Abstract
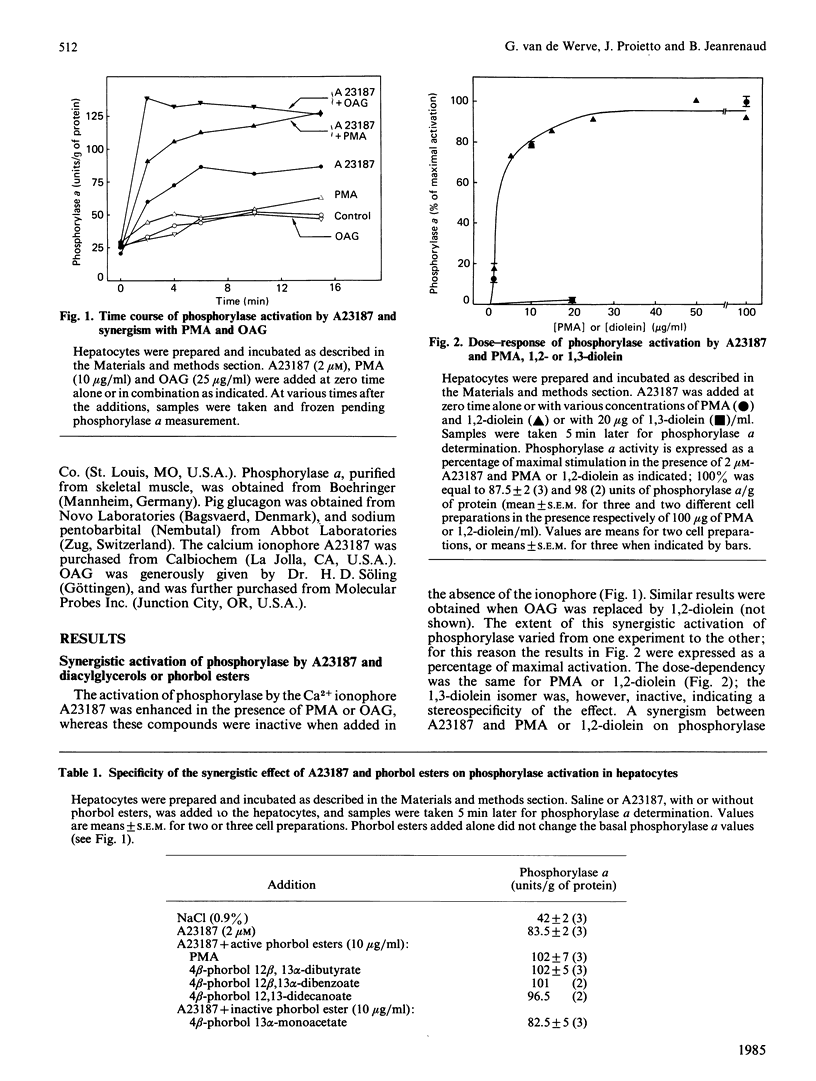
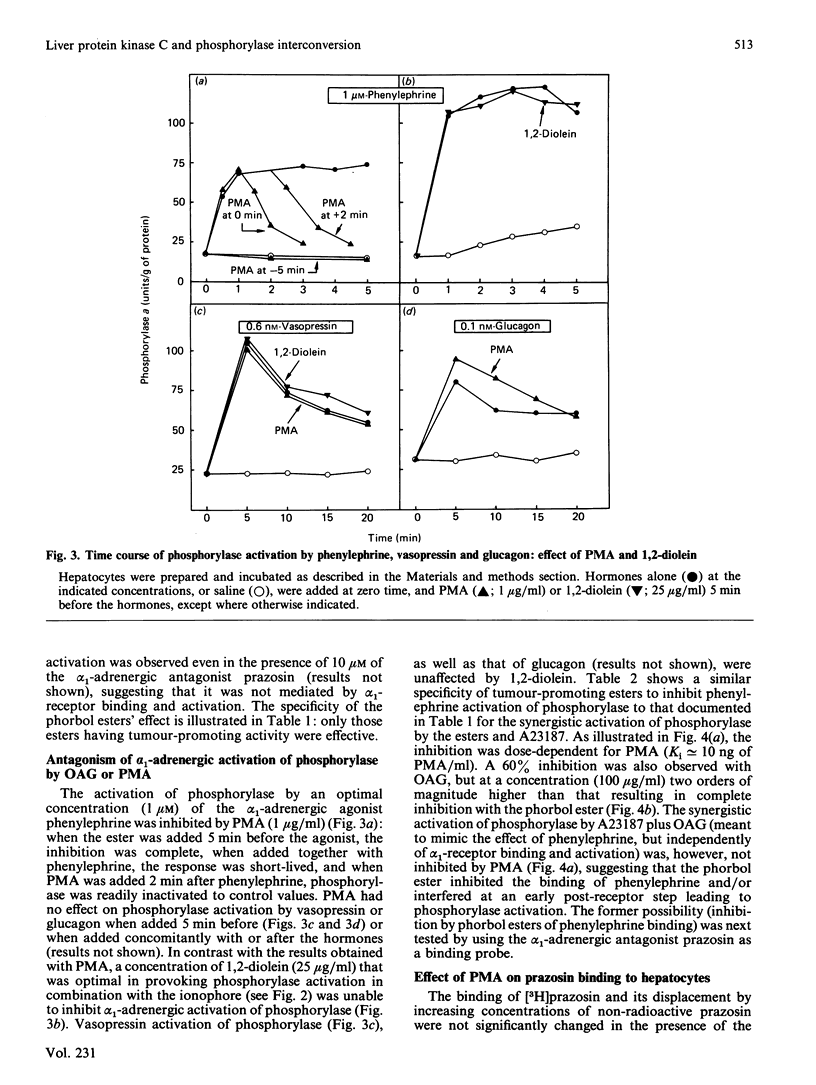
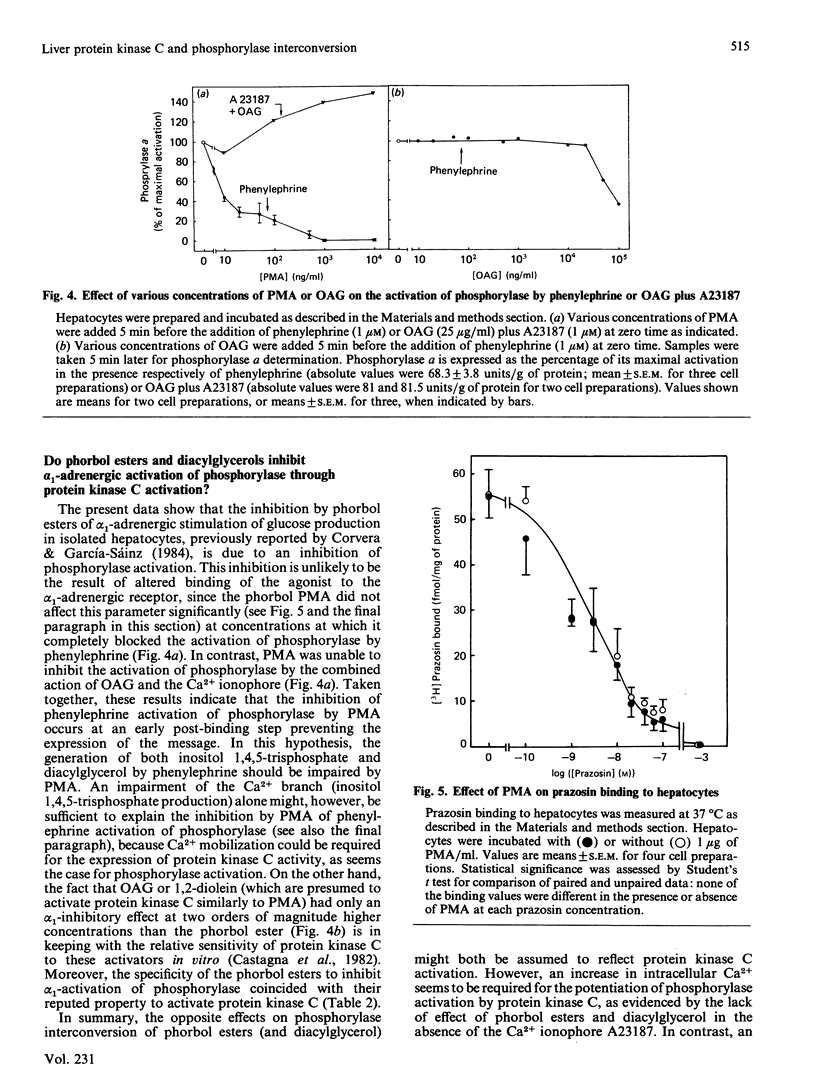
In isolated rat hepatocytes: phosphorylase activation by the ionophore A23187 was enhanced in the presence of tumour-promoting phorbol esters and 1,2- (but not 1,3-) diacylglycerols (dioleoyl- and oleoylacetyl-glycerol), with a similar dose-dependency; the activation of phosphorylase by phenylephrine (1 microM) (but not by vasopressin or glucagon) was inhibited both by tumour-promoting phorbol esters and diacylglycerols, but with a different dose-dependency: complete inhibition was achieved with concentrations of phorbol esters two orders of magnitude lower than those of diacylglycerol; binding of the alpha 1-adrenergic antagonist [3H]prazosin and its displacement by unlabelled prazosin was not significantly affected in the presence of the phorbol esters. The possible involvement of protein kinase C in the control of phosphorylase interconversion is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assimacopoulos-Jeannet F. D., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Studies on alpha-adrenergic activation of hepatic glucose output. Studies on role of calcium in alpha-adrenergic activation of phosphorylase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2662–2669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Godfrey P. P., McKinney J. S., Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F., Putney J. W., Jr The second messenger linking receptor activation to internal Ca release in liver. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):63–66. doi: 10.1038/309063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrisman T. D., Jordan J. E., Exton J. H. Purification of rat liver phosphorylase kinase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10798–10804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. H., Coll K. E., Williamson J. R. Differential effects of phorbol ester on phenylephrine and vasopressin-induced Ca2+ mobilization in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3281–3288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvera S., García-Sáinz J. A. Phorbol esters inhibit alpha 1 adrenergic stimulation of glycogenolysis in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Mar 30;119(3):1128–1133. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90892-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couturier A., Bazgar S., Castagna M. Further characterization of tumor-promoter-mediated activation of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jun 15;121(2):448–455. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90203-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defreyn G., Goris J., Merlevede W. A deinhibitor protein neutralizing the effect of the protein inhibitors on dog liver phosphorylase phosphatase. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 1;79(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80365-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doorneweerd D. D., Tan A. W., Nuttall F. Q. Liver phosphorylase kinase: characterization of two interconvertible forms and partial purification of phosphorylase kinase a. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Aug 20;47(1):45–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00241565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N., Li S. Y., Litosch I., Wallace M. Synergistic activation of rat hepatocyte glycogen phosphorylase by A23187 and phorbol ester. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 29;119(1):88–94. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91622-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrison J. C., Johnsen D. E., Campanile C. P. Evidence for the role of phosphorylase kinase, protein kinase C, and other Ca2+-sensitive protein kinases in the response of hepatocytes to angiotensin II and vasopressin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3283–3292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodhardt M., Ferry N., Aggerbeck M., Hanoune J. The hepatic alpha 1-adrenergic receptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Mar 15;33(6):863–868. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90439-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goris J., Parker P. J., Waelkens E., Merlevede W. The deinhibitor protein: regulation by phosphorylation-dephosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Apr 30;120(2):405–410. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91268-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hems D. A., Whitton P. D. Control of hepatic glycogenolysis. Physiol Rev. 1980 Jan;60(1):1–50. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Thomas A. P., Williams R. J., Irvine R. F., Williamson J. R. myo-Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. A second messenger for the hormonal mobilization of intracellular Ca2+ in liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3077–3081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppens S., Vandenheede J. R., De Wulf H. On the role of calcium as second messenger in liver for the hormonally induced activation of glycogen phosphorylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Feb 28;496(2):448–457. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90327-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoo J. C., Steinberg D. Stimulation of rat liver phosphorylase kinase by micromolar concentrations of Ca2+. FEBS Lett. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):68–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80154-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Kaibuchi K., Castagna M., Yamanishi J., Sano K., Tanaka Y., Miyake R., Takai Y., Nishizuka Y. Protein phosphorylation and mechanism of action of tumor-promoting phorbol esters. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;17:437–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Nagasaki K., Adachi I., Yamaguchi K., Fujiki H., Abe K. Stimulation of hepatic glycogenolysis by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) via a calcium requiring process. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):1057–1064. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91198-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A., Freychet P. Neutral amino acid transport. Characterization of the A and L systems in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):148–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch C. J., Charest R., Bocckino S. B., Exton J. H., Blackmore P. F. Inhibition of hepatic alpha 1-adrenergic effects and binding by phorbol myristate acetate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2844–2851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon S. O., Palfrey H. C., King A. C. Phorbol esters potentiate tyrosine phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptors in A431 membranes by a calcium-independent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2298–2302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pointer R. H., Butcher F. R., Fain J. N. Studies on the role of cyclic guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate and extracellular Ca2+ in the regulation of glycogenolysis in rat liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 25;251(10):2987–2992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. R., Young N. The stereospecific activation of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):818–823. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach P. J., Goldman M. Modification of glycogen synthase activity in isolated rat hepatocytes by tumor-promoting phorbol esters: evidence for differential regulation of glycogen synthase and phosphorylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7170–7172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai K., Matsumura S., Okimura Y., Yamamura H., Nishizuka Y. Liver glycogen phosphorylase kinase. Partial purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6631–6637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimazu T., Amakawa A. Regulation of glycogen metabolism in liver by the autonomic nervous system. VI. Possible mechanism of phosphorylase activation by the splanchnic nerve. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 7;385(2):242–256. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90352-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalmans W., De Wulf H., Hue L., Hers H. G. The sequential inactivation of glycogen phosphorylase and activation of glycogen synthetase in liver after the administration of glucose to mice and rats. The mechanism of the hepatic threshold to glucose. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jan 3;41(1):127–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalmans W., Hers H. G. The stimulation of liver phosphorylase b by AMP, fluoride and sulfate. A technical note on the specific determination of the a and b forms of liver glycogen phosphorylase. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):341–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs M., Kirk C. J., Hems D. A. Role of extracellular calcium in the action of vasopressin on hepatic glycogenolysis. FEBS Lett. 1976 Oct 15;69(1):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80686-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenheede J. R., Keppens S., De Wulf H. Inactivation and reactivation of liver phosphorylase b kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Apr 12;481(2):463–470. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90279-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Werve G., Hue L., Hers H. G. Hormonal and ionic control of the glycogenolytic cascade in rat liver. Biochem J. 1977 Jan 15;162(1):135–142. doi: 10.1042/bj1620135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Werve G., Proietto J., Jeanrenaud B. Tumour-promoting phorbol esters increase basal and inhibit insulin-stimulated lipogenesis in rat adipocytes without decreasing insulin binding. Biochem J. 1985 Jan 15;225(2):523–527. doi: 10.1042/bj2250523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


