Abstract
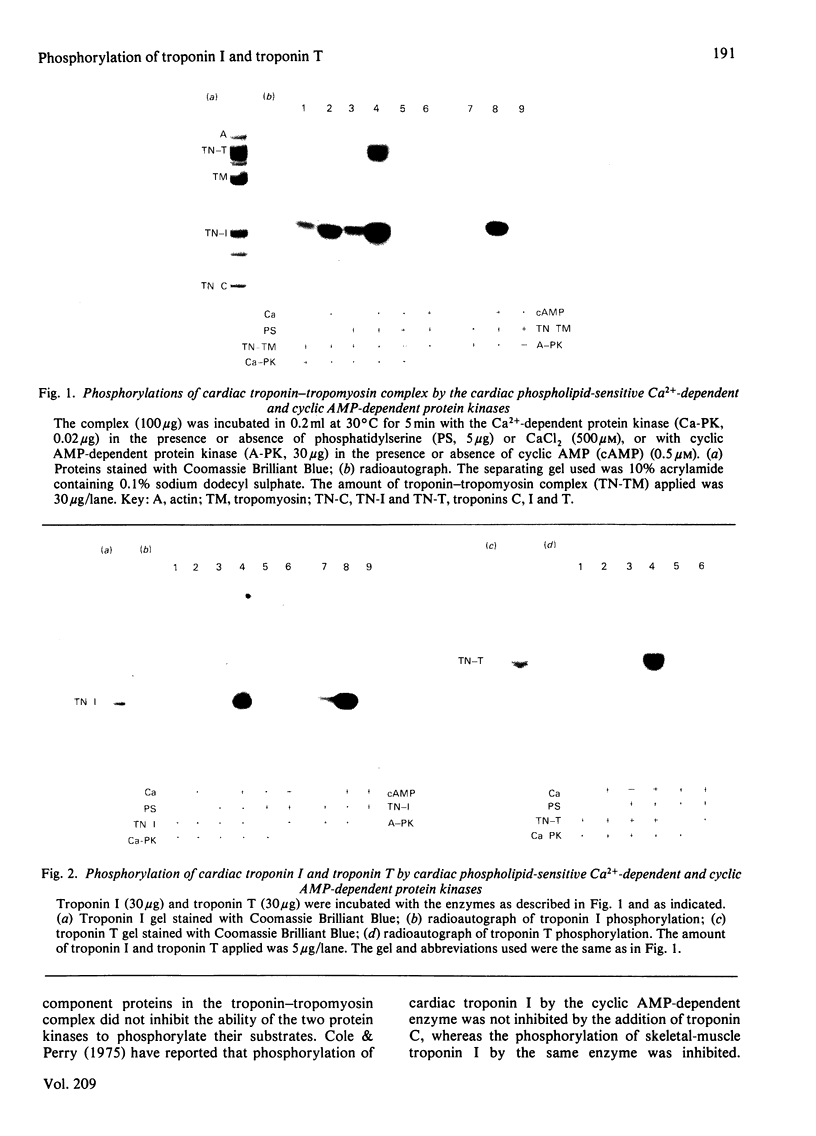
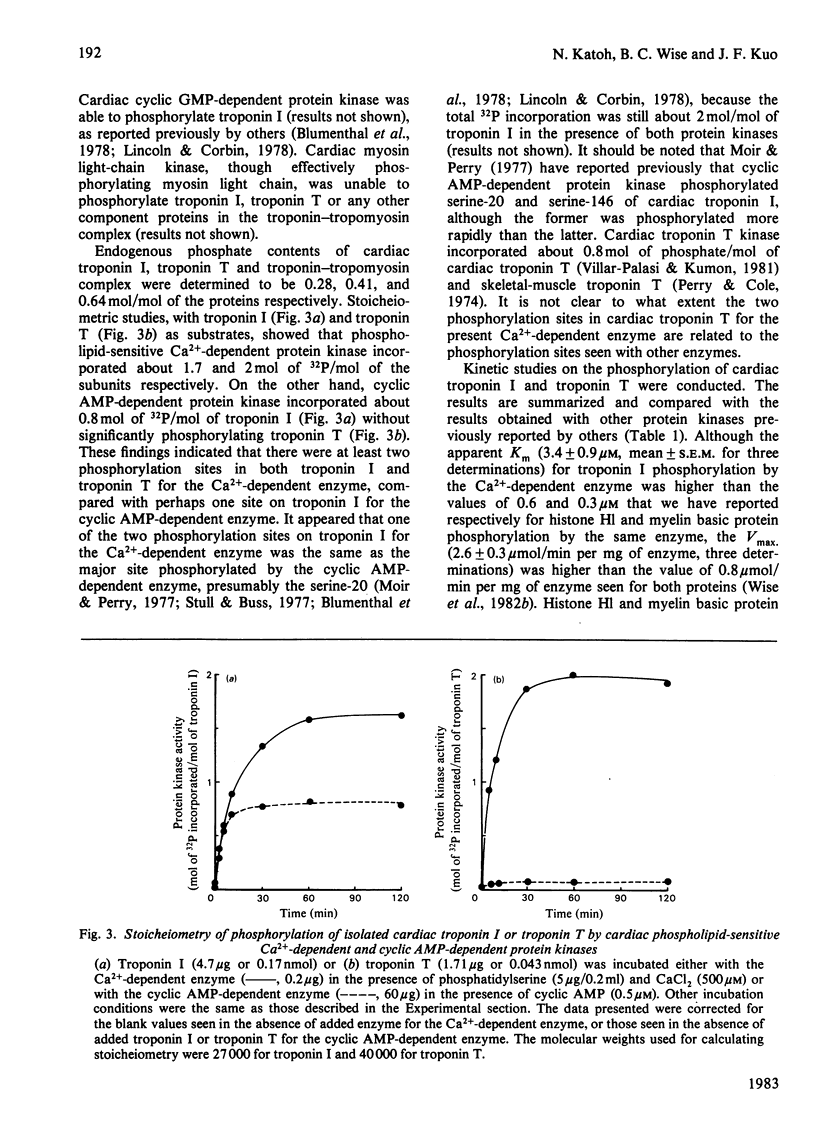
Cardiac phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase phosphorylated cardiac troponin inhibitory subunit (troponin I) and tropomyosin-binding subunit (troponin T), present either as the free form or as the troponin-tropomyosin complex. Exhaustive phosphorylation of troponin I and of troponin T revealed that 1.7 and 2 mol of phosphate was incorporated/mol of the subunits respectively. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, though incorporating 0.8 mol of phosphate/mol of troponin I, was unable to phosphorylate troponin T. Phosphorylation of troponin I (apparent Km = 3.4 microM; Vmax. = 2.6 mumol/min per mg of enzyme) or troponin T (apparent Km = 0.3 microM; Vmax. = 0.5 mumol/min per mg of enzyme) by the Ca2+-dependent enzyme was inhibited by various agents, such as adriamycin, palmitoylcarnitine, trifluoperazine, melittin and N-(6-aminohexyl)-5-chloronaphthalene-1-sulphonamide (compound W-7). Ca2+ antagonists (such as verapamil), forskolin and ouabain were ineffective. These findings indicate that troponin I and troponin T were effective substrates for this species of Ca2+-dependent protein kinase, suggesting its potential regulatory role in the contractile activity of myofibrils modulated by troponin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailin G. Phosphorylation of a bovine cardiac actin complex. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jan;236(1):C41–C46. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1979.236.1.C41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole H. A., Perry S. V. The phosphorylation of troponin I from cardiac muscle. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):525–533. doi: 10.1042/bj1490525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. W., Padgett W., Seamon K. B. Activation of cyclic AMP-generating systems in brain membranes and slices by the diterpene forskolin: augmentation of receptor-mediated responses. J Neurochem. 1982 Feb;38(2):532–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb08660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England P. J. Studies on the phosphorylation of the inhibitory subunit of troponin during modification of contraction in perfused rat heart. Biochem J. 1976 Nov 15;160(2):295–304. doi: 10.1042/bj1600295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusev N. B., Dobrovolskii A. B., Severin S. E. Isolation and some properties of troponin T kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1980 Aug 1;189(2):219–226. doi: 10.1042/bj1890219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Yamaki T., Totsuka T., Asano M. Selective inhibitors of Ca2+-binding modulator of phosphodiesterase produce vascular relaxation and inhibit actin-myosin interaction. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Jan;15(1):49–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itaya K., Ui M. A new micromethod for the colorimetric determination of inorganic phosphate. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Sep;14(3):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh N., Kuo J. F. Subcellular distribution of phospholipid-sensitive calcium-dependent protein kinase in guinea pig heart, spleen and cerebral cortex, and inhibition of the enzyme by Triton X-100. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):590–595. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91151-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh N., Raynor R. L., Wise B. C., Schatzman R. C., Turner R. S., Helfman D. M., Fain J. N., Kuo J. F. Inhibition by melittin of phospholipid-sensitive and calmodulin-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinases. Biochem J. 1982 Jan 15;202(1):217–224. doi: 10.1042/bj2020217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh N., Wise B. C., Wrenn R. W., Kuo J. F. Inhibition by adriamycin of calmodulin-sensitive and phospholipid-sensitive calcium-dependent phosphorylation of endogenous proteins from heart. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):199–205. doi: 10.1042/bj1980199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh N., Wrenn R. W., Wise B. C., Shoji M., Kuo J. F. Substrate proteins for calmodulin-sensitive and phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinases in heart, and inhibition of their phosphorylation by palmitoylcarnitine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4813–4817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A. M. Role of the contractile proteins and sarcoplasmic reticulum in the response of the heart to catecholamines: an historical review. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;11:303–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Andersson R. G., Wise B. C., Mackerlova L., Salomonsson I., Brackett N. L., Katoh N., Shoji M., Wrenn R. W. Calcium-dependent protein kinase: widespread occurrence in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom and comparison of effects of phospholipid, calmodulin, and trifluoperazine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7039–7043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln T. M., Corbin J. D. Purified cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase catalyzes the phosphorylation of cardiac troponin inhibitory subunit (TN-1). J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):337–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner E., Dohadwalla A. N., Bhattacharya B. K. Positive inotropic and blood pressure lowering activity of a diterpene derivative isolated from Coleus forskohli: Forskolin. Arzneimittelforschung. 1978;28(2):284–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moir A. J., Cole H. A., Perry S. V. The phosphorylation sites of troponin T from white skeletal muscle and the effects of interaction with troponin C on their phosphorylation by phosphorylase kinase. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 1;161(2):371–382. doi: 10.1042/bj1610371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moir A. J., Perry S. V. Phosphorylation of rabbit cardiac-muscle troponin I by phosphorylase kinase. The effect of adrenaline. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):547–554. doi: 10.1042/bj1910547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moir A. J., Perry S. V. The sites of phosphorylation of rabbit cardiac troponin I by adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Effect of interaction with troponin C. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 1;167(2):333–343. doi: 10.1042/bj1670333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moir A. J., Solaro R. J., Perry S. V. The site of phosphorylation of troponin I in the perfused rabbit heart. The effect of adrenaline. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 1;185(2):505–513. doi: 10.1042/bj1850505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrie W. T., Perry S. V. An electrophoretic study of the low-molecular-weight components of myosin. Biochem J. 1970 Aug;119(1):31–38. doi: 10.1042/bj1190031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry S. V., Cole H. A. Phosphorylation of troponin and the effects of interactions between the components of the complex. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):733–743. doi: 10.1042/bj1410733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray K. P., England P. J. Phosphorylation of the inhibitory subunit of troponin and its effect on the calcium dependence of cardiac myofibril adenosine triphosphatase. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov;70(1):11–16. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80716-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy Y. S., Wyborny L. E. Phosphorylation of guinea pig cardiac natural actomyosin and its effect on ATPase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Dec 6;73(3):703–709. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90867-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamon K., Daly J. W. Activation of adenylate cyclase by the diterpene forskolin does not require the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9799–9801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji M., Patrick J. G., Davis C. W., Kuo J. F. Guanosine cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from foetal calf heart. Purification, general properties and catalytic subunit. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 1;161(2):213–221. doi: 10.1042/bj1610213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solaro R. J., Moir A. J., Perry S. V. Phosphorylation of troponin I and the inotropic effect of adrenaline in the perfused rabbit heart. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):615–617. doi: 10.1038/262615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull J. T., Brostrom C. O., Krebs E. G. Phosphorylation of the inhibitor component of troponin by phosphorylase kinase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5272–5274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull J. T., Buss J. E. Phosphorylation of cardiac troponin by cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):851–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull J. T. Phosphorylation of contractile proteins in relation to muscle function. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1980;13:39–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Iwasa Y., Kawahara Y., Mori T., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-dependent activation of a multifunctional protein kinase by membrane phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3692–3695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villar-Palasi C., Kumon A. Purification and properties of dog cardiac troponin T kinase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7409–7415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M. P., Vallet B., Autric F., Demaille J. G. Purification and characterization of bovine cardiac calmodulin-dependent myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):12136–12144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise B. C., Glass D. B., Chou C. H., Raynor R. L., Katoh N., Schatzman R. C., Turner R. S., Kibler R. F., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase from heart. II. Substrate specificity and inhibition by various agents. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8489–8495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise B. C., Raynor R. L., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase from heart. I. Purification and general properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8481–8488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrenn R. W., Katoh N., Schatzman R. C., Kuo J. F. Inhibition by phenothiazine antipsychotic drugs of calcium-dependent phosphorylation of cerebral cortex proteins regulated by phospholipid or calmodulin. Life Sci. 1981 Aug 17;29(7):725–733. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrenn R. W., Katoh N., Wise B. C., Kuo J. F. Stimulation by phosphatidylserine and calmodulin of calcium-dependent phosphorylation of endogenous proteins from cerebral cortex. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):12042–12046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]