Abstract
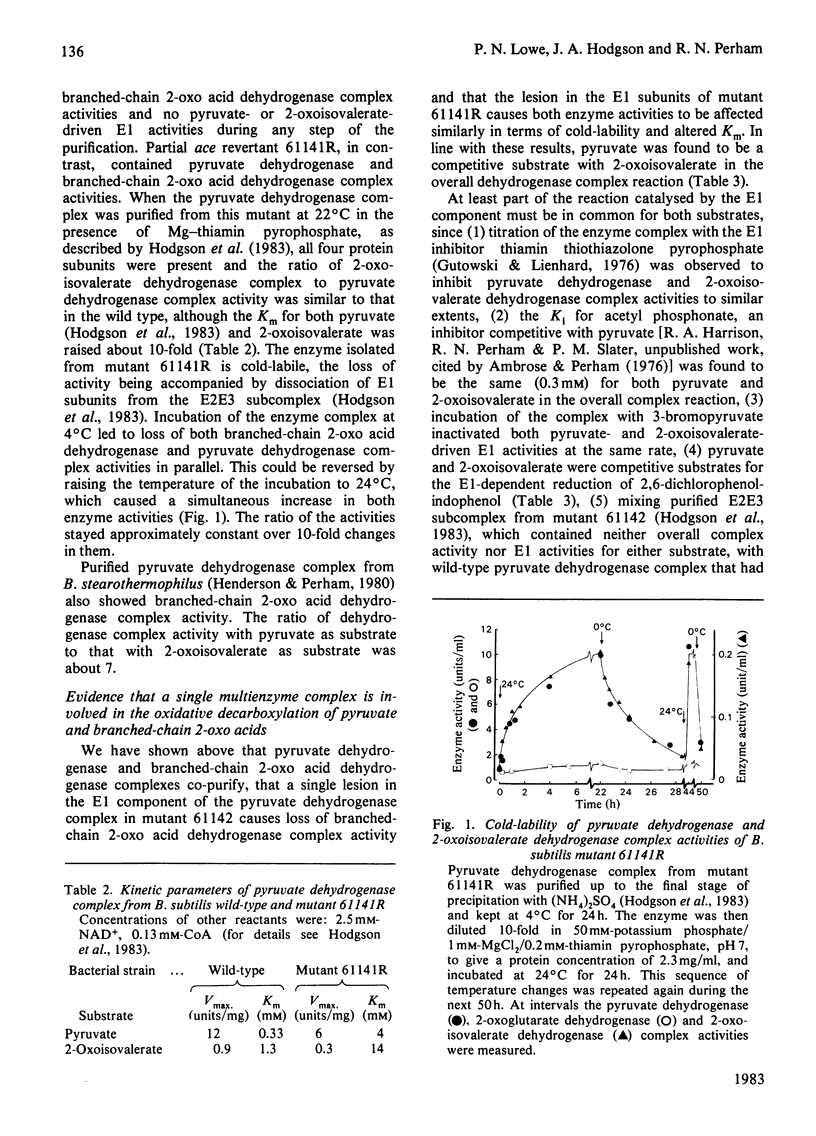
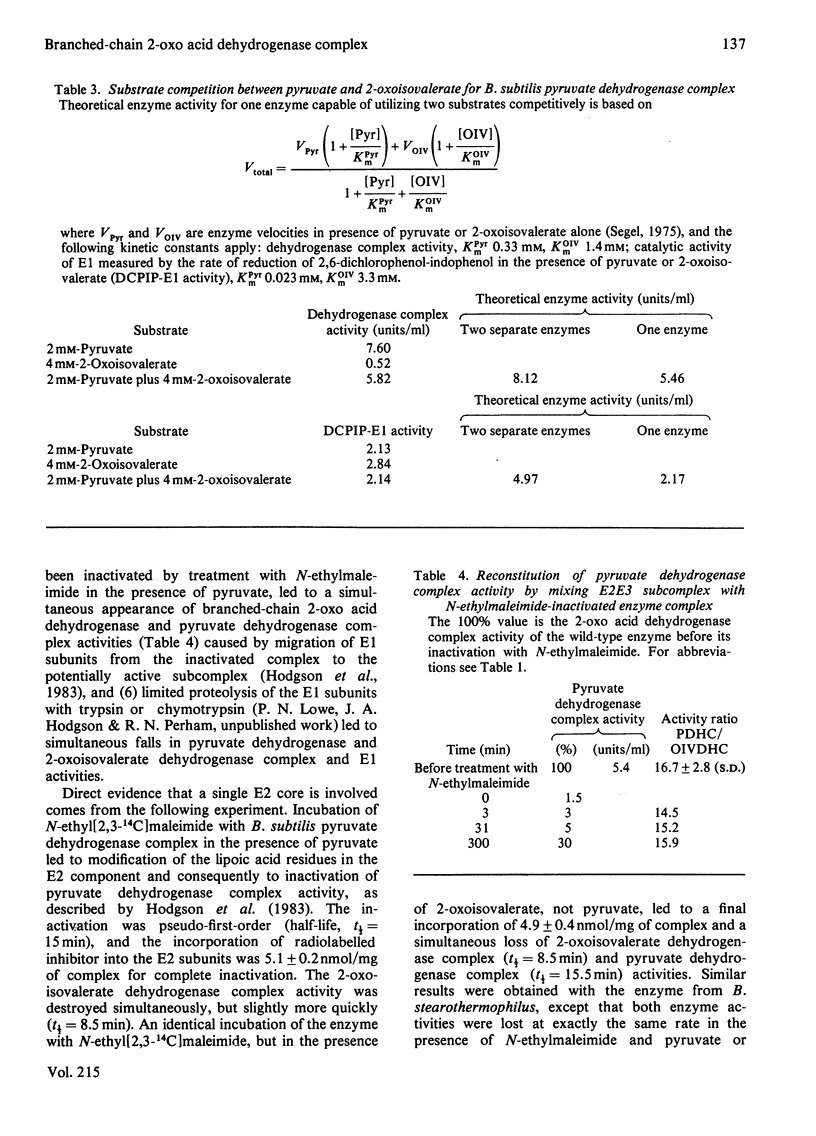
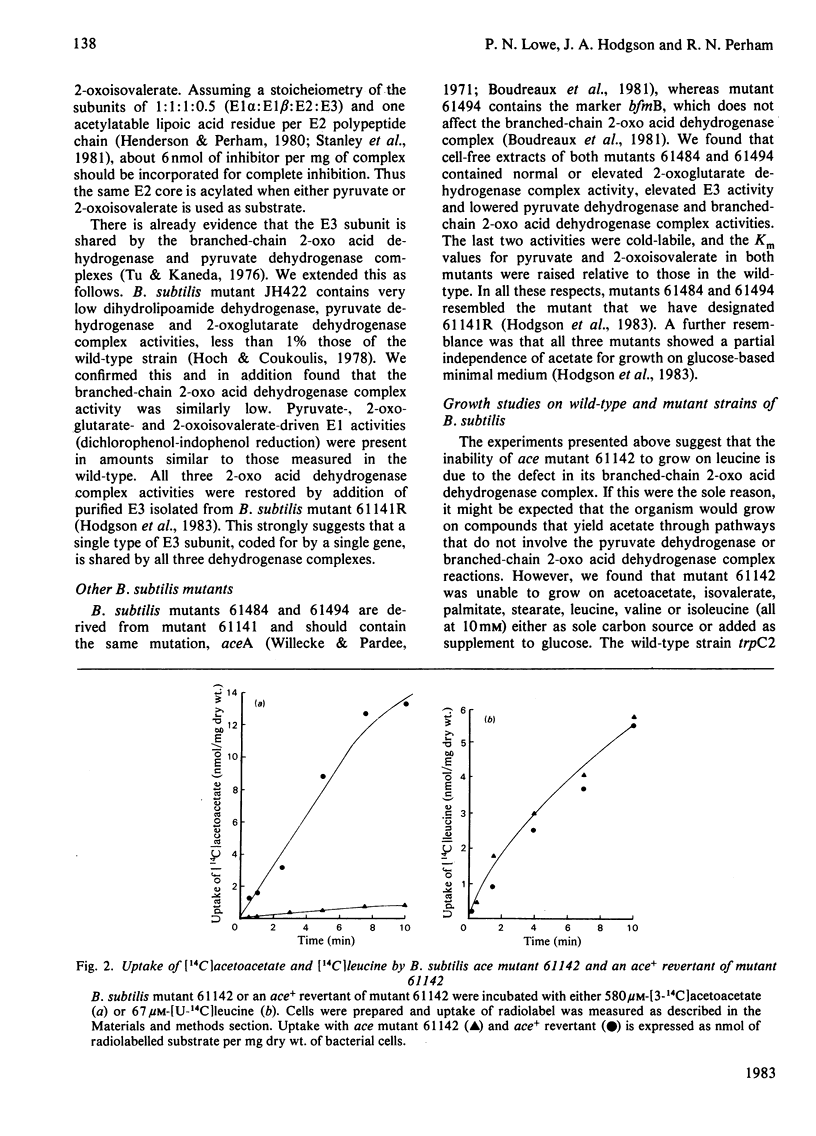
The pyruvate dehydrogenase and branched-chain 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase activities of Bacillus subtilis were found to co-purify as a single multienzyme complex. Mutants of B. subtilis with defects in the pyruvate decarboxylase (E1) and dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (E3) components of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex were correspondingly affected in branched-chain 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase complex activity. Selective inhibition of the E1 or lipoate acetyltransferase (E2) components in vitro led to parallel losses in pyruvate dehydrogenase and branched-chain 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase complex activity. The pyruvate dehydrogenase and branched-chain 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase complexes of B. subtilis at the very least share many structural components, and are probably one and the same. The E3 component appeared to be identical for the pyruvate dehydrogenase, 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase and branched-chain 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase complexes in this organism and to be the product of a single structural gene. Long-chain branched fatty acids are thought to be essential for maintaining membrane fluidity in B. subtilis, and it was observed that the ace (pyruvate dehydrogenase complex) mutant 61142 was unable rapidly to take up acetoacetate, unlike the wild-type, indicative of a defect in membrane permeability. A single pyruvate dehydrogenase and branched-chain 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase complex can be seen as an economical means of supplying two different sets of essential metabolites.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambrose M. C., Perham R. N. Spin-label study of the mobility of enzyme-bound lipoic acid in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1976 May 1;155(2):429–432. doi: 10.1042/bj1550429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danner D. J., Lemmon S. K., Besharse J. C., Elsas L. J., 2nd Purification and characterization of branched chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase from bovine liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5522–5526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortnagel P., Freese E. Analysis of sporulation mutants. II. Mutants blocked in the citric acid cycle. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1431–1438. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1431-1438.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese E., Fortnagel U. Growth and sporulation of Bacillus subtilis mutants blocked in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):745–756. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.745-756.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R., Creaghan I. T. Gene-protein relationships of the alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes of Escherichia coli K12: isolation and characterization of lipoamide dehydrogenase mutants. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Mar;75(1):197–210. doi: 10.1099/00221287-75-1-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutowski J. A., Lienhard G. E. Transition state analogs for thiamin pyrophosphate-dependent enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2863–2866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson C. E., Perham R. N., Finch J. T. Structure and symmetry of B. stearothermophilus pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex and implications for eucaryote evolution. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson C. E., Perham R. N. Purificaton of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Bacillus stearothermophilus and resolution of its four component polypeptides. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 1;189(1):161–172. doi: 10.1042/bj1890161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J. A., Coukoulis H. J. Genetics of the alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):265–269. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.265-269.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson J. A., Lowe P. N., Perham R. N. Wild-type and mutant forms of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex from Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J. 1983 May 1;211(2):463–472. doi: 10.1042/bj2110463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda T. Biosynthesis of branched long-chain fatty acids from the related short-chain -keto acid substrates by a cell-free system of Bacillus subtilis. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Jan;19(1):87–96. doi: 10.1139/m73-013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klofat W., Picciolo G., Chappelle E. W., Freese E. Production of adenosine triphosphate in normal cells and sporulation mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3270–3276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba Y., Yoshizawa K., Ejima A., Hayashi T., Kaneda T. Coenzyme A- and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-dependent branched chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase. I. Purification and properties of the enzyme from Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4437–4447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perham R. N., Harrison R. A., Brown J. P. The lipoamide dehydrogenase component of the 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes of Escherichia coli. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(1):47–50. doi: 10.1042/bst0060047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perham R. N. Self-assembly of biological macromolecules. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Nov 6;272(915):123–136. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettit F. H., Yeaman S. J., Reed L. J. Purification and characterization of branched chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex of bovine kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4881–4885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg B., Hoch J. A. Citric acid cycle: gene-enzyme relationships in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):826–833. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.826-833.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley C. J., Packman L. C., Danson M. J., Henderson C. E., Perham R. N. Intramolecular coupling of active sites in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes from bacterial and mammalian sources. Biochem J. 1981 Jun 1;195(3):715–721. doi: 10.1042/bj1950715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu C. L., Kaneda T. Activities of alpha-ketoisovalerate, pyruvate, and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenases in a mutant of Bacillus subtilis. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Apr;22(4):592–597. doi: 10.1139/m76-088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willecke K., Pardee A. B. Fatty acid-requiring mutant of bacillus subtilis defective in branched chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 10;246(17):5264–5272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


