Abstract
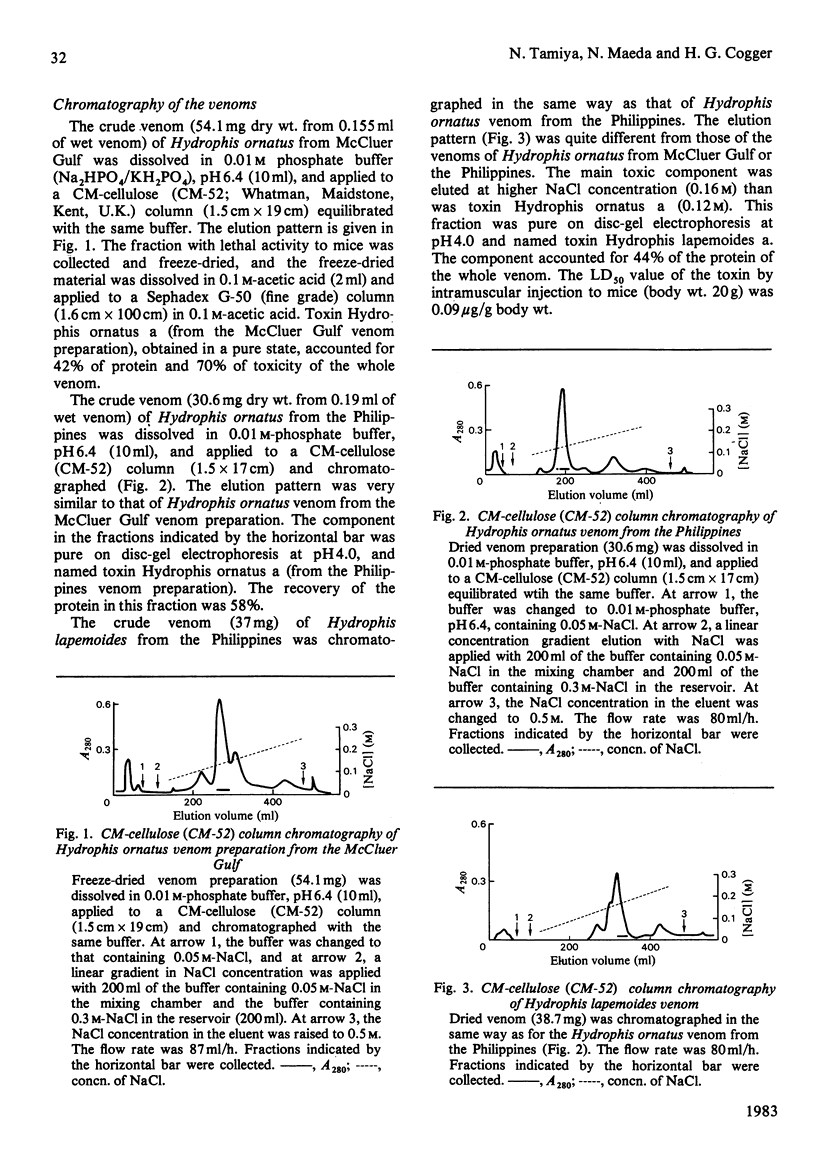
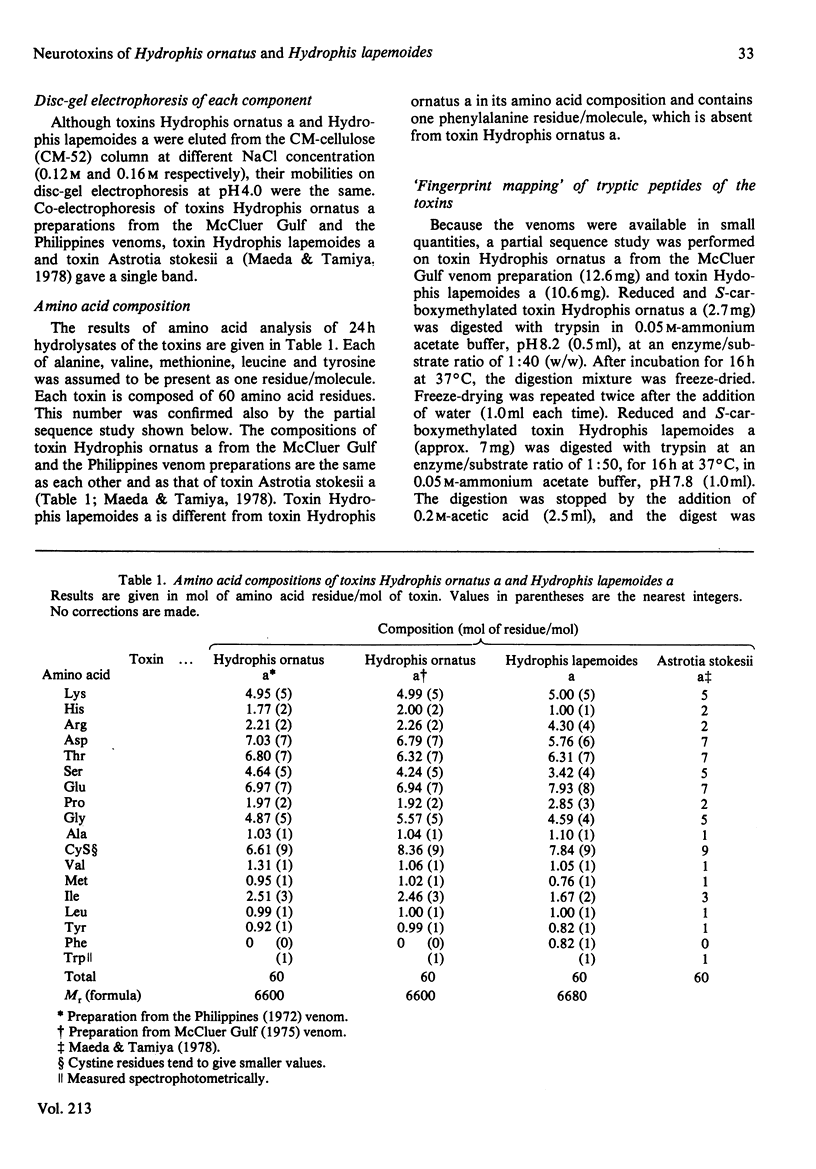
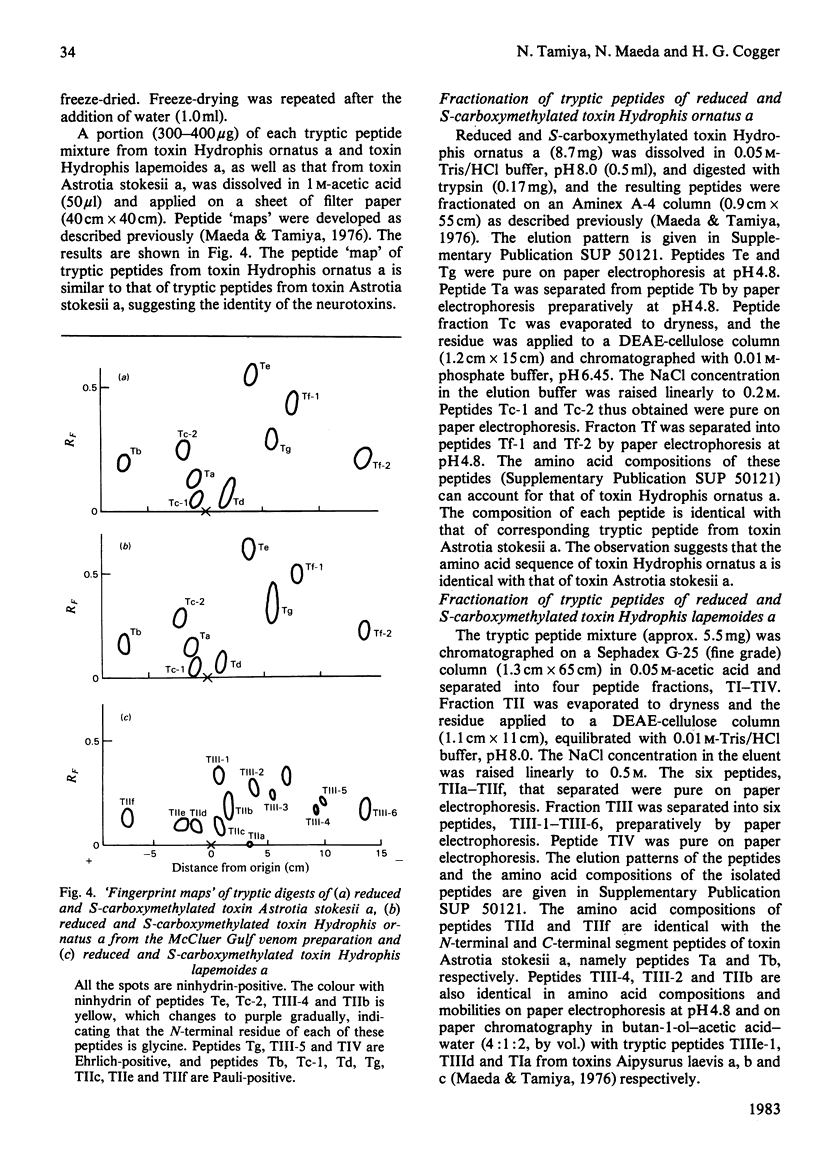
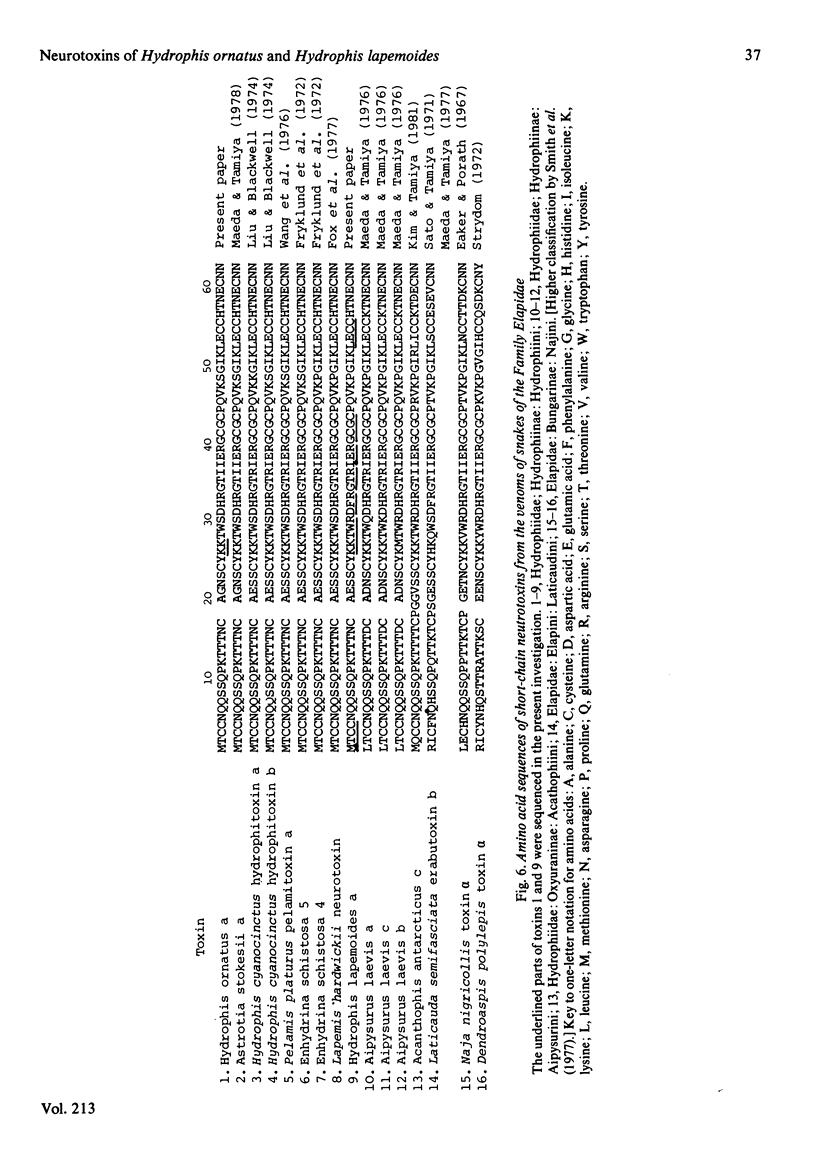
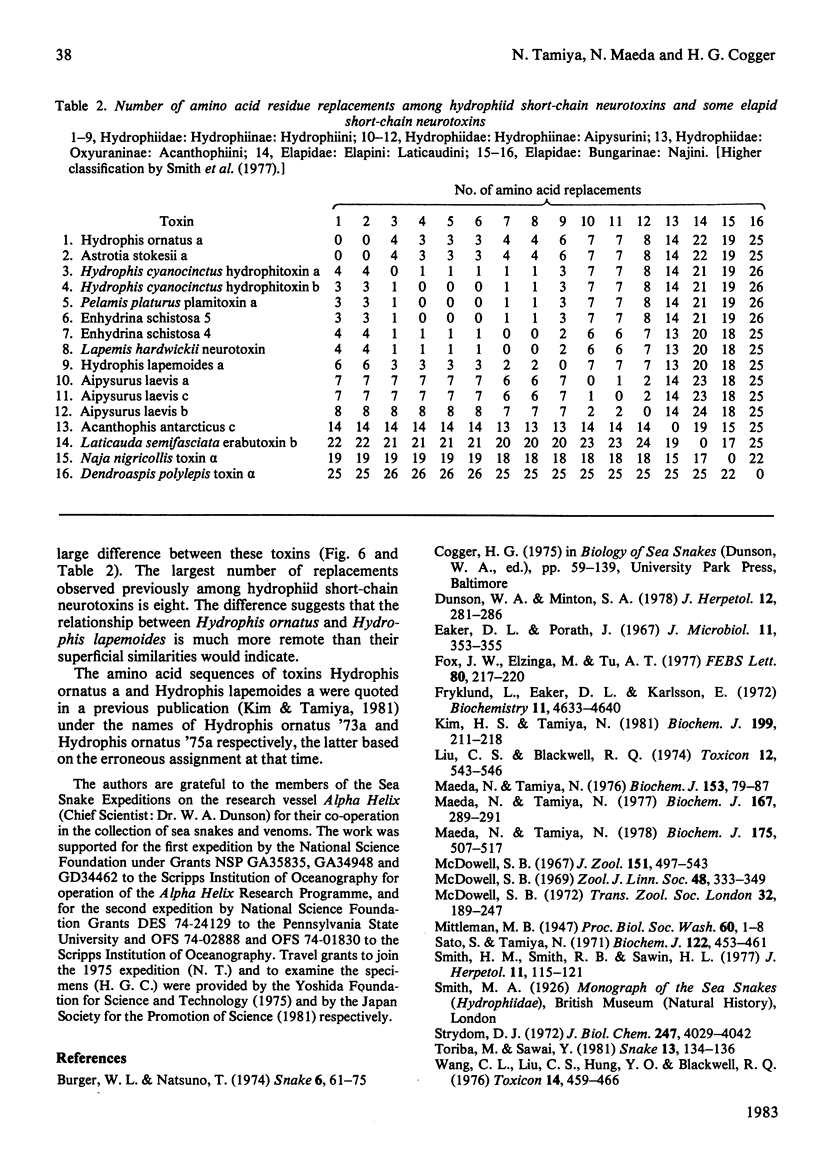
The main neurotoxic components, toxins Hydrophis ornatus a and Hydrophis lapemoides a, were isolated from the venoms of the sea snakes Hydrophis ornatus and Hydrophis lapemoides respectively. The amino acid sequence of toxin Hydrophis ornatus a was deduced to be identical with that of toxin Astrotia stokesii a [Maeda & Tamiya (1978) Biochem. J. 175, 507-517] on the basis of identity of the tryptic peptide 'map' and the amino acid composition of each peptide. The amino acid sequence of toxin Hydrophis lapemoides a was determined mainly on the basis of identity of the amino acid compositions, mobilities on paper electrophoresis and migration positions on paper chromatography of the tryptic peptides with those of other sea-snake toxins whose sequences are known. Both toxins Hydrophis ornatus a and Hydrophis lapemoides a consisted of 60 amino acid residues and there were six amino acid replacements between them. The taxonomy of sea snakes in the Hydrophis ornatus complex has long been confused, and the above snakes were originally assigned to taxa that proved to be inconsistent with the relationships indicated by the neurotoxin amino acid sequences obtained. A subsequent re-examination of the specimens revealed an error in the original identifications and demonstrated the value of the protein amino acid sequences in systematic and phylogenetic studies. The isolation procedure and results of amino acid analysis of the tryptic peptides have been deposited as Supplementary Publication SUP 50121 (8 pages) with the British Library Lending Division, Boston Spa, Wetherby, West Yorkshire LS23 7BQ, U.K., from whom copies may be obtained as indicated in Biochem. J. (1983) 209, 5.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fox J. W., Elzinga M., Tu A. T. Amino acid sequence of a snake neurotoxin from the venom of Lapemis hardwickii and the detection of a sulfhydryl group by laser Raman spectroscopy. FEBS Lett. 1977 Aug 1;80(1):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80443-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryklund L., Eaker D., Karlsson E. Amino acid sequences of the two principal neurotoxins of Enhydrina schistosa venom. Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 21;11(24):4633–4640. doi: 10.1021/bi00774a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. S., Tamiya N. The amino acid sequence and position of the free thiol group of a short-chain neurotoxin from common-death-adder (Acanthophis antarcticus) venom. Biochem J. 1981 Oct 1;199(1):211–218. doi: 10.1042/bj1990211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. S., Blackwell R. Q. Hydrophitoxin b from Hydrophis cyanocinctus venom. Toxicon. 1974 Oct;12(5):543–546. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(74)90047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Tamiya N. Correction of partial amino acid sequence of erabutoxins. Biochem J. 1977 Oct 1;167(1):289–291. doi: 10.1042/bj1670289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Tamiya N. Isolation, properties and amino acid sequences of three neurotoxins from the venom of a sea snake, Aipysurus laevis. Biochem J. 1976 Jan 1;153(1):79–87. doi: 10.1042/bj1530079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Tamiya N. Three neurotoxins from the venom of a sea snake Astrotia stokesii, including two long-chain neurotoxic proteins with amidated C-termini. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):507–517. doi: 10.1042/bj1750507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S., Tamiya N. The amino acid sequences of erabutoxins, neurotoxic proteins of sea-snake (Laticauda semifasciata) venom. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):453–461. doi: 10.1042/bj1220453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strydom D. J. Snake venom toxins. The amino acid sequences of two toxins from Dendroaspis polylepis polylepis (black mamba) venom. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):4029–4042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. L., Liu C. S., Hung Y. O., Blackwell R. Q. Amino acid sequence of pelamitoxin a, the main neurotoxin of the sea snake, Pelamis platurus. Toxicon. 1976;14(6):459–466. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(76)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


