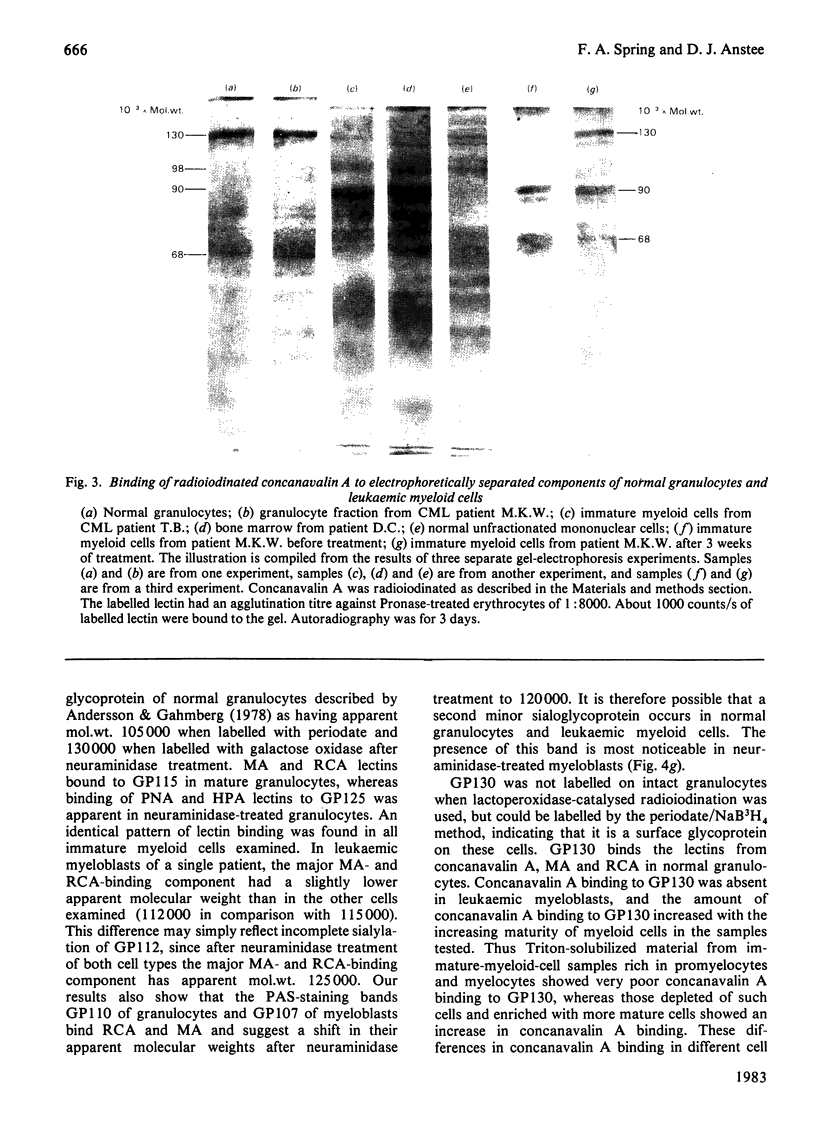
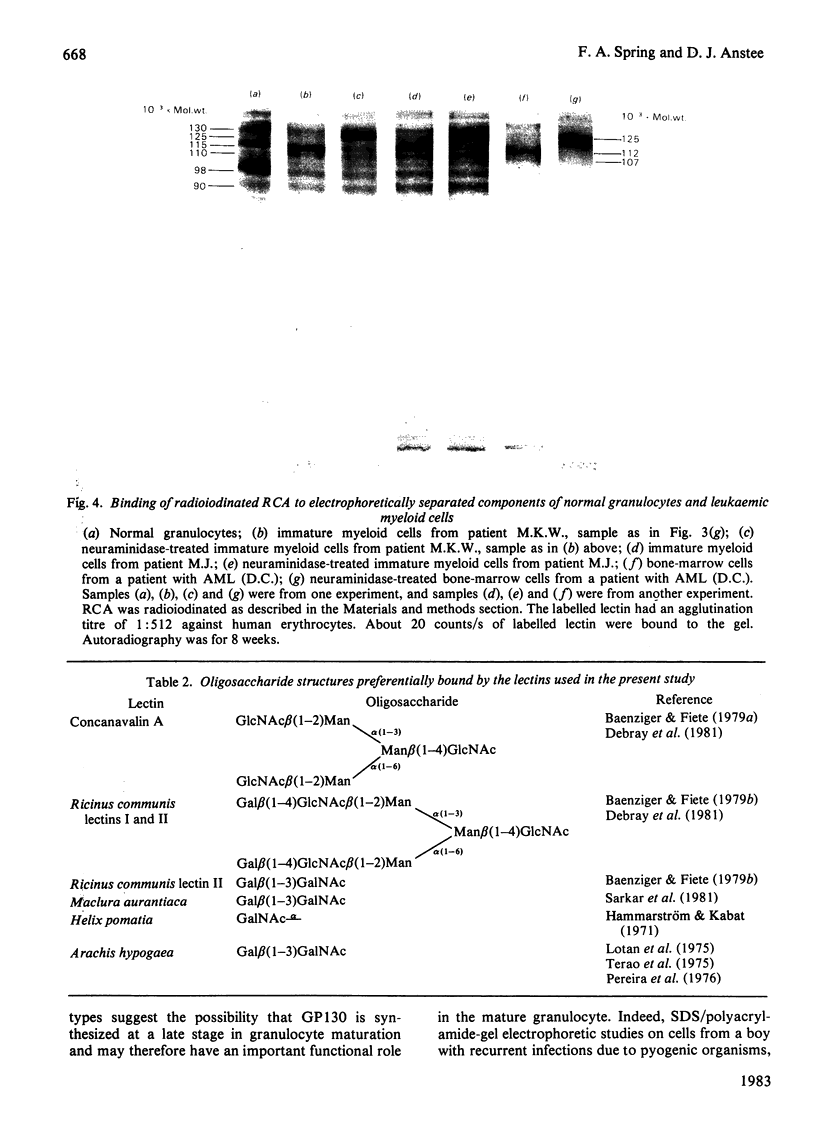
Abstract
A panel of lectins was used to analyse glycoproteins of normal granulocytes and leukaemic myeloid cells. The glycoproteins of detergent-solubilized whole cells were separated by sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis and their lectin-binding properties determined by incubation of the fixed gels with radioiodinated lectins. Normal granulocytes and leukaemic myeloid cells in different stages of maturation possess a cell-surface sialic acid-rich glycoprotein of apparent mol.wt. 115 000 (GP115), that can be labelled by both the lactoperoxidase and periodate/NaB3H4 cell-surface labelling techniques. The sialoglycoprotein of leukaemic myeloblasts has a slightly lower apparent mol.wt., 112000 (GP112). After neuraminidase treatment before cell solubilization, both GP115 and GP112 bind the lectins from Arachis hypogaea (peanut) and Helix pomatia (snail) and have an increased apparent molecular weight of 125000. Two concanavalin A-binding glycoproteins of apparent mol.wts. 98000 and 90000 are present in leukaemic myeloblasts. Concanavalin A binding to these glycoproteins is decreased in more mature leukaemic cells and absent in granulocytes. As concanavalin A binding decreases in the maturer forms, there is a concomitant increase in the binding of Ricinus communis (castor bean) and Maclura aurantiaca (osage orange) lectins to these glycoproteins. Whole granulocytes, but not leukaemic myeloblasts, contain a major cell-surface concanavalin A binding glycoprotein of apparent mol.wt. 130000, which is labelled by the periodate/NaB3H4 technique. Concanavalin A binding to this glycoprotein increases as the morphology of leukaemic cells approaches that of mature granulocytes.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguado M. T., Pujol N., Rubiol E., Tura M., Celada A. Separation of granulocytes from peripheral blood in a single step using discontinuous density gradients of Ficoll-Urografin. A comparative study with separation by dextran. J Immunol Methods. 1980;32(1):41–50. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson L. C., Gahmberg C. G., Siimes M. A., Teerenhovi L., Vuopio P. Cell surface glycoprotein analysis: a diagnostic tool in human leukemias. Int J Cancer. 1979 Mar 15;23(3):306–311. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910230306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson L. C., Gahmberg C. G. Surface glycoproteins of human white blood cells. Analysis by surface labeling. Blood. 1978 Jul;52(1):57–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anstee D. J., Barker D. M., Judson P. A., Tanner M. J. Inherited sialoglycoprotein deficiencies in human erythrocytes of type En[a-]. Br J Haematol. 1977 Feb;35(2):309–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb00587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anstee D. J., Mawby W. J., Tanner M. J. Abnormal blood-group-Ss-active sialoglycoproteins in the membrane of Miltenberger class III, IV and V human erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 1;183(2):193–203. doi: 10.1042/bj1830193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnaout M. A., Pitt J., Cohen H. J., Melamed J., Rosen F. S., Colten H. R. Deficiency of a granulocyte-membrane glycoprotein (gp150) in a boy with recurrent bacterial infections. N Engl J Med. 1982 Mar 25;306(12):693–699. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198203253061201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baenziger J. U., Fiete D. Structural determinants of Ricinus communis agglutinin and toxin specificity for oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9795–9799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baenziger J. U., Fiete D. Structural determinants of concanavalin A specificity for oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2400–2407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debray H., Decout D., Strecker G., Spik G., Montreuil J. Specificity of twelve lectins towards oligosaccharides and glycopeptides related to N-glycosylproteins. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun;117(1):41–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahmberg C. G., Andersson L. C. Identification and characterization of normal and malignant human blood leukocytes by surface glycoprotein patterns. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 20;312:240–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb16806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström S., Kabat E. A. Studies on specificity and binding properties of the blood group A reactive hemagglutinin from Helix pomatia. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 27;10(9):1684–1692. doi: 10.1021/bi00785a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinman N. R., Taylor R. B. General methods for the study of cells and serum during the immune response: the response to dinitrophenyl in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Apr;4(4):473–487. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R., Skutelsky E., Danon D., Sharon N. The purification, composition, and specificity of the anti-T lectin from peanut (Arachis hypogaea). J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8518–8523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S., Woodrow C. F., McClelland D. B. Isolation of membrane components associated with human red cell antigens Rh(D), (c), (E) and Fy. Nature. 1982 Feb 11;295(5849):529–531. doi: 10.1038/295529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. E., Kabat E. A., Lotan R., Sharon N. Immunochemical studies on the specificity of the peanut (Arachis hypogaea) agglutinin. Carbohydr Res. 1976 Oct;51(1):107–118. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)84040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisner Y., Biniaminov M., Rosenthal E., Sharon N., Ramot B. Interaction of peanut agglutinin with normal human lymphocytes and with leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):447–451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostas J. A., Kelly P. T., Cotman C. W. The identification of membrane glycocomponents in polyacrylamide gels: a rapid method using 125I-labeled lectins. Anal Biochem. 1977 Jun;80(2):366–372. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90657-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar M., Wu A. M., Kabat E. A. Immunochemical studies on the carbohydrate specificity of Maclura pomifera lectin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Jun;209(1):204–218. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90273-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. The organization of proteins in the human red blood cell membrane. A review. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):1–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama K., Tomida M., Hozumi M. Differentiation-associated changes in membrane proteins of mouse myeloid leukemia cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 4;587(2):169–179. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90351-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner M. J., Anstee D. J. A method for the direct demonstration of the lectin-binding components of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):265–270. doi: 10.1042/bj1530265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terao T., Irimura T., Osawa T. Purification and characterization of a hemagglutinin from Arachis hypogeae. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Nov;356(11):1685–1692. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.2.1685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]