Abstract
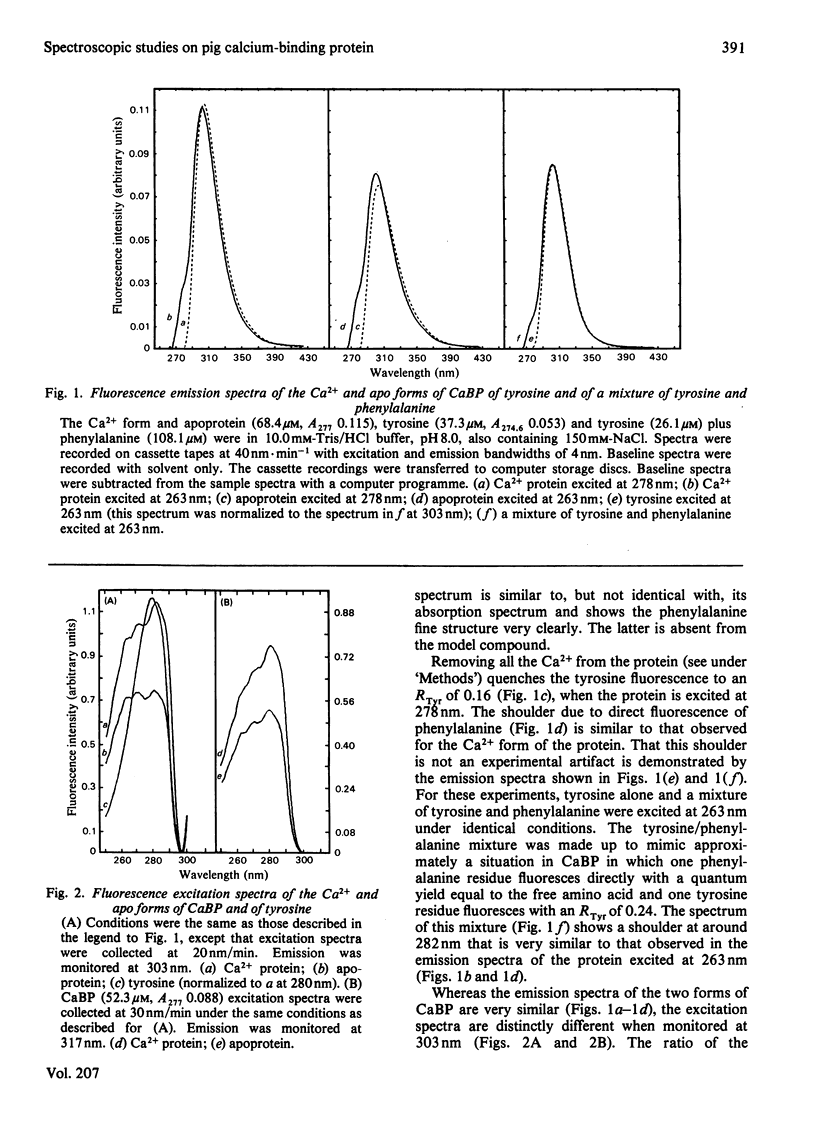
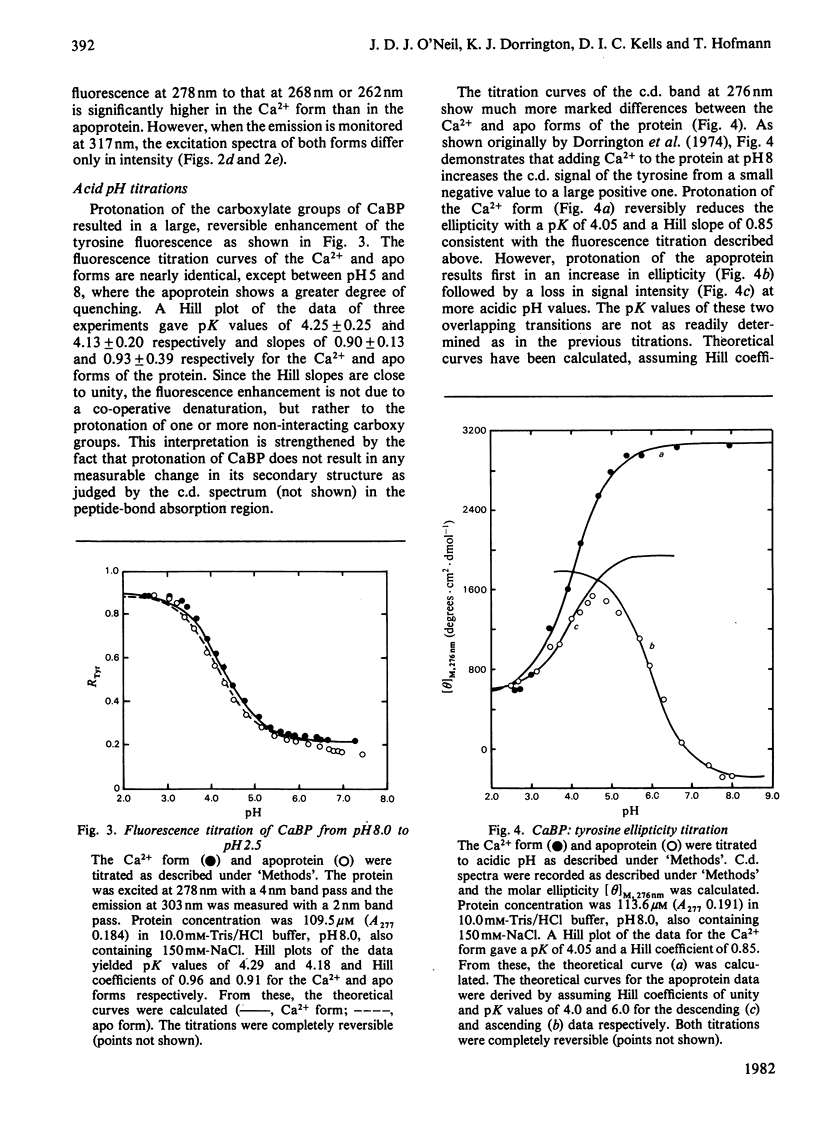
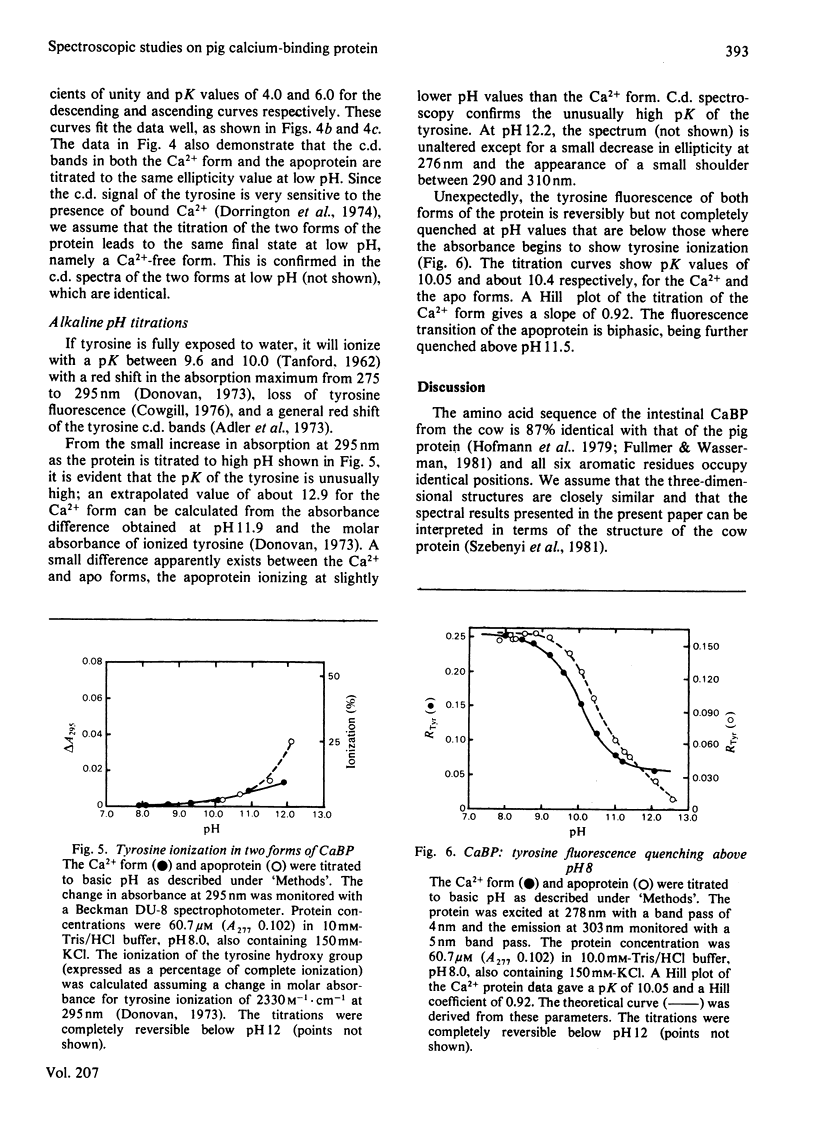
Spectral properties of pig intestinal Ca2+-binding protein (CaBP) and its apoprotein have been examined by fluorescence, absorption and c.d. Direct fluorescence from some of the five phenylalanine residues is observed and excitation spectra show that there is also energy transfer from some phenylalanine residues to the tyrosine. Absorption and c.d. spectra show that the tyrosine hydroxy group does not ionize significantly below pH 12. Tyrosine fluorescence is reversibly quenched by a lysine residue with a pK of 10.05 in the Ca2+ form. At low pH the tyrosine fluorescence is enhanced with transitions with pK values of approx. 4.2. The c.d. spectrum of the Ca2+ form shows a decrease of the ellipticity band at 276nm with a transition similar to that of the fluorescence titration. The apoprotein, however, shows an additional transition with a pK of about 6. The results are interpreted in terms of the recently published structure of the cow intestinal CaBP [Szebenyi, Obendorf & Moffat (1981) Nature (London) 294, 327-332]. The single tyrosine has a very high pK, although it apparently lies on the surface of the protein molecule.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler A. J., Greenfield N. J., Fasman G. D. Circular dichroism and optical rotatory dispersion of proteins and polypeptides. Methods Enzymol. 1973;27:675–735. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(73)27030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker W. C., Dayhoff M. O. Evolution of homologous physiological mechanisms based on protein sequence data. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1979;62(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(79)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):19–27. doi: 10.1126/science.6243188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowgill R. W. Fluorescence and protein structure. XIV. Tyrosine fluorescence in helical muscle proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Dec 3;168(3):417–430. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan J. W. Spectrophotometric titration of the functional groups of proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1973;27:525–548. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(73)27025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorrington K. J., Hui A., Hofmann T., Hitchman A. J., Harrison J. E. Porcine intestinal calcium-binding protein. Molecular properties and the effect of binding calcium ions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):199–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorrington K. J., Kells D. I., Hitchman A. J., Hartison J. E., Hofmann T. Spectroscopic studies on the binding of divalent cations to porcine intestinal calcium-binding protein. Can J Biochem. 1978 Jun;56(6):492–499. doi: 10.1139/o78-076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drescher D., DeLuca H. F. Vitamin D stimulated calcium binding protein from rat intestinal mucosa. Purification and some properties. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 8;10(12):2302–2307. doi: 10.1021/bi00788a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Mikawa T., Hirata M., Nonomura Y. The regulatory role of calcium in muscle. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Apr 28;307:451–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb41975.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullmer C. S., Wasserman R. H. The amino acid sequence of bovine intestinal calcium-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5669–5674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchman A. J., Harrison J. E. Calcium binding proteins in the duodenal mucosa of the chick, rat, pig, and human. Can J Biochem. 1972 Jul;50(7):758–765. doi: 10.1139/o72-106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann T., Kawakami M., Hitchman A. J., Harrison J. E., Dorrington K. J. The amino acid sequence of porcine intestinal calcium-binding protein. Can J Biochem. 1979 Jun;57(6):737–748. doi: 10.1139/o79-092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallfelz F. A., Taylor A. N., Wasserman R. H. Vitamin D-induced calcium binding factor in rat intestinal mucosa. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 May;125(1):54–58. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Crouch T. H., Richman P. G. Calmodulin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:489–515. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H. The informational role of calcium in the cytosol. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;11:1–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. R., Dedman J. R. Calmodulin--an intracellular calcium receptor. Nature. 1980 May 8;285(5760):73–77. doi: 10.1038/285073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray T. M., Arnold B. M., Tam W. H., Hitchman A. J., Harrison J. E. A radioimmunoassay for a procine intestinal calcium-binding protein. Metabolism. 1974 Sep;23(9):829–837. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(74)90116-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry S. V. The regulation of contractile activity in muscle. Biochem Soc Trans. 1979 Aug;7(4):593–617. doi: 10.1042/bst0070593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Goodman D. B. Relationships between calcium and cyclic nucleotides in cell activation. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jul;57(3):421–509. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.3.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szebenyi D. M., Obendorf S. K., Moffat K. Structure of vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein from bovine intestine. Nature. 1981 Nov 26;294(5839):327–332. doi: 10.1038/294327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER G., ROSENHECK K. PROTON-TRANSFER EFFECTS IN THE QUENCHING OF FLUORESCENCE OF TYROSINE COPOLYMERS. Biopolym Symp. 1964;13:333–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE A. Effect of pH on fluorescence of tryosine, tryptophan and related compounds. Biochem J. 1959 Feb;71(2):217–220. doi: 10.1042/bj0710217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman R. H., Corradino R. A., Taylor A. N. Vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein. Purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 25;243(14):3978–3986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


