Abstract
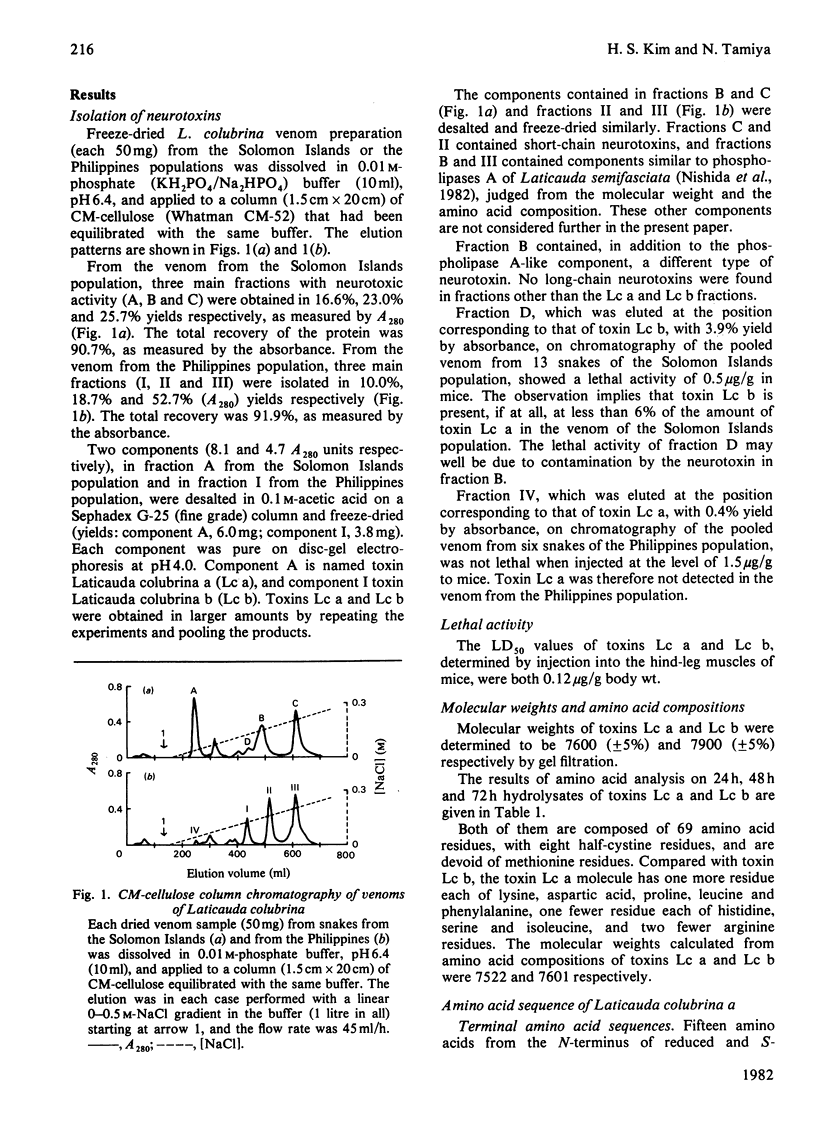
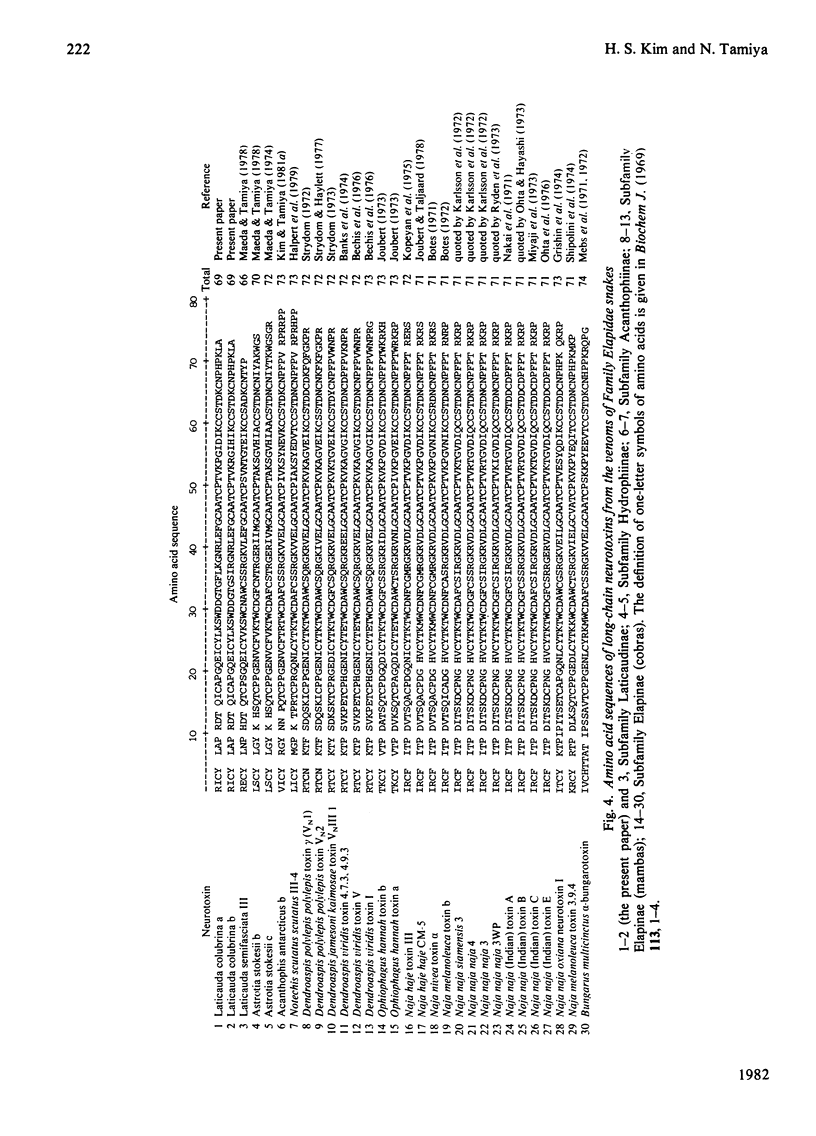
From the venom of a population of the sea snake Laticauda colubrina from the Solomon Islands, a neurotoxic component, Laticauda colubrina a (toxin Lc a), was isolated in 16.6% (A280) yield. Similarly, from the venom of a population of L. colubrina from the Philippines, a neurotoxic component, Laticauda colubrina b (toxin Lc b), was obtained in 10.0% (A280) yield. The LD50 values of these toxins were 0.12 microgram/g body wt. on intramuscular injection in mice. Toxins Lc a and Lc b were each composed of molecules containing 69 amino acid residues with eight half-cystine residues. The complete amino acid sequences of these two toxins were elucidated. Toxins Lc a and Lc b are different from each other at five positions of their sequences, namely at positions 31 (Phe/Ser), 32 (Leu/Ile), 33 (Lys/Arg), 50 (Pro/Arg) and 53 (Asp/His) (residues in parentheses give the residues in toxins Lc a and Lc b respectively). Toxins Lc a and Lc b have a novel structure in that they have only four disulphide bridges, although the whole amino acid sequences are homologous to those of other known long-chain neurotoxins. It is remarkable that toxins Lc a and Lc b are not coexistent at the detection error of 6% of the other toxin. Populations of Laticauda colubrina from the Solomon Islands and from the Philippines have either toxin Lc a or toxin Lc b and not both of them.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banks B. E., Miledi R., Shipolini R. A. The primary sequences and neuromuscular effects of three neurotoxic polypeptides from the venom of Dendroaspis viridis. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 15;45(2):457–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03570.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechis G., Granier C., Van Rietschoten J., Jover E., Rochat H., Miranda F. Purification of six neurotoxins from the venom of Dendroaspis viridis. Primary structure of two long toxins. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep 15;68(2):445–456. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10832.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botes D. P. Snake venom toxins. The amino acid sequences of toxins and from Naja nivea venom and the disulfide bonds of toxin . J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7383–7391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botes D. P. Snake venom toxins. The amino acid sequences of toxins b and d from Naja melanoleuca venom. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2866–2871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grishin E. V., Sukhikh A. P., Slobodyan L. N., Ovchinnikov YuA, Sorokin V. M. Amino acid sequence of neurotoxin I from Naja naja oxiana venom. FEBS Lett. 1974 Sep 1;45(1):118–121. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80825-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpert J., Fohlman J., Eaker D. Amino acid sequence of a postsynaptic neurotoxin from the venom of the Australian tiger snake Notechis scutatus scutatus. Biochimie. 1979;61(5-6):719–723. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(79)80172-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joubert F. J. Snake venom toxins the amino acid sequences of two toxins from Ophiophagus hannah (King cobra) venom. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 12;317(1):85–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joubert F., Taljaard N. Purification, some properties and the primary structures of three reduced and S-carboxymethylated toxins (CM-5, CM-6 and CM-10a) from Naje haje haje (Egyptian cobra) venom. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 20;537(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90597-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson E., Eaker D., Ponterius G. Modification of amino groups in Naja naja neurotoxins and the preparation of radioactive derivatives. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 29;257(2):235–248. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90275-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. S., Tamiya N. Isolation, properties and amino acid sequence of a long-chain neurotoxin, Acanthophis antarcticus b, from the venom of an Australian snake (the common death adder, Acanthophis antarcticus). Biochem J. 1981 Mar 1;193(3):899–906. doi: 10.1042/bj1930899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. S., Tamiya N. The amino acid sequence and position of the free thiol group of a short-chain neurotoxin from common-death-adder (Acanthophis antarcticus) venom. Biochem J. 1981 Oct 1;199(1):211–218. doi: 10.1042/bj1990211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopeyan C., Miranda F., Rochat H. Amino-acid sequence of toxin III of Naja haje. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Oct 1;58(1):117–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02355.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Tamiya N. Correction of partial amino acid sequence of erabutoxins. Biochem J. 1977 Oct 1;167(1):289–291. doi: 10.1042/bj1670289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Tamiya N. The primary structure of the toxin Laticauda semifasciata III, a weak and reversibly acting neurotoxin from the venom of a sea snake, Laticauda semifasciata. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;141(2):389–400. doi: 10.1042/bj1410389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Tamiya N. Three neurotoxins from the venom of a sea snake Astrotia stokesii, including two long-chain neurotoxic proteins with amidated C-termini. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):507–517. doi: 10.1042/bj1750507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. G., Fish W. W. Protein polypeptide chain molecular weights by gel chromatography in guanidinium chloride. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:28–42. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebs D., Narita K., Iwanaga S., Samejima Y., Lee C. Y. Amino acid sequence of -bungarotoxin from the venom of Bungarus multicinctus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Aug 6;44(3):711–716. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80141-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebs D., Narita K., Iwanaga S., Samejima Y., Lee C. Y. Purification, properties and amino acid sequence of -bungarotoxin from the venom of Bungarus multicinctus. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 Feb;353(2):243–262. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1972.353.1.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai K., Sasaki T., Hayashi K. Amino acid sequence of toxin A from the venom of the Indian cobra (Naja naja). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Aug 20;44(4):893–897. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90795-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickerson P. A., Kumar V. Electron microscopic studies of acetylcholinesterase from Bungarus fasciatus venom. Toxicon. 1974 Jan;12(1):83–84. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(74)90103-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ota M., Hayashi K. Localization of the five disulfide bridges in toxin B from the venom of the Indian cobra (Naja naja). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 16;55(2):431–438. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91105-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydén L., Gabel D., Eaker D. A model of the three-dimensional structure of snake venom neurotoxins based on chemical evidence. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1973;5(4):261–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1973.tb03460.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S., Tamiya N. The amino acid sequences of erabutoxins, neurotoxic proteins of sea-snake (Laticauda semifasciata) venom. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):453–461. doi: 10.1042/bj1220453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipolini R. A., Bailey G. S., Banks B. E. The separation of neurotoxin from the venom of Naja melanoleuca and the primary sequence determination. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Feb 15;42(1):203–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03330.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strydom D. J. Protease inhibitors as snake venom toxins. Nat New Biol. 1973 May 16;243(124):88–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strydom D. J. Snake venom toxins. The amino acid sequences of two toxins from Dendroaspis polylepis polylepis (black mamba) venom. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):4029–4042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda M., Yoshida H., Tamiya N. Biosynthesis of erabutoxins in the sea snake, Laticauda semif asciata. Toxicon. 1974 Dec;12(6):633–641. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(74)90198-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamiya N., Abe H. The isolation, properties and amino acid sequence of erabutoxin c, a minor neurotoxic component of the venom of a sea snake Katicauda semifasciata. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(2):547–555. doi: 10.1042/bj1300547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamiya N. Erabutoxins a, b and c in sea snake Laticauda semifasciata venom. Toxicon. 1973 Jan;11(1):95–97. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(73)90158-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


