Abstract
Since the exposure of rats to cadmium causes zinc to accumulate in metallothionein in liver and kidney but not in a similar protein in the testes, the properties of the low-Mr cadmium-binding proteins were investigated in rat testes. Weanling rats that had been given dietary cadmium for 6 weeks were injected with 109CdCl2 and subsequently killed, and the 109Cd-labelled low-Mr proteins from testes were purified. The pooled low-Mr cadmium-containing fractions from the gel-filtration (Sephadex G-75) columns were eluted through DEAE-Sephacel columns, yielding two peaks. Each of the individual peaks from this Sephacel column was further purified by rechromatography on DEAE-Sephacel and on Bio-Gel P-10 columns. Amino acid analysis of the two purified proteins revealed a low cysteine (about 3%) content, with aspartate, glutamate and glycine as the predominant amino acids. Thus these low-Mr cadmium-binding proteins induced by cadmium in rat testes do not appear to be metallothionein.
Full text
PDF
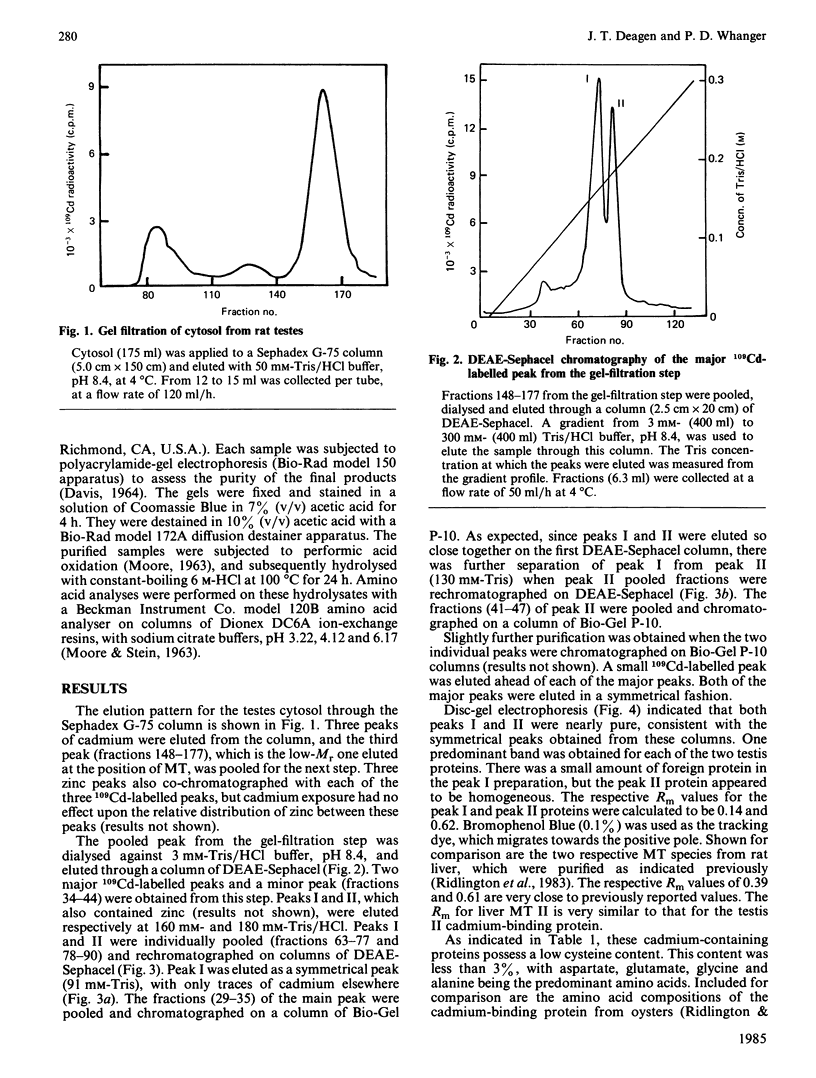
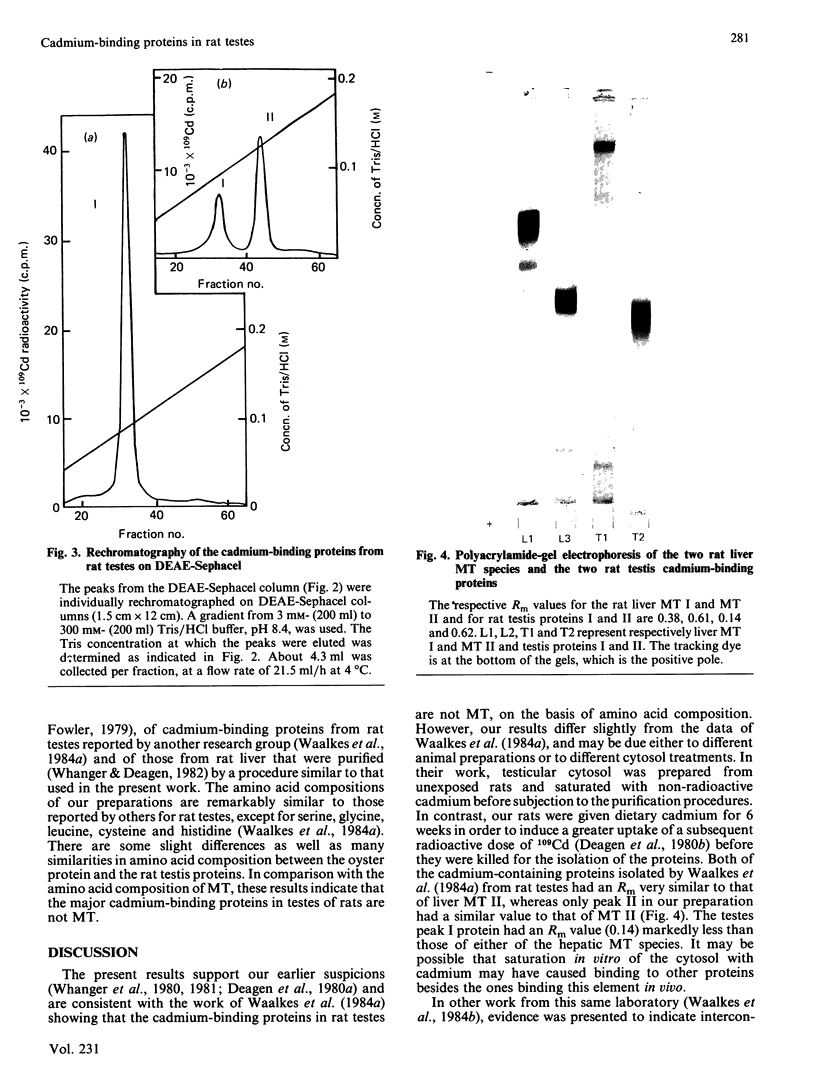
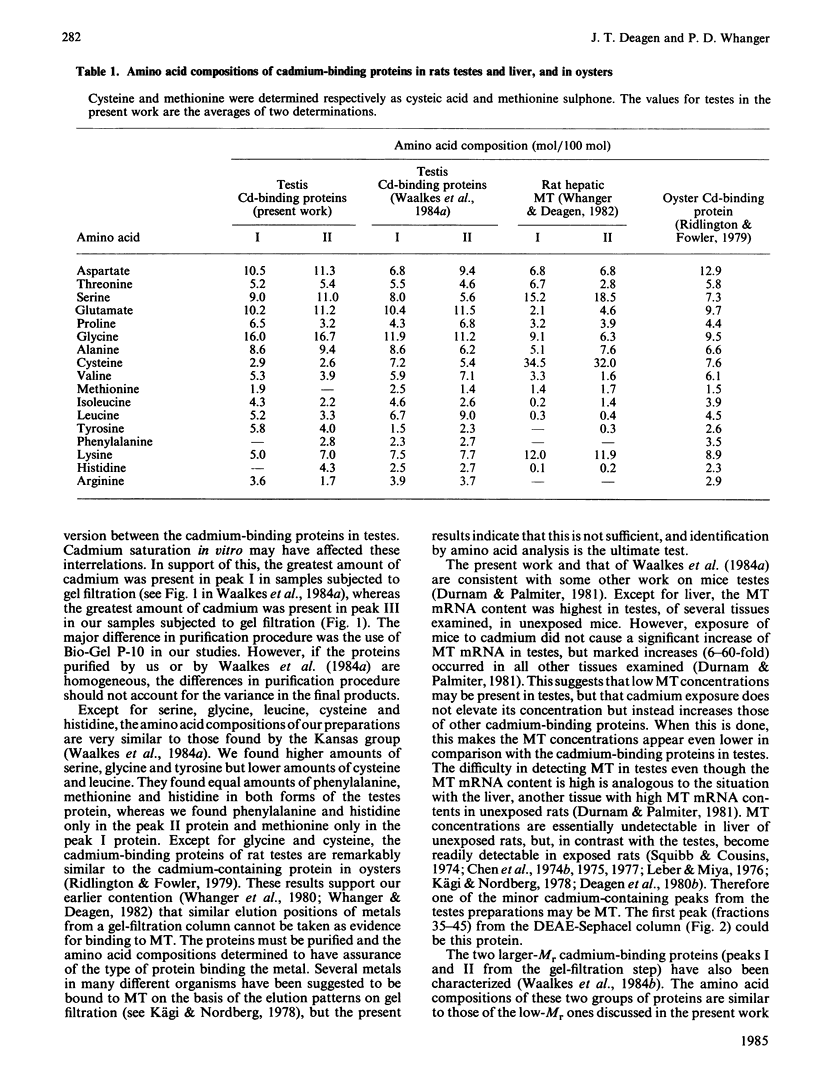

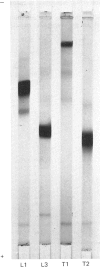
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen R. W., Ganther H. E. Some properties of a unique cadmium-binding moiety in the soluble fraction of rat testes. Environ Physiol Biochem. 1975;5(4):235–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. W., Vasey E. J., Whanger P. D. Accumulation and depletion of zinc in rat liver and kidney metallothionens. J Nutr. 1977 May;107(5):805–813. doi: 10.1093/jn/107.5.805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. W., Wagner P. A., Hoekstra W. G., Ganther H. E. Affinity labelling studies with 109cadmium in cadmium-induced testicular injury in rats. J Reprod Fertil. 1974 Jun;38(2):293–306. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0380293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. W., Whanger P. D., Weswig P. H. Biological function of metallothionein. I. Synthesis and degradation of rat liver metallothionein. Biochem Med. 1975 Feb;12(2):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(75)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the mouse metallothionein-I gene by heavy metals. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5712–5716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazier J. M. Bioaccumulation of cadmium in marine organisms. Environ Health Perspect. 1979 Feb;28:75–79. doi: 10.1289/ehp.792875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGI J. H., VALLEE B. L. Metallothionein: a cadmium and zinc-containign protein from equine renal cortex. II. Physico-chemical properties. J Biol Chem. 1961 Sep;236:2435–2442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leber A. P., Miya T. S. A mechanism for cadmium- and zinc-induced tolerance to cadmium toxicity: involvement of metallothionein. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1976 Sep;37(3):403–414. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(76)90202-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridlington J. W., Fowler B. A. Isolation and partial characterization of a cadmium-binding protein from the American oyster (Crassostrea virginica). Chem Biol Interact. 1979 May;25(2-3):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(79)90041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh Z. A., Smith J. C. The biosynthesis of metallothionein rat liver and kidney after administration of cadmium. Chem Biol Interact. 1976 Dec;15(4):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(76)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh K., Nath R., Chakravarti R. N. Isolation and characterization of cadmium-binding protein from rat testes. J Reprod Fertil. 1974 Feb;36(2):257–265. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0360257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squibb K. S., Cousins R. J. Control of cadmium binding protein synthesis in rat liver. Environ Physiol Biochem. 1974;4(1):24–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waalkes M. P., Chernoff S. B., Klaassen C. D. Cadmium-binding proteins of rat testes. Apparent source of the protein of low molecular mass. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 15;220(3):819–824. doi: 10.1042/bj2200819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waalkes M. P., Chernoff S. B., Klaassen C. D. Cadmium-binding proteins of rat testes. Characterization of a low-molecular-mass protein that lacks identity with metallothionein. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 15;220(3):811–818. doi: 10.1042/bj2200811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb M. Biochemical effects of Cd 2+ -injury in the rat and mouse testis. J Reprod Fertil. 1972 Jul;30(1):83–98. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0300083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whanger P. D., OH S. H., Deagen J. T. Ovine and bovine metallothioneins: accumulation and depletion of zinc in various tissues. J Nutr. 1981 Jul;111(7):1196–1206. doi: 10.1093/jn/111.7.1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whanger P. D., Ridlington J. W., Holcomb C. L. Interactions of zinc and selenium on the binding of cadmium to rat tissue proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;355:333–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb21351.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winge D. R., Rajagopalan K. V. Purification and some properties of Cd-binding protein from rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Dec;153(2):755–762. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90395-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewska-Knypl J., Jablońska J., Myślak Z. Binding of cadmium on metallothionein in man: an analysis of a fatal poisoning by cadmium iodide. Arch Toxikol. 1971;28(1):46–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00349627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]