Abstract
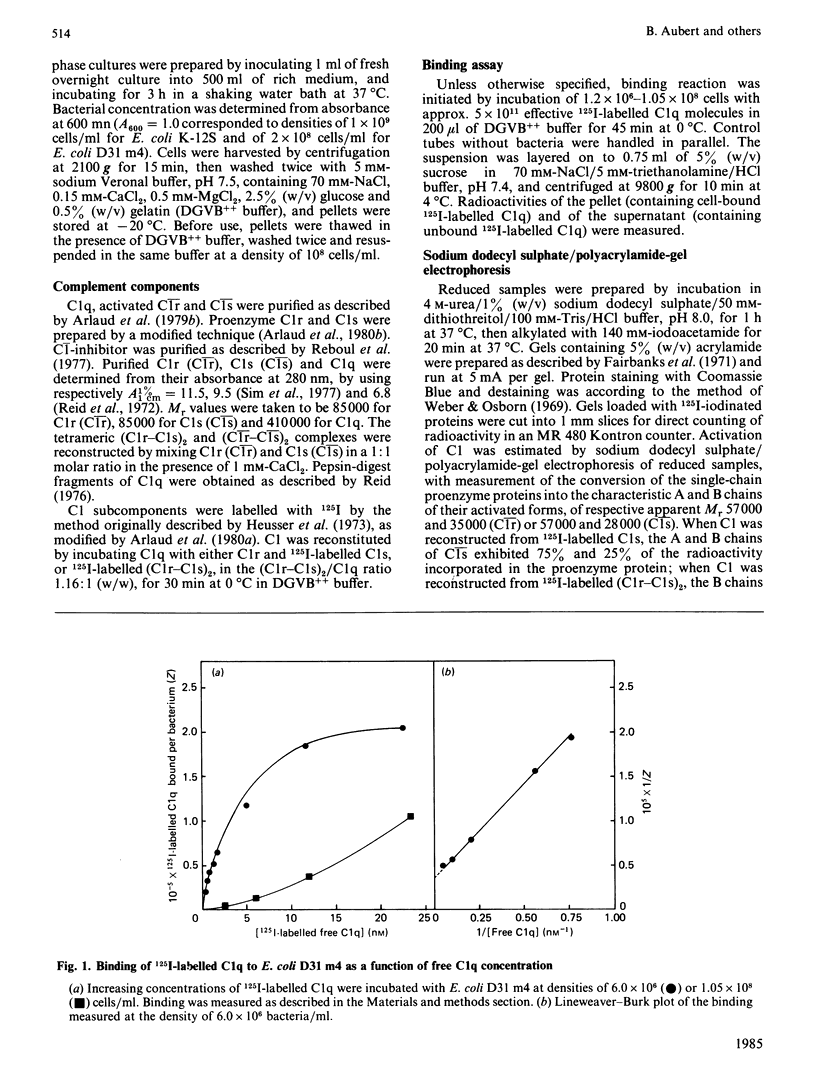
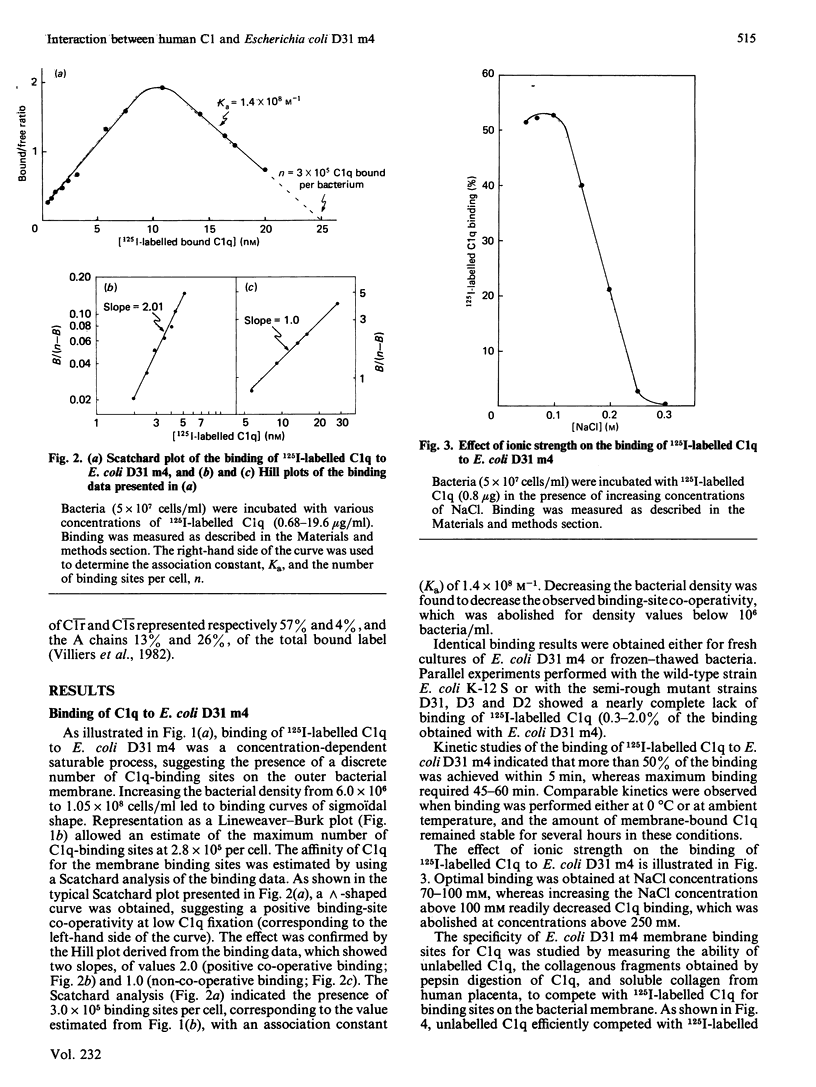
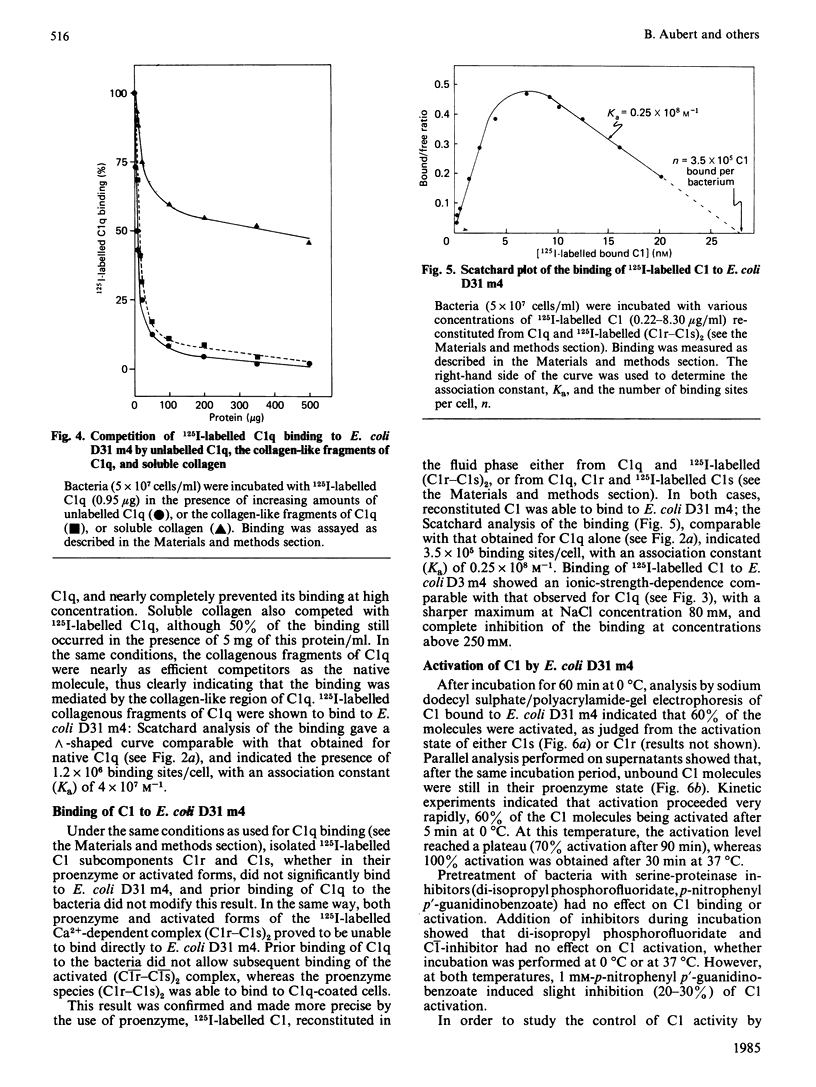
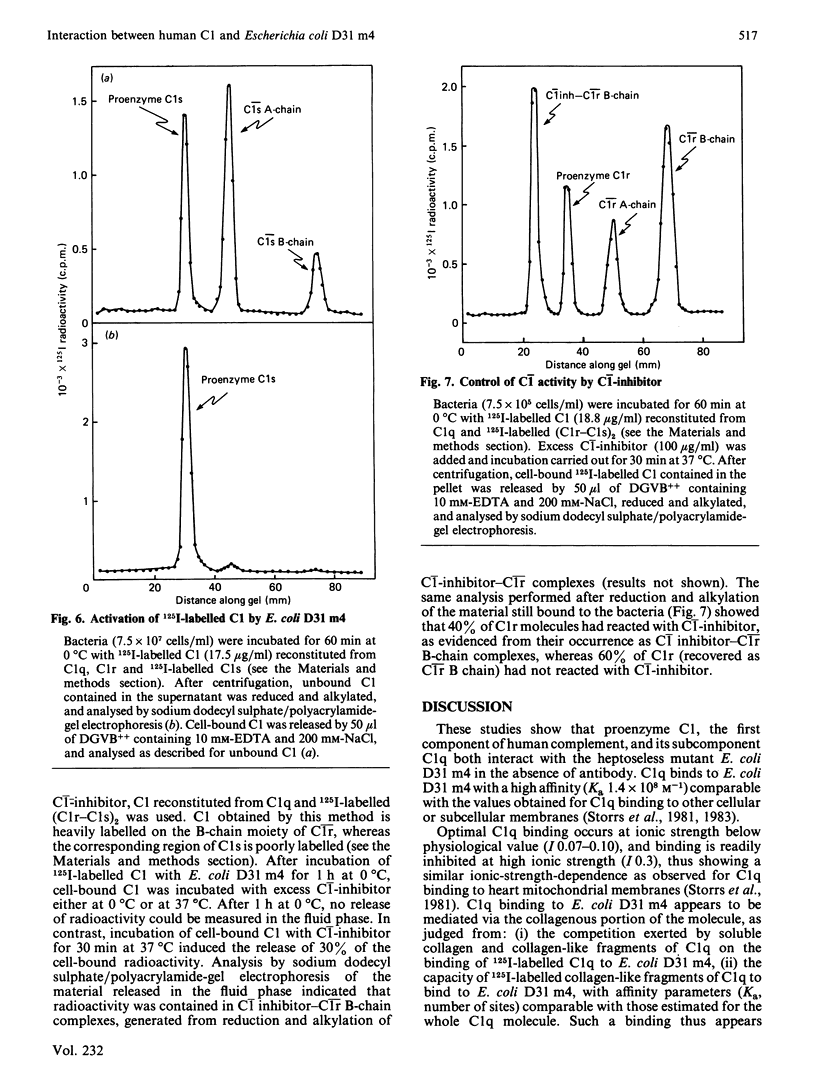
The heptoseless mutant of Escherichia coli, E. coli D31 m4, binds C1q and C1 at 0 degrees C and at low ionic strength (I0.07). Under these conditions, the maximum C1q binding averages 3.0 X 10(5) molecules per bacterium, with a Ka of 1.4 X 10(8) M-1. Binding involves the collagen-like region of C1q, as shown by the capacity of C1q pepsin-digest fragments to bind to E. coli D31 m4, and to compete with native C1q. Proenzyme and activated forms of C1 subcomponents C1r and C1s and their Ca2+-dependent association (C1r-C1s)2 do not bind to E. coli D31 m4. In contrast, the C1 complex binds very effectively, with an average fixation of 3.5 X 10(5) molecules per bacterium, and a Ka of 0.25 X 10(8) M-1, both comparable with the values obtained for C1q binding. C1 bound to E. coli D31 m4 undergoes rapid activation at 0 degrees C. The activation process is not affected by C1-inhibitor, and only slightly inhibited by p-nitrophenyl p'-guanidinobenzoate. No turnover of the (C1r-C1s)2 subunit is observed. Once activated, C1 is only partially dissociated by C1-inhibitor. Our observations are in favour of a strong association between C1 and the outer membrane of E. coli D31 m4, involving mainly the collagen-like moiety of C1.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arlaud G. J., Chesne S., Villiers C. L., Colomb M. G. A study on the structure and interactions of the C1 sub-components C1r and C1s in the fluid phase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 6;616(1):105–115. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlaud G. J., Sim R. B., Duplaa A. M., Colomb M. G. Differential elution of Clq, Clr and Cls from human Cl bound to immune aggregates. Use in the rapid purification of Cl subcomponents. Mol Immunol. 1979 Jul;16(7):445–450. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90069-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlaud G. J., Villiers C. L., Chesne S., Colomb M. G. Purified proenzyme C1r. Some characteristics of its activation and subsequent proteolytic cleavage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 6;616(1):116–129. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvieux J., Reboul A., Bensa J. C., Colomb M. G. Characterization of the C1q receptor on a human macrophage cell line, U937. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 1;218(2):547–555. doi: 10.1042/bj2180547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew R. M., Esser A. F. Mechanism of antibody-independent activation of the first component of complement (Cl) on retrovirus membranes. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 24;19(13):2847–2853. doi: 10.1021/bi00554a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz S. J., Isliker H. Antibody-independent interactions between Escherichia coli J5 and human complement components. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1748–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G., Jonsson S., Monner D., Normark S., Bloom G. D. Cell-surface alterations in Escherichia coli K-12 with chromosmal mutations changing ampicillin resistance. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 11;182:342–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb30670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G., Monner D. A. Characterization of lipopolysaccharides from Escherichia coli K-12 mutants. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):455–464. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.455-464.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clas F., Loos M. Antibody-independent binding of the first component of complement (C1) and its subcomponent C1q to the S and R forms of Salmonella minnesota. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1138–1144. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1138-1144.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper N. R., Morrison D. C. Binding and activation of the first component of human complement by the lipid A region of lipopolysaccharides. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):1862–1868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodds A. W., Sim R. B., Porter R. R., Kerr M. A. Activation of the first component of human complement (C1) by antibody-antigen aggregates. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):383–390. doi: 10.1042/bj1750383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusser C., Boesman M., Nordin J. H., Isliker H. Effect of chemical and enzymatic radioiodination on in vitro human Clq activities. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):820–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes-Jones N. C., Gardner B. Reaction between the isolated globular sub-units of the complement component C1q and IgG-complexes. Mol Immunol. 1979 Sep;16(9):697–701. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilchherr E., Fuchs H., Tschopp J., Engel J. Dissociation of C1 and concentration dependence of its activation kinetics. Mol Immunol. 1982 May;19(5):683–691. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90370-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loos M., Bitter-Suermann D., Dierich M. Interaction of the first (C1), the second (C2) and the fourth (C4) component of complement with different preparations of bacterial lipopolysaccharides and with lipid A. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):935–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loos M. The classical complement pathway: mechanism of activation of the first component by antigen-antibody complexes. Prog Allergy. 1982;30:135–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loos M., Wellek B., Thesen R., Opferkuch W. Antibody-independent interaction of the first component of complement with Gram-negative bacteria. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):5–9. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.5-9.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Kline L. F. Activation of the classical and properdin pathways of complement by bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS). J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):362–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. R. The Croonian Lecture, 1980. The complex proteases of the complement system. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Nov 28;210(1181):477–498. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1980.0148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prehm P., Stirm S., Jann B., Jann K. Cell-wall lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli B. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 1;56(1):41–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02205.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reboul A., Arlaud G. J., Sim R. B., Colomb M. G. A simplified procedure for the purification of C1-inactivator from human plasma. Interaction with complement subcomponents C1r and C1s. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 1;79(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80347-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B. Isolation, by partial pepsin digestion, of the three collagen-like regions present in subcomponent Clq of the first component of human complement. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 1;155(1):5–17. doi: 10.1042/bj1550005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Lowe D. M., Porter R. R. Isolation and characterization of C1q, a subcomponent of the first component of complement, from human and rabbit sera. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(3):749–763. doi: 10.1042/bj1300749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Porter R. R. The proteolytic activation systems of complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:433–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner M. R., Tang J., Barzilay I., Khorana H. G. Structure of the lipopolysaccharide from an Escherichia coli heptose-less mutant. I. Chemical degradations and identification of products. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5906–5917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Arlaud G. J., Colomb M. G. C1 inhibitor-dependent dissociation of human complement component C1 bound to immune complexes. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 1;179(3):449–457. doi: 10.1042/bj1790449a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Porter R. R., Reid K. B., Gigli I. The structure and enzymic activities of the C1r and C1s subcomponents of C1, the first component of human serum complement. Biochem J. 1977 May 1;163(2):219–227. doi: 10.1042/bj1630219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storrs S. B., Kolb W. P., Olson M. S. C1q binding and C1 activation by various isolated cellular membranes. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):416–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storrs S. B., Kolb W. P., Pinckard R. N., Olson M. S. Characterization of the binding of purified human C1q to heart mitochondrial membranes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10924–10929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain S. M., Fesik S. W., Armitage I. M. Characterization of lipopolysaccharide from a heptoseless mutant of Escherichia coli by carbon 13 nuclear magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2906–2910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner A. J., Cooper N. R. Analysis of receptor-mediated C1q binding to human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1658–1664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner A. J., Ziccardi R. J., Cooper N. R. Antibody-independent C1 activation by E. coli. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):886–891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villiers C. L., Chesne S., Lacroix M. B., Arlaud G. J., Colomb M. G. Structural features of the first component of human complement, C1, as revealed by surface iodination. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 1;203(1):185–191. doi: 10.1042/bj2030185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wautier J. L., Souchon H., Reid K. B., Peltier A. P., Caen J. P. Studies on the mode of reaction of the first component of complement with platelets: interaction between the collagen-like portion of C1q and platelets. Immunochemistry. 1977 Nov-Dec;14(11-12):763–766. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(77)90351-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziccardi R. J., Cooper N. R. Active disassembly of the first complement component, C-1, by C-1 inactivator. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):788–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziccardi R. J. Spontaneous activation of the first component of human complement (C1) by an intramolecular autocatalytic mechanism. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2500–2504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


