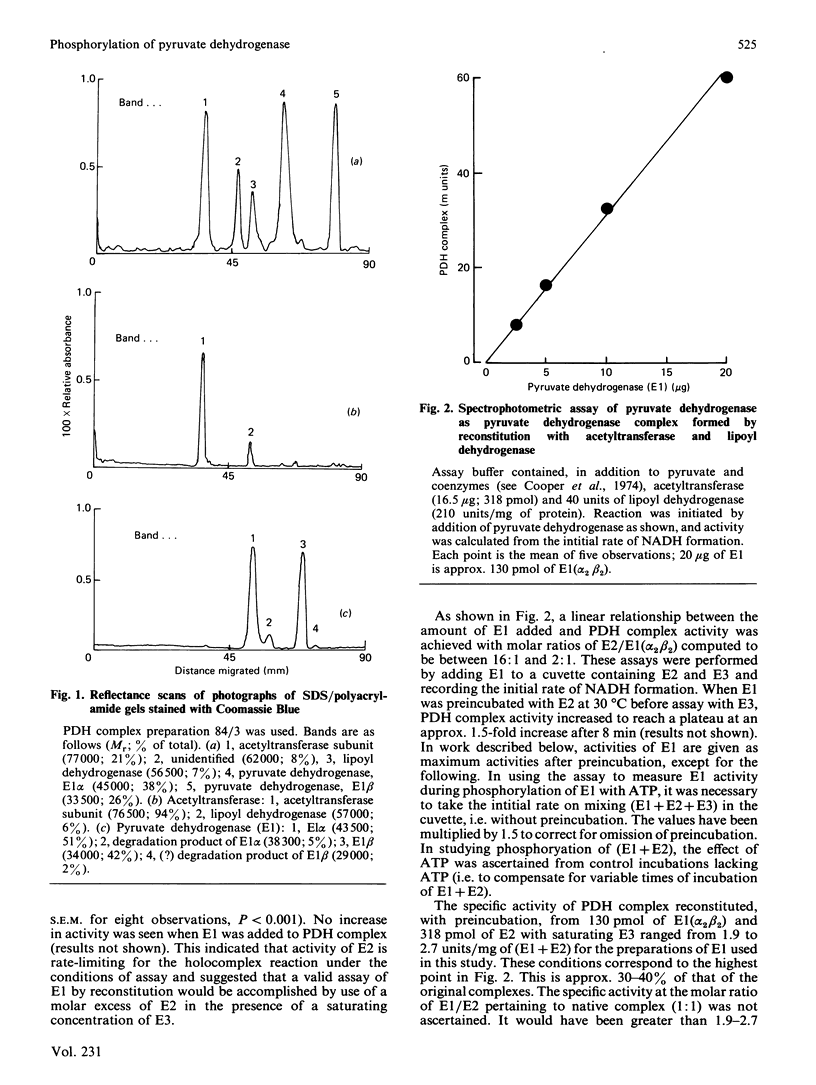
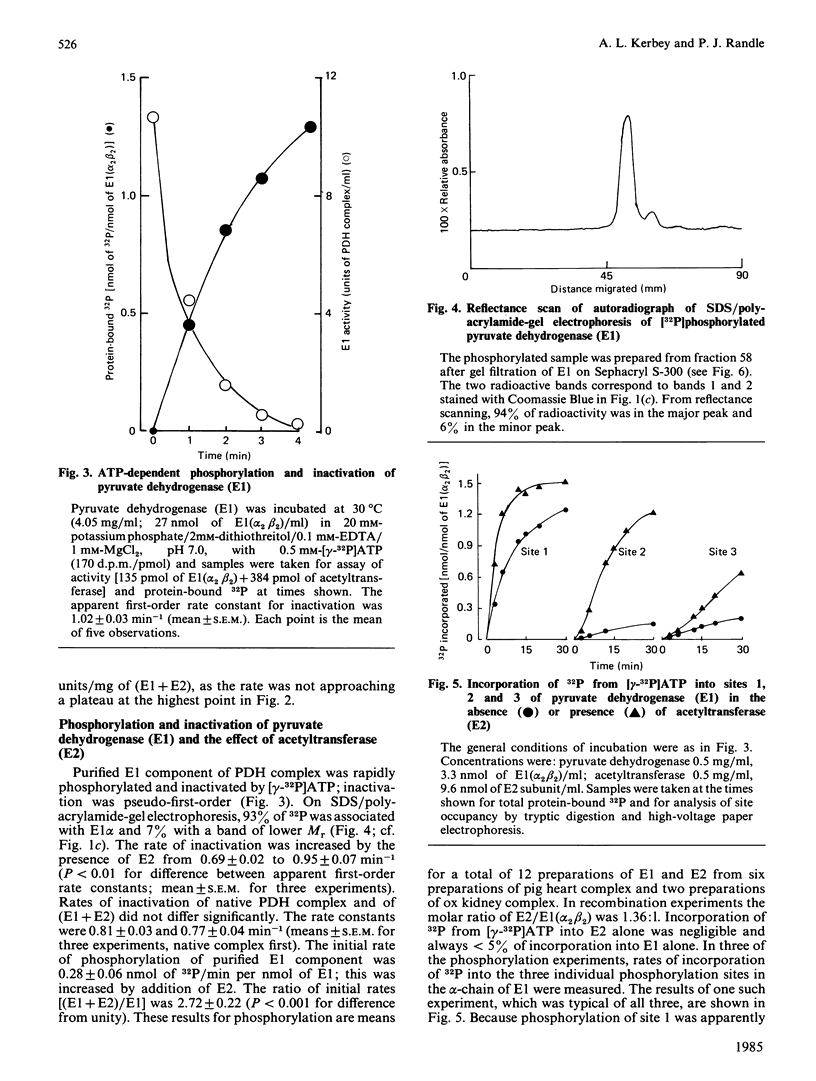
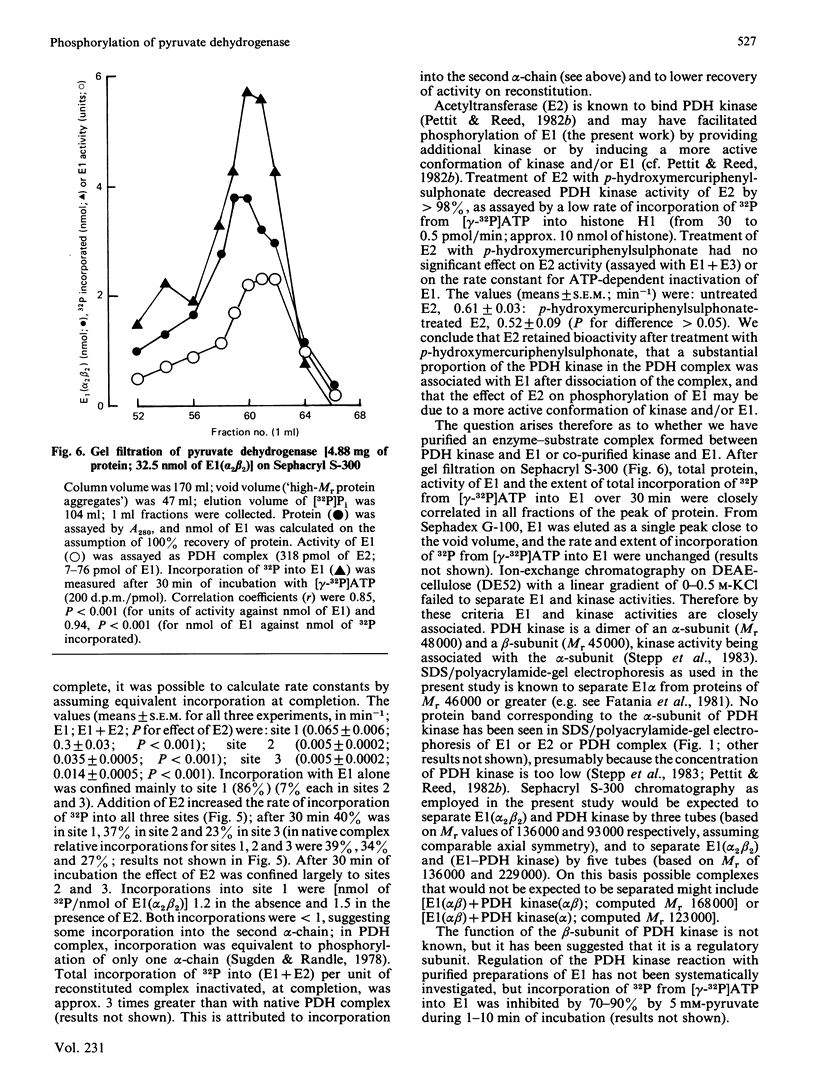
Abstract
The pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1) and acetyltransferase (E2) components of pig heart and ox kidney pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex were separated and purified. The E1 component was phosphorylated (alpha-chain) and inactivated by MgATP. Phosphorylation was mainly confined to site 1. Addition of E2 accelerated phosphorylation of all three sites in E1 alpha and inactivation of E1. On the basis of histone H1 phosphorylation, E2 is presumed to contain PDH kinase, which was removed (greater than 98%) by treatment with p-hydroxymercuriphenylsulphonate. Stimulation of ATP-dependent inactivation of E1 by E2 was independent of histone H1 kinase activity of E2. The effect of E2 is attributed to conformational change(s) induced in E1 and/or E1-associated PDH kinase. PDH kinase activity associated with E1 could not be separated from it be gel filtration or DEAE-cellulose chromatography. Subunits of PDH kinase were not detected on sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide gels of E1 or E2, presumably because of low concentration. The activity of pig heart PDH complex was increased by E2, but not by E1, indicating that E2 is rate-limiting in the holocomplex reaction. ATP-dependent inactivation of PDH complex was accelerated by E1 or by phosphorylated E1 plus associated PDH kinase, but not by E2 plus presumed PDH kinase. It is suggested that a substantial proportion of PDH kinase may accompany E1 when PDH complex is dissociated into its component enzymes. The possibility that E1 may possess intrinsic PDH kinase activity is considered unlikely, but may not have been fully excluded.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxter M. A., Coore H. G. The mode of regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase of lactating rat mammary gland. Effects of starvation and insulin. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 15;174(2):553–561. doi: 10.1042/bj1740553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cate R. L., Roche T. E., Davis L. C. Rapid intersite transfer of acetyl groups and movement of pyruvate dehydrogenase component in the kidney pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7556–7562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. H., Randle P. J., Denton R. M. Regulation of heart muscle pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase. Biochem J. 1974 Dec;143(3):625–641. doi: 10.1042/bj1430625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marcucci O. L., Hunter A., Lindsay J. G. Low immunogenicity of the common lipoamide dehydrogenase subunit (E3) of mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase and 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 1;226(2):509–517. doi: 10.1042/bj2260509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fatania H. R., Lau K. S., Randle P. J. Inactivation of purified ox kidney branched-chain 2-oxoacid dehydrogenase complex by phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 1981 Sep 28;132(2):285–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutson N. J., Randle P. J. Enhanced activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase in rat heart mitochondria in alloxan-diabetes or starvation. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 1;92(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80724-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbey A. L., Radcliffe P. M., Randle P. J., Sugden P. H. Regulation of kinase reactions in pig heart pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 1;181(2):427–433. doi: 10.1042/bj1810427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbey A. L., Randle P. J. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase/activator in rat heart mitochondria, Assay, effect of starvation, and effect of protein-synthesis inhibitors of starvation. Biochem J. 1982 Jul 15;206(1):103–111. doi: 10.1042/bj2060103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbey A. L., Randle P. J. Thermolabile factor accelerates pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase reaction in heart mitochondria of starved or alloxan-diabetic rats. FEBS Lett. 1981 May 18;127(2):188–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80201-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbey A. L., Richardson L. J., Randle P. J. The roles of intrinsic kinase and of kinase/activator protein in the enhanced phosphorylation of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in starvation. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 15;176(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80923-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau K. S., Fatania H. R., Randle P. J. Inactivation of rat liver and kidney branched chain 2-oxoacid dehydrogenase complex by adenosine triphosphate. FEBS Lett. 1981 Apr 6;126(1):66–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. C., Pelley J. W., Pettit F. H., Hucho F., Randall D. D., Reed L. J. -Keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. XV. Purification and properties of the component enzymes of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes from bovine kidney and heart. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Feb;148(2):327–342. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90151-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. C., Pettit F. H., Reed L. J. Alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. X. Regulation of the activity of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from beef kidney mitochondria by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jan;62(1):234–241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.1.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettit F. H., Reed L. J. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from bovine kidney and heart. Methods Enzymol. 1982;89(Pt 500):376–386. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)89067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettit F. H., Yeaman S. J., Reed L. J. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase from bovine kidney. Methods Enzymol. 1982;90(Pt E):195–200. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)90126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt M. L., Roche T. E., Dyer D. W., Cate R. L. Enhanced dissociation of pyruvate dehydrogenase from the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex following phosphorylation and regulatory implications. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Nov 14;91(1):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90616-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed L. J. Regulation of mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase complex by a phosphorylation-dephosphorylation cycle. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1981;18:95–106. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152818-8.50012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley C. J., Perham R. N. Purification of 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes from ox heart by a new method. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 1;191(1):147–154. doi: 10.1042/bj1910147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stepp L. R., Pettit F. H., Yeaman S. J., Reed L. J. Purification and properties of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase from bovine kidney. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9454–9458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden P. H., Randle P. J. Regulation of pig heart pyruvate dehydrogenase by phosphorylation. Studies on the subunit and phosphorylation stoicheiometries. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 1;173(2):659–668. doi: 10.1042/bj1730659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teague W. M., Pettit F. H., Wu T. L., Silberman S. R., Reed L. J. Purification and properties of pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase from bovine heart and kidney. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5585–5592. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


