Abstract
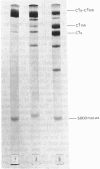
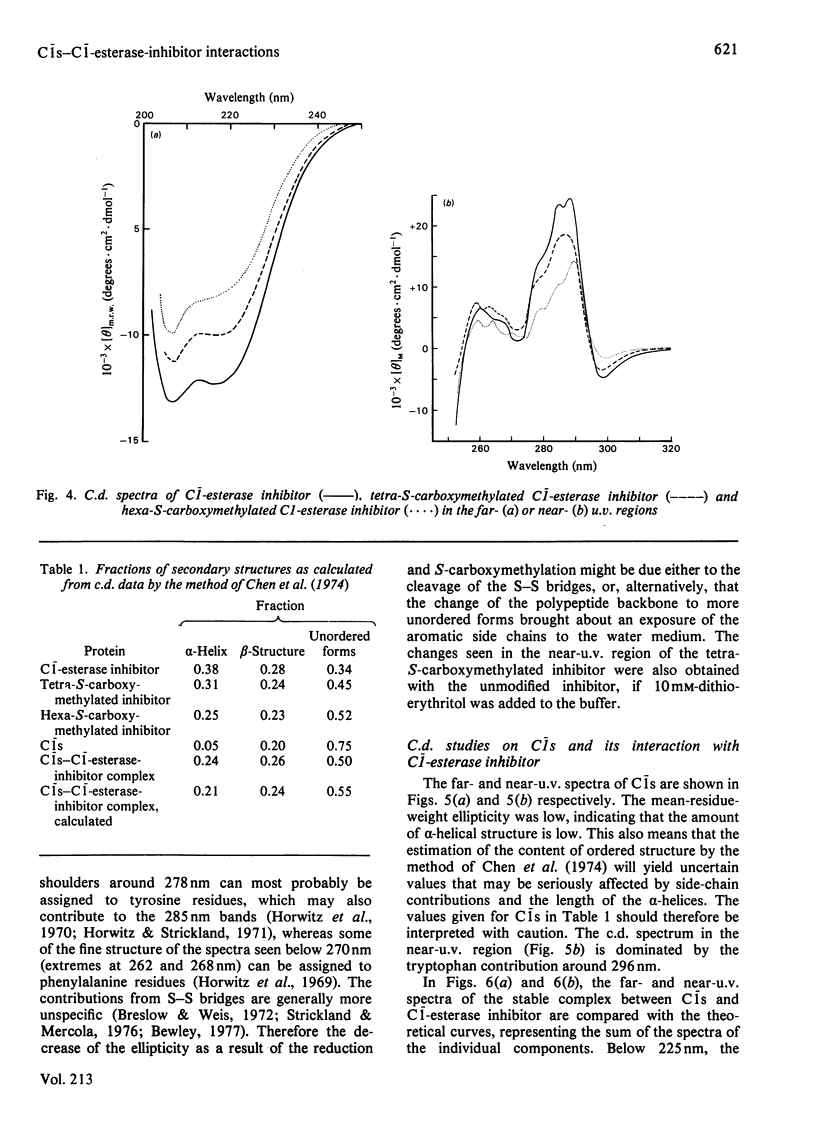
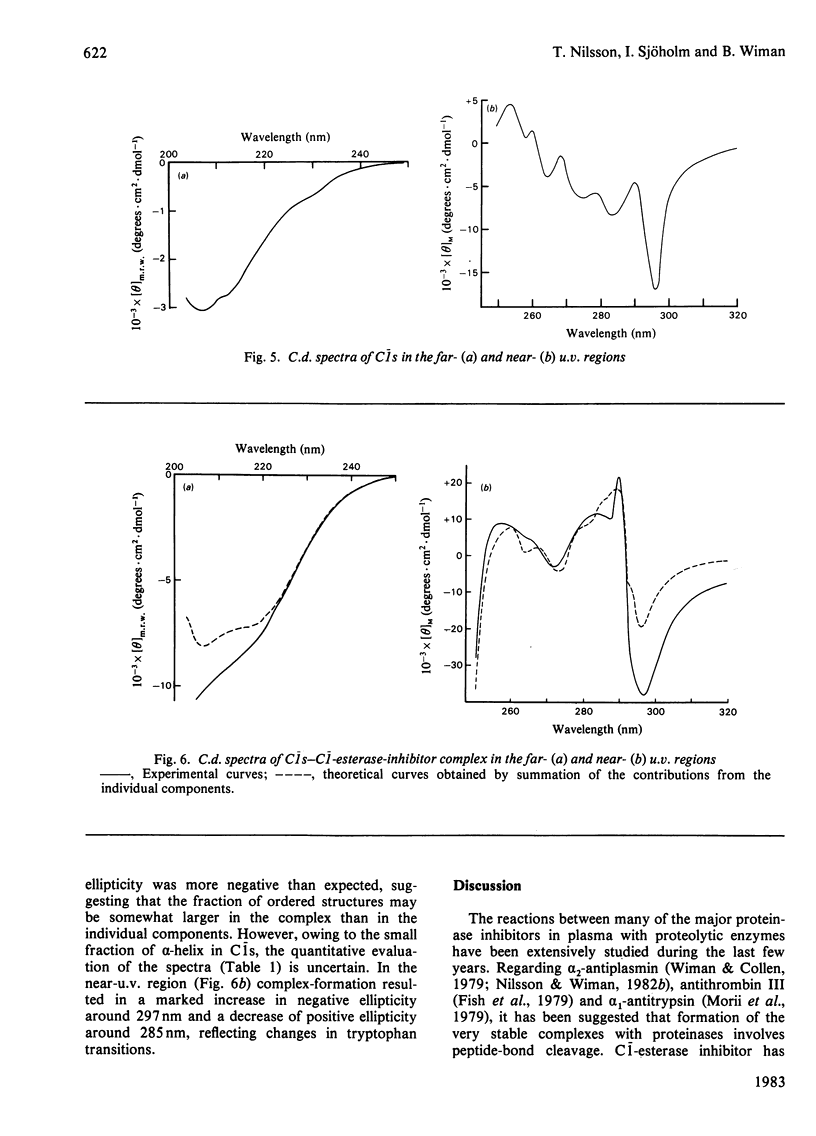
The reaction between complement factor C1s and C1-esterase inhibitor has been investigated by sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis, N-terminal amino acid analysis and c.d. studies. It is confirmed that a very stable stoichiometric 1:1 complex with a molecular weight of about 180000 is formed, involving the light chain of C1s. On the sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide gels a small peptide with a molecular weight of about 5000 can be seen, which may be released from the C-terminal portion of the inhibitor moiety in a manner analogous to that occurring in other similar proteinase-inhibitor reactions. By N-terminal amino acid analysis, a newly formed threonine residue is found in the complex, suggesting that the inhibitor peptide chain is cleaved in the complex between C1s and C1-esterase inhibitor. The stabilizing bond may therefore be an ester bond. C.d. studies of the native C1-esterase inhibitor indicated the presence of about 38% alpha-helix, about 24% beta-structure and about 38% unordered structure. By gradual cleavage of the disulphide bridges under non-denaturating conditions, gradual changes in the c.d. spectra occurred, suggesting loss of ordered secondary structures. The c.d. spectra of the complex between C1s and C1-esterase inhibitor indicate that tryptophan residues are affected by the complex-formation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bewley T. A. Optical activity of disulfide bonds in proteins: studies on human choriomammotropin and bovine pituitary somatotropin. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 4;16(20):4408–4414. doi: 10.1021/bi00639a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom J. W., Hunter M. J. Interactions of alpha1-antitrypsin with trypsin and chymotrypsin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):547–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow E., Weis J. Contribution of tyrosine to circular dichroism changes accompanying neurophysin-hormone interaction. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 29;11(18):3474–3482. doi: 10.1021/bi00768a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapuis R. M., Isliker H., Assimeh S. N. Studies on the precursor form of the first component of complement--I. Isolation of the proenzyme forms of Clr and Cls. Immunochemistry. 1977 May;14(5):313–317. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(77)90229-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Yang J. T., Chau K. H. Determination of the helix and beta form of proteins in aqueous solution by circular dichroism. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3350–3359. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesne S., Villiers C. L., Arlaud G. J., Lacroix M. B., Colomb M. G. Fluid-phase interaction of C1 inhibitor (C1 Inh) and the subcomponents C1r and C1s of the first component of complement, C1. Biochem J. 1982 Jan 1;201(1):61–70. doi: 10.1042/bj2010061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish W. W., Orre K., Björk I. The production of an inactive form of antithrombin through limited proteolysis by thrombin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Feb 1;98(1):103–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Porter R. R., Sim R. B. The unactivated form of the first component of human complement, C1. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):541–548. doi: 10.1042/bj1570541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. C1 inactivator. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:751–750. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C., Cooper N. R. Studies on human plasma C1 inactivator-enzyme interactions. I. Mechanisms of interaction with C1s, plasmin, and trypsin. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):593–604. doi: 10.1172/JCI107967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz J., Strickland E. H. Absorption and circular dichroism spectra of ribonuclease-S at 77 degrees K. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3749–3752. doi: 10.2172/4043504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz J., Strickland E. H., Billups C. Analysis of the vibrational structure in the near-ultraviolet circular dichroism and absorption spectra of tyrosine derivatives and ribonuclease-A at 77 degrees K. J Am Chem Soc. 1970 Apr 8;92(7):2119–2129. doi: 10.1021/ja00710a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz J., Strickland E. H., Billups C. Analysis of vibrational structure in the near-ultraviolet circular dichroism and absorption spectra of phenylalanine and its derivatives. J Am Chem Soc. 1969 Jan 1;91(1):184–190. doi: 10.1021/ja01029a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morii M., Odani S., Ikenaka T. Characterization of a peptide released during the reaction of human alpha 1-antitrypsin and bovine alpha-chymotrypsin. J Biochem. 1979 Oct;86(4):915–921. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muntz R. H., Castaldi P. A. Use of rabbit antisera in the preparation of factor-XII-free platelet-rich and platelet-poor plasma. Haemostasis. 1977;6(1):35–40. doi: 10.1159/000214163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Sjöholm I., Wiman B. Circular dichroism studies on alpha 2-antiplasmin and its interactions with plasmin and plasminogen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jul 26;705(2):264–270. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90187-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Wiman B. Kinetics of the reaction between human C1-esterase inhibitor and C1r or C1s. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jan 1;129(3):663–667. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Wiman B. On the structure of the stable complex between plasmin and alpha-2-antiplasmin. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jun 1;142(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Wiman B. Purification and characterization of human C1-esterase inhibitor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jul 26;705(2):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90188-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Scott C. F., Colman R. W. Contribution of plasma protease inhibitors to the inactivation of kallikrein in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1982 Feb;69(2):462–468. doi: 10.1172/JCI110470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Arlaud G. J., Colomb M. G. Kinetics of reaction of human C1-inhibitor with the human complement system proteases C1r and C1s. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 11;612(2):433–449. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90126-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Reboul A., Arlaud G. J., Villiers C. L., Colomb M. G. Interaction of 125I-labelled complement subcomponents C-1r and C-1s with protease inhibitors in plasma. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jan 1;97(1):111–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland E. H., Horwitz J., Billups C. Fine structure in the near-ultraviolet circular dichroism and absorption spectra of tryptophan derivatives and chymotrypsinogen A at 77 degrees K. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3205–3213. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland E. H., Horwitz J., Kay E., Shannon L. M., Wilchek M., Billups C. Near-ultraviolet absorption bands of tryptophan. Studies using horseradish peroxidase isoenzymes, bovine and horse heart cytochrome c, and N-stearyl-L-tryptophan n-hexyl ester. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2631–2638. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland E. H., Mercola D. Near-ultraviolet tyrosyl circular dichroism of pig insulin monomers, dimers, and hexamers. Dipole-dipole coupling calculations in the monopole approximation. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 24;15(17):3875–3884. doi: 10.1021/bi00662a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Collen D. On the mechanism of the reaction between human alpha 2-antiplasmin and plasmin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9291–9297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Jacobsson L., Andersson M., Mellbring G. Determination of plasmin-alpha 2-antiplasmin complex in plasma samples by means of a radioimmunoassay. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1983 Feb;43(1):27–33. doi: 10.1080/00365518309168219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]