Abstract
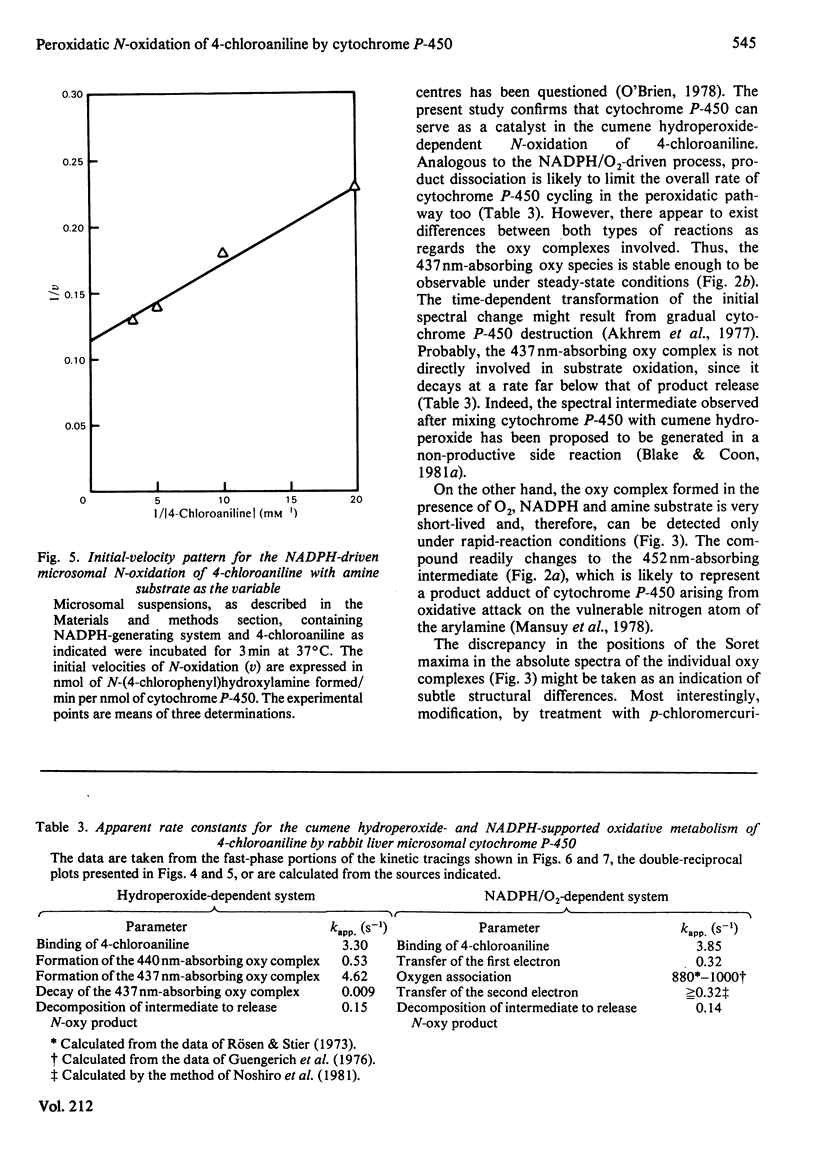
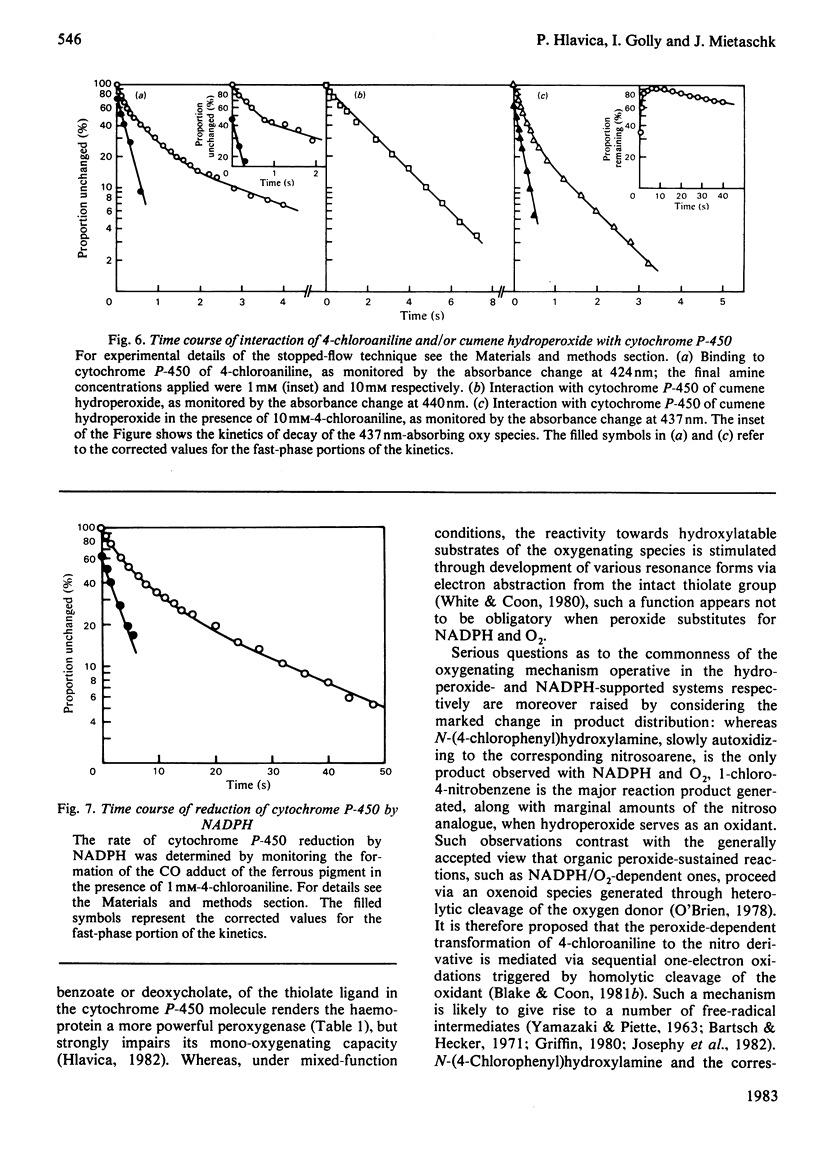
The present study confirms that cytochrome P-450 can act as a catalyst in the cumene hydroperoxide-supported N-oxidation of 4-chloroaniline. Analogous to the NADPH/O2-driven N-oxidation process, product dissociation is likely to limit the overall rate of cytochrome P-450 cycling also in the peroxidatic pathway. The oxy complexes involved in either metabolic route differ with respect to stability, spectral properties and need for thiolate-mediated resonance stabilization. With the organic hydroperoxide, the metabolic profile is shifted from the preponderant production of N-(4-chlorophenyl)hydroxylamine to the formation of 1-chloro-4-nitrobenzene. This finding suggests that the peroxide-sustained N-oxidation mechanism differs in several ways from that functional in the NADPH/O2-dependent oxenoid reaction. Thus one-electron oxidation, triggered by homolytic cleavage of the oxygen donor, is proposed as the mechanism of peroxidatic transformation of 4-chloroaniline.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhrem A. A., Bokut S. B., Metelitza D. I. Kinetics of cumene hydroperoxide-dependent aniline hydroxylation involving cytochrome P-450 in microsomal and solubilized forms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 11;77(1):20–27. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80159-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Autor A. P., Kaschnitz R. M., Heidema J. K., Coon M. J. Sedimentation and other properties of the reconstituted liver microsomal mixed-function oxidase system containing cytochrome P-450, reduced triphosphopyridine nucleotide-cytochrome P-450 reductase, and phosphatidylcholine. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 Jan;9(1):93–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartsch H., Hecker E. On the metabolic activation of the carcinogen N-hydroxy-N-2-acetylaminofluorene. 3. Oxidation with horseradish peroxidase to yield 2-nitrosofluorene and N-acetoxy-N-2-acetylaminofluorene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 22;237(3):567–578. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake R. C., 2nd, Coon M. J. On the mechanism of action of cytochrome P-450. Evaluation of homolytic and heterolytic mechanisms of oxygen-oxygen bond cleavage during substrate hydroxylation by peroxides. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12127–12133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake R. C., 2nd, Coon M. J. On the mechanism of action of cytochrome P-450. Role of peroxy spectral intermediates in substrate hydroxylation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5755–5763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Strobel H. W. NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase from rat liver: purification by affinity chromatography and characterization. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 22;16(6):1116–1123. doi: 10.1021/bi00625a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estabrook R. W., Hildebrandt A. G., Baron J., Netter K. J., Leibman K. A new spectral intermediate associated with cytochrome P-450 function in liver microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jan 8;42(1):132–139. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90372-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Ballou D. P., Coon M. J. Spectral intermediates in the reaction of oxygen with purified liver microsomal cytochrome P-450. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jun 7;70(3):951–956. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90684-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERR F., KIESE M. Bestimmung von Nitrosobenzol im Blute. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1959;235(4):351–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hlavica P. Biological oxidation of nitrogen in organic compounds and disposition of N-oxidized products. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982;12(1):39–101. doi: 10.3109/10409238209105850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hlavica P., Hülsmann S. Studies on the mechanism of hepatic microsomal N-oxide formation. N-oxidation of NN-dimethylaniline by a reconstituted rabbit liver microsomal cytochrome P-448 enzyme system. Biochem J. 1979 Jul 15;182(1):109–116. doi: 10.1042/bj1820109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimura Y., Ullrich V., Peterson J. A. Oxygenated cytochrome P-450 and its possible role in enzymic hydroxylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jan 8;42(1):140–146. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90373-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephy P. D., Eling T., Mason R. P. The horseradish peroxidase-catalyzed oxidation of 3,5,3',5'-tetramethylbenzidine. Free radical and charge-transfer complex intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3669–3675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenberger F., Nastainczyk W., Ullrich V. Cytochrome P450 as an oxene transferase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jun 7;70(3):939–946. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90682-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansuy D., Beaune P., Cresteil T., Bacot C., Chottard J. C., Gans P. Formation of complexes between microsomal cytochrome P-450-Fe(II) and nitrosoarenes obtained by oxidation of arylhydroxylamines or reduction of nitroarenes in situ. Eur J Biochem. 1978 May 16;86(2):573–579. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12341.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noshiro M., Ullrich V., Omura T. Cytochrome b5 as electron donor for oxy-cytochrome P-450. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun 1;116(3):521–526. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05367.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMURA T., SATO R. THE CARBON MONOXIDE-BINDING PIGMENT OF LIVER MICROSOMES. I. EVIDENCE FOR ITS HEMOPROTEIN NATURE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2370–2378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. A., Ebel R. E., O'Keeffe D. H. Dual-wavelength stopped-flow spectrophotometric measurement of NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase. Methods Enzymol. 1978;52:221–226. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)52025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rösen P., Stier A. Kinetics of CO and O 2 complexes of rabbit liver microsomal cytochrome P 450 . Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Apr 2;51(3):603–611. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZARKOWSKA L., KLINGENBERG M. ON THE ROLE OF UBIQUINONE IN MITOCHONDRIA. SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC AND CHEMICAL MEASUREMENTS OF ITS REDOX REACTIONS. Biochem Z. 1963;338:674–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkman J. B., Remmer H., Estabrook R. W. Spectral studies of drug interaction with hepatic microsomal cytochrome. Mol Pharmacol. 1967 Mar;3(2):113–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stier A., Beitz I., Sackmann E. Radical accumulation in liver microsomal membranes during biotransformation of aromatic amines and nitro compounds. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1972;274(2):189–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00501853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sum C. Y., Cho A. K. The metabolism of N-hydroxyphentermine by rat liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos. 1979 Mar-Apr;7(2):65–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. E., Coon M. J. Oxygen activation by cytochrome P-450. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:315–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.001531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAZAKI I., PIETTE L. H. THE MECHANISM OF AEROBIC OXIDASE REACTION CATALYZED BY PEROXIDASE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 3;77:47–64. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90468-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Jagow R., Kampffmeyer H., Kiese M. The preparation of microsomes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1965 Jun 1;251(1):73–87. doi: 10.1007/BF00245731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


