Abstract
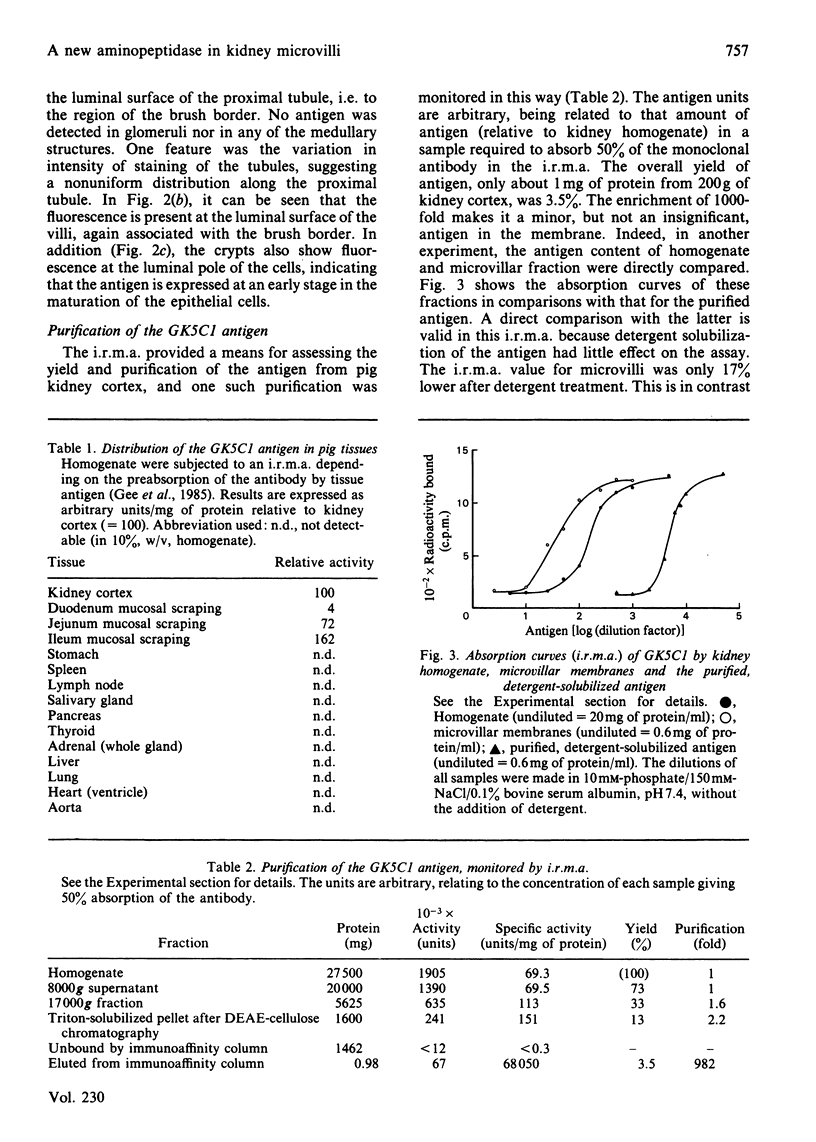
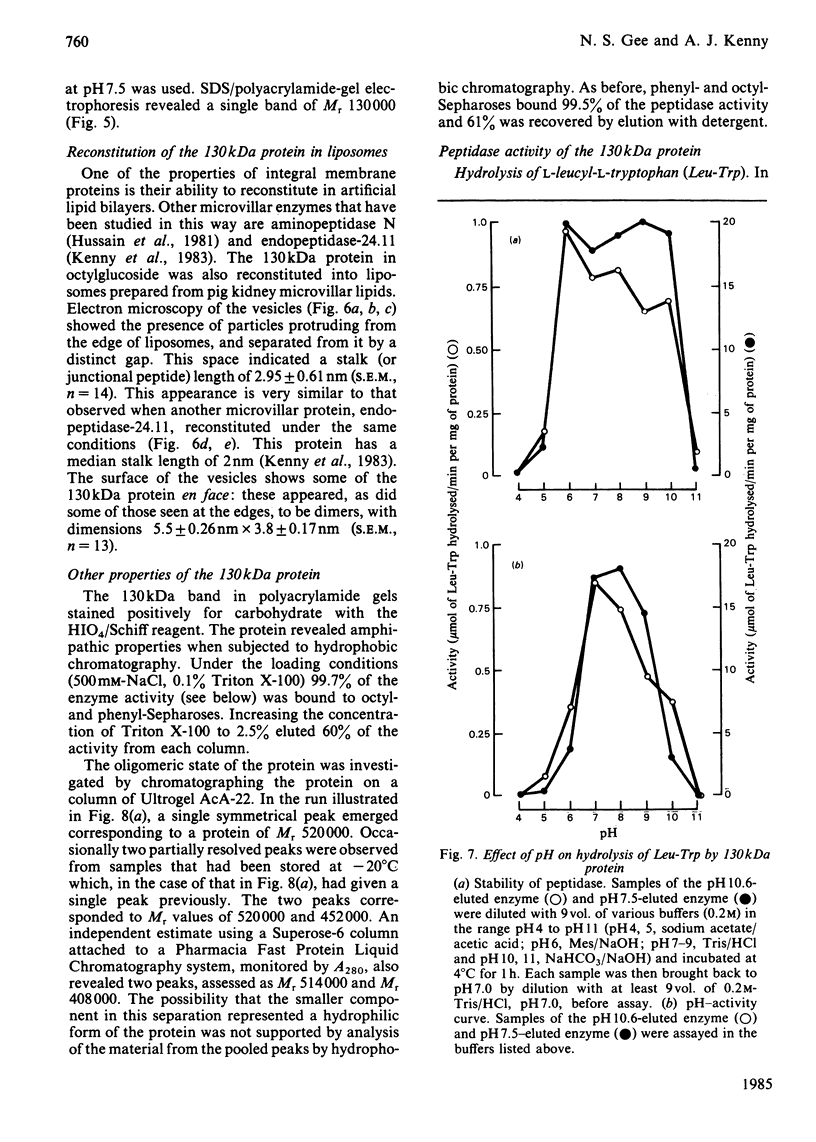
The hybridoma GK5C1, secreting a monoclonal IgG1 antibody, was generated after immunizing a mouse with pig kidney microvillar membranes. An immunoradiometric assay showed that only kidney and intestine contained detectable amounts of the antigen recognized by the antibody, the highest concentration being observed in the ileum. Immunocytochemistry confirmed this observation and revealed that the antigen was associated with renal and intestinal brush borders. By 'Western' blotting, the antigen in kidney microvilli was shown to be a 130 kDa polypeptide. Papain treatment of the membrane before blotting converted the antigen to a 125 kDa polypeptide, no longer associated with membrane. Immunoaffinity chromatography of detergent-solubilized kidney membranes yielded a pure 130 kDa protein. When one purification was monitored by the immunoradiometric assay, the yield was 3.5% and the purification factor was 1000-fold. The antigen constituted about 0.8% of the microvillar membrane protein. The protein could be reconstituted into liposomes, where electron microscopy revealed an asymmetric orientation, similar to that of ectoenzymes in this membrane. The stalk length was about 3 nm. In electron micrographs the purified protein appeared to be dimeric. A search for enzymic activity was rewarded when L-leucyl-L-tryptophan was observed to be hydrolysed. Failure to hydrolyse N-blocked peptides and the ability to release the N-terminal residue from extended peptides, including Leu-Trp-Leu and Leu-Trp-Met-Arg, showed that the activity was that of an aminopeptidase. The enzyme was maximally active at pH 7.5 and irreversibly inactivated outside the range pH 6-10. This activity could not be attributed to trace contamination with aminopeptidase N. The best substrates so far identified for the 130 kDa protein were those with tryptophan in the P1', position. This protein is a new microvillar enzyme and it is proposed that it be called aminopeptidase W.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong D. J., Mukhopadhyay S. K., Campbell B. J. Physicochemical characterization of renal dipeptidase. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 9;13(8):1745–1750. doi: 10.1021/bi00705a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth A. G., Kenny A. J. A rapid method for the preparation of microvilli from rabbit kidney. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):575–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1420575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth A. G., Kenny A. J. Proteins of the kidney microvillus membrane. Identification of subunits after sodium dodecylsullphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1976 Nov;159(2):395–407. doi: 10.1042/bj1590395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell B. J., Forrester L. J., Zahler W. L., Burks M. Beta-lactamase activity of purified and partially characterized human renal dipeptidase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14586–14590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsen E. M., Norén O., Sjöström H., Ingram J., Kenny A. J. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. Aspartate aminopeptidase: purification by immunoadsorbent chromatography and properties of the detergent- and proteinase-solubilized forms. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 1;189(3):591–603. doi: 10.1042/bj1890591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher I. S., Chaplin M. F., Kenny A. J. Endopeptidase-24.11 purified from pig intestine is differently glycosylated from that in kidney. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 1;215(2):317–323. doi: 10.1042/bj2150317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher I. S., Kenny A. J. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. The amphipathic forms of endopeptidase purified from pig kidneys. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 1;211(3):743–753. doi: 10.1042/bj2110743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee N. S., Bowes M. A., Buck P., Kenny A. J. An immunoradiometric assay for endopeptidase-24.11 shows it to be a widely distributed enzyme in pig tissues. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj2280119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee N. S., Matsas R., Kenny A. J. A monoclonal antibody to kidney endopeptidase-24.11. Its application in immunoadsorbent purification of the enzyme and immunofluorescent microscopy of kidney and intestine. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 15;214(2):377–386. doi: 10.1042/bj2140377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George S. G., Kenny J. Studies on the enzymology of purified preparations of brush border from rabbit kidney. Biochem J. 1973 May;134(1):43–57. doi: 10.1042/bj1340043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedeager-Sørensen S., Kenny A. J. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. Purification and properties of carboxypeptidase P from pig kidneys. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 1;229(1):251–257. doi: 10.1042/bj2290251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain M. M., Tranum-Jensen J., Norén O., Sjöström H., Christiansen K. Reconstitution of purified amphiphilic pig intestinal microvillus aminopeptidase. Mode of membrane insertion and morphology. Biochem J. 1981 Oct 1;199(1):179–186. doi: 10.1042/bj1990179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Booth A. G., George S. G., Ingram J., Kershaw D., Wood E. J., Young A. R. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV, a kidney brush-border serine peptidase. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):169–182. doi: 10.1042/bj1570169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Fulcher I. S., McGill K. A., Kershaw D. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. Reconstitution of endopeptidase in liposomes shows that it is a short-stalked protein. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 1;211(3):755–762. doi: 10.1042/bj2110755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Maroux S. Topology of microvillar membrance hydrolases of kidney and intestine. Physiol Rev. 1982 Jan;62(1):91–128. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak E. M., Tate S. S. Glutathione-degrading enzymes of microvillus membranes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6322–6327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnair D. C., Kenny A. J. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. The amphipathic form of dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Biochem J. 1979 May 1;179(2):379–395. doi: 10.1042/bj1790379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Fulcher I. S., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. Substance P and [Leu]enkephalin are hydrolyzed by an enzyme in pig caudate synaptic membranes that is identical with the endopeptidase of kidney microvilli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3111–3115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]