Abstract
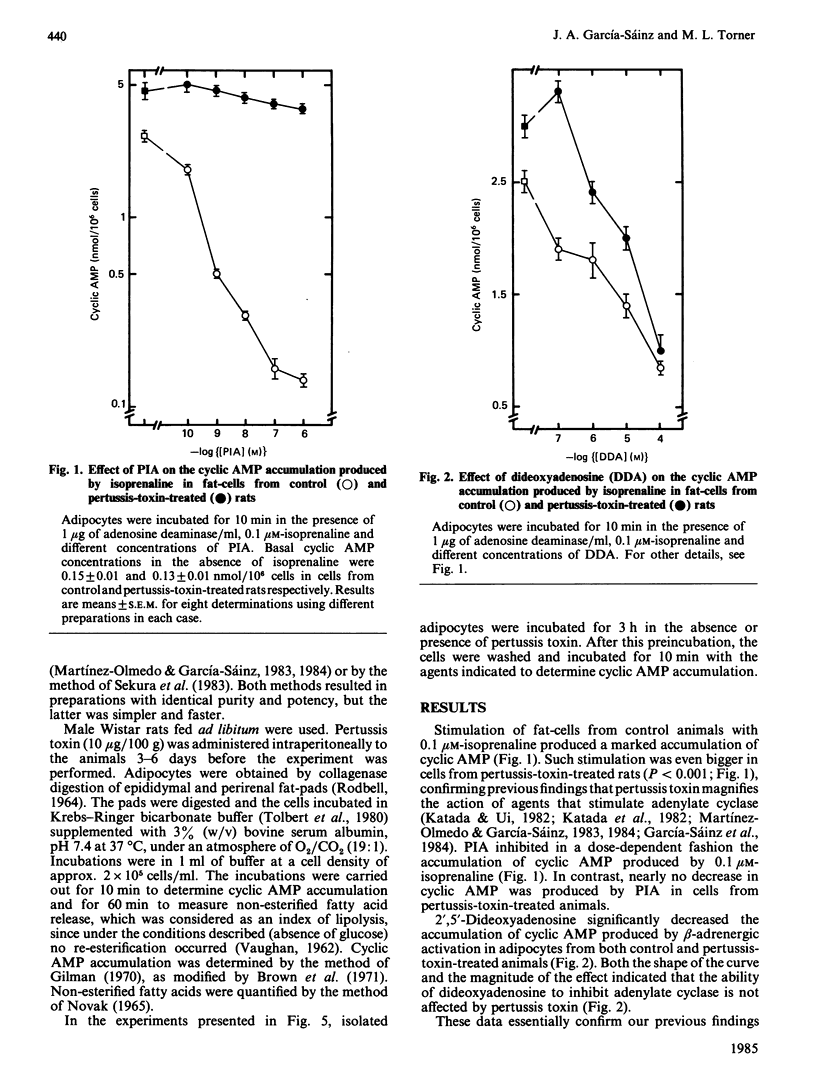
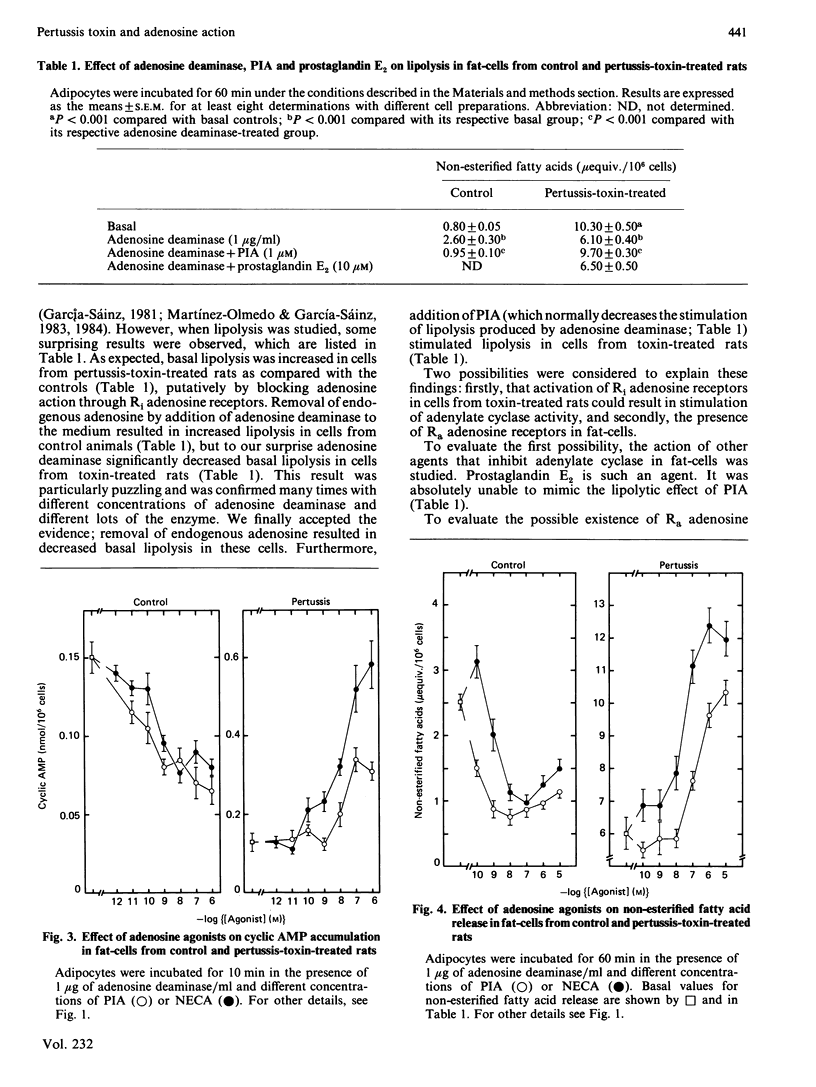
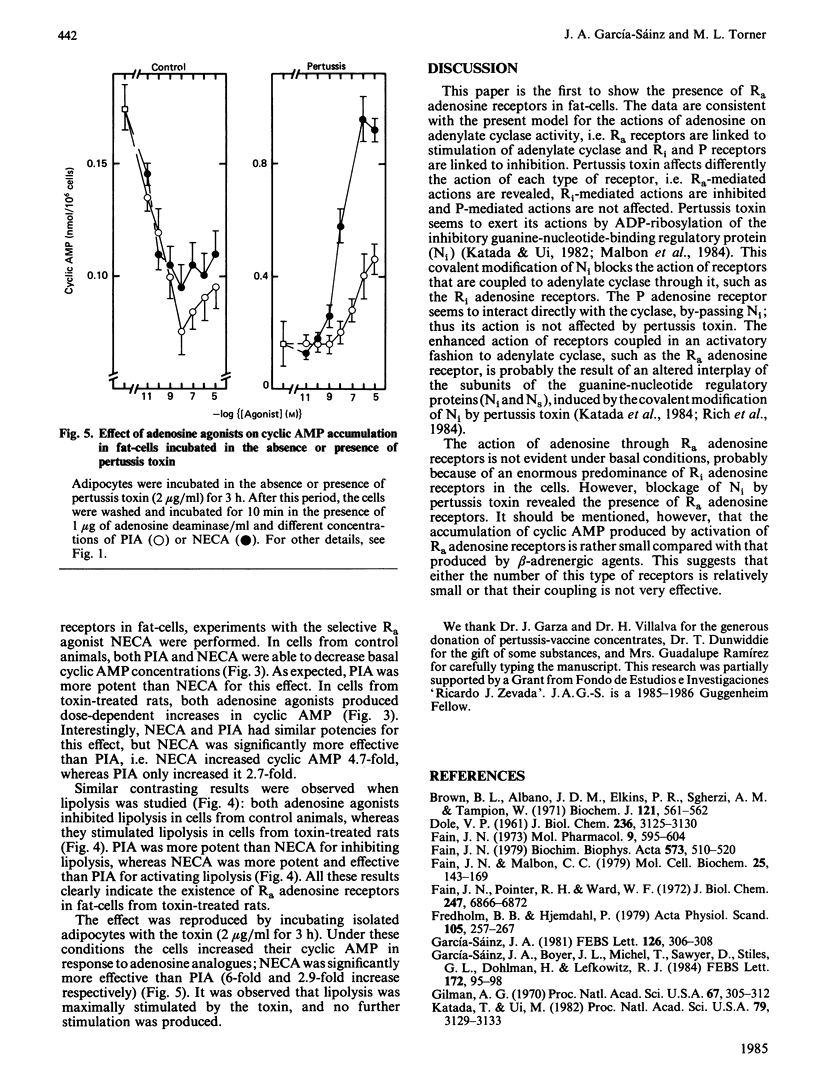
Activation of rat adipocyte R1 adenosine receptors by phenylisopropyladenosine (PIA) decreased cyclic AMP and lipolysis; this effect was blocked in cells from pertussis-toxin-treated rats. In contrast, the ability of 2',5'-dideoxyadenosine to decrease cyclic AMP was not affected by pertussis-toxin treatment. Addition of adenosine deaminase to the medium in which adipocytes from control animals were incubated resulted in activation of lipolysis. Interestingly, adipocytes from toxin-treated rats (which had an already increased basal lipolysis) responded in an opposite fashion to the addition of adenosine deaminase, i.e. the enzyme decreased lipolysis, which suggested that adenosine might be increasing lipolysis in these cells. Studies with the selective agonists N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (NECA) and PIA indicated that adenosine increases lipolysis and cyclic AMP accumulation in these cells and that these actions are mediated through Ra adenosine receptors. Adenosine-mediated accumulation of cyclic AMP was also observed in cells preincubated with pertussis toxin (2 micrograms/ml) for 3 h. In these studies NECA was also more effective than PIA. Our results indicate that there are three types of adenosine receptors in fat-cells, whose actions are affected differently by pertussis toxin, i.e. Ri-mediated actions are abolished, Ra-mediated actions are revealed and P-mediated actions are not affected.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown B. L., Albano J. D., Ekins R. P., Sgherzi A. M. A simple and sensitive saturation assay method for the measurement of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(3):561–562. doi: 10.1042/bj1210561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P. Effect of nucleic acid metabolites on lipolysis in adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1961 Dec;236:3125–3130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N. Effect of lipolytic agents on adenosine and AMP formation by fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 21;573(3):510–520. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90225-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N. Inhibition of adenosine cyclic 3', 5'-monophosphate accumulation in fat cells by adenosine, N6-(phenylisopropyl) adenosine, and related compounds. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 Sep;9(5):595–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N., Malbon C. C. Regulation of adenylate cyclase by adenosine. Mol Cell Biochem. 1979 Jun 15;25(3):143–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00235364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N., Pointer R. H., Ward W. F. Effects of adenosine nucleosides on adenylate cyclase, phosphodiesterase, cyclic adenosine monophosphate accumulation, and lipolysis in fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6866–6872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Hjemdahl P. Uptake and release of adenosine in isolated rat fat cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1979 Mar;105(3):257–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1979.tb06340.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Sáinz J. A., Boyer J. L., Michel T., Sawyer D., Stiles G. L., Dohlman H., Lefkowitz R. J. Effect of pertussis toxin on alpha 2-adrenoceptors: decreased formation of the high-affinity state for agonists. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jun 25;172(1):95–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80881-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Sáinz J. A. Decreased sensitivity to alpha 2 adrenergic amines, adenosine and prostaglandins in white fat cells from hamsters treated with pertussis vaccine. FEBS Lett. 1981 Apr 20;126(2):306–308. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Amano T., Ui M. Modulation by islet-activating protein of adenylate cyclase activity in C6 glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3739–3746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Bokoch G. M., Smigel M. D., Ui M., Gilman A. G. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Subunit dissociation and the inhibition of adenylate cyclase in S49 lymphoma cyc- and wild type membranes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3586–3595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londos C., Cooper D. M., Schlegel W., Rodbell M. Adenosine analogs inhibit adipocyte adenylate cyclase by a GTP-dependent process: basis for actions of adenosine and methylxanthines on cyclic AMP production and lipolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5362–5366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londos C., Cooper D. M., Wolff J. Subclasses of external adenosine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2551–2554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londos C., Wolff J. Two distinct adenosine-sensitive sites on adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5482–5486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon C. C., Rapiejko P. J., Garciá-Sáinz J. A. Pertussis toxin catalyzes the ADP-ribosylation of two distinct peptides, 40 and 41 kDa, in rat fat cell membranes. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 29;176(2):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81184-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Olmedo M. A., García-Sáinz J. A. Direct action of pertussis toxin in isolated hamster fat cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Mar 16;99(1):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90441-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Olmedo M. A., García-Sáinz J. A. Effect of pertussis toxin on the hormonal regulation of cyclic AMP levels in hamster fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Oct 18;760(2):215–220. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90166-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVAK M. COLORIMETRIC ULTRAMICRO METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF FREE FATTY ACIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:431–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich K. A., Codina J., Floyd G., Sekura R., Hildebrandt J. D., Iyengar R. Glucagon-induced heterologous desensitization of the MDCK cell adenylyl cyclase. Increases in the apparent levels of the inhibitory regulator (Ni). J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7893–7901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe U., Ebert R., Erbler H. C. Adenosine release from fat cells: effect on cyclic AMP levels and hormone actions. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;5:569–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe U., Ebert R., Erbler H. C. Adenosine release from isolated fat cells and its significance for the effects of hormones on cyclic 3',5'-AMP levels and lipolysis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1973;276(2):133–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00501186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe U., Ebert R. Stimulation of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate accumulation and lipolysis in fat cells by adenosine deaminase. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1974;282(1):33–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00647401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekura R. D., Fish F., Manclark C. R., Meade B., Zhang Y. L. Pertussis toxin. Affinity purification of a new ADP-ribosyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14647–14651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolbert M. E., White A. C., Aspry K., Cutts J., Fain J. N. Stimulation by vasopressin and alpha-catecholamines of phosphatidylinositol formation in isolated rat liver parenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1938–1944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turpin B. P., Duckworth W. C., Solomon S. S. Perifusion of isolated rat adipose cells. Modulation of lipolysis by adenosine. J Clin Invest. 1977 Aug;60(2):442–448. doi: 10.1172/JCI108794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAUGHAN M. The production and release of glycerol by adipose tissue incubated in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1962 Nov;237:3354–3358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


