Abstract
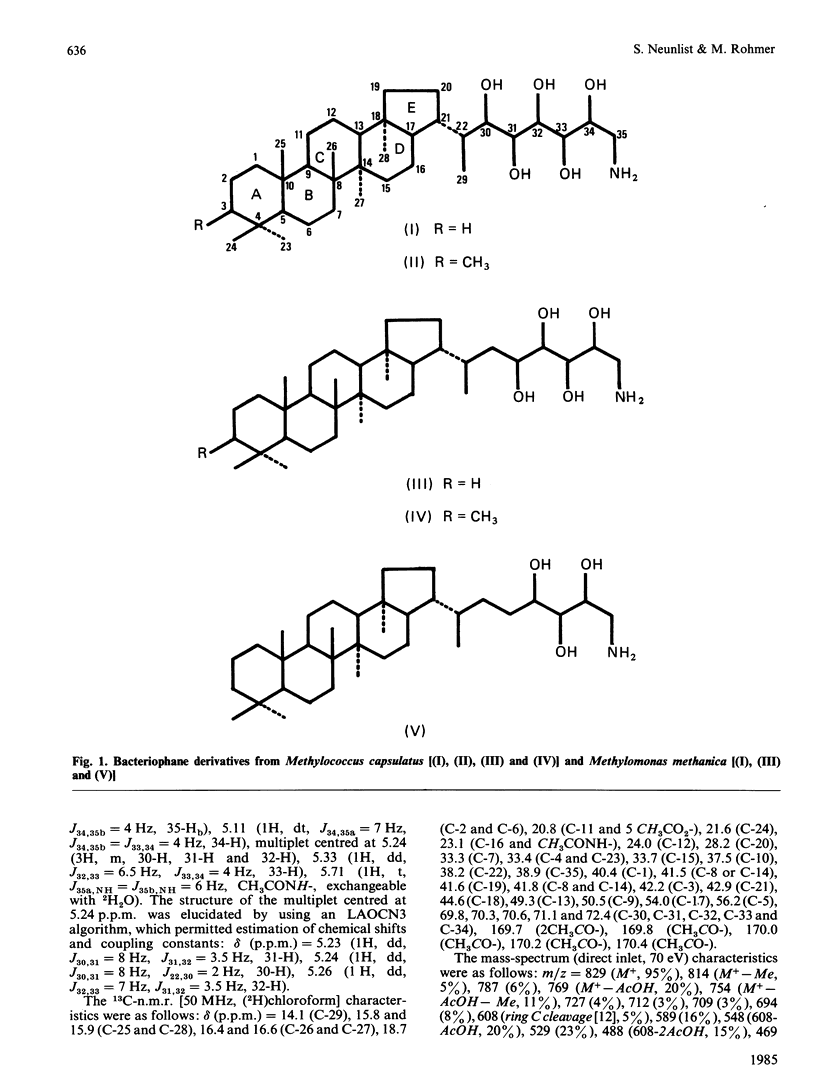
The major hopanoid of the methylotrophic bacteria Methylococcus capsulatus and Methylomonas methanica was identified by spectroscopic methods as (22S)-35-aminobacteriohopane-30,31,32,33,34-pentol. Minor companions were, in both bacteria, 35-aminobacteriohopane-31,32,33,34-tetrol and in Methylomonas methanica, 35-aminobacteriohopane-32,33,34-triol. In Methylococcus capsulatus the aminopentol and the aminotetrol were accompanied by their homologues possessing an extra methyl group at C-3. Bacterial hopanoids with a functionalized C-30 carbon atom such as these two new aminopentols are possible precursors of widespread C29 hopanoid chemical fossils.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benz R., Hallmann D., Poralla K., Eibl H. Interaction of hopanoids with phosphatidylcholines containing oleic and omega-cyclohexyldodecanoic acid in lipid bilayer membranes. Chem Phys Lipids. 1983 Dec;34(1):7–24. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(83)90056-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird C. W., Lynch J. M., Pirt F. J., Reid W. W. Steroids and squalene in Methylococcus capsulatus grown on methane. Nature. 1971 Apr 16;230(5294):473–474. doi: 10.1038/230473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisseret P., Wolff G., Albrecht A. M., Tanaka T., Nakatani Y., Ourisson G. A direct study of the cohesion of lecithin bilayers: the effect of hopanoids and alpha, omega-dihydroxycarotenoids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 14;110(1):320–324. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91298-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier P., Rohmer M., Benveniste P., Ourisson G. Delta8(14)-steroids in the bacterium Methylococcus capsulatus. Biochem J. 1976 Nov;159(2):267–271. doi: 10.1042/bj1590267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langworthy T. A., Mayberry W. R., Smith P. F. A sulfonolipid and novel glucosamidyl glycolipids from the extreme thermoacidophile Bacillus acidocaldarius. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 22;431(3):550–569. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90220-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neunlist S., Holst O., Rohmer M. Prokaryotic triterpenoids. The hopanoids of the purple non-sulphur bacterium Rhodomicrobium vannielii: an aminotriol and its aminoacyl derivatives, N-tryptophanyl and N-ornithinyl aminotriol. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 15;147(3):561–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neunlist S., Rohmer M. A novel hopanoid, 30-(5'-adenosyl)hopane, from the purple non-sulphur bacterium Rhodopseudomonas acidophila, with possible DNA interactions. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 15;228(3):769–771. doi: 10.1042/bj2280769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poralla K., Kannenberg E., Blume A. A glycolipid containing hopane isolated from the acidophilic, thermophilic Bacillus acidocaldarius, has a cholesterol-like function in membranes. FEBS Lett. 1980 Apr 21;113(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80506-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohmer M., Bouvier P., Ourisson G. Molecular evolution of biomembranes: structural equivalents and phylogenetic precursors of sterols. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):847–851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohmer M., Bouvier P., Ourisson G. Non-specific lanosterol and hopanoid biosynthesis be a cell-free system from the bacterium Methylococcus capsulatus. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Dec;112(3):557–560. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zundel M., Rohmer M. Prokaryotic triterpenoids. 1. 3 beta-Methylhopanoids from Acetobacter species and Methylococcus capsulatus. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jul 1;150(1):23–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


