Abstract
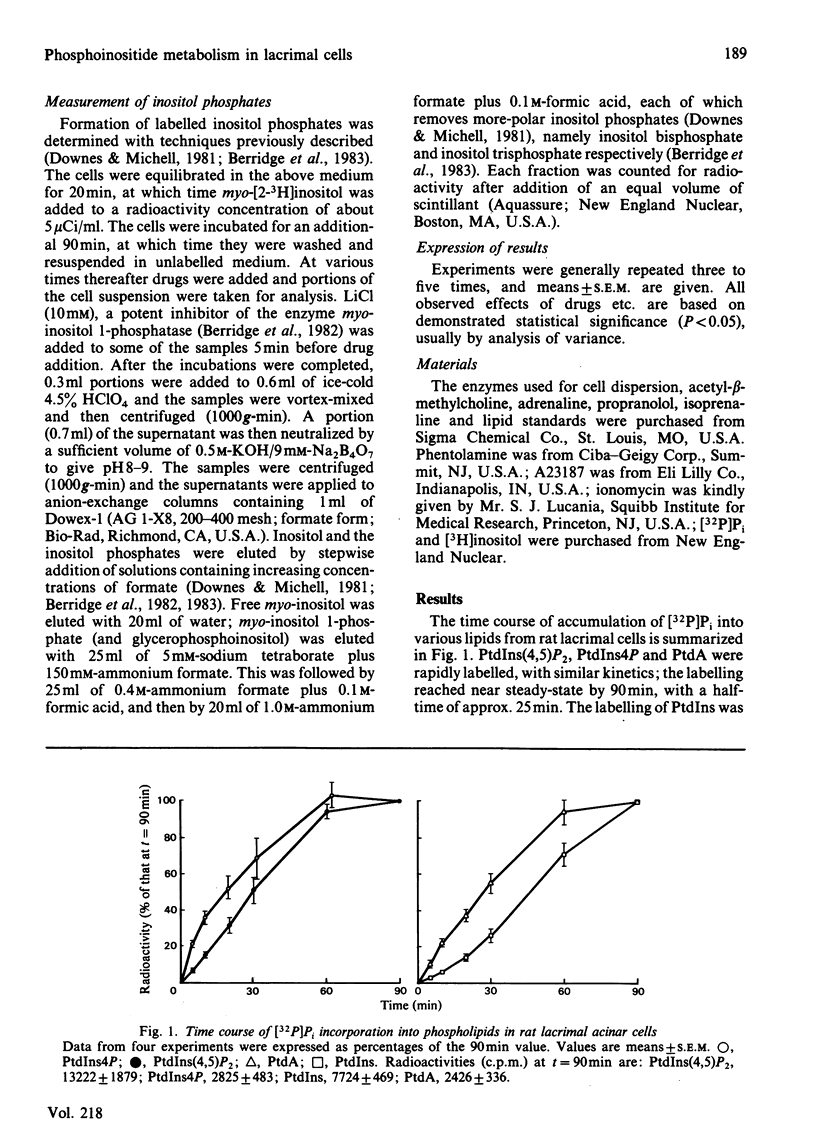
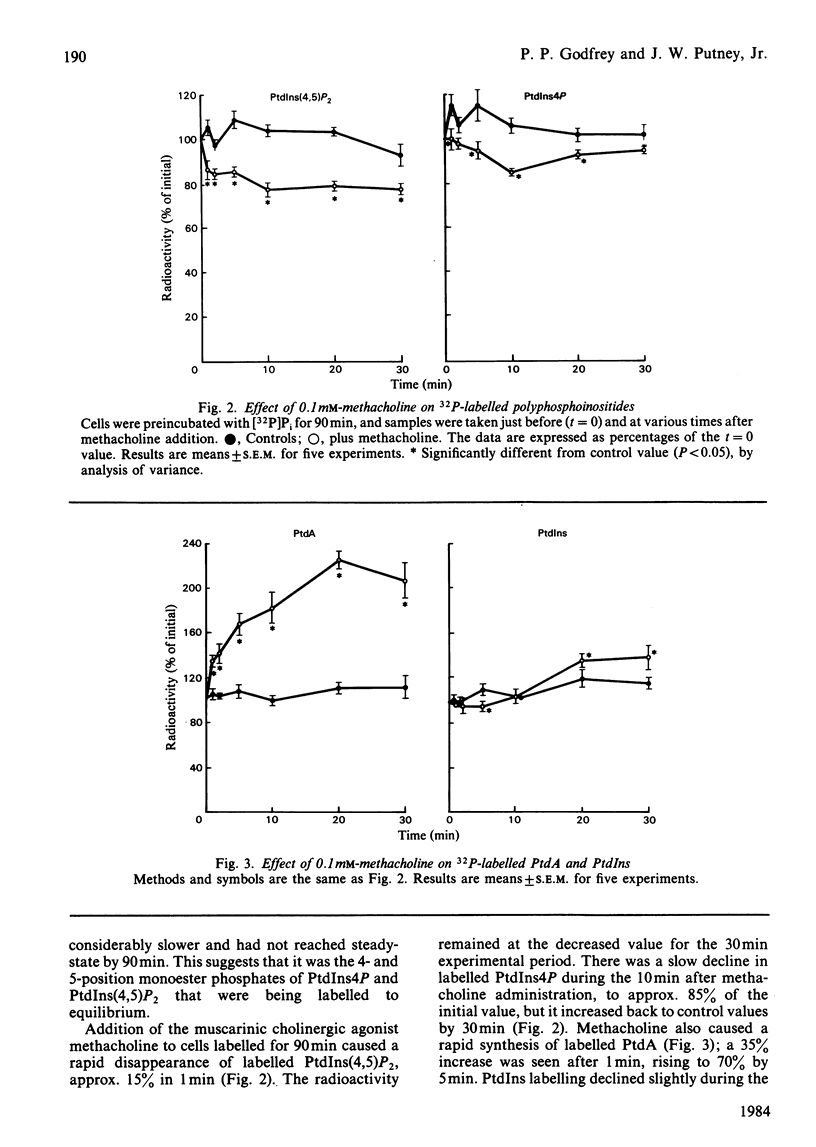
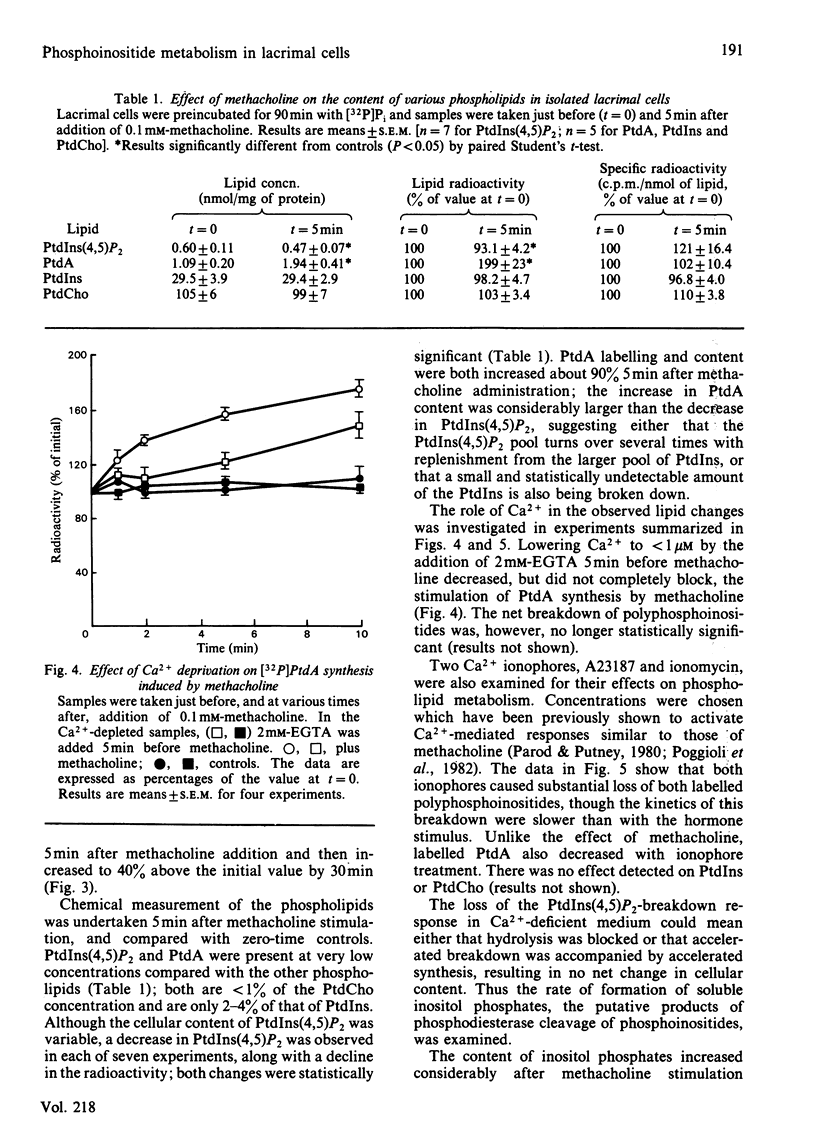
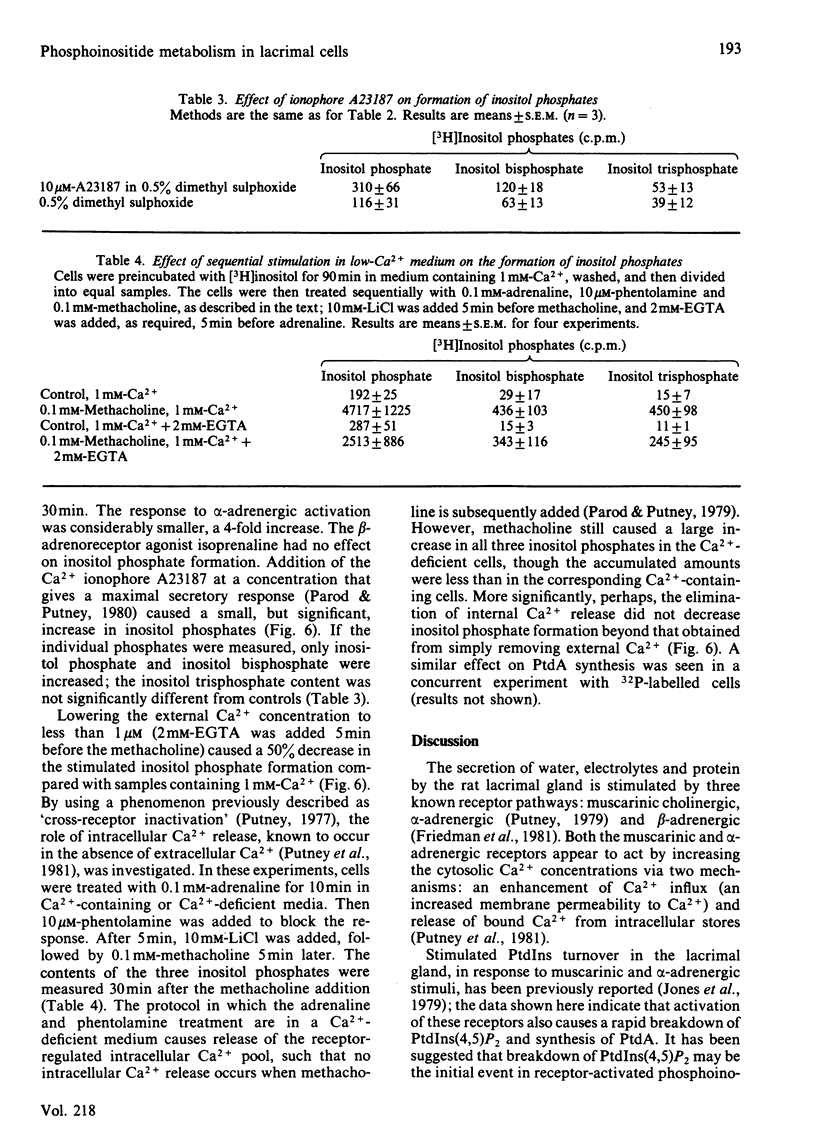
The metabolism of the inositol lipids and phosphatidic acid in rat lacrimal acinar cells was investigated. The muscarinic cholinergic agonist methacholine caused a rapid loss of 15% of [32P]phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PtdIns(4,5)P2] and a rapid increase in [32P]phosphatidic acid (PtdA). Chemical measurements indicated that the changes in 32P labelling of these lipids closely resembled changes in their total cellular content. Chelation of extracellular Ca2+ with excess EGTA caused a significant decrease in the PtdA labelling and an apparent loss of PtdIns(4,5)P2 breakdown. The calcium ionophores A23187 and ionomycin provoked a substantial breakdown of [32P]PtdIns(4,5)P2 and phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PtdIns4P); however, a decrease in [32P]PtdA was also observed. Increases in inositol phosphate, inositol bisphosphate and inositol trisphosphate were observed in methacholine-stimulated cells, and this increase was greatly amplified in the presence of 10 mM-LiCl; alpha-adrenergic stimulation also caused a substantial increase in inositol phosphates. A23187 provoked a much smaller increase in the formation of inositol phosphates than did either methacholine or adrenaline. Experiments with excess extracellular EGTA and with a protocol that eliminates intracellular Ca2+ release indicated that the labelling of inositol phosphates was partially dependent on the presence of extracellular Ca2+ and independent of intracellular Ca2+ mobilization. Thus, in the rat lacrimal gland, there appears to be a rapid phospholipase C-mediated breakdown of PtdIns(4,5)P2 and a synthesis of PtdA, in response to activation of receptors that bring about an increase in intracellular Ca2+. The results are consistent with a role for these lipids early in the stimulus-response pathway of the lacrimal acinar cell.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhtar R. A., Abdel-Latif A. A. Calcium ion requirement for acetylcholine-stimulated breakdown of triphosphoinositide in rabbit iris smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 Mar;204(3):655–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Downes C. P., Hanley M. R. Lithium amplifies agonist-dependent phosphatidylinositol responses in brain and salivary glands. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):587–595. doi: 10.1042/bj2060587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis: a multifunctional transducing mechanism. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1981 Nov;24(2):115–140. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(81)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Degradation of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate is insensitive to CA2+ mobilization in stimulated platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Nov 16;109(1):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91587-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Platelet-activating factor stimulates metabolism of phosphoinositides in horse platelets: possible relationship to Ca2+ mobilization during stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):965–968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Rapid decrease of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in thrombin-stimulated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12705–12708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Brewster G., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. Rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in rat hepatocytes stimulated by vasopressin and other Ca2+-mobilizing hormones. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):733–747. doi: 10.1042/bj2120733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Michell R. H. The polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase of erythrocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):133–140. doi: 10.1042/bj1980133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes P., Michell R. H. Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate: lipids in search of a function. Cell Calcium. 1982 Oct;3(4-5):467–502. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(82)90031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman Z. Y., Lowe M., Selinger Z. beta-Adrenergic receptors stimulated peroxidase secretion from rat lacrimal gland. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 11;675(1):40–45. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawthorne J. N. Is phosphatidylinositol now out of the calcium gate? Nature. 1982 Jan 28;295(5847):281–282. doi: 10.1038/295281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai A., Ishizuka Y., Kawai K., Nozawa Y. Evidence for coupling of phosphatidic acid formation and calcium influx in thrombin-activated human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Sep 30;108(2):752–759. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90893-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai A., Nakashima S., Nozawa Y. The rapid polyphosphoinositide metabolism may be a triggering event for thrombin-mediated stimulation of human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 14;110(1):108–115. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91267-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itaya K., Ui M. A new micromethod for the colorimetric determination of inorganic phosphate. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Sep;14(3):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Cockcroft S., Michell R. H. Stimulation of phosphatidylinositol turnover in various tissues by cholinergic and adrenergic agonists, by histamine and by caerulein. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 15;182(3):669–676. doi: 10.1042/bj1820669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Hoshijima M., Takai Y., Nishizuka Y. Phosphatidylinositol turnover in platelet activation; calcium mobilization and protein phosphorylation. Cell Calcium. 1982 Oct;3(4-5):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(82)90020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Michell R. H. Hormone-stimulated metabolism of inositol lipids and its relationship to hepatic receptor function. Biochem Soc Trans. 1981 Oct;9(5):377–379. doi: 10.1042/bst0090377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Billah M. M., Cuatrecasas P. The initial action of thrombin on platelets. Conversion of phosphatidylinositol to phosphatidic acid preceding the production of arachidonic acid. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5037–5040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G. Metabolism of inositides and the activation of platelets. Life Sci. 1983 May 2;32(18):2069–2082. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Kirk C. J., Jones L. M., Downes C. P., Creba J. A. The stimulation of inositol lipid metabolism that accompanies calcium mobilization in stimulated cells: defined characteristics and unanswered questions. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Dec 18;296(1080):123–138. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1981.0177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Stimulated inositol lipid metabolism: an introduction. Cell Calcium. 1982 Oct;3(4-5):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(82)90017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parod R. J., Putney J. W., Jr Stimulation of 45Ca efflux from rat lacrimal gland slices by carbachol and epinephrine. Life Sci. 1979 Dec 24;25(26):2211–2215. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parod R. J., Putney J. W., Jr Stimulus-permeability coupling in rat lacrimal gland. Am J Physiol. 1980 Aug;239(2):G106–G113. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1980.239.2.G106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poggioli J., Leslie B. A., McKinney J. S., Weiss S. J., Putney J. W., Jr Actions of ionomycin in rat parotid gland. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Apr;221(1):247–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prpić V., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Phosphatidylinositol breakdown induced by vasopressin and epinephrine in hepatocytes is calcium-dependent. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11323–11331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Burgess G. M., Halenda S. P., McKinney J. S., Rubin R. P. Effects of secretagogues on [32P]phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate metabolism in the exocrine pancreas. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):483–488. doi: 10.1042/bj2120483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr Inositol lipids and cell stimulation in mammalian salivary gland. Cell Calcium. 1982 Oct;3(4-5):369–383. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(82)90024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr Muscarinic, alpha-adrenergic and peptide receptors regulate the same calcium influx sites in the parotid gland. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(1):139–149. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Poggioli J., Weiss S. J. Receptor regulation of calcium release and calcium permeability in parotid gland cells. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Dec 18;296(1080):37–45. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1981.0169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr Recent hypotheses regarding the phosphatidylinositol effect. Life Sci. 1981 Sep 21;29(12):1183–1194. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90221-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr Stimulus-permeability coupling: role of calcium in the receptor regulation of membrane permeability. Pharmacol Rev. 1978 Jun;30(2):209–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Prpić V., Exton J. H., Blackmore P. F. Stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis in hepatocytes by vasopressin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2770–2773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacht J. Purification of polyphosphoinositides by chromatography on immobilized neomycin. J Lipid Res. 1978 Nov;19(8):1063–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman W. R., Leavitt A. L., Honchar M. P., Hallcher L. M., Phillips B. E. Evidence that lithium alters phosphoinositide metabolism: chronic administration elevates primarily D-myo-inositol-1-phosphate in cerebral cortex of the rat. J Neurochem. 1981 Jun;36(6):1947–1951. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb10819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soukup J., Schanberg S. Involvement of alpha noradrenergic receptors in mediation of brain polyphosphoinositides metabolism in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Jul;222(1):209–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. P., Marks J. S., Coll K. E., Williamson J. R. Quantitation and early kinetics of inositol lipid changes induced by vasopressin in isolated and cultured hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5716–5725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., McKinney J. S., Putney J. W., Jr Receptor-mediated net breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in parotid acinar cells. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):555–560. doi: 10.1042/bj2060555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., McKinney J. S., Putney J. W., Jr Regulation of phosphatidate synthesis by secretagogues in parotid acinar cells. Biochem J. 1982 May 15;204(2):587–592. doi: 10.1042/bj2040587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


