Abstract
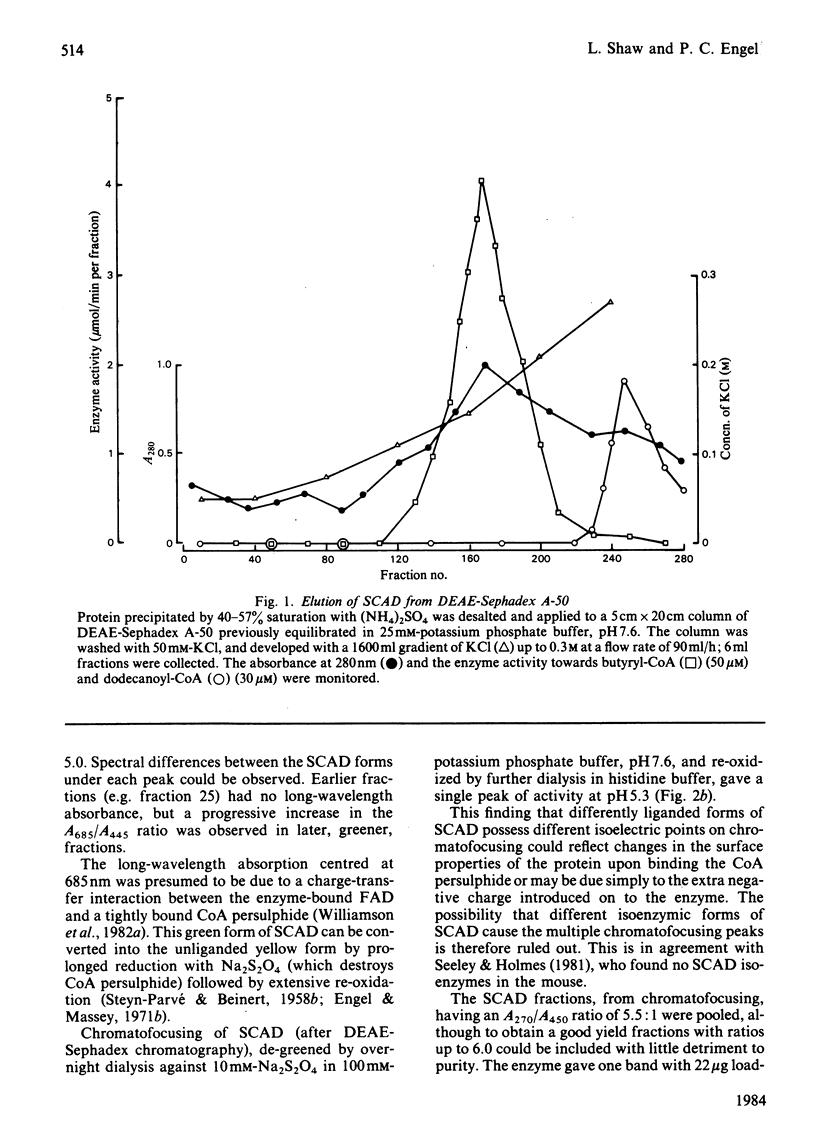
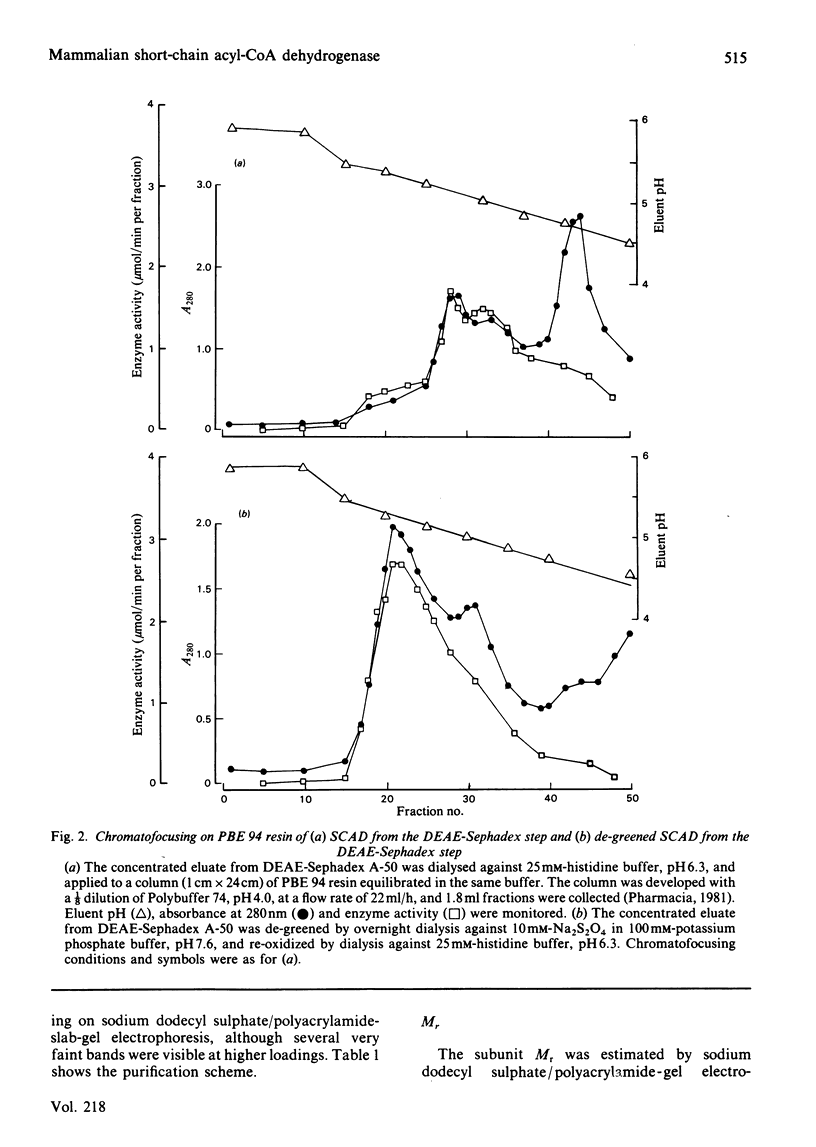
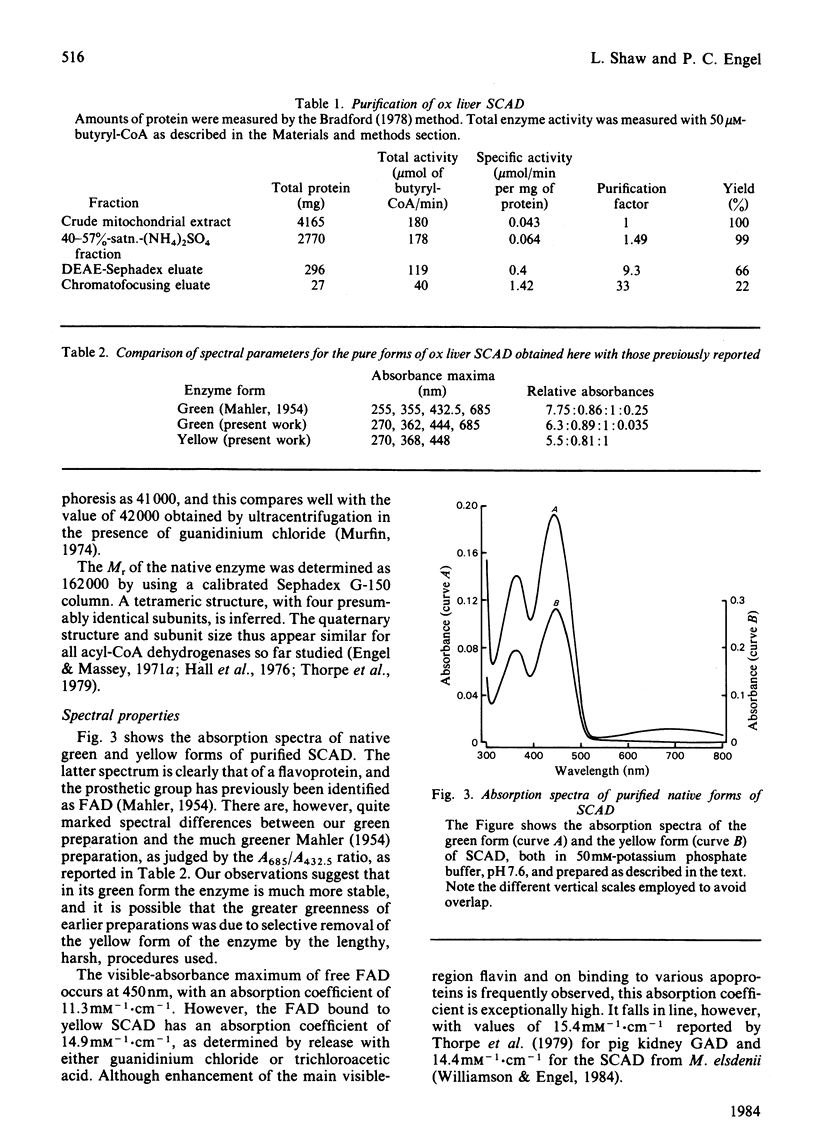
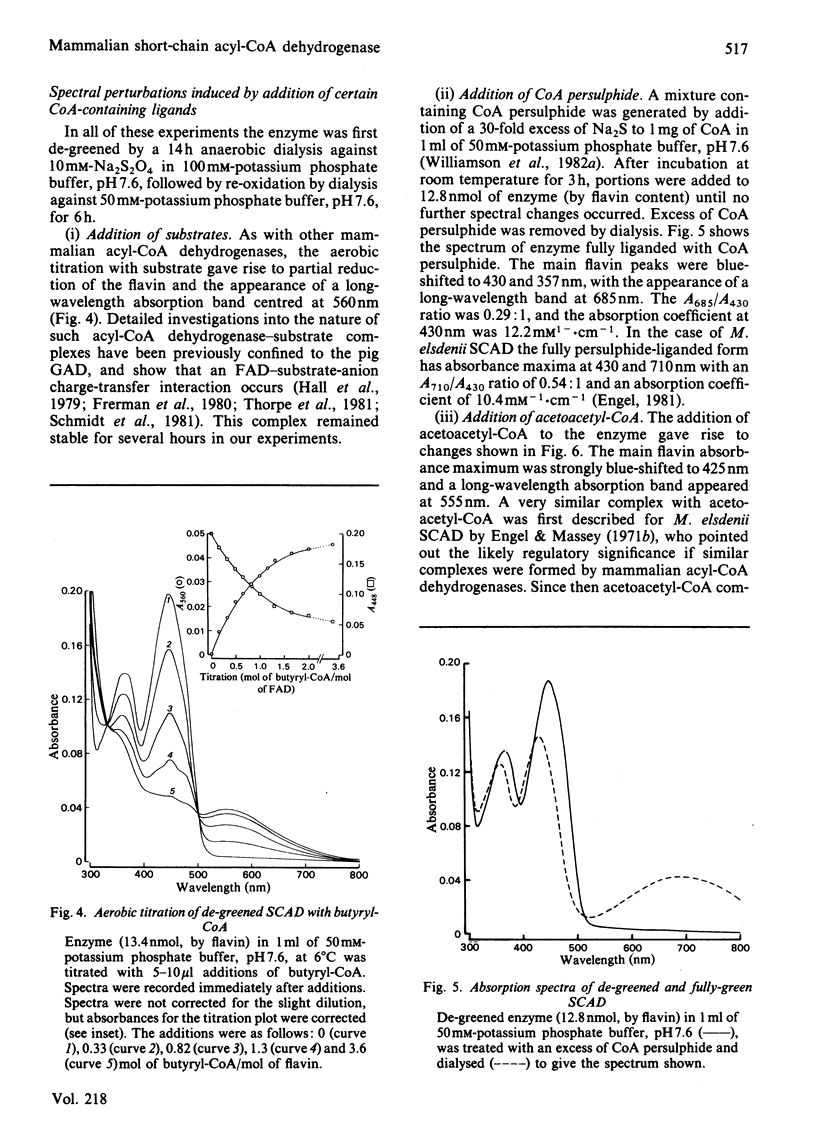
The FAD-containing short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase was purified from ox liver mitochondria by using (NH4)2SO4 fractionation, DEAE-Sephadex A-50 and chromatofocusing on PBE 94 resin. The enzyme is a tetramer, with a native Mr of approx. 162 000 and a subunit Mr of 41 000. Short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenases are usually isolated in a green form. The chromatofocusing step in the purification presented here partially resolved the enzyme into a green form and a yellow form. In the dye-mediated assay system, the enzyme exhibited optimal activity towards 50 microM-butyryl-CoA at pH 7.1. Kinetic parameters were also determined for a number of other straight-chain acyl-CoA substrates. The u.v.- and visible-absorption characteristics of the native forms of the enzyme are described, together with complexes formed by addition of butyryl-CoA, acetoacetyl-CoA and CoA persulphide.
Full text
PDF


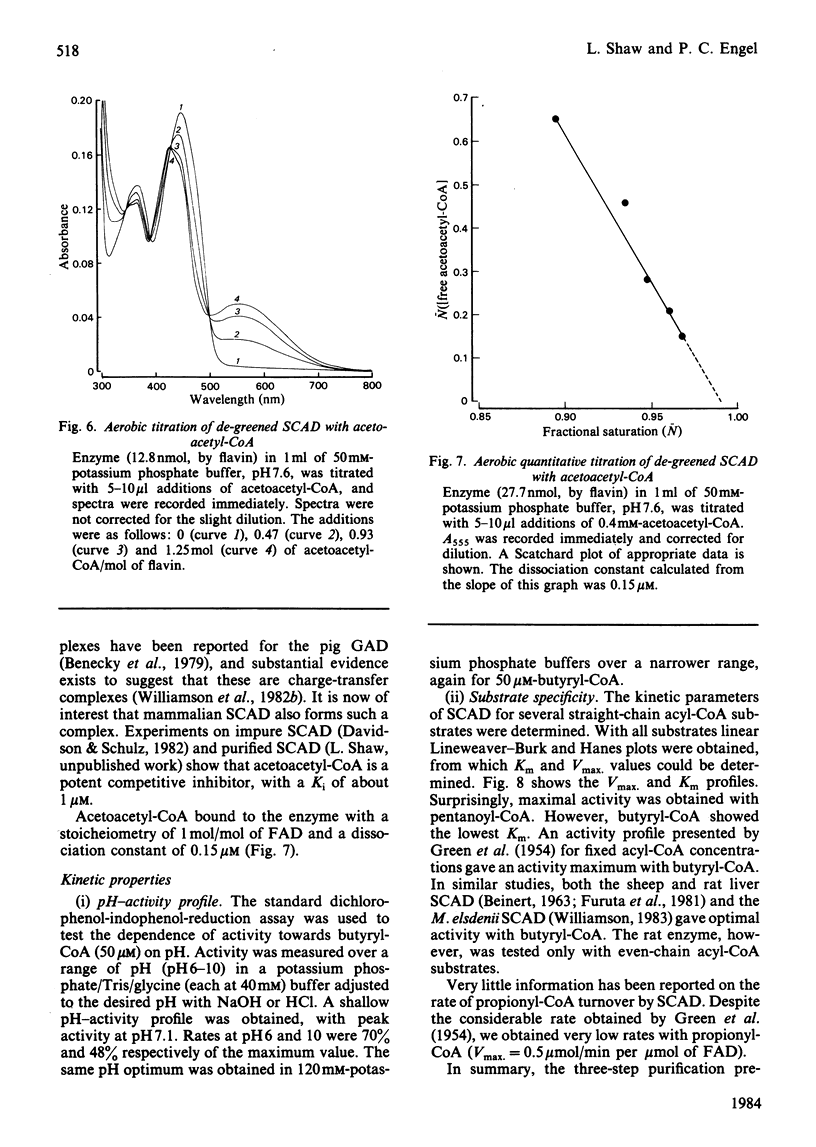
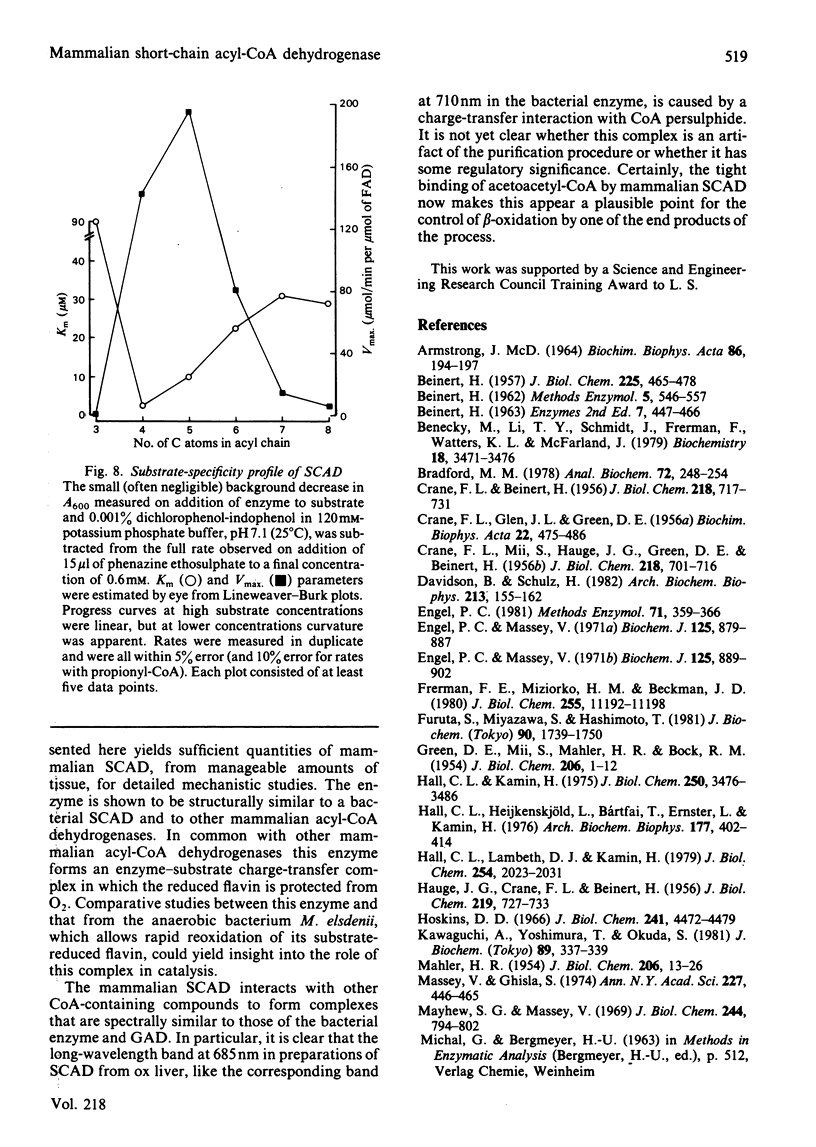

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG J. M. THE MOLAR EXTINCTION COEFFICIENT OF 2,6-DICHLOROPHENOL INDOPHENOL. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Apr 4;86:194–197. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEINERT H. Evidence for an intermediate in the oxidation-reduction of flavoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1957 Mar;225(1):465–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benecky M., Li T. Y., Schmidt J., Frerman F., Watters K. L., McFarland J. Resonance Raman study of flavins and the flavoprotein fatty acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 7;18(16):3471–3476. doi: 10.1021/bi00583a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRANE F. L., BEINERT H. On the mechanism of dehydrogenation of fatty acyl derivatives of coenzyme A. II. The electron-transferring flavoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):717–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRANE F. L., GLENN J. L., GREEN D. E. Studies on the electron transfer system. IV. The electron transfer particle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Dec;22(3):475–487. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRANE F. L., MII S., HAUGE J. G., GREEN D. E., BEINERT H. On the mechanism of dehydrogenation of fatty acyl derivatives of coenzyme A. I. The general fatty acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):701–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson B., Schulz H. Separation, properties, and regulation of acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenases from bovine heat and liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Jan;213(1):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90450-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frerman F. E., Miziorko H. M., Beckmann J. D. Enzyme-activated inhibitors, alternate substrates, and a dead end inhibitor of the general acyl-CoA dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11192–11198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuta S., Miyazawa S., Hashimoto T. Purification and properties of rat liver acyl-CoA dehydrogenases and electron transfer flavoprotein. J Biochem. 1981 Dec;90(6):1739–1750. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN D. E., MII S., MAHLER H. R., BOCK R. M. Studies on the fatty acid oxidizing system of animal tissues. III. Butyryl coenzyme A dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jan;206(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUGE J. G., CRANE F. L., BEINERT H. On the mechanism of dehydrogenation of fatty acyl derivatives of coenzyme A. III. Palmityl coA dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):727–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. L., Heijkenskjöld L., Bártfai T., Ernster L., Kamin H. Acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenases and electron-transferring flavoprotein from beef hart mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Dec;177(2):402–414. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90453-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. L., Kamin H. The purification and some properties of electron transfer flavoprotein and general fatty acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase from pig liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3476–3486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. L., Lambeth J. D., Kamin H. Acyl-CoA complexes of general acyl-CoA dehydrogenase and electron transfer flavoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):2023–2031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoskins D. D. The electron-transferring flavoprotein as a common intermediate in the mitochondrial oxidation of butyryl coenzyme A and sarcosine. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 10;241(19):4472–4479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi A., Yoshimura T., Okuda S. A new method for the preparation of acyl-CoA thioesters. J Biochem. 1981 Feb;89(2):337–339. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHLER H. R. Studies on the fatty acid oxidizing system of animal tissues. IV. The prosthetic group of butyryl coenzyme A dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jan;206(1):13–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhew S. G., Massey V. Purification and characterization of flavodoxin from Peptostreptococcus elsdenii. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):794–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda C., Rhead W. J., Tanaka K. Isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase: demonstration in rat liver mitochondria by ion exchange chromatography and isoelectric focusing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2646–2650. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERN J. R. Optical properties of aceto-acetyl-S-coenzyme A and its metal chelates. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jul;221(1):33–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEYN-PARVE E. P., BEINERT H. On the mechanism of dehydrogenation of fatty acyl derivatives of coenzyme A. VI. Isolation and properties of stable enzyme-substrate complexes. J Biol Chem. 1958 Oct;233(4):843–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEYN-PARVE E. P., BEINERT H. On the mechanism of dehydrogenation of fatty acyl derivatives of coenzyme A. VII. The nature of the green color of butyryl dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1958 Oct;233(4):853–861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Reinsch J., McFarland J. T. Mechanistic studies on fatty acyl-CoA dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11667–11670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeley T. L., Holmes R. S. Genetics and ontogeny of butyryl CoA dehydrogenase in the mouse and linkage of Bcd-1 with Dao-1. Biochem Genet. 1981 Apr;19(3-4):333–345. doi: 10.1007/BF00504278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe C., Ciardelli T. L., Stewart C. J., Wieland T. Interaction of long-chain acyl-CoA analogs with pig kidney general acyl-CoA dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Aug;118(2):279–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06397.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe C., Matthews R. G., Williams C. H., Jr Acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase from pig kidney. Purification and properties. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 23;18(2):331–337. doi: 10.1021/bi00569a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson G., Engel P. C. Butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase from Megasphaera elsdenii. Specificity of the catalytic reaction. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 1;218(2):521–529. doi: 10.1042/bj2180521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson G., Engel P. C., Mizzer J. P., Thorpe C., Massey V. Evidence that the greening ligand in native butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase is a CoA persulfide. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4314–4320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson G., Engel P. C., Nishina Y., Shiga K. A resonance Raman study on the nature of charge-transfer interactions in butyryl CoA dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1982 Feb 8;138(1):29–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80387-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


