Abstract
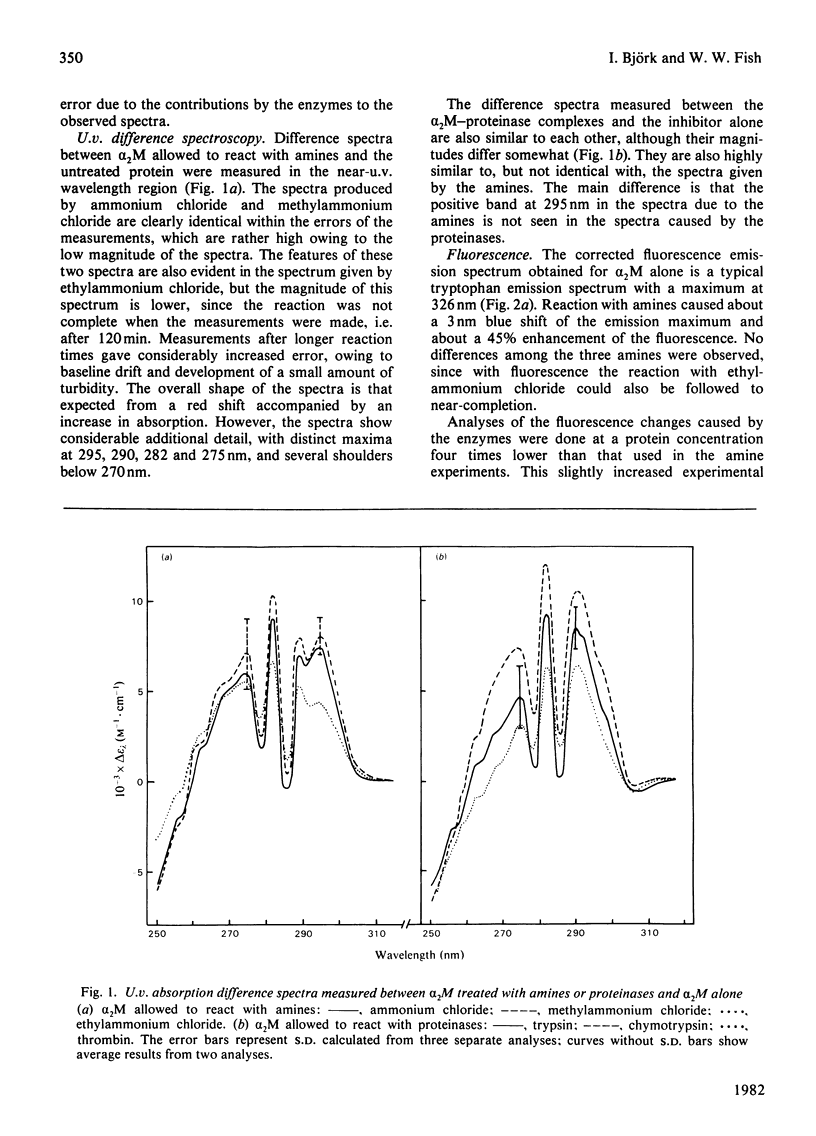
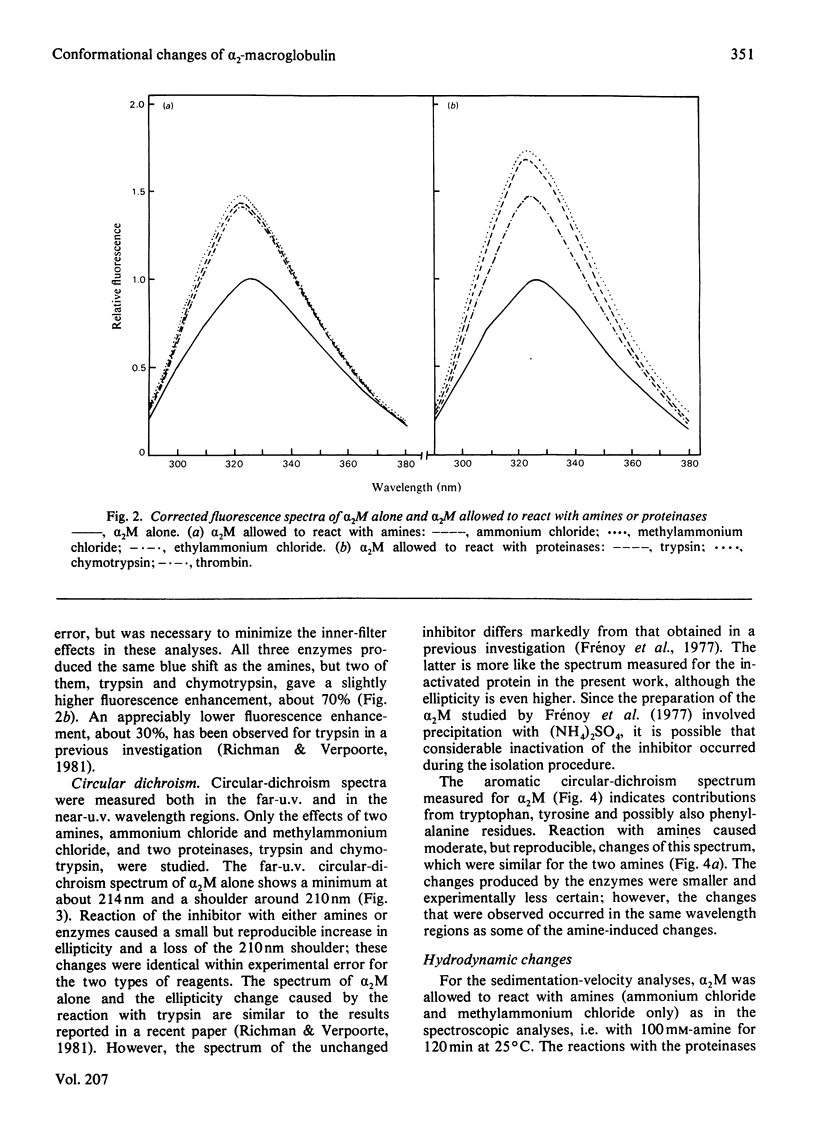
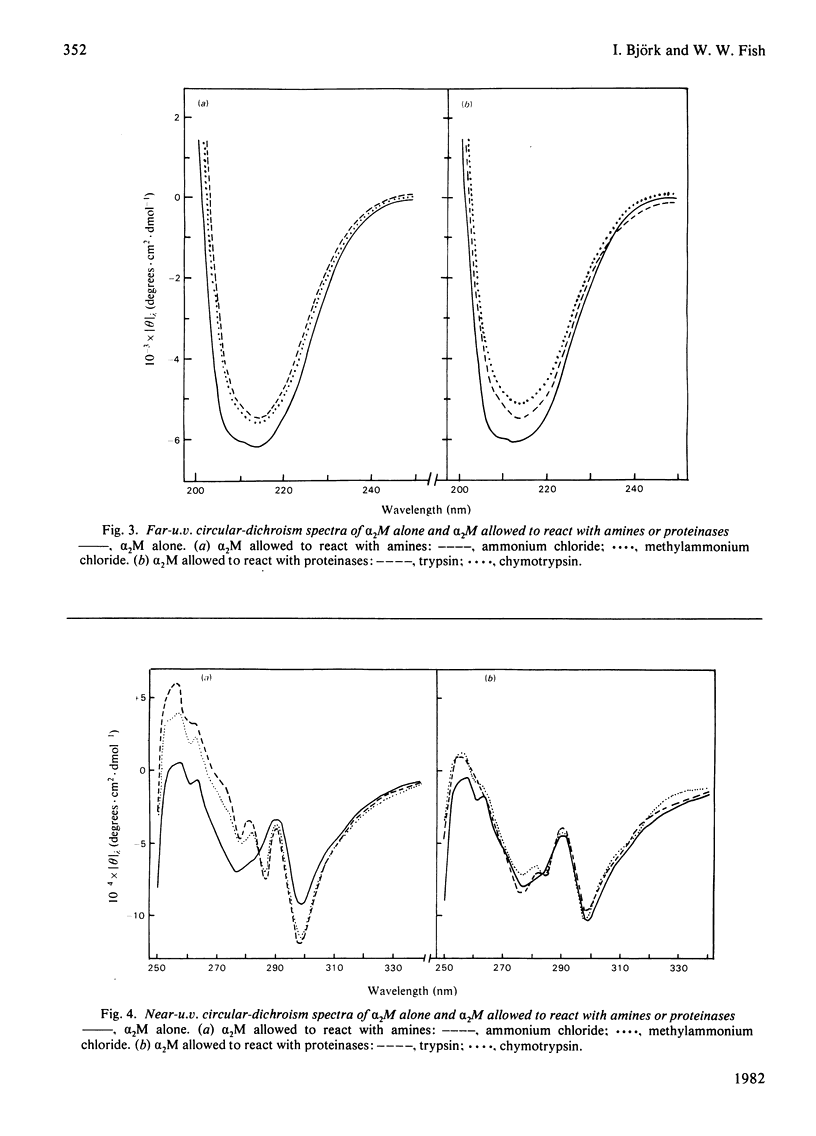
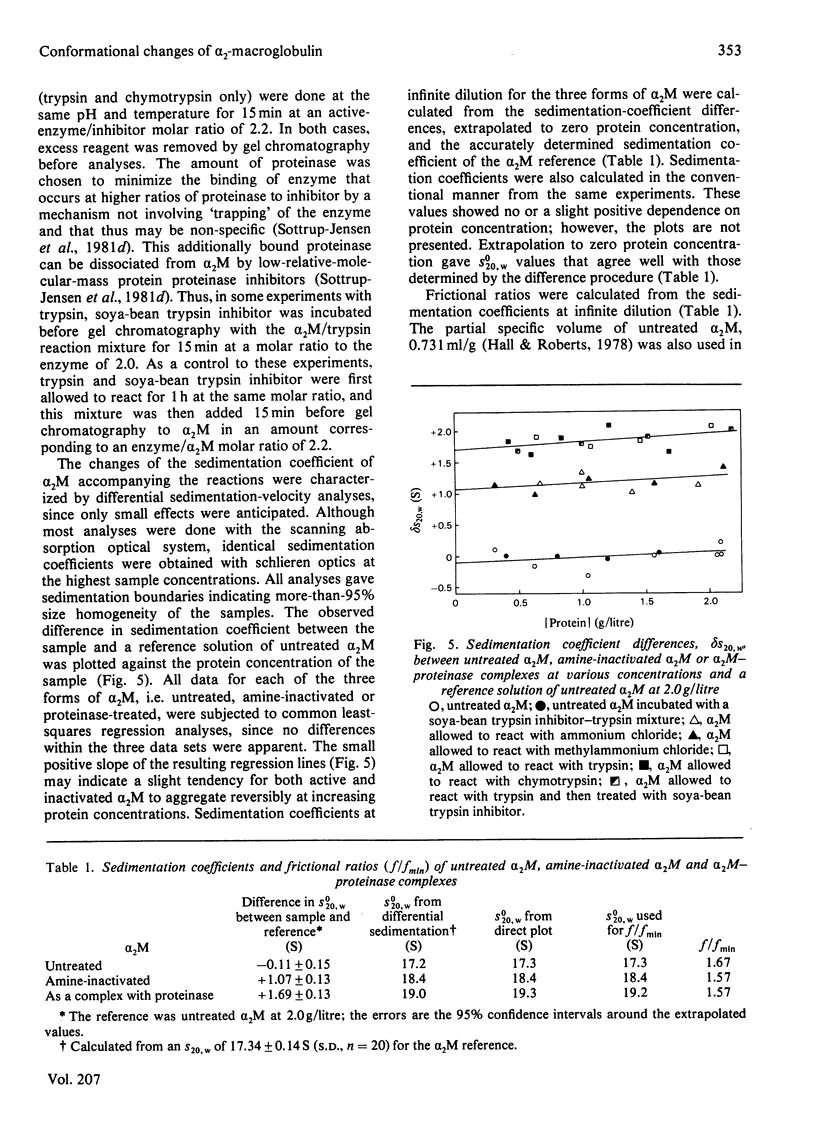
Reactions of α2-macroglobulin (α2M) with primary amines (ammonium chloride, methylammonium chloride and ethylammonium chloride) or proteolytic enzymes (trypsin, chymotrypsin and thrombin) resulted in changes of the absorption, fluorescence and circular-dichroism spectra and of the sedimentation coefficient of the inhibitor. All physico-chemical changes caused by the inactivation of α2M by the amines were identical with, or highly similar to, those induced by the formation of the enzyme–inhibitor complexes. This suggests that similar conformational changes of the inhibitor occur in the two types of reactions. The frictional ratio, calculated from the increase in sedimentation coefficient, decreased from 1.67 for untreated α2M to 1.57 for the amine- or proteinase-treated inhibitor. This change is due to a decrease in either asymmetry or hydration of the protein, resulting in a slightly smaller hydrodynamic volume. The circular-dichroism analyses indicated that the reaction of α2M with either amines or proteinases is accompanied by a loss of the small amount (about 5%) of α-helix of the untreated protein. The changes of u.v. absorption and fluorescence suggested that about one out of the eight to ten tryptophan residues of each α2M subunit is buried as a result of the conformational change. All spectroscopic and hydrodynamic changes that were observed are compatible with a spatial rearrangement of the subunits of α2M, as implicated by the `trap' hypothesis for the mechanism of inhibition of proteinases. However, a conformational change involving a decrease in the hydrodynamic volume of each subunit cannot be excluded.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett A. J., Brown M. A., Sayers C. A. The electrophoretically 'slow' and 'fast' forms of the alpha 2-macroglobulin molecule. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 1;181(2):401–418. doi: 10.1042/bj1810401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Starkey P. M. The interaction of alpha 2-macroglobulin with proteinases. Characteristics and specificity of the reaction, and a hypothesis concerning its molecular mechanism. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;133(4):709–724. doi: 10.1042/bj1330709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlström A. S., Liedén K., Björk I. Decreased binding of heparin to antithrombin following the interaction between antithrombin and thrombin. Thromb Res. 1977 Dec;11(6):785–797. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Yang J. T., Martinez H. M. Determination of the secondary structures of proteins by circular dichroism and optical rotatory dispersion. Biochemistry. 1972 Oct 24;11(22):4120–4131. doi: 10.1021/bi00772a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONOVAN J. W. THE SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC TITRATION OF THE SULFHYDRYL AND PHENOLIC GROUPS OF ALDOLASE. Biochemistry. 1964 Jan;3:67–74. doi: 10.1021/bi00889a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debanne M. T., Bell R., Dolovich J. Uptake of proteinase-alpha-macroglobulin complexes by macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 5;411(2):295–304. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90309-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan J. W. Ultraviolet difference spectroscopy--new techniques and applications. Methods Enzymol. 1973;27:497–525. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(73)27024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. T., Spiro R. G. The alpha 2-macroglobulin of human plasma. I. Isolation and composition. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 10;242(23):5549–5555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish W. W., Orre K., Björk I. The production of an inactive form of antithrombin through limited proteolysis by thrombin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Feb 1;98(1):103–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frénoy J. P., Bourrillon R., Lippoldt R., Edelhoch H. Stability and subunit structure of human alpha2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1129–1133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganrot P. O. The combining ratio between trypsin and serum alpha-2-macroglobulin. Acta Chem Scand. 1966;20(8):2299–2300. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.20-2299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield N., Fasman G. D. Computed circular dichroism spectra for the evaluation of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):4108–4116. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTLEY B. S. AMINO-ACID SEQUENCE OF BOVINE CHYMOTRYPSINOGEN-A. Nature. 1964 Mar 28;201:1284–1287. doi: 10.1038/2011284a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. K., Roberts R. C. Physical and chemical properties of human plasma alpha2-macroglobulin. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 1;173(1):27–38. doi: 10.1042/bj1730027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Human alpha2-macroglobulin. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:639–652. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Studies on human plasma alpha 2-macroglobulin-enzyme interactions. Evidence for proteolytic modification of the subunit chain structure. J Exp Med. 1973 Sep 1;138(3):508–521. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.3.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley B. S., Kauffman D. L. Corrections to the amino acid sequence of bovine chymotrypsinogen A. Biochem J. 1966 Oct;101(1):229–231. doi: 10.1042/bj1010229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. B. Reactive site in human alpha 2-macroglobulin: circumstantial evidence for a thiolester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2235–2239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imber M. J., Pizzo S. V. Clearance and binding of two electrophoretic "fast" forms of human alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8134–8139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. M., Creeth J. M., Kekwick R. A. Thio reduction of human 2 -macroglobulin. The subunit structure. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):187–197. doi: 10.1042/bj1270187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J., Nielsen M. L. Analysis of macrophage surface receptors. I. Binding of alpha-macroglobulin . protease complexes to rabbit alveolar macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7323–7328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J., Nielsen M. L. Analysis of macrophage surface receptors. II. Internalization of alpha-macroglobulin . trypsin complexes by rabbit alveolar macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7329–7335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J., Ray F. A., Keogh E. A. Recognition of nucleophile-treated alpha 2-macroglobulin by the alveolar macrophage alpha-macroglobulin . protease complex receptor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7705–7707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurecki T., Kress L. F., Laskowski M., Sr Purification of human plasma alpha 2 macroglobulin and alpha 1 proteinase inhibitor using zinc chelate chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;99(2):415–420. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pochon F., Amand B., Lavalette D., Bieth J. Rotational relaxation of free and protease-bound alpha2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7496–7499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman J. B., Verpoorte J. A. The optical properties of alpha 2-macroglobulin from normal and from cystic fibrosis plasma. Can J Biochem. 1981 Jul;59(7):519–523. doi: 10.1139/o81-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson N. C., Tye R. W., Neurath H., Walsh K. A. Isolation of trypsins by affinity chromatography. Biochemistry. 1971 Jul 6;10(14):2743–2747. doi: 10.1021/bi00790a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWERT G. W., KAUFMAN S. The molecular size and shape of the pancreatic proteases. III. alpha-Chymotrypsin. J Biol Chem. 1951 Jun;190(2):807–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvesen G. S., Barrett A. J. Covalent binding of proteinases in their reaction with alpha 2-macroglobulin. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 1;187(3):695–701. doi: 10.1042/bj1870695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvesen G. S., Sayers C. A., Barrett A. J. Further characterization of the covalent linking reaction of alpha 2-macroglobulin. Biochem J. 1981 May 1;195(2):453–461. doi: 10.1042/bj1950453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumaker V., Adams P. Differential sedimentation coefficients. I. Precise measurement. Determination of concentration dependence for IgG-immunoglobulin. Biochemistry. 1968 Oct;7(10):3422–3427. doi: 10.1021/bi00850a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottrup-Jensen L., Hansen H. F., Mortensen S. B., Petersen T. E., Magnusson S. Sequence location of the reactive thiol ester in human alpha 2-macroglobulin. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jan 12;123(1):145–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80039-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottrup-Jensen L., Lønblad P. B., Stepanik T. M., Petersen T. E., Magnusson S., Jörnvall H. Primary structure of the 'bait' region for proteinases in alpha 2-macroglobulin. Nature of the complex. FEBS Lett. 1981 May 18;127(2):167–173. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80197-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottrup-Jensen L., Petersen T. E., Magnusson S. A thiol-ester in alpha 2-macroglobulin cleaved during proteinase complex formation. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 1;121(2):275–279. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80361-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottrup-Jensen L., Petersen T. E., Magnusson S. Trypsin-induced activation of the thiol esters in alpha 2-macroglobulin generates a short-lived intermediate ('nascent' alpha 2-M) that can react rapidly to incorporate not only methylamine or putrescine but also proteins lacking proteinase activity. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 1;128(1):123–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbuch M., Pejaudier L., Quentin M., Martin V. Molecular alteration of alpha-2-macroglobulin by aliphatic amines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 22;154(1):228–231. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90277-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson R. P., Howard J. B. Amino acid sequence of the tryptic peptide containing the alkylamine-reactive site from human alpha 2-macroglobulin. Identification of gamma-glutamylmethylamide. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8087–8091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson R. P., Howard J. B. Characterization of alkylamine-sensitive site in alpha 2-macroglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4313–4316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson R. P., Howard J. B. Structural characterization of human alpha2-macroglobulin subunits. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4452–4456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIETZE F. Molecular-kinetic properties of crystalline trypsinogen. J Biol Chem. 1953 Sep;204(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Leuven F., Cassiman J. J., Van Den Berghe H. Demonstration of an alpha2-macroglobulin receptor in human fibroblasts, absent in tumor-derived cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5155–5160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALSH K. A., NEURATH H. TRYPSINOGEN AND CHYMOTRYPSINOGEN AS HOMOLOGOUS PROTEINS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:884–889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Wu K., Feinman R. D. Alpha 2-macroglobulin-protease reactions: relationship of covalent bond formation, methylamine reactivity, and specific proteolysis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Oct 1;211(1):500–506. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90483-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu K., Wang D., Feinman R. D. Inhibition of proteases by alpha 2-macroglobulin. The role of lysyl amino groups of trypsin in covalent complex formation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10409–10414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yung B. Y., Trowbridge C. G. Resolution of alpha and beta anhydrotrypsin by affinity chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Aug 4;65(3):927–930. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80474-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


