2):267–276. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato R. Characteristics and differences in the hepatic mixed function oxidases of different species. Pharmacol Ther. 1979;6(1):41–98. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(79)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremers P., Pasleau F., Gielen J. E. Is steroid-16alpha-hydroxylase supported by more than one monooxygenase? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 16;84(3):706–712. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90762-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Padmanaban G. Studies on the synthesis of cytochrome P-450 and cytochrome P-448 in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):522–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuntzman R., Levin W., Jacobson M., Conney A. H. Studies on microsomal hydroxylation and the demonstration of a new carbon monoxide binding pigment in liver microsomes. Life Sci II. 1968 Feb 15;7(4):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(68)90309-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. Y., West S. B. Multiplicity of mammalian microsomal cytochromes P-45. Pharmacol Rev. 1979 Dec;31(4):277–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh P. R., Peacock A. C., Gelboin H. V. The induction of liver microsomal proteins by 3-methylcholanthrene in rats of different age, sex and strain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 7;627(3):290–300. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90460-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negishi M., Nebert D. W. Structural gene products of the Ah complex. Increases in large mRNA from mouse liver associated with cytochrome P1-450 induction by 3-methylcholanthrene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):3085–3091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMURA T., SATO R. THE CARBON MONOXIDE-BINDING PIGMENT OF LIVER MICROSOMES. II. SOLUBILIZATION, PURIFICATION, AND PROPERTIES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2379–2385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrenius S., Ericsson J. L., Ernster L. Phenobarbital-induced synthesis of the microsomal drug-metabolizing enzyme system and its relationship to the proliferation of endoplasmic membranes. A morphological and biochemical study. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jun;25(3):627–639. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.3.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett C. B., Jeter R. L., Morin J., Lu A. Y. Electroimmunochemical quantitation of cytochrome P-450, cytochrome P-448, and epoxide hydrolase in rat liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8815–8820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shephard E. A., Phillips I. R., Pike S. F., Ashworth A., Rabin B. R. Differential effect of phenobarbital and beta-naphthoflavone on the mRNAs coding for cytochrome P450 and NADPH cytochrome P450 reductase. FEBS Lett. 1982 Dec 27;150(2):375–380. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80771-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiels A., Phillips I., Jeffery S., Shephard E., Carter N. Synthesis of rat muscle carbonic anhydrase III in a cell-free translation system. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 1;148(1):122–125. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81256-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stäubli W., Hess R., Weibel E. R. Correlated morphometric and biochemical studies on the liver cell. II. Effects of phenobarbital on rat hepatocytes. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jul;42(1):92–112. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. E., Korzeniowski D., Ryan D., Levin W. Preparation of monospecific antibodies against two forms of rat liver cytochrome P-450 and quantitation of these antigens in microsomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Feb;192(2):524–532. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90122-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. E., Reik L. M., Ryan D. E., Levin W. Regulation of three forms of cytochrome P-450 and epoxide hydrolase in rat liver microsomes. Effects of age, sex, and induction. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):1044–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlasuk G. P., Ghrayeb J., Ryan D. E., Reik L., Thomas P. E., Levin W., Walz F. G., Jr Multiplicity strain differences, and topology of phenobarbital-induced cytochromes P-450 in rat liver microsomes. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 16;21(4):789–798. doi: 10.1021/bi00533a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlasuk G. P., Walz F. G., Jr Liver microsomal polypeptides from Fischer-344 rats affected by age, sex, and xenobiotic induction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Mar;214(1):248–259. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Smith R. L. Lowry determination of protein in the presence of Triton X-100. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):414–417. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90363-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Hoeven T. A., Coon M. J. Preparation and properties of partially purified cytochrome P-450 and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-cytochrome P-450 reductase from rabbit liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6302–6310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]