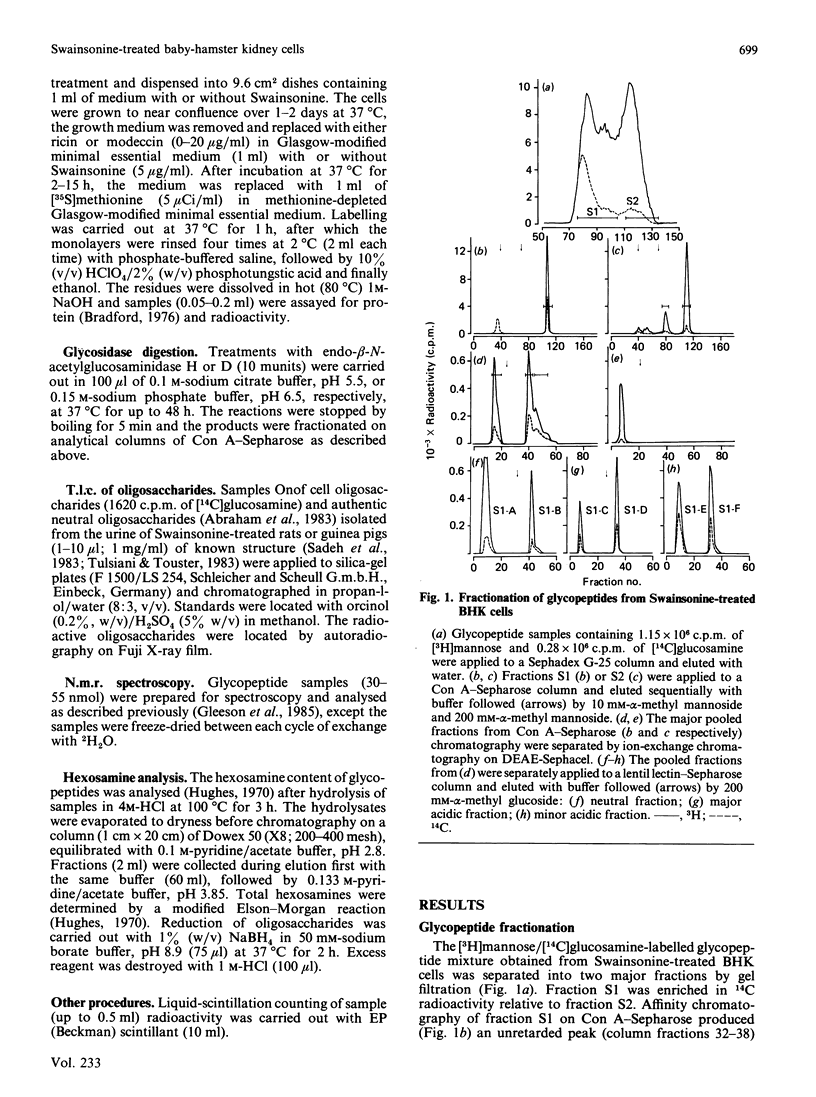
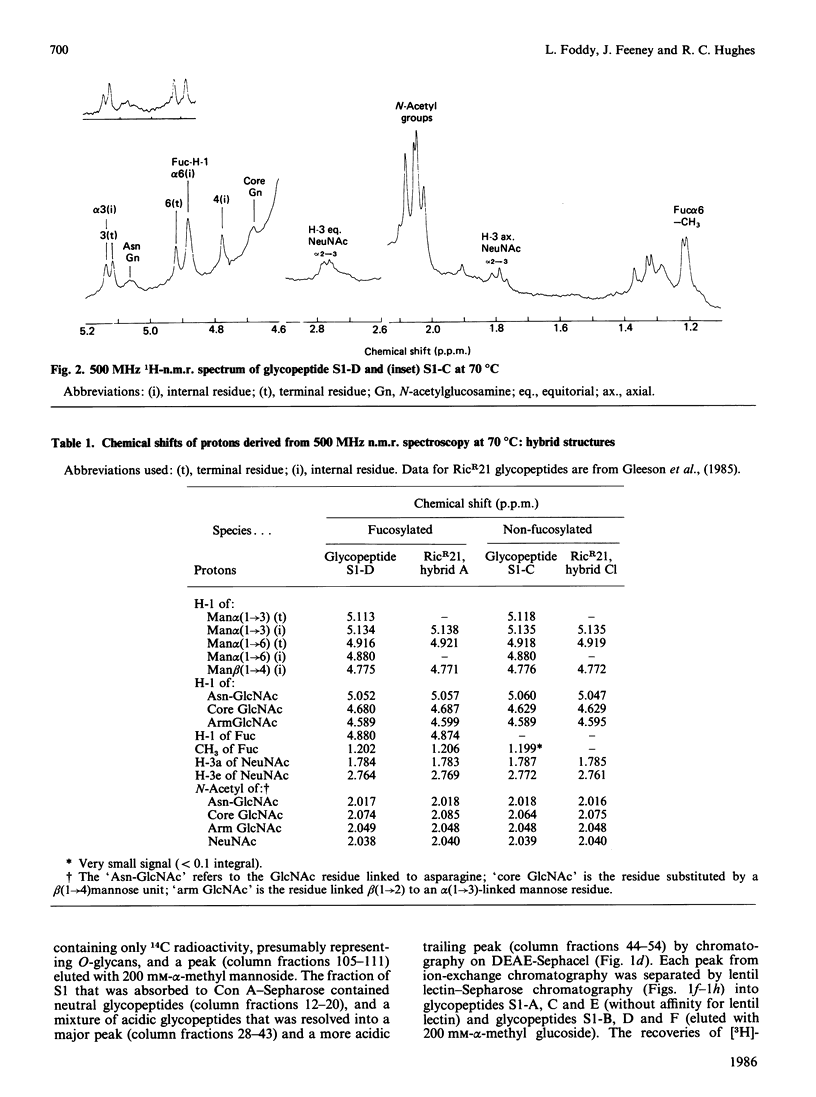
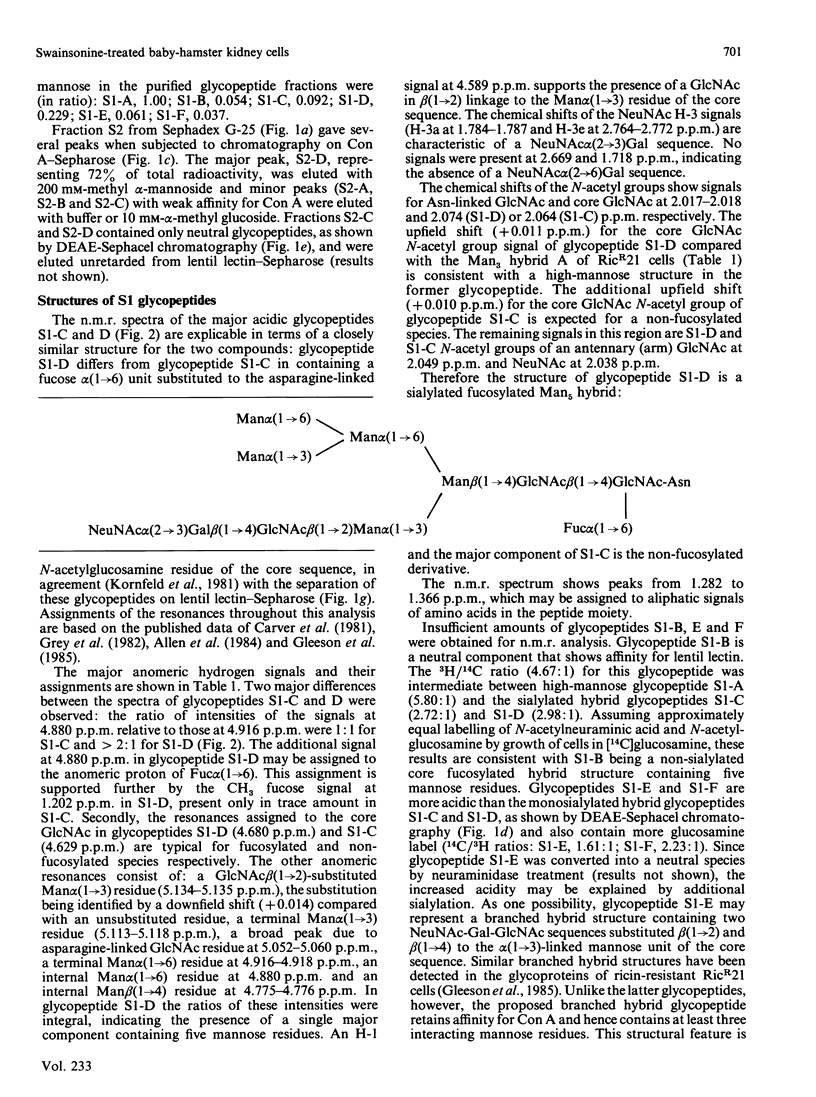
Abstract
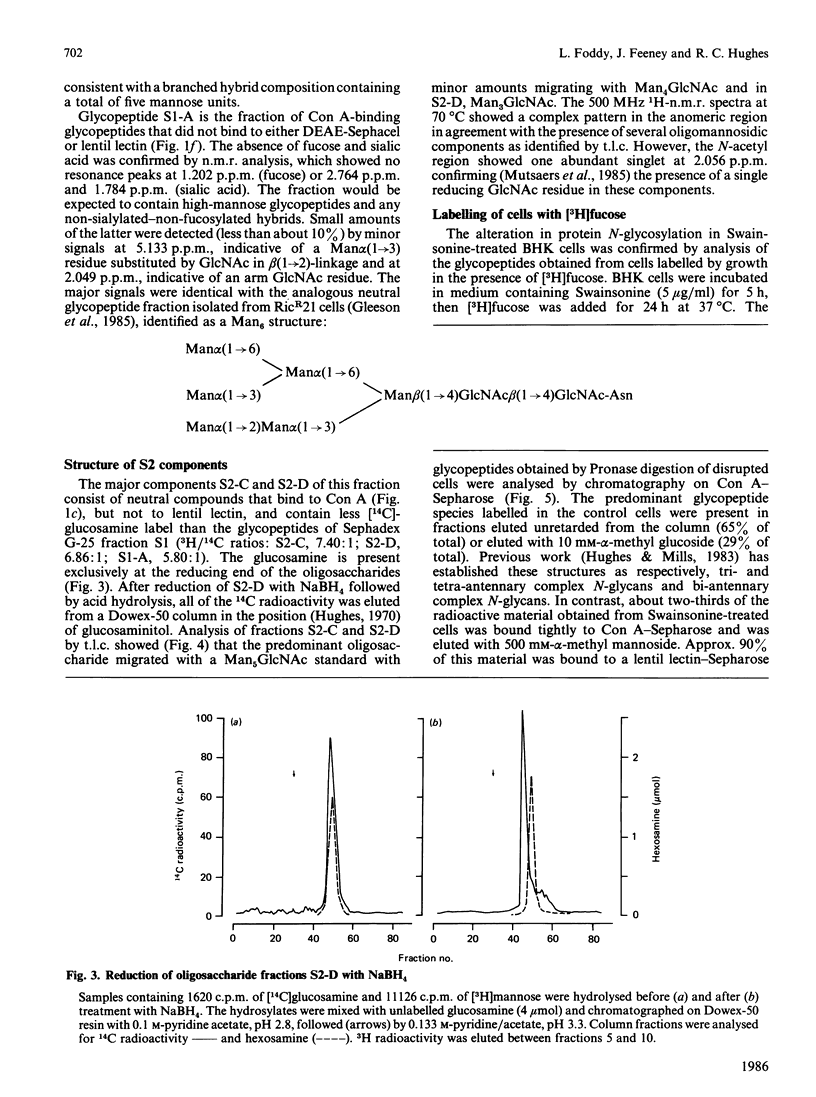
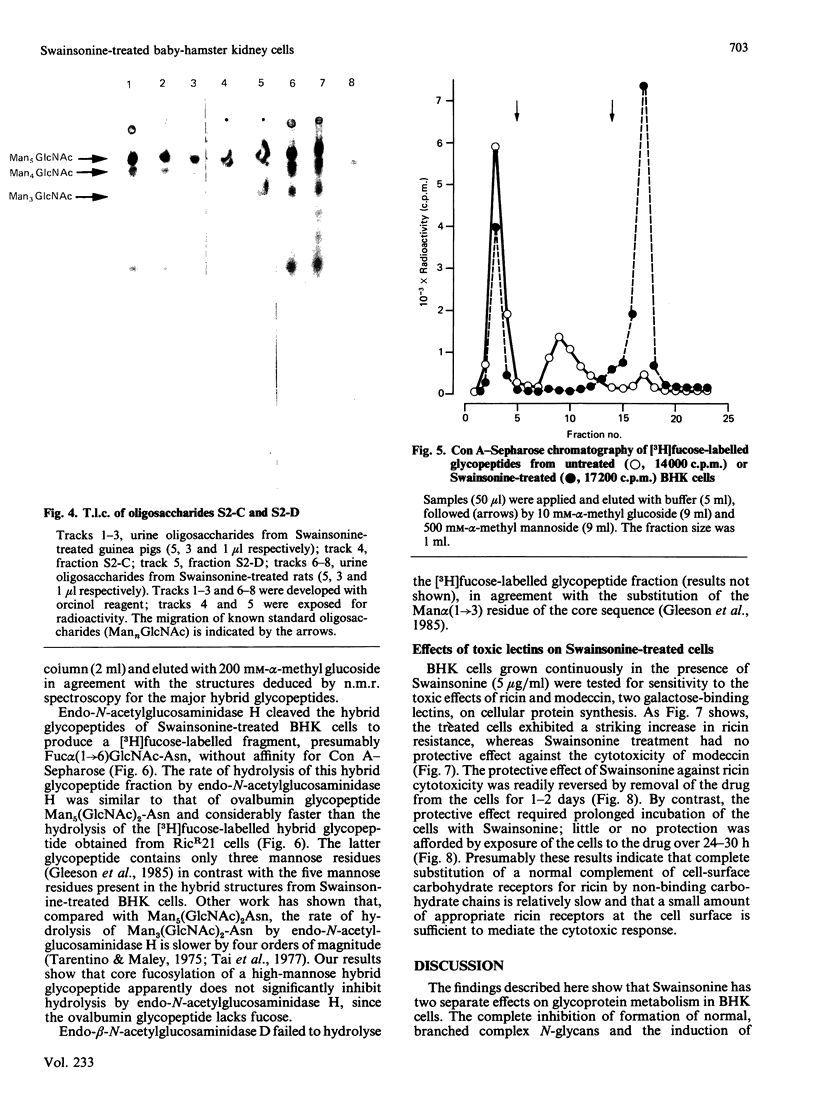
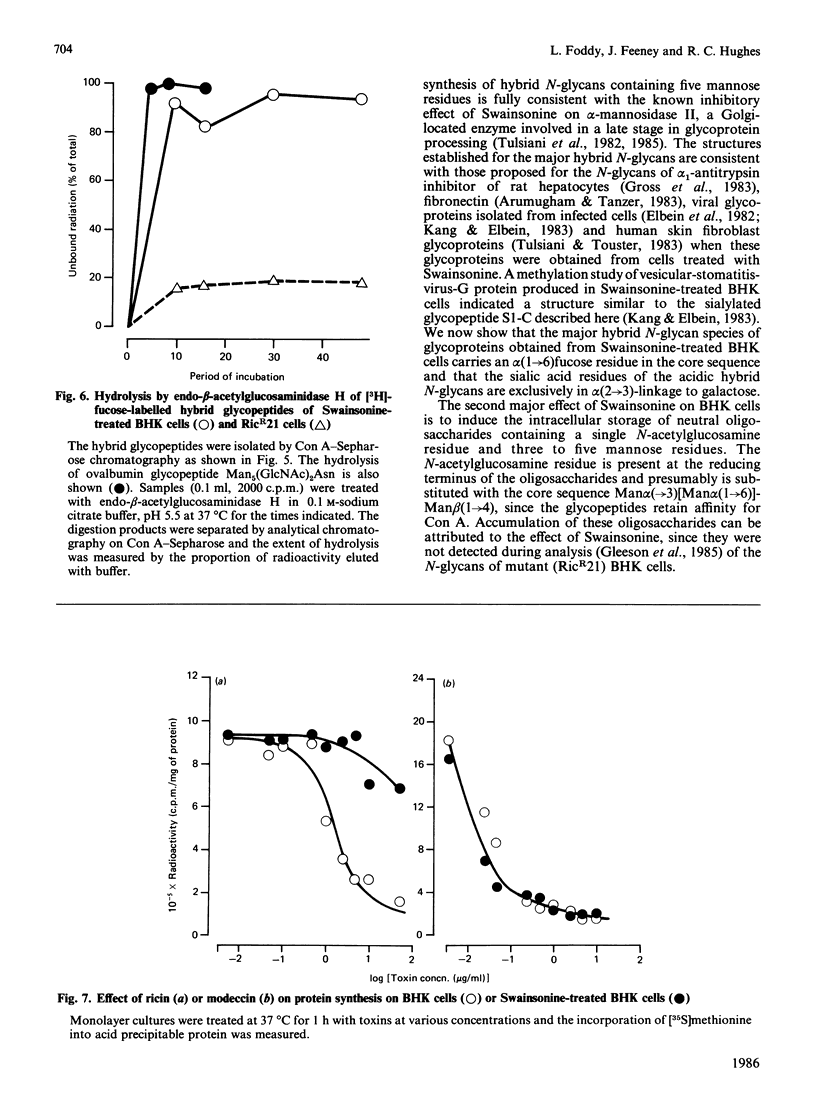
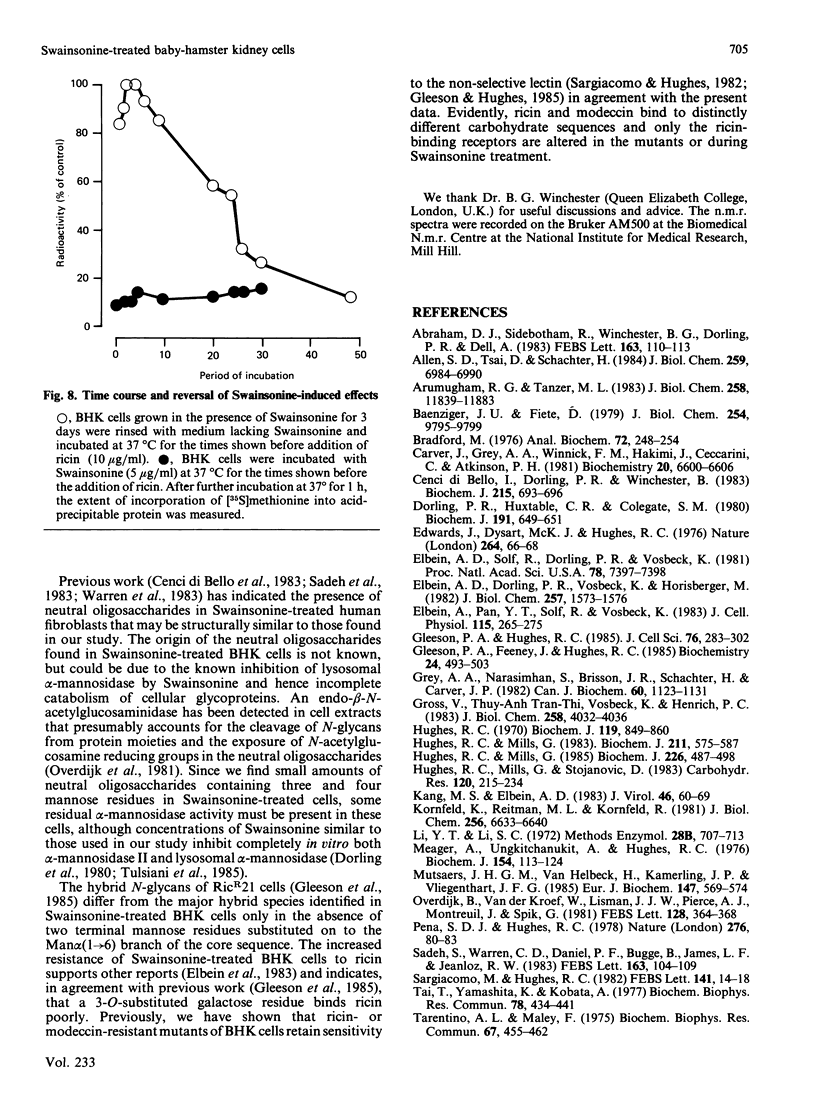
Baby-hamster kidney (BHK) cells were grown continuously in long-term monolayer culture in the presence of Swainsonine, an inhibitor of alpha-mannosidase II, a processing enzyme involved in glycoprotein biosynthesis. The asparagine-linked oligosaccharides (N-glycans) were isolated from Pronase-digested cells by gel filtration, ion-exchange chromatography and affinity chromatography on concanavalin A--Sepharose and lentil lectin--Sepharose. The major N-glycans, analysed by 500 MHz 1H-n.m.r. spectroscopy, were identified as hybrid structures containing five mannose residues and neutral high-mannose N-glycans. The major hybrid species contained a core-substituted fucose alpha(1----6) residue and a NeuNAc alpha(2----3)Gal beta(1----4)GlcNAc terminal sequence; smaller amounts of non-sialylated and non-fucosylated hybrid structures were also detected. Swainsonine-treated cells also produced neutral oligosaccharides containing a single reducing N-acetylglucosamine residue substituted with polymannose sequences. The glycopeptide composition of Swainsonine-treated BHK cells resembles closely that of the ricin-resistant BHK cell mutant, RicR21 [P. A. Gleeson, J. Feeney and R. C. Hughes (1985) Biochemistry 24, 493-503], except the hybrid structures of RicR21 cells contain three, not five, mannose residues. Like RicR21 cells, Swainsonine-treated BHK cells showed a greatly increased resistance to ricin cytotoxicity, but not to modeccin, another galactose-binding lectin. These effects were readily reversed on removal of Swainsonine and growth in normal medium.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham D. J., Sidebothom R., Winchester B. G., Dorling P. R., Dell A. Swainsonine affects the processing of glycoproteins in vivo. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 31;163(1):110–113. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81174-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen S. D., Tsai D., Schachter H. Control of glycoprotein synthesis. The in vitro synthesis by hen oviduct membrane preparations of hybrid asparagine-linked oligosaccharides containing 5 mannose residues. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):6984–6990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arumugham R. G., Tanzer M. L. Abnormal glycosylation of human cellular fibronectin in the presence of swainsonine. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11883–11889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baenziger J. U., Fiete D. Structural determinants of Ricinus communis agglutinin and toxin specificity for oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9795–9799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carver J. P., Grey A. A., Winnik F. M., Hakimi J., Ceccarini C., Atkinson P. H. Determination of the Structure of four glycopeptides from hen ovalbumin using 360-MHz proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 10;20(23):6600–6606. doi: 10.1021/bi00526a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cenci di Bello I., Dorling P., Winchester B. The storage products in genetic and swainsonine-induced human mannosidosis. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 1;215(3):693–696. doi: 10.1042/bj2150693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorling P. R., Huxtable C. R., Colegate S. M. Inhibition of lysosomal alpha-mannosidase by swainsonine, an indolizidine alkaloid isolated from Swainsona canescens. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):649–651. doi: 10.1042/bj1910649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. G., Dysart J. M., Hughes R. C. Cellular adhesiveness reduced in ricin-resistant hamster fibroblasts. Nature. 1976 Nov 4;264(5581):66–68. doi: 10.1038/264066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D., Dorling P. R., Vosbeck K., Horisberger M. Swainsonine prevents the processing of the oligosaccharide chains of influenza virus hemagglutinin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1573–1576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D., Pan Y. T., Solf R., Vosbeck K. Effect of swainsonine, an inhibitor of glycoprotein processing, on cultured mammalian cells. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Jun;115(3):265–275. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041150309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D., Solf R., Dorling P. R., Vosbeck K. Swainsonine: an inhibitor of glycoprotein processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7393–7397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson P. A., Feeney J., Hughes R. C. Structures of N-glycans of a ricin-resistant mutant of baby hamster kidney cells. Synthesis of high-mannose and hybrid N-glycans. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 15;24(2):493–503. doi: 10.1021/bi00323a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson P. A., Hughes R. C. Binding and uptake of the toxic lectin modeccin by baby hamster kidney (BHK) cells. Isolation of mutants defective in the internalization of modeccin. J Cell Sci. 1985 Jun;76:283–301. doi: 10.1242/jcs.76.1.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey A. A., Narasimhan S., Brisson J. R., Schachter H., Carver J. P. Structure of the glycopeptides of a human gamma 1-immunoglobulin G (Tem) myeloma protein as determined by 360-megahertz nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Can J Biochem. 1982 Dec;60(12):1123–1131. doi: 10.1139/o82-144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross V., Tran-Thi T. A., Vosbeck K., Heinrich P. C. Effect of swainsonine on the processing of the asparagine-linked carbohydrate chains of alpha 1-antitrypsin in rat hepatocytes. Evidence for the formation of hybrid oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):4032–4036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. C. Autolysis of isolated cell walls of Bacillus licheniformis N.C.T.C. 6346 and Bacillus subtilis Marburg Strain 168. Separation of the products and characterization of the mucopeptide fragments. Biochem J. 1970 Oct;119(5):849–860. doi: 10.1042/bj1190849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. C., Mills G. Analysis by lectin affinity chromatography of N-linked glycans of BHK cells and ricin-resistant mutants. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 1;211(3):575–587. doi: 10.1042/bj2110575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. C., Mills G. Hybrid sialylated N-glycans are minor constituents of normal BHK-cell glycoproteins and a prominent feature in glycoproteins of some ricin-resistant cell lines. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 1;226(2):487–498. doi: 10.1042/bj2260487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. C., Mills G., Stojanovic D. Hybrid, sialylated N-glycans accumulate in a ricin-resistant mutant of baby hamster kidney BHK cells. Carbohydr Res. 1983 Aug 16;120:215–234. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(83)88018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang M. S., Elbein A. D. Alterations in the structure of the oligosaccharide of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein by swainsonine. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):60–69. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.60-69.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld K., Reitman M. L., Kornfeld R. The carbohydrate-binding specificity of pea and lentil lectins. Fucose is an important determinant. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6633–6640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meager A., Ungkitchanukit A., Hughes R. C. Variants of hamster fibroblasts resistant to Ricinus communis toxin (ricin). Biochem J. 1976 Jan 15;154(1):113–124. doi: 10.1042/bj1540113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutsaers J. H., van Halbeek H., Kamerling J. P., Vliegenthart J. F. Determination of the structure of the carbohydrate chains of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase from sheep. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 15;147(3):569–574. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-2956.1985.00569.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overdijk B., van der Kroef W. M., Lisman J. J., Pierce R. J., Montreuil J., Spik G. Demonstration and partial characterization of endo-N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase in human tissues. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 15;128(2):364–366. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pena S. D., Hughes R. C. Fibronectin-plasma membrane interactions in the adhesion and spreading of hamster fibroblasts. Nature. 1978 Nov 2;276(5683):80–83. doi: 10.1038/276080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadeh S., Warren C. D., Daniel P. F., Bugge B., James L. F., Jeanloz R. W. Characterization of oligosaccharides from the urine of loco-intoxicated sheep. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 31;163(1):104–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81173-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargiacomo M., Hughes R. C. Interaction of ricin-sensitive and ricin-resistant cell lines with other carbohydrate-binding toxins. FEBS Lett. 1982 May 3;141(1):14–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai T., Yamashita K., Kobata A. The substrate specificities of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases CII and H. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):434–441. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91273-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Maley F. A comparison of the substrate specificities of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases from Streptomyces griseus and Diplococcus Pneumoniae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):455–462. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90337-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulsiani D. R., Broquist H. P., Touster O. Marked differences in the swainsonine inhibition of rat liver lysosomal alpha-D-mannosidase, rat liver Golgi mannosidase II, and jack bean alpha-D-mannosidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Jan;236(1):427–434. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90643-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulsiani D. R., Harris T. M., Touster O. Swainsonine inhibits the biosynthesis of complex glycoproteins by inhibition of Golgi mannosidase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):7936–7939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulsiani D. R., Touster O. Swainsonine causes the production of hybrid glycoproteins by human skin fibroblasts and rat liver Golgi preparations. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7578–7585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren C. D., Sadeh S., Daniel P. F., Bugge B., James L. F., Jeanloz R. W. Induced mannosidosis-excretion of oligosaccharides by locoweed-intoxicated sheep. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 31;163(1):99–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]