Abstract
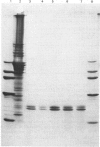
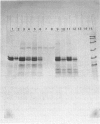
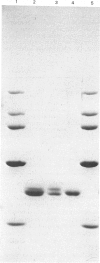
Hepatic microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase activity was rendered extremely unstable by a variety of techniques: (a) incubation at pH 5.0; (b) extraction of the microsomal fraction in the presence of 1% Lubrol; (c) various purification procedures. These techniques all result in the removal of a 21 kDa polypeptide from the fraction containing glucose-6-phosphatase activity. The 21 kDa protein was purified to apparent homogeneity by solubilization in the detergent Lubrol 12A-9 and chromatography on Fractogel TSK DEAE-650(S) and centrifugation at 105 000 g. The 21 kDa protein stabilizes glucose-6-phosphatase activity, whereas other purified hepatic microsomal proteins do not. The 21 kDa protein appears to be a potential regulator of glucose-6-phosphatase activity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arion W. J., Lange A. J., Ballas L. M. Quantitative aspects of relationship between glucose 6-phosphate transport and hydrolysis for liver microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase system. Selective thermal inactivation of catalytic component in situ at acid pH. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6784–6790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arion W. J., Lange A. J., Walls H. E., Ballas L. M. Evidence for the participation of independent translocation for phosphate and glucose 6-phosphate in the microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase system. Interactions of the system with orthophosphate, inorganic pyrophosphate, and carbamyl phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10396–10406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arion W. J., Wallin B. K., Lange A. J., Ballas L. M. On the involvement of a glucose 6-phosphate transport system in the function of microsomal glucose 6-phosphatase. Mol Cell Biochem. 1975 Feb 28;6(2):75–83. doi: 10.1007/BF01732001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bickerstaff G. F., Burchell B. Studies on the purification of glucose 6-phosphatase from rabbit liver microsomal fraction [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1980 Jun;8(3):389–390. doi: 10.1042/bst0080389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchell A. A simple method for purification of rat hepatic microsomal cytochrome b5. Biochem J. 1985 Feb 15;226(1):339–341. doi: 10.1042/bj2260339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
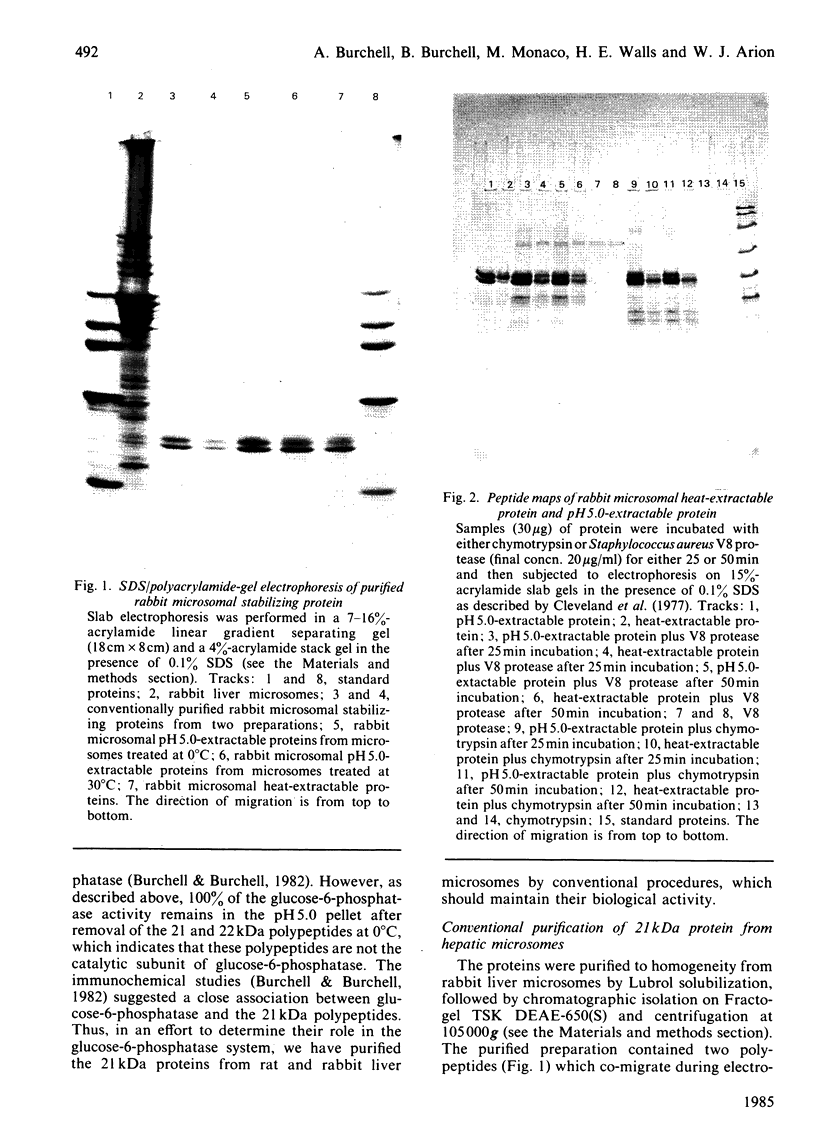
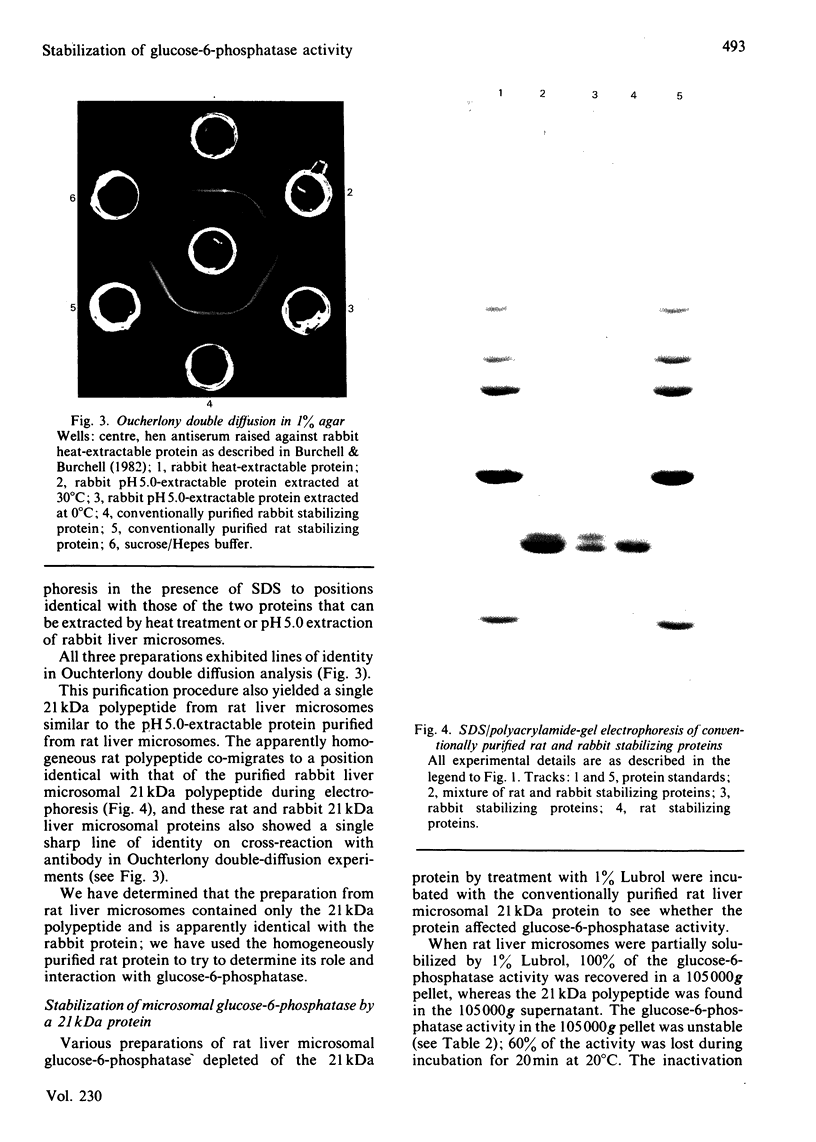
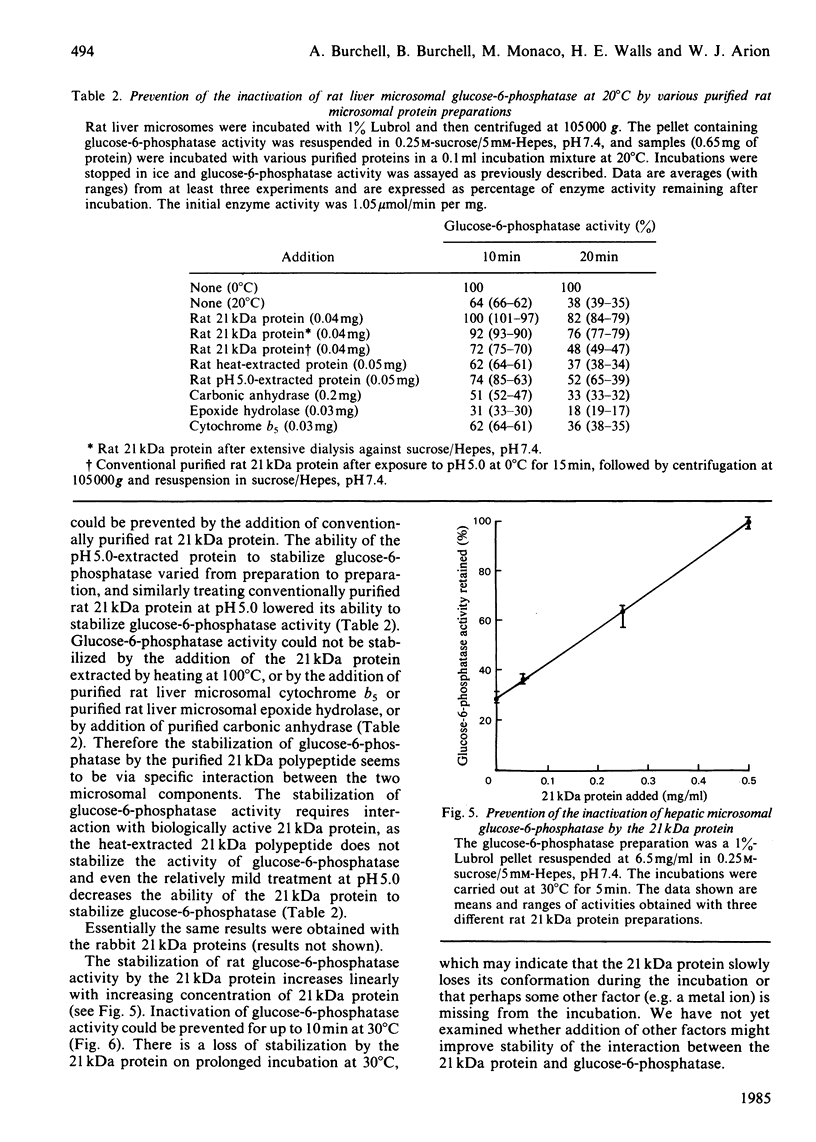
- Burchell A., Burchell B. Identification and purification of a liver microsomal glucose 6-phosphatase. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 1;205(3):567–573. doi: 10.1042/bj2050567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
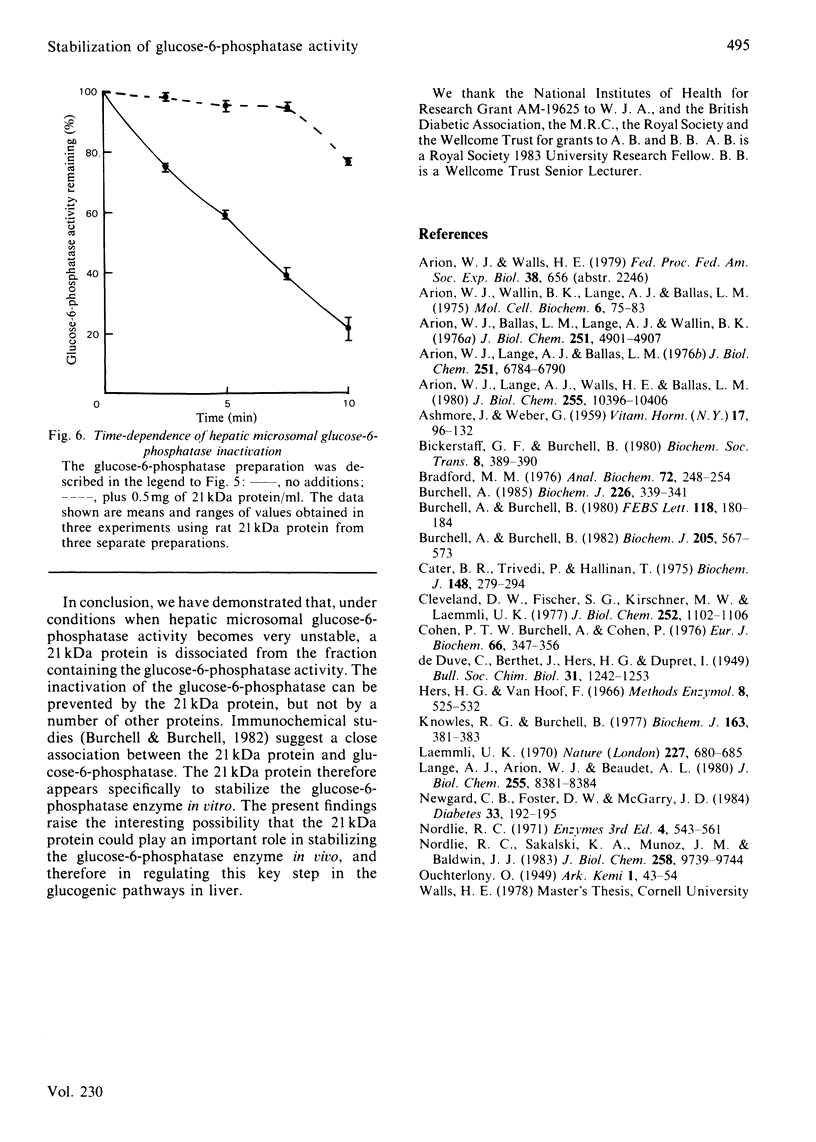
- Burchell A., Burchell B. Stabilization of partially-purified glucose 6-phosphatase by fluoride. Is enzyme inactivation caused by dephosphorylation? FEBS Lett. 1980 Sep 8;118(2):180–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80214-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cater B. R., Trivedi P., Hallinan T. Inhibition of glucose 6-phosphatase by pure and impure C-type phospholipases. Reactivation by phospholipid dispersions and protection by serum albumin. Biochem J. 1975 May;148(2):279–294. doi: 10.1042/bj1480279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. T., Burchell A., Cohen P. The molecular basis of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase deficiency. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 1;66(2):347–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10524.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Burchell B. A simple method for purification of epoxide hydratase from rat liver. Biochem J. 1977 May 1;163(2):381–383. doi: 10.1042/bj1630381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange A. J., Arion W. J., Beaudet A. L. Type Ib glycogen storage disease is caused by a defect in the glucose-6-phosphate translocase of the microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase system. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8381–8384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newgard C. B., Foster D. W., McGarry J. D. Evidence for suppression of hepatic glucose-6-phosphatase with carbohydrate feeding. Diabetes. 1984 Feb;33(2):192–195. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.2.192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlie R. C., Sukalski K. A., Muñoz J. M., Baldwin J. J. Type Ic, a novel glycogenosis. Underlying mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9739–9744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]