Abstract
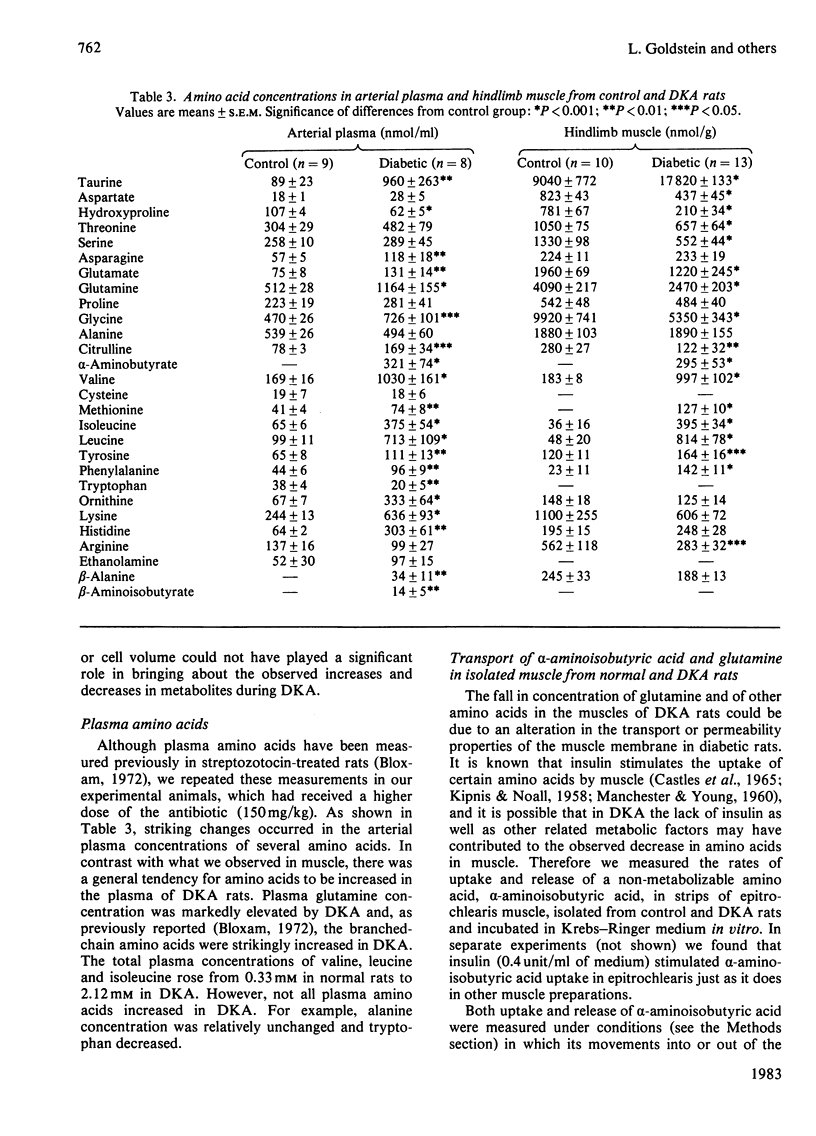
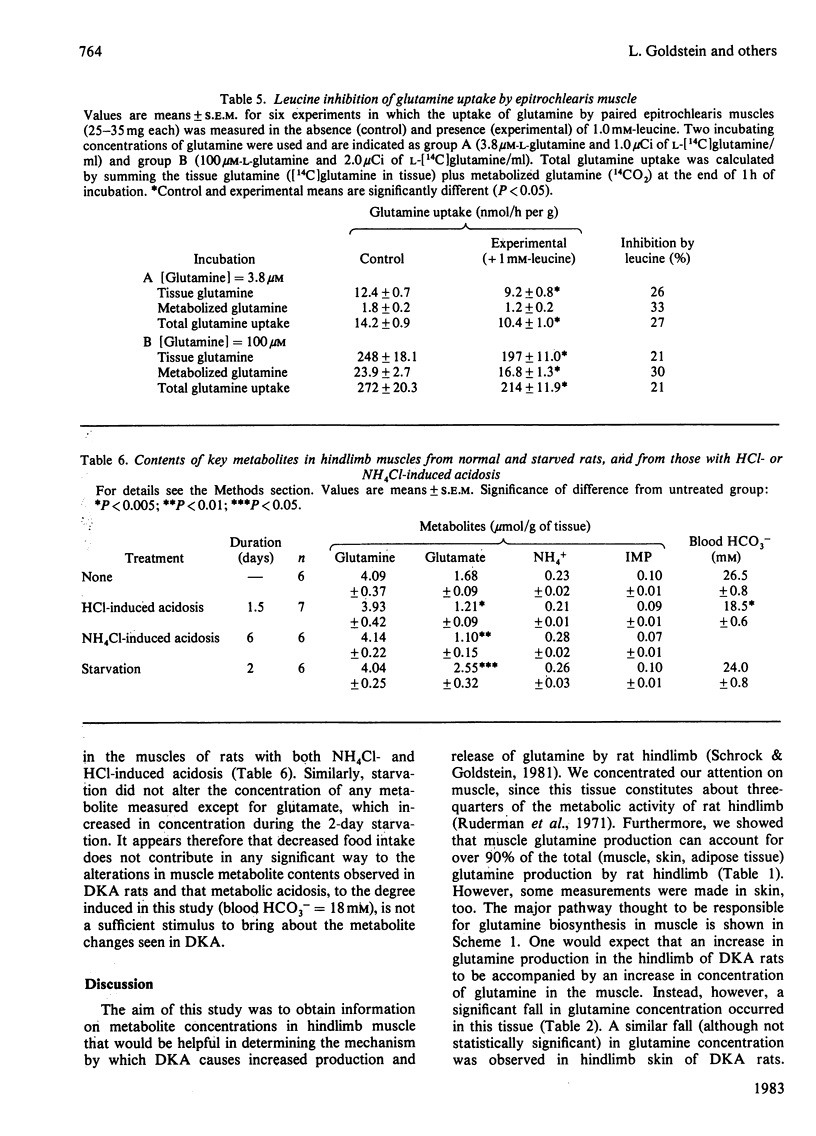
The mechanism of activation of glutamine production by the hindlimb during diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) was investigated in rats. Muscle glutamine production was estimated to account for over 90% of the total glutamine produced by the hindlimb. DKA produced significant increases in the concentrations of NH4+ and IMP in hindlimb muscles, suggesting that AMP deaminase is activated by DKA. NH4Cl- and HCl-induced acidosis did not produce these changes, indicating either that acidosis itself is not the stimulus for increased AMP deaminase activity or that the more severe degree of acidosis accompanying DKA is necessary for activation. Muscle glutamine concentrations were depressed in DKA. Experiments with isolated epitrochlearis muscle showed that the transport and permeability properties of the muscle cells (as judged by uptake and release of alpha-aminoisobutyrate and glutamine) were not altered by DKA. However, glutamine uptake by muscle cells was significantly inhibited by L-leucine, the concentration of which, along with other branched-chain amino acids, is markedly elevated in DKA.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albuquerque E. X., Warnick J. E., Tasse J. R., Sansone F. M. Effects of vinblastine and colchicine on neural regulation of the fast and slow skeletal muscles of the rat. Exp Neurol. 1972 Dec;37(3):607–634. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(72)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström J., Fürst P., Norée L. O., Vinnars E. Intracellular free amino acid concentration in human muscle tissue. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Jun;36(6):693–697. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.36.6.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloxam D. L. Nutritional aspects of amino acid metabolism. 3. The effects of diabetes on blood and liver amino acid concentrations in the rat. Br J Nutr. 1972 Mar;27(2):249–259. doi: 10.1079/bjn19720091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. R. The rapid separation of nucleotides in cell extracts using high-pressure liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1970 Oct 21;52(2):257–272. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)96573-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASTLES J. J., WOOL I. G., MOYER A. N. THE EFFECT OF DIABETES ON AMINO ACID ACCUMULATION AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN ISOLATED RAT DIAPHRAGM. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 May 4;100:609–612. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlmann B., Schroeter C., Herbertz L., Reinauer H. Myofibrillar protein degradation and muscle proteinases in normal and diabetic rats. Biochem Med. 1979 Feb;21(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(79)90052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Marliss E., Ohman J. L., Cahill C. F., Jr Plasma amino acid levels in diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes. 1970 Oct;19(10):727–728. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.10.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber A. J., Karl I. E., Kipnis D. M. Alanine and glutamine synthesis and release from skeletal muscle. I. Glycolysis and amino acid release. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 10;251(3):826–835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L., Boylan J. M., Schröck H. Adaptation of renal ammonia production in the diabetic ketoacidotic rat. Kidney Int. 1980 Jan;17(1):57–65. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M. N., Lowenstein J. M. The purine nucleotide cycle. Studies of ammonia production by skeletal muscle in situ and in perfused preparations. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5054–5060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen B. C., Pek S., Koerker D. J., Goodner C. J., Wolfe R. A., Schielke G. P. Neural influences on oscillations in basal plasma levels of insulin in monkeys. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jan;240(1):E5–11. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.1.E5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIPNIS D. M., NOALL M. W. Stimulation of amino acid transport by insulin in the isolated rat diaphragm. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Apr;28(1):226–227. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90466-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. L. Single-column system for accelerated amino acid analysis of physiological fluids using five lithium buffers. Biochem Med. 1974 Jun;10(2):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(74)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANCHESTER K. L., YOUNG F. G. The effect of insulin in vitro on the accumulation of amino acids by isolated rat diaphragm. Biochem J. 1960 Jun;75:487–495. doi: 10.1042/bj0750487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozefsky T., Felig P., Tobin J. D., Soeldner J. S., Cahill G. F., Jr Amino acid balance across tissues of the forearm in postabsorptive man. Effects of insulin at two dose levels. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2273–2282. doi: 10.1172/JCI106193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preedy V. R., Garlick P. J. Rates of protein synthesis in skin and bone, and their importance in the assessment of protein degradation in the perfused rat hemicorpus. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 15;194(1):373–376. doi: 10.1042/bj1940373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Berger M. The formation of glutamine and alanine in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5500–5506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Houghton C. R., Hems R. Evaluation of the isolated perfused rat hindquarter for the study of muscle metabolism. Biochem J. 1971 Sep;124(3):639–651. doi: 10.1042/bj1240639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharff R., Wool I. G. Effect of diabetes on the concentration of amino acids in plasma and heart muscle of rats. Biochem J. 1966 Apr;99(1):173–178. doi: 10.1042/bj0990173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischler M. E., Goldberg A. L. Leucine degradation and release of glutamine and alanine by adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8074–8081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


