Abstract
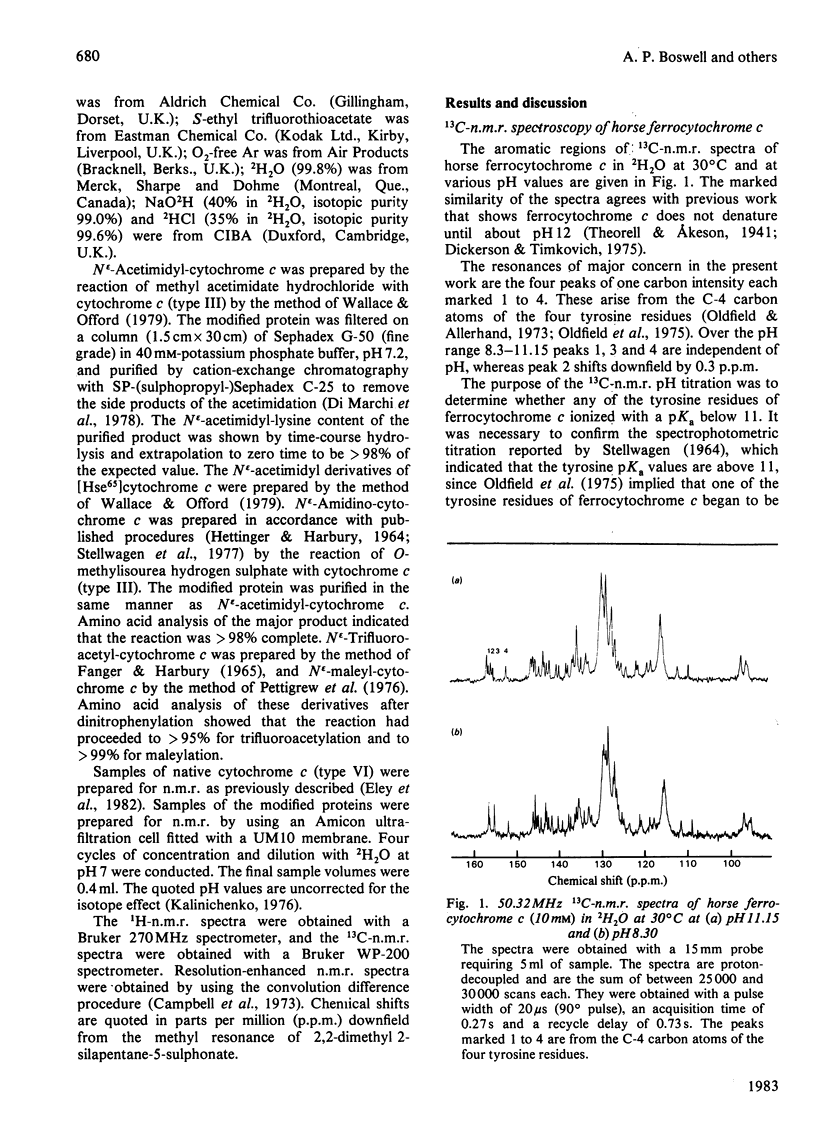
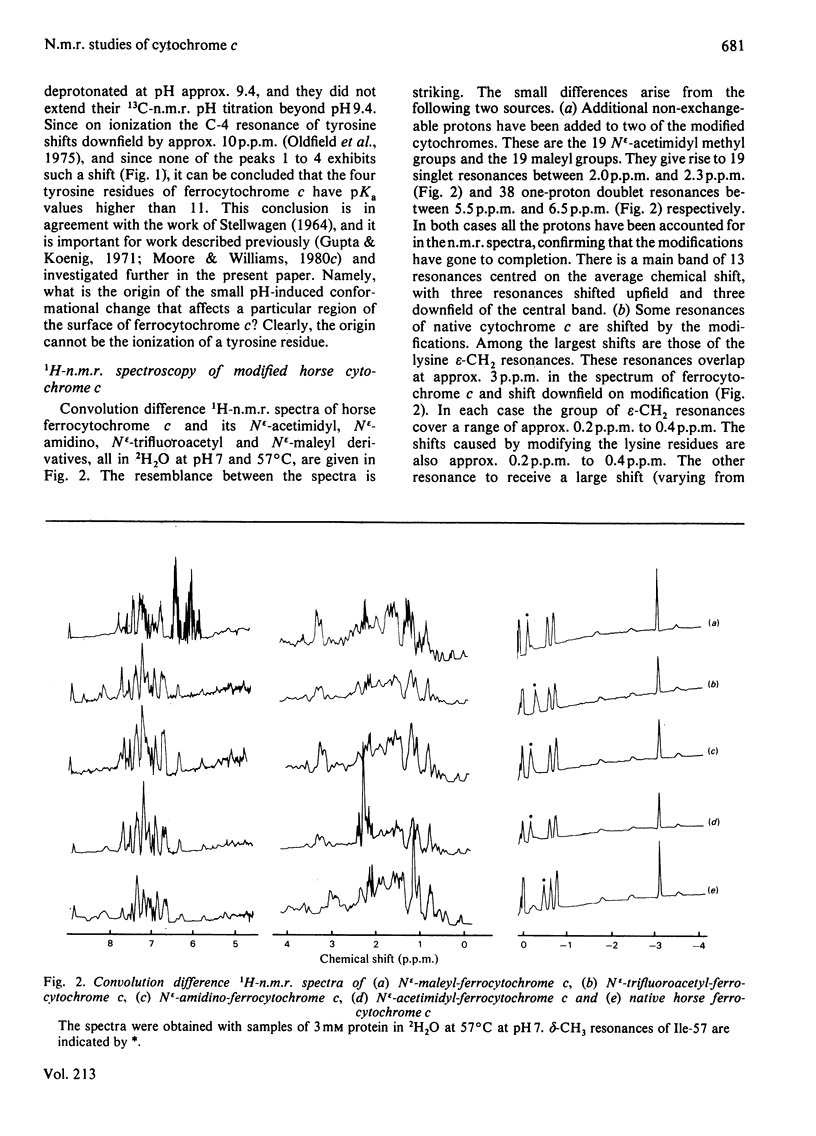
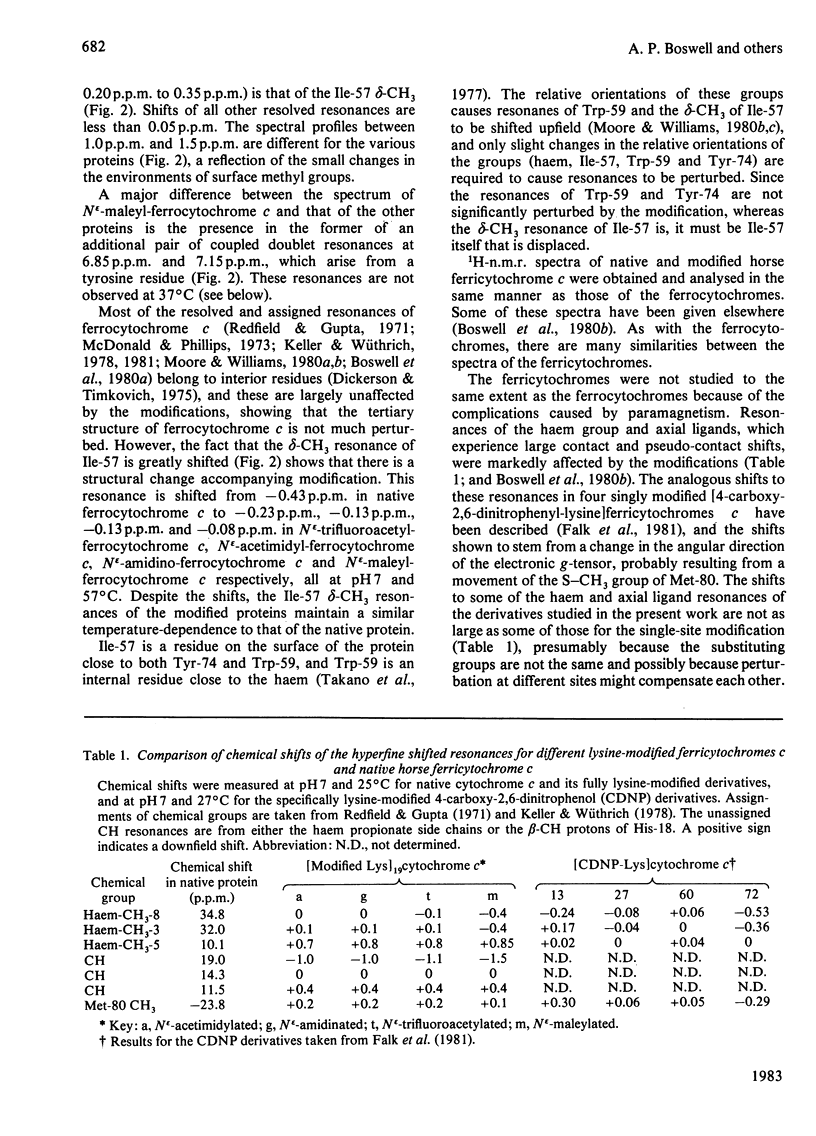
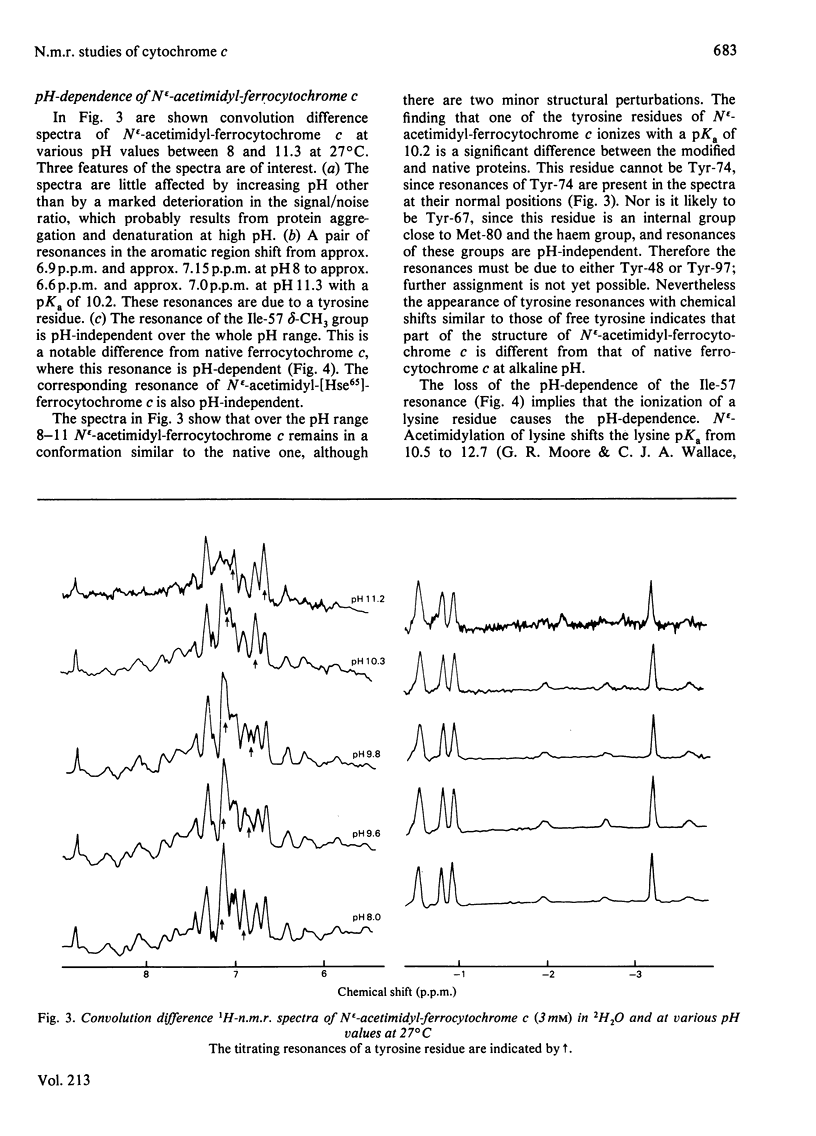
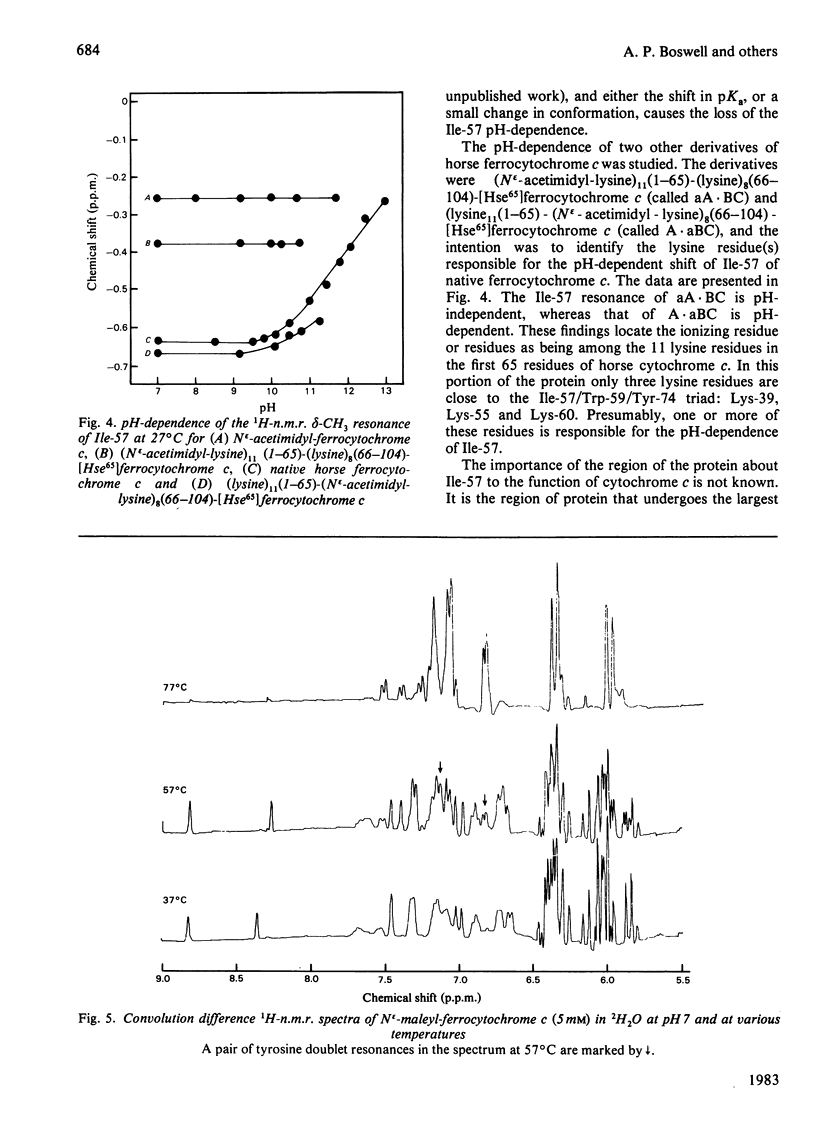
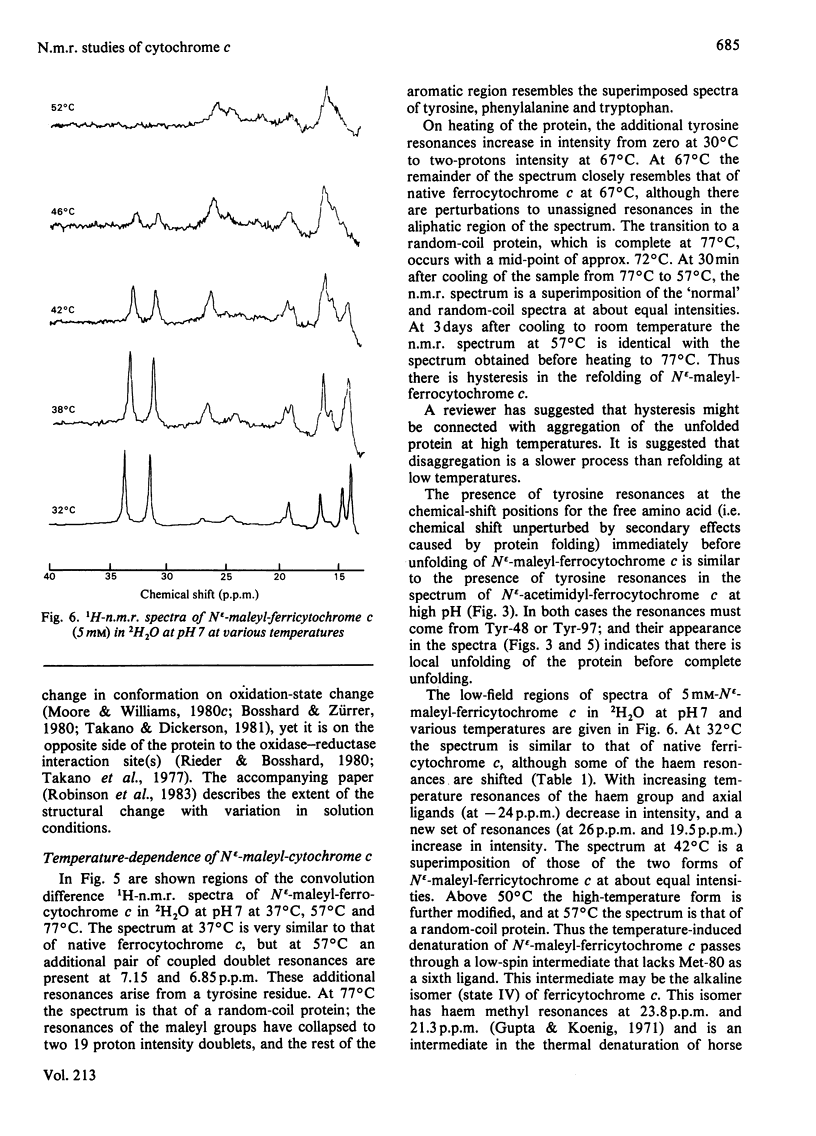
1H-n.m.r. and 13C-n.m.r. spectroscopy of horse cytochrome c and 1H-n.m.r. spectroscopy of the lysine-modified proteins N epsilon-acetimidyl-, N epsilon-amidino-, N epsilon-trifluoroacetyl- and N epsilon-maleyl-cytochrome c have shown that, although the lysine modifications do not greatly perturb the protein structure at pH7 and 27 degrees C, at higher temperature or at alkaline pH some parts of the structure are markedly perturbed. At pH7 and 27 degrees C the region of the protein about Ile-57 is affected in all the modified proteins, though not all to the same degree. N epsilon-Maleylation most seriously affects the protein structure, and the fully maleylated protein is readily unfolded. At 27 degrees C all four of the tyrosine residues of native horse cytochrome c have pKa values above 11, but in N epsilon-acetimidyl-cytochrome c the pKa of one tyrosine residue is 10.2.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bosshard H. R., Zürrer M. The conformation of cytochrome c in solution. Localization of a conformational difference between ferri- and ferrocytochrome c on the surface of the molecule. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6694–6699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boswell A. P., McClune G. J., Moore G. R., Williams R. J., Pettigrew G. W., Inubishi T., Yonetani T., Harris D. E. Nuclear-magnetic-resonance study of the interaction of cytochrome c with cytochrome c peroxidase. Biochem Soc Trans. 1980 Oct;8(5):637–638. doi: 10.1042/bst0080637b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boswell A. P., Moore G. R., Williams R. J., Chien J. C., Dickinson L. C. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the phenylalanine residues of eukaryotic cytochrome c. J Inorg Biochem. 1980 Dec;13(4):347–352. doi: 10.1016/s0162-0134(00)80254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMarchi R. D., Garner W. H., Wang C. C., Hanania G. I., Gurd F. R. Characterization of the reaction of methyl acetimidate with sperm whale myoglobin. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 11;17(14):2822–2828. doi: 10.1021/bi00607a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk K. E., Jovall P. A., Angström J. N.m.r. and e.p.r. characterization of [4-carboxy-2,6-dinitrophenyl-lysine]cytochromes c. Biochem J. 1981 Mar 1;193(3):1021–1024. doi: 10.1042/bj1931021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson-Miller S., Brautigan D. L., Margoliash E. Definition of cytochrome c binding domains by chemical modification. III. Kinetics of reaction of carboxydinitrophenyl cytochromes c with cytochrome c oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 10;253(1):149–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. K., Koenig S. H. Some aspects of pH and temperature dependence of the NMR spectra of cytochrome C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Dec 3;45(5):1134–1143. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HETTINGER T. P., HARBURY H. A. GUANIDINATED CYTOCHROME C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52:1469–1476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R. M., Wüthrich K. 1H-NMR studies of structural homologies between the heme environments in horse cytochrome c and in cytochrome c-552 from Euglena gracilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 28;668(2):307–320. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90038-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R. M., Wüthrich K. Assignment of the heme c resonances in the 360 MHz H NMR spectra of cytochrome c. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 28;533(1):195–208. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90564-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald C. C., Phillips W. D. Proton magnetic resonance studies of horse cytochrome c. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 14;12(17):3170–3186. doi: 10.1021/bi00741a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. R., Williams R. J. Nuclear-magnetic-resonance studies of eukaryotic cytochrome c. Assignment of resonances of aliphatic amino acids. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Feb;103(3):503–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb05974.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. R., Williams R. J. Nuclear-magnetic-resonance studies of eukaryotic cytochrome c. Assignment of resonances of aromatic amino acids. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Feb;103(3):493–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb05973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. R., Williams R. J. Nuclear-magnetic-resonance studies of ferrocytochrome c. pH and temperature dependence. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Feb;103(3):513–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb05975.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield E., Norton R. S., Allerhand A. Studies of individual carbon sites of proteins in solution by natural abundance carbon 13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Strategies for assignments. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6381–6402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheroff N., Borden D., Koppenol W. H., Margoliash E. Electrostatic interactions in cytochrome c. The role of interactions between residues 13 and 90 and residues 79 and 47 in stabilizing the heme crevice structure. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1689–1697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal P. K., Verma B., Myer Y. P. Conformational and functional studies of chemically modified cytochrome c: nitrated and iodinated cytochromes c. Biochemistry. 1975 Sep 23;14(19):4325–4334. doi: 10.1021/bi00690a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettigrew G. W., Aviram I., Schejter A. The role of the lysines in the alkaline heme-linked ionization of ferric cytochrome c. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 9;68(3):807–813. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91217-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettigrew G. Mapping an electron transfer site on cytochrome c. FEBS Lett. 1978 Feb 1;86(1):14–16. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfield A. G., Gupta R. K. Pulsed NMR study of the structure of cytochrome c. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1972;36:405–411. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1972.036.01.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder R., Bosshard H. R. Comparison of the binding sites on cytochrome c for cytochrome c oxidase, cytochrome bc1, and cytochrome c1. Differential acetylation of lysyl residues in free and complexed cytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4732–4739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. N., Boswell A. P., Huang Z. X., Eley C. G., Moore G. R. The conformation of eukaryotic cytochrome c around residues 39, 57, 59 and 74. Biochem J. 1983 Sep 1;213(3):687–700. doi: 10.1042/bj2130687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STELLWAGEN E. THE SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC TITRATION OF THE PHENOLIC GROUPS OF HORSE HEART CYTOCHROME C. Biochemistry. 1964 Jul;3:919–923. doi: 10.1021/bi00895a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schejter A., Aviram I., Sokolovsky M. Nitrocytochrome c. II. Spectroscopic properties and chemical reactivity. Biochemistry. 1970 Dec 22;9(26):5118–5122. doi: 10.1021/bi00828a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schejter A., Zuckerman M., Aviram I. The contribution of electrostatic factors to the stabilization of the conformation of cytochrome c. Studies on the maleylated protein. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7042–7046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. T., Millett F. Involvement of lysines-72 and -79 in the alkaline isomerization of horse heart ferricytochrome c. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 18;19(6):1117–1120. doi: 10.1021/bi00547a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. T., Staudenmayer N., Millett F. Use of specific lysine modifications to locate the reaction site of cytochrome c with cytochrome oxidase. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 15;16(23):4971–4974. doi: 10.1021/bi00642a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellwagen E., Smith L. M., Cass R., Ledger R., Wilgus H. Characterization of guanidinated cytochrome c by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1977 Aug 9;16(16):3672–3679. doi: 10.1021/bi00635a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano T., Dickerson R. E. Conformation change of cytochrome c. II. Ferricytochrome c refinement at 1.8 A and comparison with the ferrocytochrome structure. J Mol Biol. 1981 Nov 25;153(1):95–115. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90529-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano T., Trus B. L., Mandel N., Mandel G., Kallai O. B., Swanson R., Dickerson R. E. Tuna cytochrome c at 2.0 A resolution. II. Ferrocytochrome structure analysis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):776–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace C. J., Offord R. E. The semisynthesis of fragments corresponding to residues 66-104 of horse heart cytochrome c. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 1;179(1):169–182. doi: 10.1042/bj1790169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


