Abstract
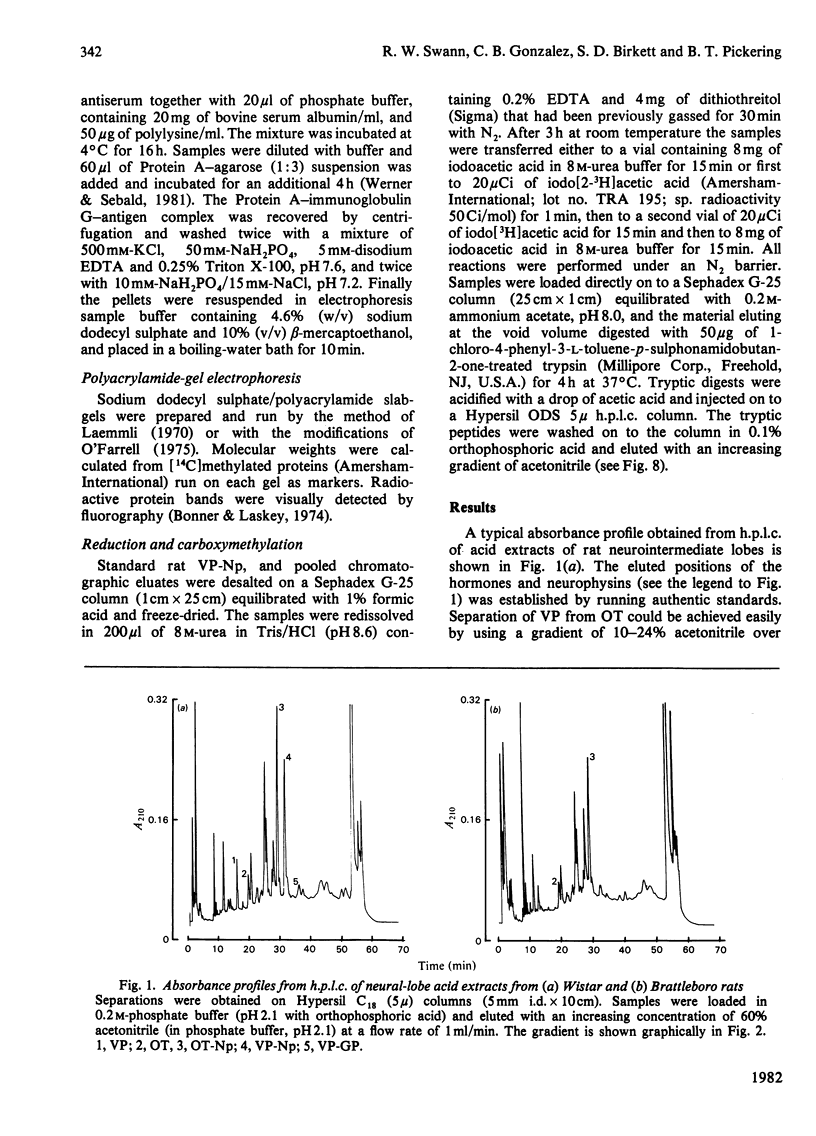
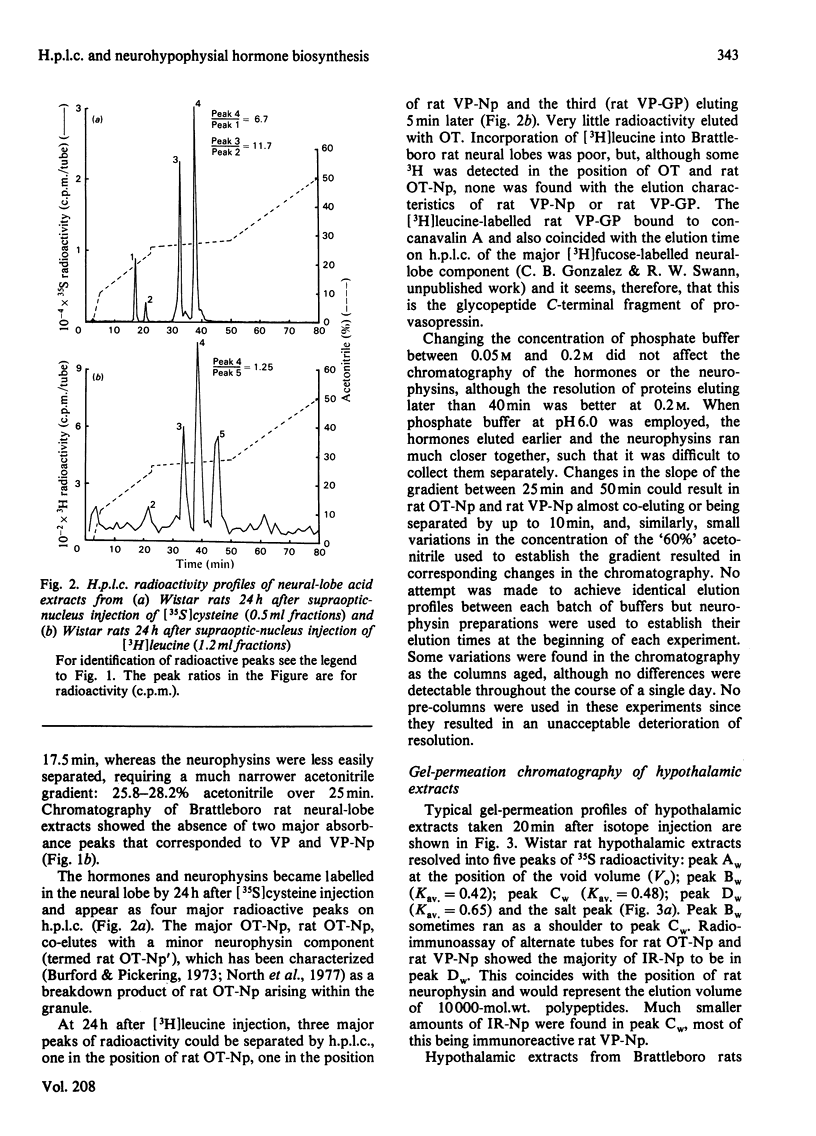
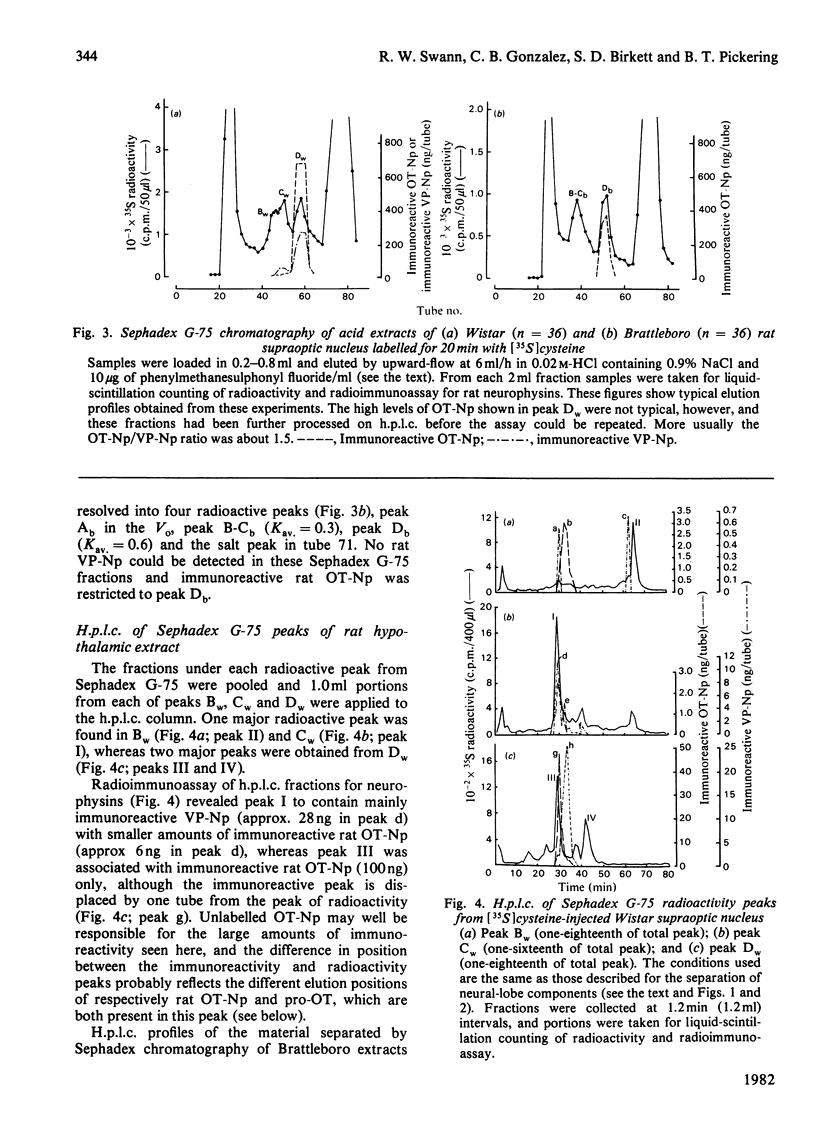
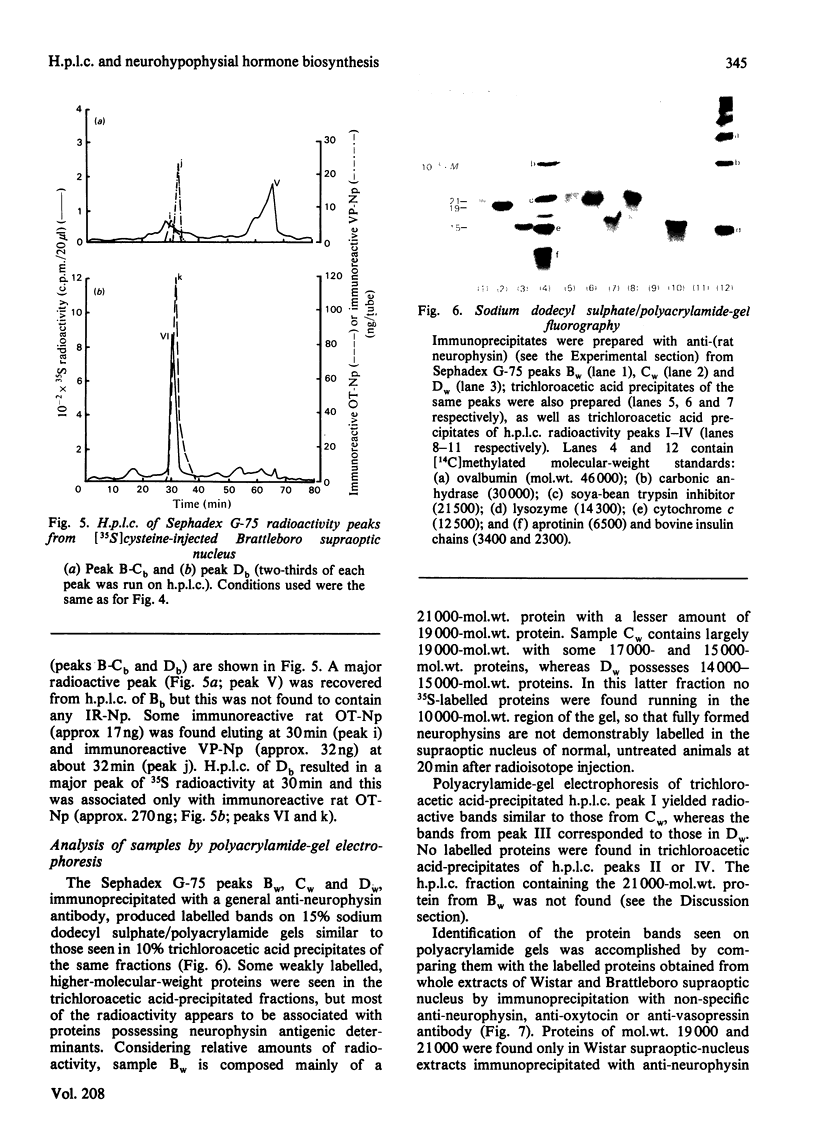
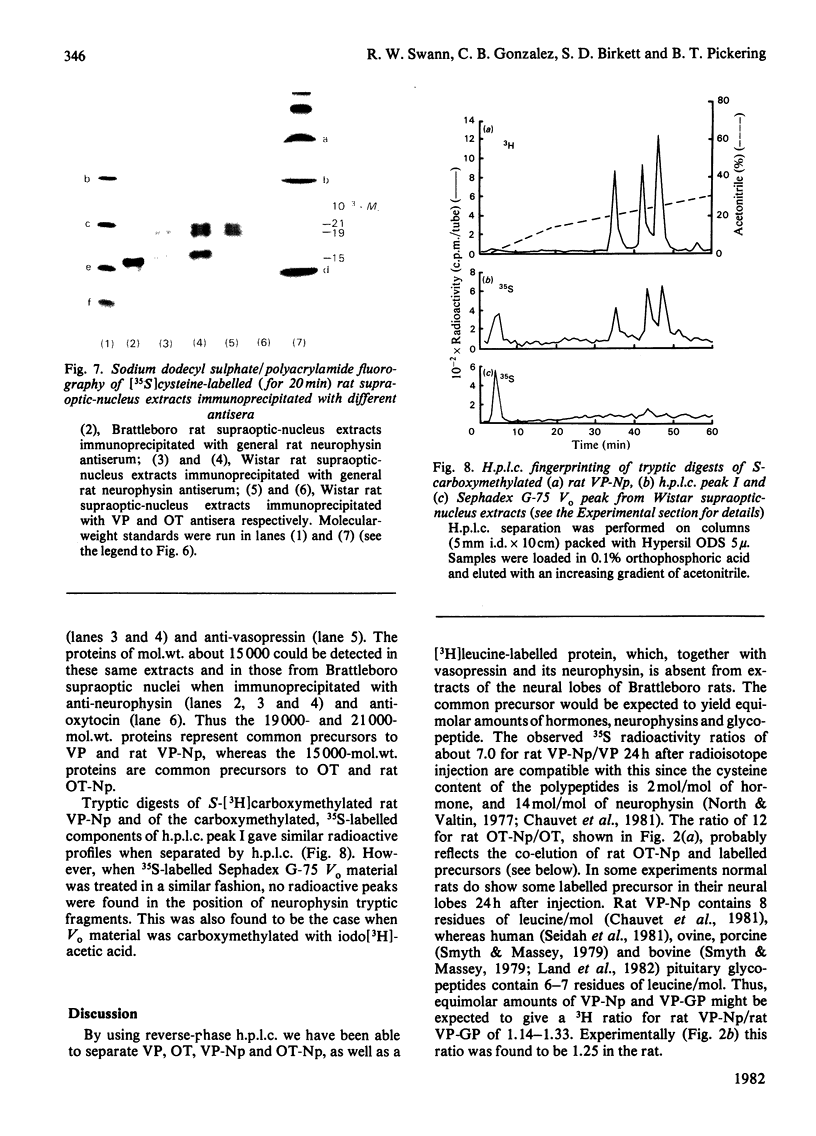
A reverse-phase high performance liquid-chromatography (h.p.l.c.) protocol has been developed, whereby all the major known posterior-pituitary components that are derived from the processing of pro-oxytocin and pro-vasopressin can be separated one from another. Thus, in a single chromatographic step, it has been possible to separate vasopressin (VP), oxytocin (OT), oxytocin-neurophysin (rOT-Np), vasopressin-neurophysin (rVP-Np) and vasopressin-glycopeptide (rVP-GP) from acid extracts of the neurointermediate lobes of rat pituitary glands. All these peptides except rVP-GP were labelled in the neural lobe by 24h after a hypothalamic injection of [35S]cysteine, whereas all except VP were labelled by 24h after a similar injection of [3H]leucine. Three major labelled proteins were isolated from 20 min [35S]cysteine-injected rats when extracts of the supraoptic nucleus were subjected to Sephadex G-75 chromatography, h.p.l.c. and sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Immunoprecipitation with antisera raised against rat neurophysins, VP and OT revealed 21000- and 19000-mol.wt. common precursors to VP and rVP-Np and a 15000-mol.wt. common precursor to OT and rOT-Np. Some immunoreactive rVP-Np could occasionally be detected in the Vo of Sephadex G-75 chromatograms of Wistar rat supraoptic-nucleus extracts, but no evidence of [35S]neurophysin in this fraction was obtained from h.p.l.c. fingerprinting of its S-carboxymethylated tryptic digests. Radioimmunoassay for rVP-Np and rOT-Np revealed that about 70-80% of the total recovered immunoreactive neurophysin (IR-Np) in the supraoptic nucleus eluted from Sephadex G-75 and h.p.l.c. in the positions of rVP-Np and rOT-Np. Evidence is presented for an approx. 20000-mol.wt. rOT-Np in both Wistar and Brattleboro rats and for an approx. 20000-mol.wt. component in the Brattleboro rat that is recognized by vasopressin-neurophysin antisera.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownstein M. J., Robinson A. G., Gainer H. Immunological identification of rat neurophysin precursors. Nature. 1977 Sep 15;269(5625):259–261. doi: 10.1038/269259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burford G. D., Jones C. W., Pickering B. T. Tentative identification of a vasopressin-neurophysin and an oxytocin-neurophysin in the rat. Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(4):809–813. doi: 10.1042/bj1240809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burford G. D., Pickering B. T. Intra-axonal transport and turnover of neurophysins in the rat. A proposal for a possible origin of the minor neurophysin component. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;136(4):1047–1052. doi: 10.1042/bj1361047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chauvet M. T., Chauvet J., Acher R. Identification of rat neurophysins: complete amino acid sequences of MSEL- and VLDV-neurophysins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Nov 30;103(2):595–603. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90493-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chauvet M. T., Chauvet J., Acher R. Phylogeny of neurophysins: partial amino acid sequence of a sheep neurophysin. FEBS Lett. 1975 Apr 1;52(2):212–215. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80808-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco-Bourland R. E., Fernstrom J. D. In vivo biosynthesis of L-[35S]Cys-arginine vasopressin, -oxytocin, and -somatostatin: rapid estimation using reversed phase high pressure liquid chromatography. Endocrinology. 1981 Oct;109(4):1097–1106. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-4-1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gainer H., Sarne Y., Brownstein M. J. Biosynthesis and axonal transport of rat neurohypophysial proteins and peptides. J Cell Biol. 1977 May;73(2):366–381. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giudice L. C., Chaiken I. M. Cell-free biosynthesis of different high molecular weight forms of bovine neurophysins I and II coded by hypothalamic mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):11767–11770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giudice L. C., Chaiken I. M. Immunological and chemical identification of a neurophysin-containing protein coded by messenger RNA from bovine hypothalamus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3800–3804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg M. D., Hope D. B. The isolation of the native hormone-binding proteins from bovine pituitary posterior lobes. Crystallization of neurophysin-I and-II as complexes with [8-arginine]-vasopressin. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(2):557–564. doi: 10.1042/bj1060557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Schütz G., Schmale H., Richter D. Nucleotide sequence of cloned cDNA encoding bovine arginine vasopressin-neurophysin II precursor. Nature. 1982 Jan 28;295(5847):299–303. doi: 10.1038/295299a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauber M., Nicolas P., Boussetta H., Fahy C., Béguin P., Camier M., Vaudry H., Cohen P. The Mr 80,000 common forms of neurophysin and vasopressin from bovine neurohypophysis have corticotropin- and beta-endorphin-like sequences and liberate by proteolysis biologically active corticotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6086–6090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C., Joseph-Bravo P., Sherman T., Chan L., McKelvy J. F. Cell-free synthesis of putative neurophysin precursors from rat and mouse hypothalamic poly (A)-RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 13;89(3):943–950. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91869-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mains R. E., Eipper B. A. Biosynthesis of adrenocorticotropic hormone in mouse pituitary tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 10;251(13):4115–4120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson M. A., Pickering B. T. Preparation of antisera to three individual rat neurophysins and their use for radioimmunoassays. J Endocrinol. 1978 Mar;76(3):461–471. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0760461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas P., Camier M., Lauber M., Masse M. J., Möhring J., Cohen P. Immunological identification of high molecular weight forms common to bovine neurophysin and vasopressin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2587–2591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North W. G., Valtin H., Morris J. F., La Rochelle F. T., Jr Evidence for metabolic conversions of rat neurophysins within neurosecretory granules of the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system. Endocrinology. 1977 Jul;101(1):110–118. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-1-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North W. G., Valtin H. The purification of rat neurophysins by a method of preparative polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1977 Apr;78(2):426–450. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare M. J., Nice E. C. Hydrophobic high-performance liquid chromatography of hormonal polypeptides and proteins on alkylsilane-bonded silica. J Chromatogr. 1979 Apr 1;171:209–226. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)95300-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palkovits M. Isolated removal of hypothalamic or other brain nuclei of the rat. Brain Res. 1973 Sep 14;59:449–450. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parish D. C., Rodríguez E. M., Birkett S. D., Pickering B. T. Effects of small doses of colchicine on the components of the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system of the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;220(4):809–827. doi: 10.1007/BF00210464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering B. T., Jones C. W. Isolation of radioactive oxytocin and vasopressin from the posterior pituitary gland of the rat after the injection of labelled tyrosine into the cerebrospinal fluid. J Endocrinol. 1971 Jan;49(1):93–103. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0490093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering B. T. The neurosecretory neurone: a model system for the study of secretion. Essays Biochem. 1978;14:45–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenior J. C., North W. G., Moore G. J. Putative precursors of vasopressin, oxytocin, and neurophysins in the rat hypothalamus. Endocrinology. 1981 Oct;109(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-4-1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. T., Brownstein M. J., Gainer H. Biosynthesis of vasopressin, oxytocin, and neurophysins: isolation and characterization of two common precursors (propressophysin and prooxyphysin). Endocrinology. 1980 Dec;107(6):1880–1891. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-6-1880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SACHS H. Vasopressin biosynthesis. I. In vivo studies. J Neurochem. 1960 May;5:297–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1960.tb13367.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs H., Fawcett P., Takabatake Y., Portanova R. Biosynthesis and release of vasopressin and neurophysin. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1969;25:447–491. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571125-8.50013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmale H., Richter D. In vitro biosynthesis and processing of composite common precursors containing amino acid sequences identified immunologically as neurophysin I/oxytocin and as neurophysin II/arginine vasopressin. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 1;121(2):358–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80381-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Benjannet S., Chrétien M. The complete sequence of a novel human pituitary glycopeptide homologous to pig posterior pituitary glycopeptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 29;100(2):901–907. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80258-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth D. G., Massey D. E. A new glycopeptide in pig, ox and sheep pituitary. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 27;87(4):1006–1010. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(79)80007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner S., Sebald W. Immunological techniques for studies on the biogenesis of mitochondrial membrane proteins. Methods Biochem Anal. 1981;27:109–170. doi: 10.1002/9780470110478.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]