Abstract
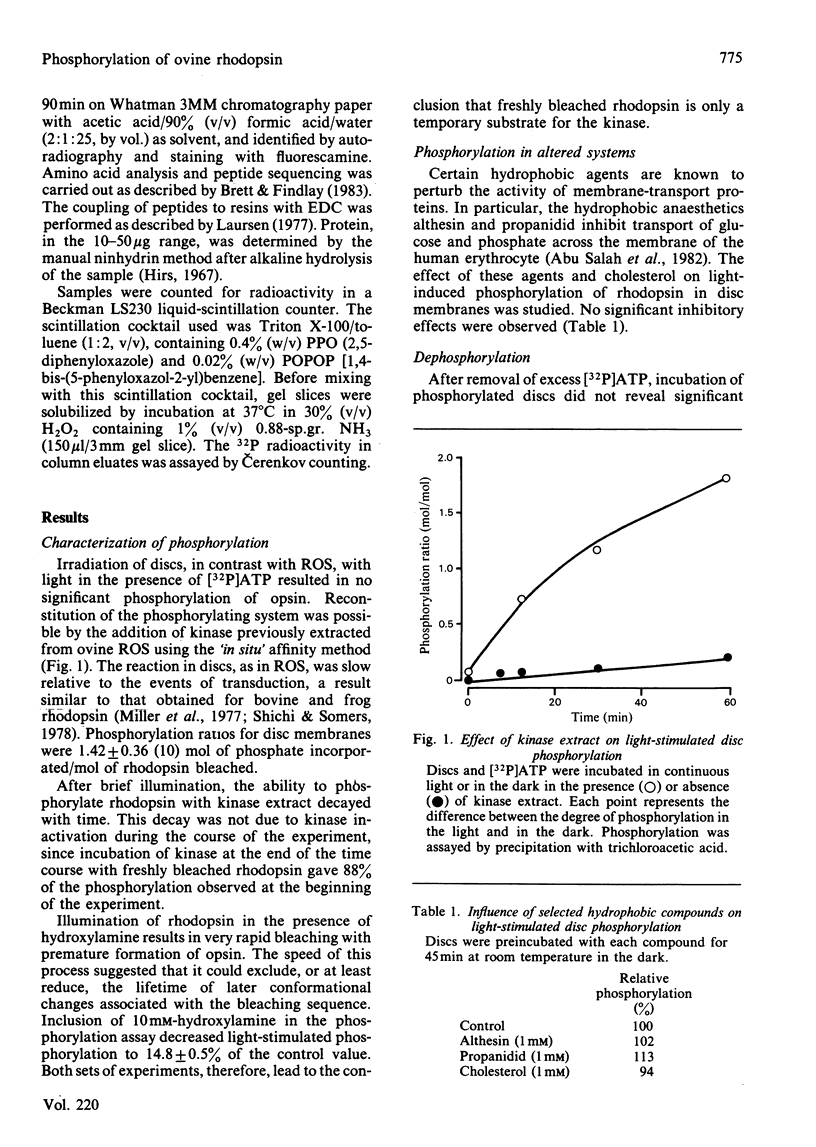
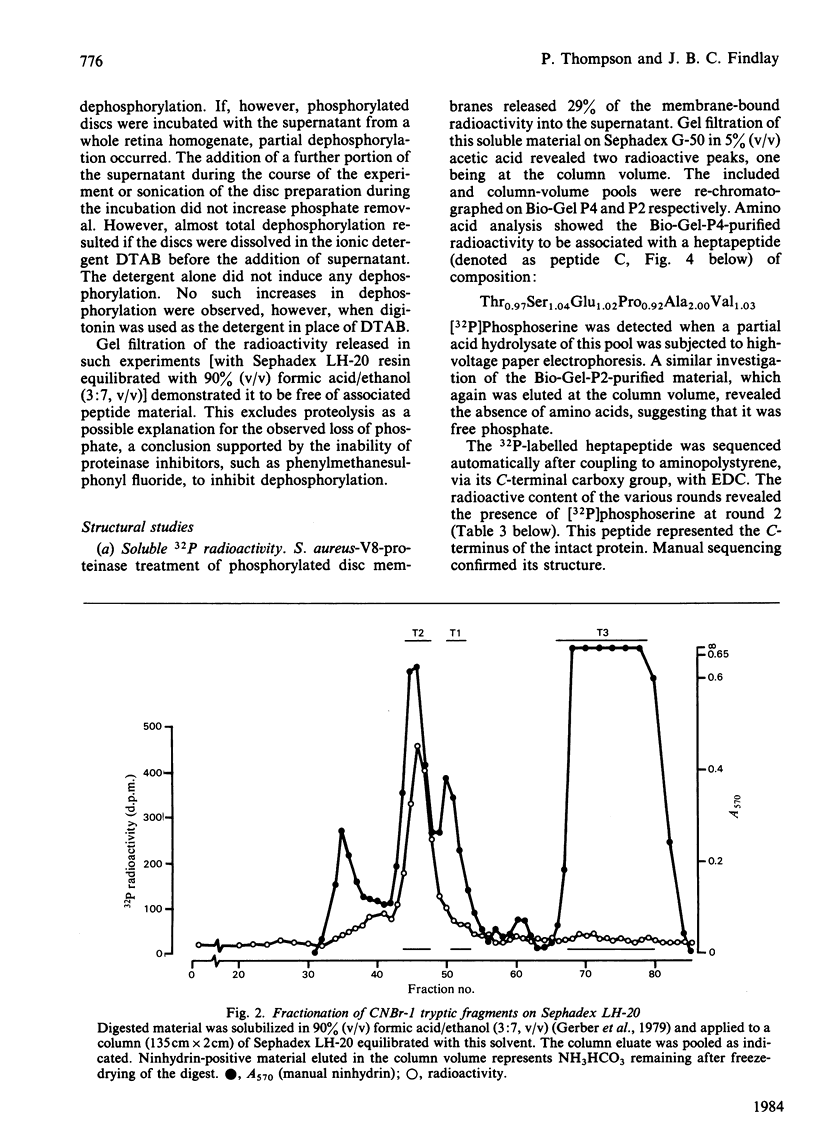
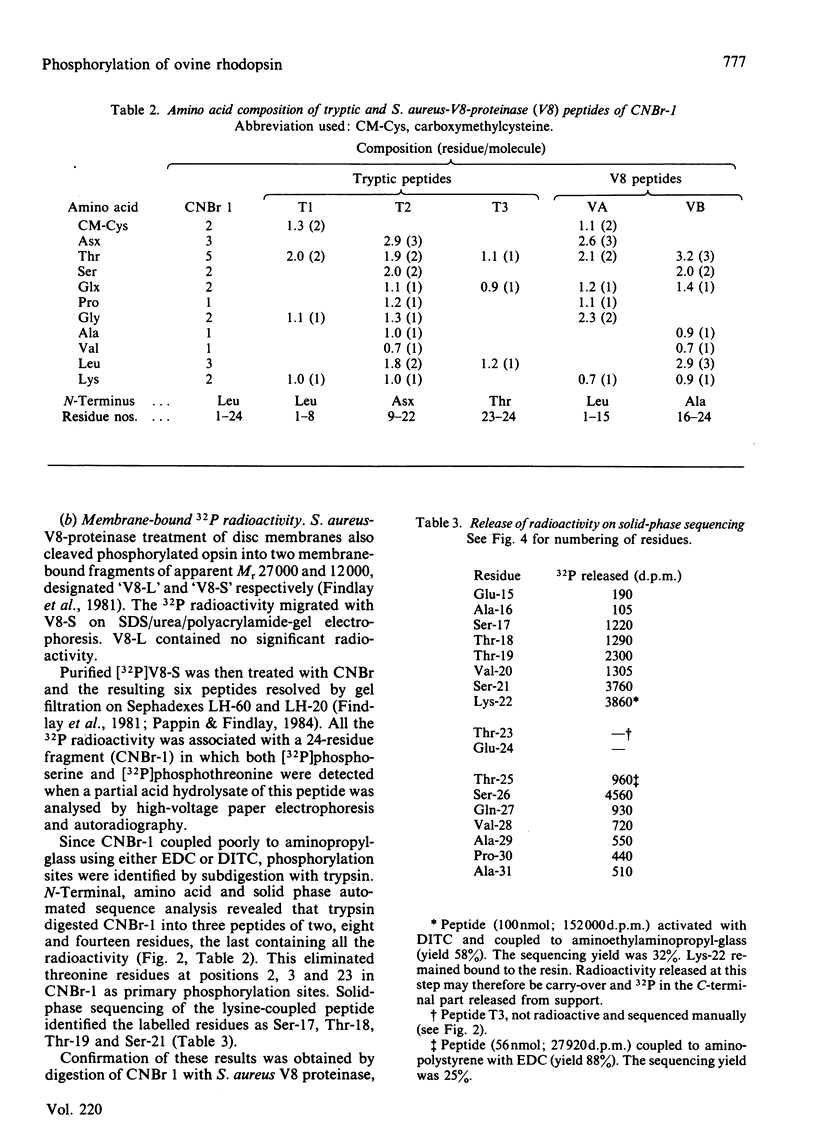
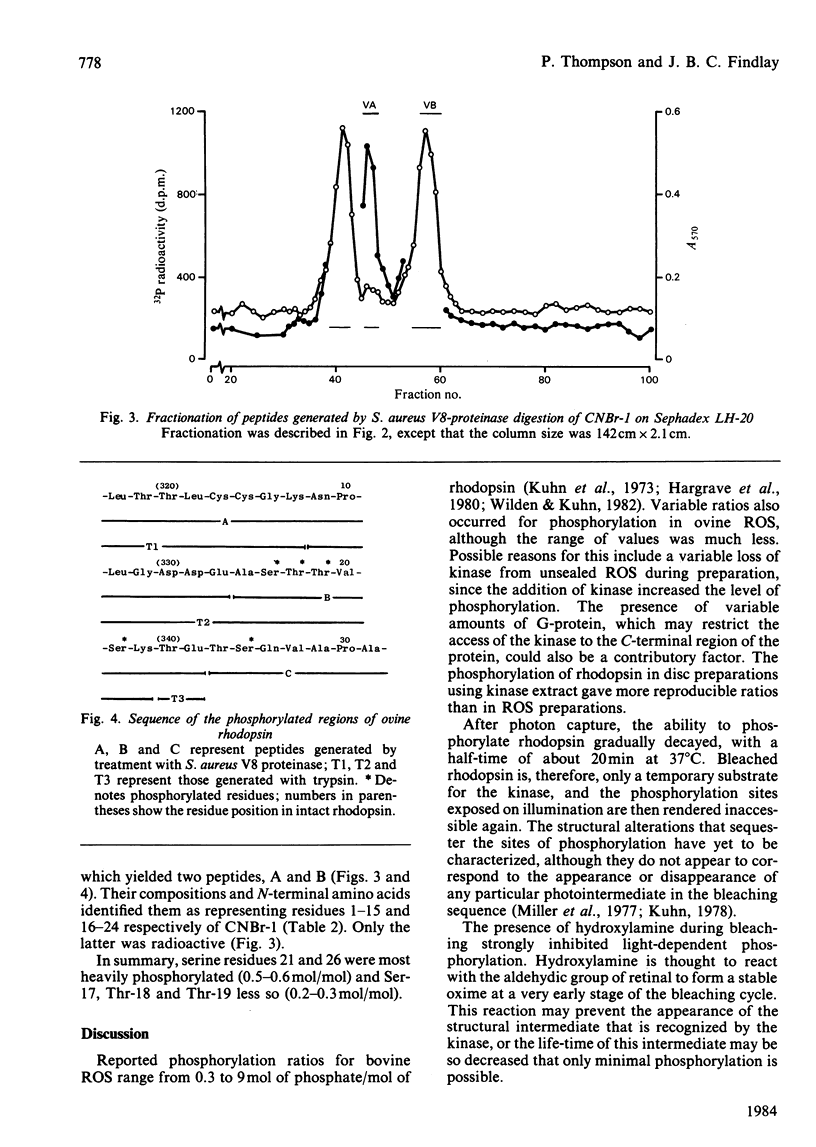
Light-dependent phosphorylation of sheep opsin was obtained in purified discs to which was added a partially purified preparation of rhodopsin kinase. A maximum ratio of 1.8 mol of phosphate/mol of rhodopsin bleached was obtained. Perturbing the lipid bilayer did not alter the phosphorylation ratio. Dephosphorylation in both segments and discs was only achieved when the supernatant fraction from a retina homogenate was added. Complete dephosphorylation required the presence of the detergent dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide in the incubation medium. Treatment of phosphorylated disc membranes with Staphylococcal aureus V8 proteinase generated two membrane-bound fragments, only one of which (V8-S, Mr 12 000) was labelled, together with a soluble seven-residue peptide that contained [32P]phosphoserine. Peptide sequencing, together with subdigestion procedures, localized the phosphorylation sites to serine residues at positions 334, 338 and 343 in the whole sequence and threonine residues at positions 335 and 336.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barclay P. L., Findlay J. B. Labelling of the cytoplasmic domains of ovine rhodopsin with hydrophilic chemical probes. Biochem J. 1984 May 15;220(1):75–84. doi: 10.1042/bj2200075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bownds D., Dawes J., Miller J., Stahlman M. Phosphorylation of frog photoreceptor membranes induced by light. Nat New Biol. 1972 May 24;237(73):125–127. doi: 10.1038/newbio237125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brett M., Findlay J. B. Investigation of the organization of rhodopsin in the sheep photoreceptor membrane by using cross-linking reagents. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):215–223. doi: 10.1042/bj1770215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brett M., Findlay J. B. Isolation and characterization of the CNBr peptides from the proteolytically derived N-terminal fragment of ovine opsin. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 1;211(3):661–670. doi: 10.1042/bj2110661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay J. B., Brett M., Pappin D. J. Primary structure of C-terminal functional sites in ovine rhodopsin. Nature. 1981 Sep 24;293(5830):314–317. doi: 10.1038/293314a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber G. E., Anderegg R. J., Herlihy W. C., Gray C. P., Biemann K., Khorana H. G. Partial primary structure of bacteriorhodopsin: sequencing methods for membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):227–231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H., Cook J. H., Dreyer W. J. Phosphorylation of rhodopsin in bovine photoreceptor membranes. A dark reaction after illumination. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 19;12(13):2495–2502. doi: 10.1021/bi00737a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H., Hargrave P. A. Light-induced binding of guanosinetriphosphatase to bovine photoreceptor membranes: effect of limited proteolysis of the membranes. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2410–2417. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H. Light-dependent phosphorylation of rhodopsin in living frogs. Nature. 1974 Aug 16;250(467):588–590. doi: 10.1038/250588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H. Light-regulated binding of rhodopsin kinase and other proteins to cattle photoreceptor membranes. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 17;17(21):4389–4395. doi: 10.1021/bi00614a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laursen R. A. Coupling techniques in solid-phase sequencing. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:277–288. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell J. H., Kühn H. Light-induced phosphorylation of rhodopsin in cattle photoreceptor membranes: substrate activation and inactivation. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 6;16(18):4054–4060. doi: 10.1021/bi00637a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. A., Paulsen R., Bownds M. D. Control of light-activated phosphorylation in frog photoreceptor membranes. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 14;16(12):2633–2639. doi: 10.1021/bi00631a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. A., Paulsen R. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of frog rod outer segment membranes as part of the visual process. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4427–4432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappin D. J., Findlay J. B. Sequence variability in the retinal-attachment domain of mammalian rhodopsins. Biochem J. 1984 Feb 1;217(3):605–613. doi: 10.1042/bj2170605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen R., Bentrop J. Activation of rhodopsin phosphorylation is triggered by the lumirhodopsin-metarhodopsin I transition. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):417–419. doi: 10.1038/302417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salah K. M., Hampton K. K., Findlay J. B. The effects of general anaesthetics on glucose and phosphate transport across the membrane of the human erythrocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 21;688(1):163–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90591-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sale G. J., Towner P., Akhtar M. Topography of the rhodopsin molecule. Identification of the domain phosphorylated. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):421–430. doi: 10.1042/bj1750421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shichi H., Somers R. L. Light-dependent phosphorylation of rhodopsin. Purification and properties of rhodopsin kinase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):7040–7046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swank R. T., Munkres K. D. Molecular weight analysis of oligopeptides by electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Anal Biochem. 1971 Feb;39(2):462–477. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacher S. M. Light-stimulated, magnesium-dependent ATPase in toad retinal rod outer segments. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 25;17(15):3005–3011. doi: 10.1021/bi00608a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller M., Virmaux N., Mandel P. Light-stimulated phosphorylation of rhodopsin in the retina: the presence of a protein kinase that is specific for photobleached rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilden U., Kühn H. Light-dependent phosphorylation of rhodopsin: number of phosphorylation sites. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 8;21(12):3014–3022. doi: 10.1021/bi00541a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


