Abstract
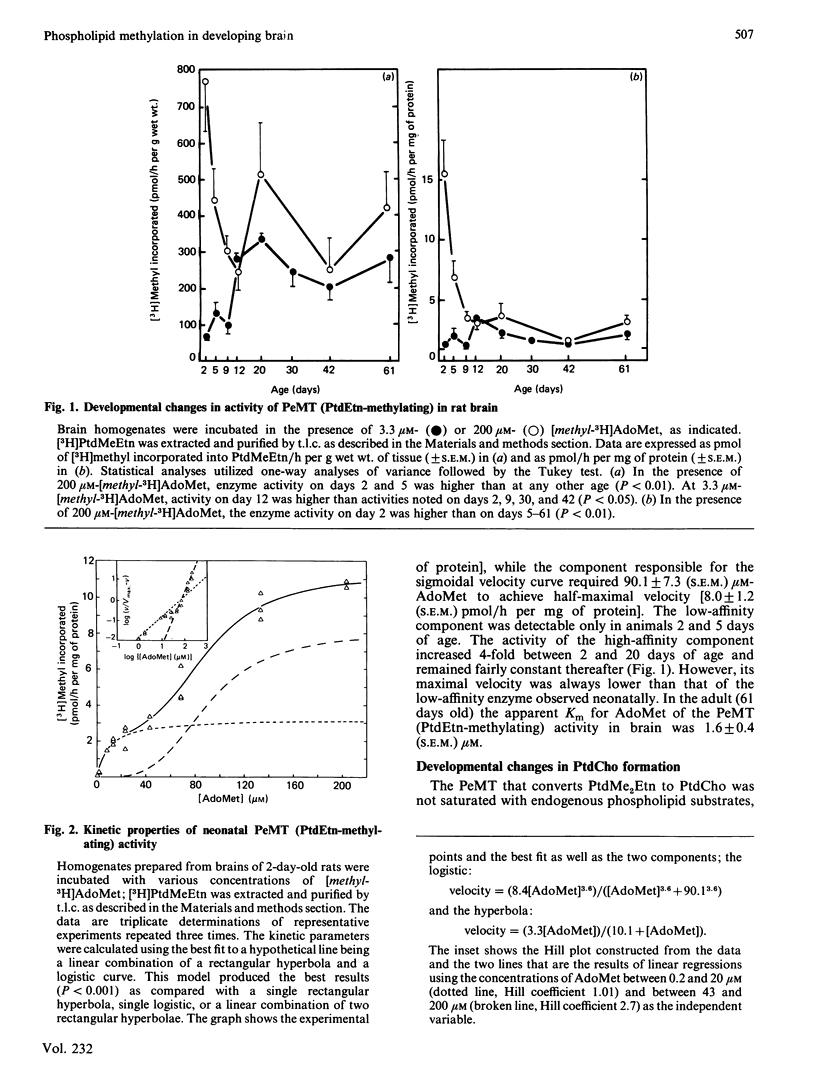
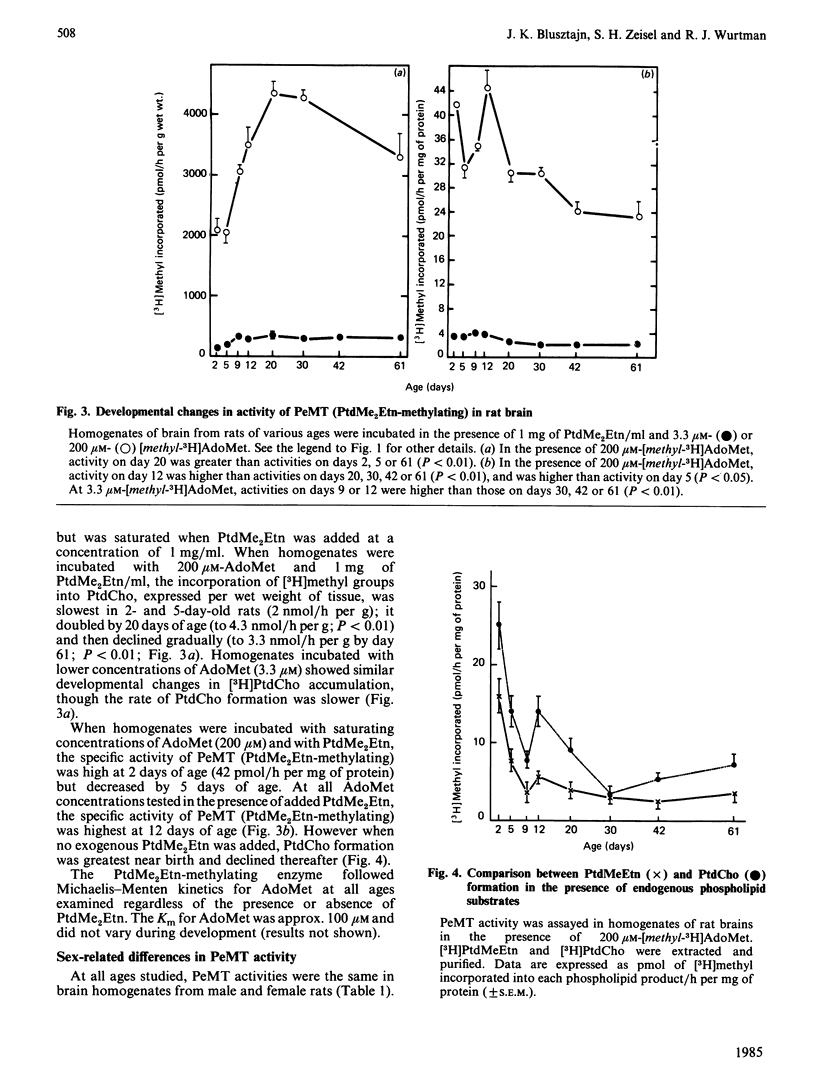
The activity of phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PeMT), an enzymic system that catalyses the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho) via sequential methylation of phosphatidylethanolamine (PtdEtn) using S-adenosylmethionine (AdoMet) as a methyl donor, was examined in brain homogenates from rats of various ages. The data thus obtained were consistent with the existence of two distinct enzyme activities within this enzyme system, i.e. one catalysing the methylation of PtdEtn [to form phosphatidyl-N-monomethylethanolamine (PtdMeEtn)], and the other catalysing the methylations of PtdMeEtn and phosphatidyl-NN-dimethylethanolamine (PtdMe2Etn) (to form PtdMe2Etn and PtdCho, respectively). PeMT (PtdEtn-methylating) activity per g of brain was 4-fold higher in neonatal than in adult brains. The enzyme activity in adult brains exhibited Michaelis-Menten kinetics for AdoMet, and its affinity for AdoMet was high (apparent Km 1.6 microM). In neonatal brain the relationships between AdoMet concentrations and PtdMeEtn formation were more complex: a sigmoidal component (with a Hill coefficient of 2.7), requiring 90 microM-AdoMet for half-saturation predominated over the high-affinity component (similar to that of the adult brain). PeMT (PtdMe2Etn-methylating) activity per g of brain increased 2-fold between the 5th and the 20th postnatal days and remained constant thereafter; it was higher than that of PeMT (PtdEtn-methylating) activity at all ages studied, and its affinity for AdoMet was low (apparent Km 99 microM). No sexual dimorphism in brain PeMT activity was observed at any age. We conclude that PeMT (PtdEtn-methylating) catalyses the rate-limiting step in PtdCho synthesis in rat brain, and that PtdCho formation via this pathway may be greatest during the neonatal period.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aeberhard E., Grippo J., Menkes J. H. Fatty acid synthesis in the developing brain. Pediatr Res. 1969 Nov;3(6):590–596. doi: 10.1203/00006450-196911000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audubert F., Vance D. E. Pitfalls and problems in studies on the methylation of phosphatidylethanolamine. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10695–10701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blusztajn J. K., Wurtman R. J. Choline biosynthesis by a preparation enriched in synaptosomes from rat brain. Nature. 1981 Apr 2;290(5805):417–418. doi: 10.1038/290417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blusztajn J. K., Zeisel S. H., Wurtman R. J. Synthesis of lecithin (phosphatidylcholine) from phosphatidylethanolamine in bovine brain. Brain Res. 1979 Dec 28;179(2):319–327. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chida N., Arakawa T. Metabolism of phosphatidylcholine in brain and liver of developing rats. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1971 Aug;104(4):359–371. doi: 10.1620/tjem.104.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews F. T., Calderini G., Battistella A., Toffano G. Age dependent changes in the methylation of rat brain phospholipids. Brain Res. 1981 Dec 14;229(1):256–259. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90767-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews F. T., Hirata F., Axelrod J. Identification and properties of methyltransferases that synthesize phosphatidylcholine in rat brain synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1980 Jun;34(6):1491–1498. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb11229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dainous F., Freysz L., Mozzi R., Dreyfus H., Louis J. C., Porcellati G., Massarelli R. Synthesis of choline phospholipids in neuronal and glial cell cultures by the methylation pathway. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 6;146(1):221–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80740-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonatas N. K., Autilio-Gambetti L., Gambetti P., Shafer B. Morphological and biochemical changes in rat synaptosome fractions during neonatal development. J Cell Biol. 1971 Nov;51(21):484–498. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.2.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins J. A. Biogenesis of endoplasmic reticulum phosphatidylcholine. Translocation of intermediates across the membrane bilayer during methylation of phosphatidylethanolamine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jan 8;640(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90527-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Axelrod J. Enzymatic synthesis and rapid translocation of phosphatidylcholine by two methyltransferases in erythrocyte membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2348–2352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Axelrod J. Phospholipid methylation and biological signal transmission. Science. 1980 Sep 5;209(4461):1082–1090. doi: 10.1126/science.6157192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Viveros O. H., Diliberto E. J., Jr, Axelrod J. Identification and properties of two methyltransferases in conversion of phosphatidylethanolamine to phosphatidylcholine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1718–1721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitzemann R. Developmental regulation of phospholipid methylation in rat brain synaptosomes. Life Sci. 1982 Apr 12;30(15):1297–1303. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90692-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotchkiss A., Jordan J. V., Hirata F., Shulman N. R., Axelrod J. Phospholipid methylation and human platelet function. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Aug 1;30(15):2089–2095. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90227-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. G., Revell E. The postnatal development of the synapse: a morphological approach utilizing synaptosomes. I. General features. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1970;111(2):179–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00339784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. P., Rios A., Nicholas H. J., Ramsey R. B. The biosynthesis of cholesterol and other sterols by brain tissue: distribution in subcellular fractions as a function of time after injection of (2-14C) mevalonic acid, sodium (2-14C)acetate and (U-14C) glucose into 15-day old rats. J Neurochem. 1975 Jan;24(1):117–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb07636.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanerva L., Tissari A. H., Suurhasko B. V., Hervonen A. Ultrastructural characterization of synaptosomes from neonatal and adult rats with special reference to monoamines. J Comp Neurol. 1977 Aug 15;174(4):631–658. doi: 10.1002/cne.901740406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leprohon C. E., Blusztajn J. K., Wurtman R. J. Dopamine stimulation of phosphatidylcholine (lecithin) biosynthesis in rat brain neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):2063–2066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.2063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGivney A., Crews F. T., Hirata F., Axelrod J., Siraganian R. P. Rat basophilic leukemia cell lines defective in phospholipid methyltransferase enzymes, Ca2+ influx, and histamine release: reconstitution by hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6176–6180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G. M., Ho W. The in vivo and in vitro synthesis of sulphatides during development. J Neurochem. 1967 Jul;14(7):717–724. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb10305.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., Johannsson A., Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Metcalfe J. C. Calcium signals and phospholipid methylation in eukaryotic cells. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 1;221(3):675–684. doi: 10.1042/bj2210675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percy A. K., Moore J. F., Waechter C. J. Properties of particulate and detergent-solubilized phospholipid N-methyltransferase activity from calf brain. J Neurochem. 1982 May;38(5):1404–1412. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb07919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REHBINDER D., GREENBERG D. M. STUDIES ON THE METHYLATION OF ETHANOLAMINE PHOSPHATIDES BY LIVER PREPARATIONS. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Jan;109:110–115. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90294-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randon J., Lecompte T., Chignard M., Siess W., Marlas G., Dray F., Vargaftig B. B. Dissociation of platelet activation from transmethylation of their membrane phospholipids. Nature. 1981 Oct 22;293(5834):660–662. doi: 10.1038/293660a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry B. V., Statham C. N., Axelrod J., Hirata F. Evidence for two methyltransferase involved in the conversion of phosphatidylethanolamine to phosphatidylcholine in the rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Oct 15;211(2):762–773. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90513-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schanche J. S., Ogreid D., Døskeland S. O., Refsnes M., Sand T. E., Ueland P. M., Christoffersen T. Evidence against a requirement for phospholipid methylation in adenylate cyclase activation by hormones. Methyltransferase inhibitors do not impair cyclic AMP accumulation induced by glucagon or beta-adrenergic agents in rat hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1982 Feb 22;138(2):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80433-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacconi M., Wurtman R. J. Phosphatidylcholine produced in rat synaptosomes by N-methylation is enriched in polyunsaturated fatty acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4828–4831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells M. A., Dittmer J. C. A comprehensive study of the postnatal changes in the concentration of the lipids of developing rat brain. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):3169–3175. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


