Abstract
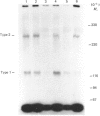
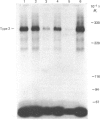
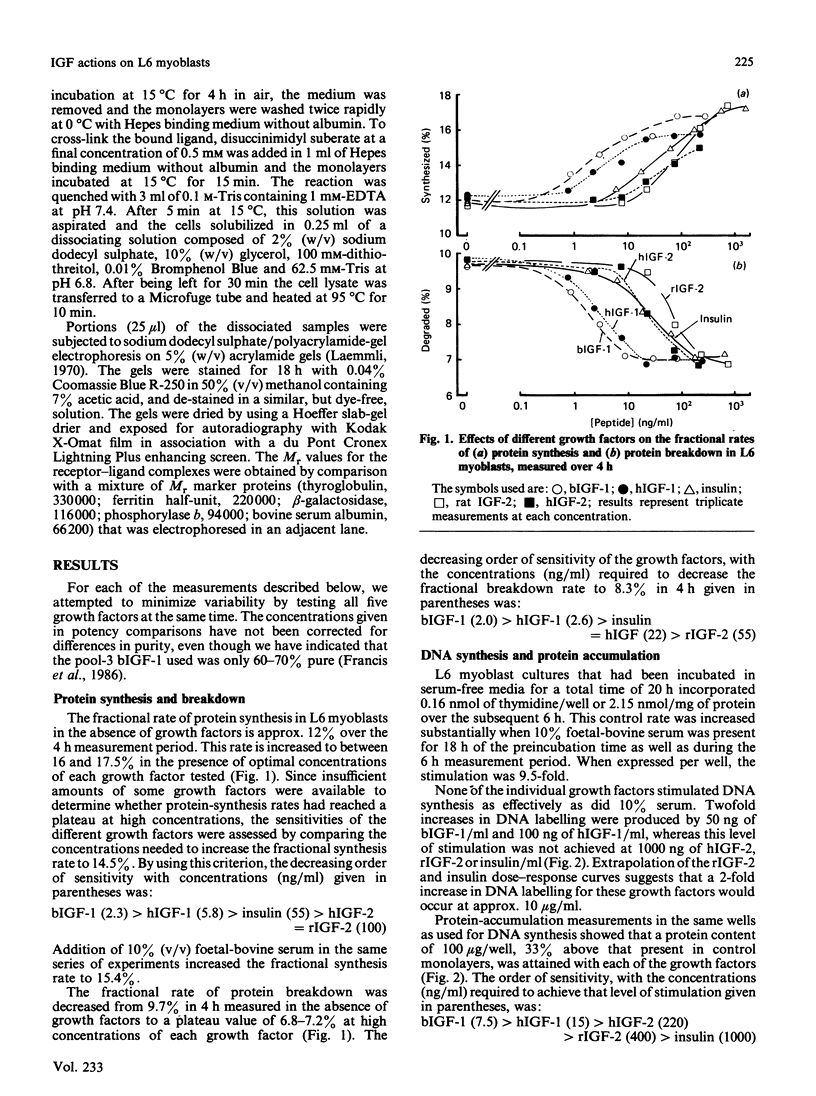
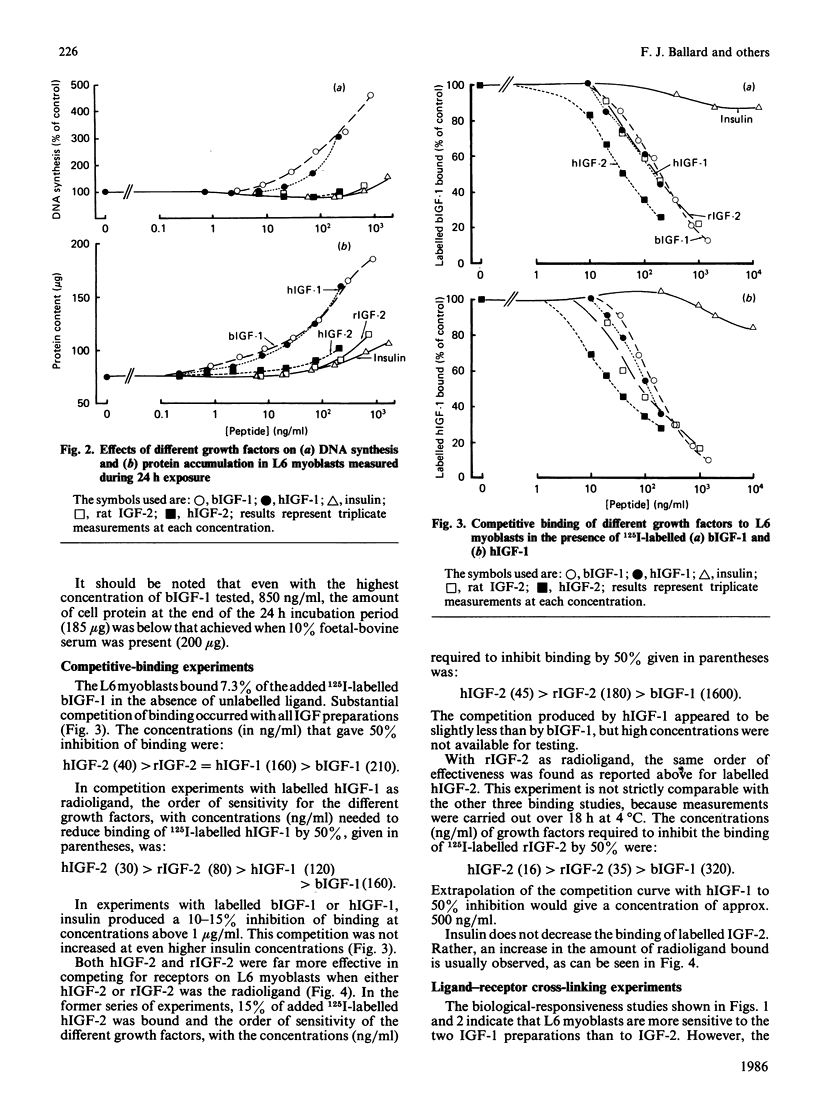
Protein synthesis in rat L6 myoblasts is stimulated and protein breakdown inhibited in a co-ordinate manner by insulin-like growth factors (IGF) or insulin. For both processes, bovine IGF-1 was somewhat more potent than human IGF-1, which was effective at a tenth the concentration of insulin, rat IGF-2 or human IGF-2. A similar order of potency is noted when DNA synthesis or protein accumulation is monitored over a 24 h period, but between 20- and 50-fold higher concentrations of each growth factor are required than those needed to produce effects in the 4 h protein-synthesis or -breakdown measurements. Binding experiments with labelled human or bovine IGF-1 as ligand demonstrated competition at concentrations of IGF-2, especially human IGF-2, lower than that of either IGF-1 preparation. This pattern was much more pronounced when the radioligand was either human IGF-2 or rat IGF-2. Insulin competed 10-15% for the binding of labelled IGF-1, but not at all with labelled IGF-2. Ligand-receptor cross-linking experiments showed that labelled bovine IGF-1 bound approximately equally to the type 1 IGF receptor (Mr 130000 after reduction) and to the type 2 IGF receptor (Mr 270000 after reduction), and that unlabelled IGF-1 competed equally with radioligand binding to both receptors. On the other hand, rat IGF-2 competed more effectively for binding to the type-2 receptor, and insulin competed only for binding to the type-1 receptor. Further cross-linking experiments with rat IGF-2 as radioligand demonstrated binding only to the type-2 receptor and to proteins with Mr values after reduction of 230000 and 200000. This binding was prevented by high rat IGF-2 concentrations, less effectively by bovine IGF-1 and not at all by insulin. The apparently conflicting biological potencies and receptor binding of the different growth factors can be explained if all the biological actions are mediated via the type-1 IGF receptor, rather than through the abundant type-2 receptor.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. O., Nissley S. P., Kasuga M., Foley T. P., Jr, Rechler M. M. Receptors for insulin-like growth factors and growth effects of multiplication-stimulating activity (rat insulin-like growth factor II) in rat embryo fibroblasts. Endocrinology. 1983 Mar;112(3):971–978. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-3-971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Francis G. L. Effects of anabolic agents on protein breakdown in L6 myoblasts. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 15;210(1):243–249. doi: 10.1042/bj2100243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Knowles S. E., Wong S. S., Bodner J. B., Wood C. M., Gunn J. M. Inhibition of protein breakdown in cultured cells is a consistent response to growth factors. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jun 2;114(2):209–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Nield M. K., Francis G. L., Knowles S. E. Regulation of intracellular protein degradation by insulin and growth factors. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1981;40(10-11):1293–1300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J. Regulation of protein accumulation in cultured cells. Biochem J. 1982 Nov 15;208(2):275–287. doi: 10.1042/bj2080275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Wong S. S., Knowles S. E., Partridge N. C., Martin T. J., Wood C. M., Gunn J. M. Insulin inhibition of protein degradation in cell monolayers. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Nov;105(2):335–346. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041050216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhaumick B., Bala R. M., Hollenberg M. D. Somatomedin receptor of human placenta: solubilization, photolabeling, partial purification, and comparison with insulin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4279–4283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borland K., Mita M., Oppenheimer C. L., Blinderman L. A., Massague J., Hall P. F., Czech M. P. The actions of insulin-like growth factors I and II on cultured Sertoli cells. Endocrinology. 1984 Jan;114(1):240–246. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-1-240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. F. Removal of fatty acids from serum albumin by charcoal treatment. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):173–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernausek S. D., Jacobs S., Van Wyk J. J. Structural similarities between human receptors for somatomedin C and insulin: analysis by affinity labeling. Biochemistry. 1981 Dec 22;20(26):7345–7350. doi: 10.1021/bi00529a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conover C. A., Hintz R. L., Rosenfeld R. G. Comparative effects of somatomedin C and insulin on the metabolism and growth of cultured human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Jan;122(1):133–141. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041220120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulley J. R., Grieve P. A. A simple technique for eliminating interference by detergents in the Lowry method of protein determination. Anal Biochem. 1975 Mar;64(1):136–141. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90415-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewton D. Z., Florini J. R. Effects of the somatomedins and insulin on myoblast differentiation in vitro. Dev Biol. 1981 Aug;86(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90312-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewton D. Z., Florini J. R. Relative effects of the somatomedins, multiplication-stimulating activity, and growth hormone on myoblasts and myotubes in culture. Endocrinology. 1980 Feb;106(2):577–583. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-2-577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis G. L., Read L. C., Ballard F. J., Bagley C. J., Upton F. M., Gravestock P. M., Wallace J. C. Purification and partial sequence analysis of insulin-like growth factor-1 from bovine colostrum. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 1;233(1):207–213. doi: 10.1042/bj2330207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunn J. M., Clark M. G., Knowles S. E., Hopgood M. F., Ballard F. J. Reduced rates of proteolysis in transformed cells. Nature. 1977 Mar 3;266(5597):58–60. doi: 10.1038/266058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall K., Sara V. R. Growth and somatomedins. Vitam Horm. 1983;40:175–233. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60435-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaton J. H., Krett N. L., Alvarez J. M., Gelehrter T. D., Romanus J. A., Rechler M. M. Insulin regulation of insulin-like growth factor action in rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2396–2402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Van Obberghen E., Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Demonstration of two subtypes of insulin-like growth factor receptors by affinity cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5305–5308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. L., Kahn C. R., Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P. Direct demonstration of separate receptors for growth and metabolic activities of insulin and multiplication-stimulating activity (an insulinlike growth factor) using antibodies to the insulin receptor. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):130–140. doi: 10.1172/JCI109826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laron Z. Somatomedin, insulin, growth hormone and growth: a review. Isr J Med Sci. 1982 Aug;18(8):823–829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Todaro G. J., Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S. Purification and primary structure of a polypeptide with multiplication-stimulating activity from rat liver cell cultures. Homology with human insulin-like growth factor II. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6859–6865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massague J., Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. Electrophoretic resolution of three major insulin receptor structures with unique subunit stoichiometries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7137–7141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Czech M. P. The subunit structures of two distinct receptors for insulin-like growth factors I and II and their relationship to the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5038–5045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monier S., Le Cam A., Le Marchand-Brustel Y. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor I. Effects on protein synthesis in isolated muscles from lean and goldthioglucose-obese mice. Diabetes. 1983 May;32(5):392–397. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.5.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monier S., Le Marchand-Brustel Y. Effects of insulin and IGF-I on RNA synthesis in isolated soleus muscle. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1984 Aug;37(1):109–114. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(84)90133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mottola C., Czech M. P. The type II insulin-like growth factor receptor does not mediate increased DNA synthesis in H-35 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12705–12713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifle B., Ditschuneit H. H., Ditschuneit H. Binding and biological actions of insulin-like growth factors on human arterial smooth muscle cells. Horm Metab Res. 1982 Aug;14(8):409–414. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1019031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. The subunit structure of the high affinity insulin receptor. Evidence for a disulfide-linked receptor complex in fat cell and liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1722–1731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poggi C., Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Zapf J., Froesch E. R., Freychet P. Effects and binding of insulin-like growth factor I in the isolated soleus muscle of lean and obese mice: comparison with insulin. Endocrinology. 1979 Sep;105(3):723–730. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-3-723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read L. C., Ballard F. J., Francis G. L., Baxter R. C., Bagley C. J., Wallace J. C. Comparative binding of bovine, human and rat insulin-like growth factors to membrane receptors and to antibodies against human insulin-like growth factor-1. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 1;233(1):215–221. doi: 10.1042/bj2330215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Zapf J., Nissley S. P., Froesch E. R., Moses A. C., Podskalny J. M., Schilling E. E., Humbel R. E. Interactions of insulin-like growth factors I and II and multiplication-stimulating activity with receptors and serum carrier proteins. Endocrinology. 1980 Nov;107(5):1451–1459. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-5-1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman R. A., Weiss J. P., Roberts S. B., Florini J. R. The effect of serum and multiplication stimulating activity on L6 myoblast growth: the lack of correlation with cyclic nucleotide changes. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Apr;103(1):63–69. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041030110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Primary structure of human insulin-like growth factor II. FEBS Lett. 1978 May 15;89(2):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2769–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld R. G., Dollar L. A. Characterization of the somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor I (SM-C/IGF-I) receptor on cultured human fibroblast monolayers: regulation of receptor concentrations by SM-C/IGF-I and insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Sep;55(3):434–440. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-3-434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon W. D., Jr, DuVall M. R. In vitro stimulation of leucine incorporation into muscle and cartilage protein by a serum fraction with sulfation factor activity: differentiation of effects from those of growth hormone and insulin. Endocrinology. 1970 Dec;87(6):1168–1180. doi: 10.1210/endo-87-6-1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher C. D., Shepard R. C., Antoniades H. N., Stiles C. D. Platelet-derived growth factor and the regulation of the mammalian fibroblast cell cycle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 10;560(2):217–241. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(79)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C., Steiner T., Froesch E. R. Preferential enhancement of myoblast differentiation by insulin-like growth factors (IGF I and IGF II) in primary cultures of chicken embryonic cells. FEBS Lett. 1983 Sep 5;161(1):117–121. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80742-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenle E., Zapf J., Humbel R. E., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factor I stimulates growth in hypophysectomized rats. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):252–253. doi: 10.1038/296252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Pouysségur J. Mitogen-potentiating action and binding characteristics of insulin and insulin-like growth factors in Chinese hamster fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Sep;147(2):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D. Retention of differentiation potentialities during prolonged cultivation of myogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):477–483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K. T., Czech M. P. The type I insulin-like growth factor receptor mediates the rapid effects of multiplication-stimulating activity on membrane transport systems in rat soleus muscle. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3090–3095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E., Froesch E. R. Nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) from human serum: recent accomplishments and their physiologic implications. Metabolism. 1978 Dec;27(12):1803–1828. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90267-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vroede M. A., Romanus J. A., Standaert M. L., Pollet R. J., Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Interaction of insulin-like growth factors with a nonfusing mouse muscle cell line: binding, action, and receptor down-regulation. Endocrinology. 1984 May;114(5):1917–1929. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-5-1917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]