Abstract
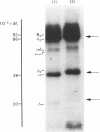
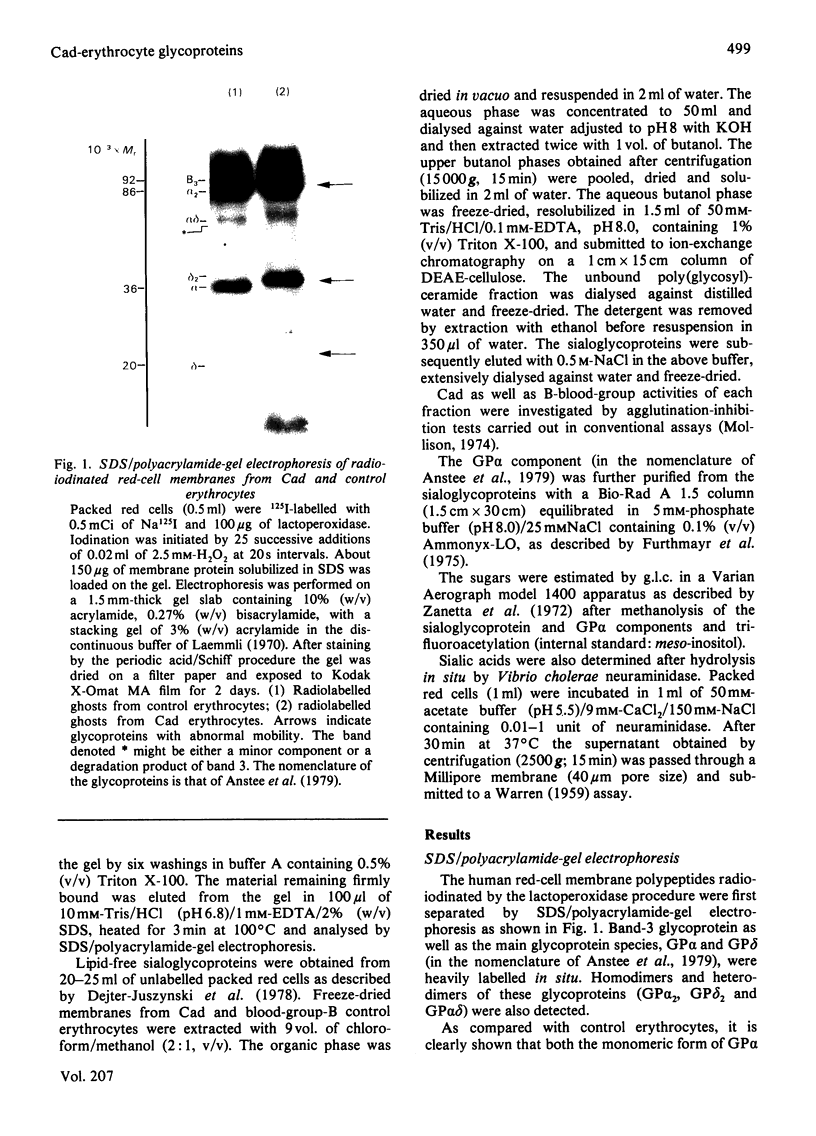
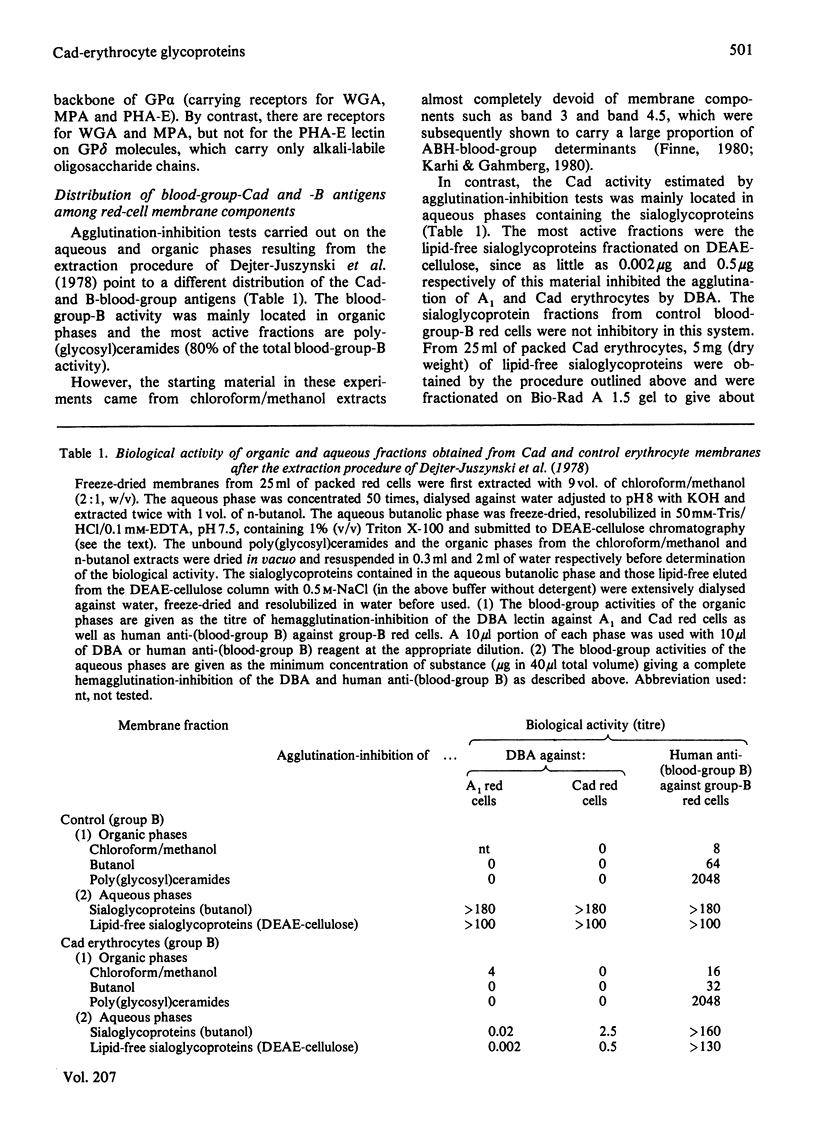
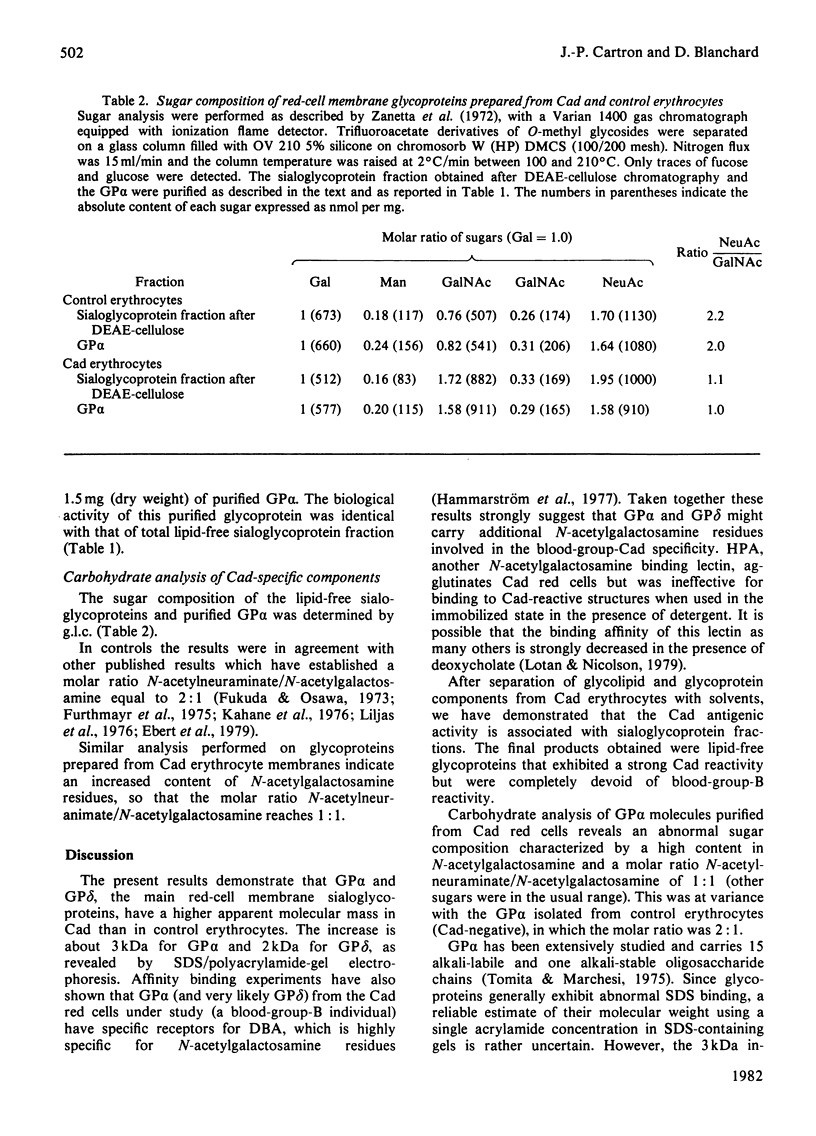
Sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis of erythrocyte membranes from a blood-group-B individual with the rare Cad phenotype indicates a lower-than-normal mobility of the main sialoglycoproteins, suggesting an increase in apparent molecular mass of 3kDa and 2kDa respectively for glycoprotein alpha (synonym glycophorin A) and glycoprotein delta (synonym glycophorin B). Since the chief structural determinant of Cad specificity is N-acetylgalactosamine, the membrane receptors have been isolated by affinity binding on immobilized Dolichos biflorus (horse gram) lectin. The predominant species eluted from the gel was the abnormal glycoprotein alpha, whereas in control experiments no material could be recovered from the adsorbent incubated with group-B Cad-negative erythrocyte membranes. After partition of the membranes with organic solvents, the blood-group-Cad activity was found in aqueous phases containing the sialoglycoproteins, but not in the organic phases containing simple or complex glycolipids, which, however, retained the blood-group-B activity. The carbohydrate composition of highly purified lipid-free glycoprotein alpha molecules prepared from Cad and control erythrocytes was determined. Interestingly the molar ratio of N-acetylneuraminic acid to N-acetylgalactosamine was equal to 2:1 in the case of controls and equal to 1:1 in the case of Cad erythrocytes. Taken together these results suggest that Cad specificity is defined by N-acetylgalactosamine residues carried by the alkali-labile oligosaccharide chains attached to the erythrocyte membrane sialo-glycoproteins.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anstee D. J., Mawby W. J., Tanner M. J. Abnormal blood-group-Ss-active sialoglycoproteins in the membrane of Miltenberger class III, IV and V human erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 1;183(2):193–203. doi: 10.1042/bj1830193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird G. W., Wingham J. Haemagglutinins from Salvia. Vox Sang. 1974 Feb;26(2):163–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird G. W., Wingham J. Some serological properties of the Cad receptor. Vox Sang. 1971 Jan;20(1):55–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1971.tb01800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bizot M., Cayla J. P. Hétéro-anticorps anti-CAD du poulet. Rev Fr Transfus. 1972 Jun;15(2):195–202. doi: 10.1016/s0035-2977(72)80017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard D., Cartron J. P., Rouger P., Salmon C. Pj variant, a new hybrid MNSs glycoprotein of the human red-cell membrane. Biochem J. 1982 May 1;203(2):419–426. doi: 10.1042/bj2030419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORNELIUS C. E., MIA A. S., ROSENFELD S. RUMINANT UROLITHIASIS. VII. STUDIES ON THE ORIGIN OF TAMM-HORSFALL URINARY MUCOPROTEIN AND ITS PRESENCE IN OVINE CALCULOUS MATRIX. Invest Urol. 1965 Mar;2:453–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartron J. P., Kornprobst M., Lemonnier M., Lambin P., Piller F., Salmon C. Isolation from human urines of a mucin with blood group SDa activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):331–337. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91114-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazal P., Monis M., Bizot M. Les antigènes Cad et leurs rapports avec les antigènes. Rev Fr Transfus. 1971 Sep;14(3):321–334. doi: 10.1016/s0035-2977(71)80023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazal P., Monis M., Caubel J., Brives J. Polyagglutinabilité héréditaire dominante: antigène privé (Cad) correspondant à un anticorps public et à une lectine de Dolichos biflorus. Rev Fr Transfus. 1968 Oct 3;11(3):209–221. doi: 10.1016/s0035-2977(68)80050-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahr W., Uhlenbruck G., Janssen E., Schmalisch R. Heterogeneity of human cell membrane sialoglycoproteins. Blut. 1976 Mar;32(3):171–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00995910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejter-Juszynski M., Harpaz N., Flowers H. M., Sharon N. Blood-group ABH-specific macroglycolipids of human erythrocytes: isolation in high yield from a crude membrane glycoprotein fraction. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Feb;83(2):363–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald A. S., Soh C. P., Watkins W. M., Morgan W. T. N-Acetyl-D-galactosaminyl-beta-(1 goes to 4)-d-galactose: a terminal non-reducing structure in human blood group Sda-active Tamm-Horsfall urinary glycoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 15;104(1):58–65. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91940-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert W., Fey J., Gärtner C., Geisen H. P., Rautenberg U., Roelcke D., Weicker H. Isolation and partial characterization of the Pr autoantigen determinants. Mol Immunol. 1979 Jun;16(6):413–419. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90109-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda M., Osawa T. Isolation and characterization of a glycoprotein from human group O erythrocyte membrane. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):5100–5105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furthmayr H., Tomita M., Marchesi V. T. Fractionation of the major sialoglycopeptides of the human red blood cell membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):113–121. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80068-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahmberg C. G., Andersson L. C. Role of sialic acid in the mobility of membrane proteins containing O-linked oligosaccharides on polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Mar 1;122(3):581–586. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerbal A., Lopez M., Chassaigne M., Genetet B., Selva J., Yvart J., Salmon C. L'antigène Cad dans la population française. Rev Fr Transfus Immunohematol. 1976 Sep;19(3):415–429. doi: 10.1016/s0338-4535(76)80018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerbal A., Lopez M., Maslet C., Salmon C. Polyagglutinability associated with the cad antigen. Haematologia (Budap) 1976;10(3-4):383–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström S., Murphy L. A., Goldstein I. J., Etzler M. E. Carbohydrate binding specificity of four N-acetyl-D-galactosamine- "specific" lectins: Helix pomatia A hemagglutinin, soy bean agglutinin, lima bean lectin, and Dolichos biflorus lectin. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 14;16(12):2750–2755. doi: 10.1021/bi00631a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane I., Furthmayr H., Marchesi V. T. Isolation of membrane glycoproteins by affinity chromatography in the presence of detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 19;426(3):464–476. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90391-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karhi K. K., Gahmberg C. G. Identification of blood group A-active glycoproteins in the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 25;622(2):344–354. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljas L., Lundahl P., Hjertén S. The major sialoglycoprotein of the human erythrocyte membrane. Release with a non-ionic detergent and purification. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 19;426(3):526–534. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90396-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R., Nicolson G. L. Purification of cell membrane glycoproteins by lectin affinity chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 20;559(4):329–376. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton J. A., Pickles M. M., Terry A. M. The Sda blood group antigen in tissues and body fluids. Vox Sang. 1970 Nov-Dec;19(5):472–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1970.tb01779.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohayon E., Ouhayoun E., Marty Y., Pris J., Ducos J. La spécificité anti-Rh de certaines cellules formant des rosettes. Rev Fr Transfus. 1972 Mar;15(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/s0035-2977(72)80027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger R., Gavin J., Tippett P., Teesdale P., Eldon K. Plant agglutinin for another human blood-group. Lancet. 1971 May 29;1(7709):1130–1130. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91865-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin B. C., Carraway K. L. Lactoperoxidase labeling of erythrocyte membranes from the inside and outside. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 29;345(2):141–153. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikri K. L., Foster C. L., Bloomfield F. J., Marshall R. D. Localization by immunofluorescence and by light- and electron-microscopic immunoperoxidase techniques of Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein in adult hamster kidney. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 1;181(3):525–532. doi: 10.1042/bj1810525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soh C. P., Morgan W. T., Watkins W. M., Donald A. S. The relationship between the N-acetylgalactosamine content and the blood group Sda activity of Tamm and Horsfall urinary glycoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 29;93(4):1132–1139. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90607-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Kant J. A. Preparation of impermeable ghosts and inside-out vesicles from human erythrocyte membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:172–180. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMM I., HORSFALL F. L., Jr Characterization and separation of an inhibitor of viral hemagglutination present in urine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 May;74(1):106–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner M. J., Anstee D. J., Mawby W. J. A new human erythrocyte variant (Ph) containing an abnormal membrane sialoglycoprotein. Biochem J. 1980 May 1;187(2):493–500. doi: 10.1042/bj1870493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. B., Winzler R. J. Structural studies on human erythrocyte glycoproteins. Alkali-labile oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 10;244(21):5943–5946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita M., Marchesi V. T. Amino-acid sequence and oligosaccharide attachment sites of human erythrocyte glycophorin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2964–2968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlenbruck G., Sprenger I., Heggen M., Leseney A. M. Diagnosis of the "Cad" blood group with agglutinins from snails and plants. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1971;141(3):290–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetta J. P., Breckenridge W. C., Vincendon G. Analysis of monosaccharides by gas-liquid chromatography of the O-methyl glycosides as trifluoroacetate derivatives. Application to glycoproteins and glycolipids. J Chromatogr. 1972 Jul 5;69(2):291–304. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)92897-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]