Abstract
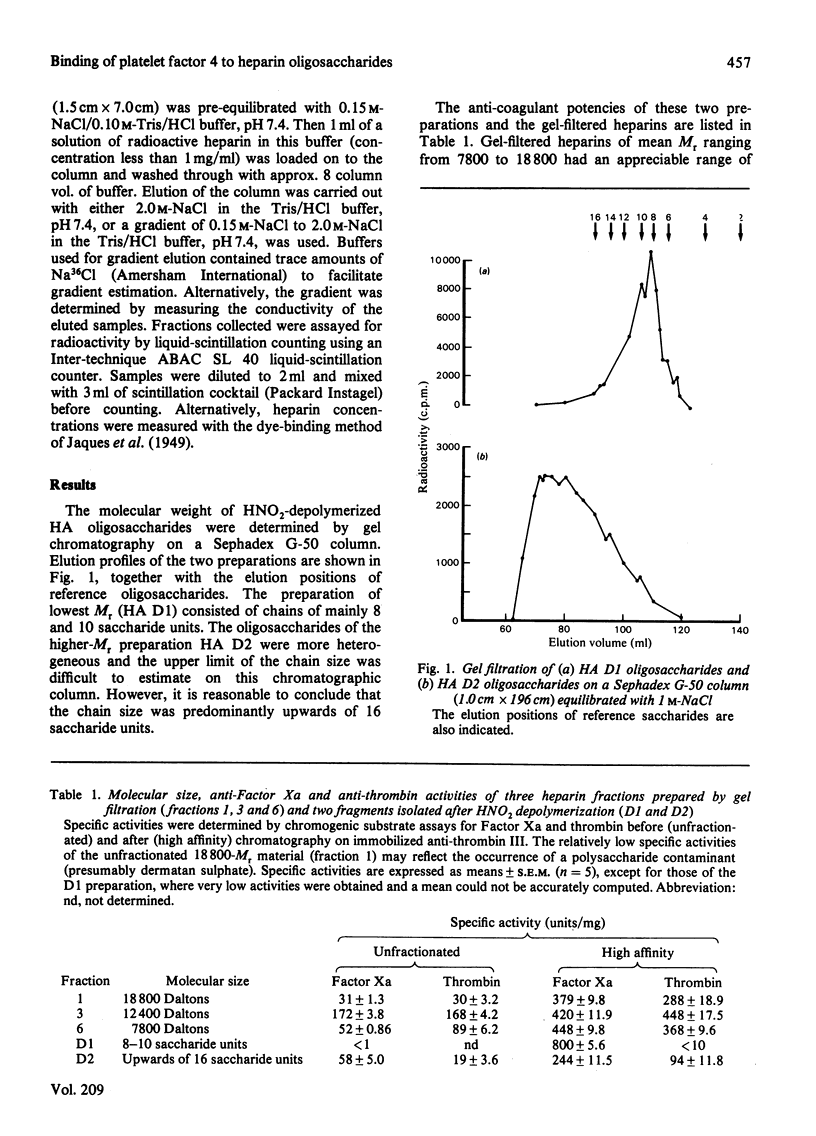
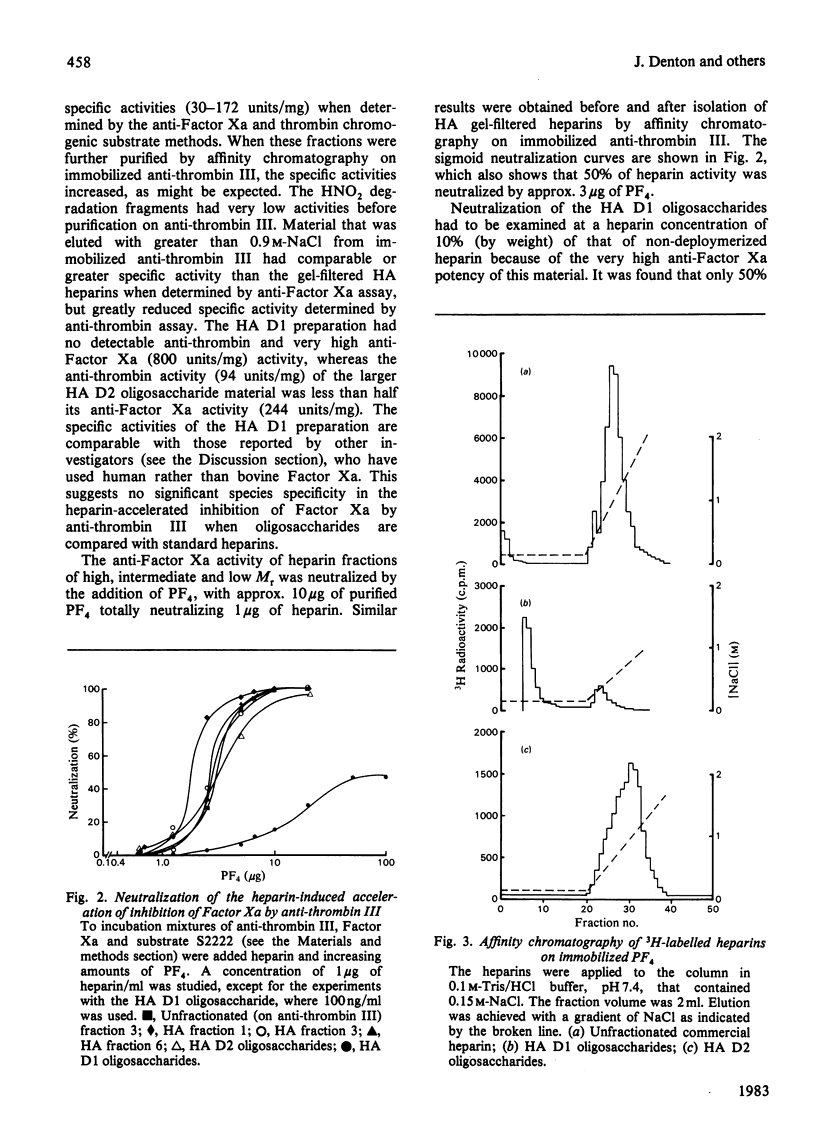
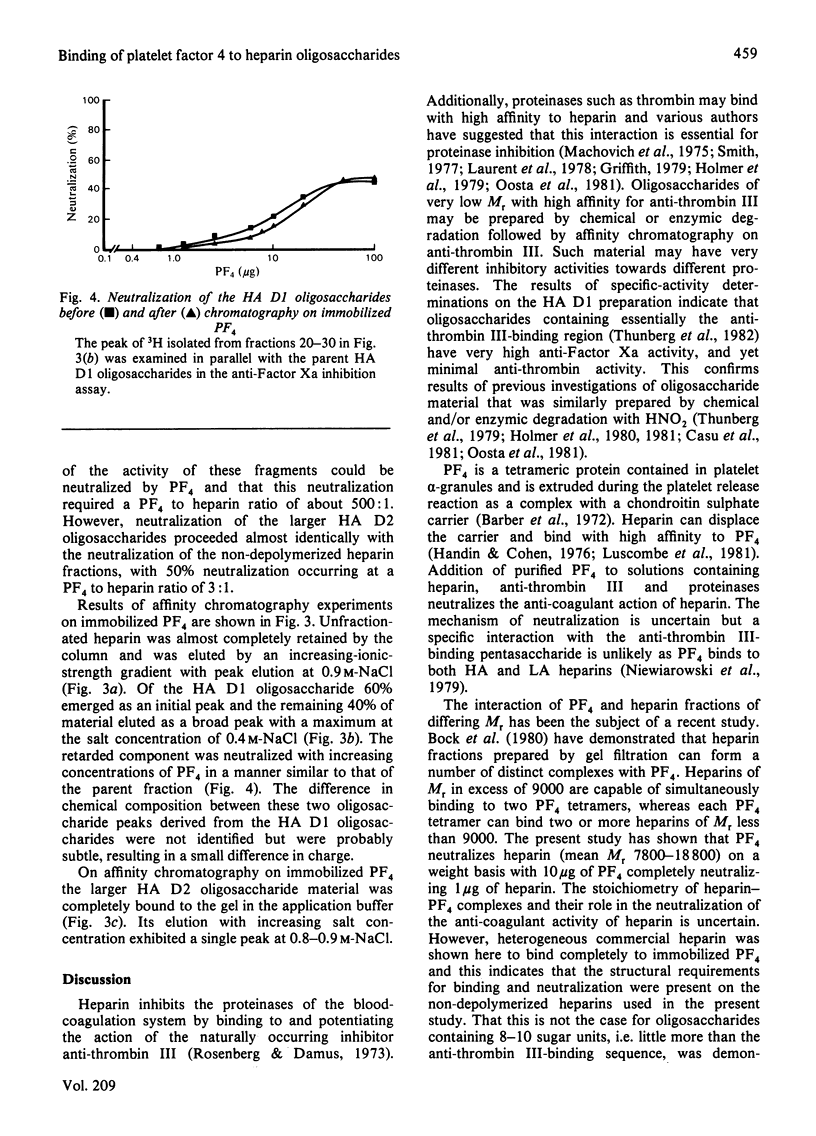
Heparin fractions of differing Mr (7800-18 800) prepared from commercial heparin by gel filtration and affinity chromatography on immobilized anti-thrombin III had specific activities when determined by anti-Factor Xa and anti-thrombin assays that ranged from 228 to 448 units/mg. The anti-Factor Xa activity of these fractions could be readily and totally neutralized by increasing concentrations of platelet factor 4 (PF4). That these fractions bound to immobilized PF4 was indicated by the complete binding under near physiological conditions of 3H-labelled unfractionated commercial heparin. An anti-thrombin III-binding oligosaccharide preparation (containing predominantly eight to ten saccharide units), prepared by degradation of heparin with HNO2 had high (800 units/mg) anti-Factor Xa, but negligible anti-thrombin, specific activity. The anti-Factor Xa activity of this material could not be readily neutralized by PF4, and the 3H-labelled oligosaccharides did not completely bind to immobilized PF4. A heterogeneous anti-thrombin III-binding preparation containing upwards of 16 saccharides had anti-thrombin specific activity of just less than one-half the anti-Factor Xa specific activity. This material was completely bound to immobilized PF4 and was eluted with similar concentrations of NaCl to those that were required to elute unfractionated heparins from these columns. Furthermore, increasing concentrations of PF4 neutralized the anti-Factor Xa activity of this material in a manner similar to that of unfractionated heparin. It is concluded that heparin oligosaccharides require saccharide units in addition to the anti-thrombin III-binding sequence in order to fully interact with PF4.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson L. O., Barrowcliffe T. W., Holmer E., Johnson E. A., Sims G. E. Anticoagulant properties of heparin fractionated by affinity chromatography on matrix-bound antithrombin iii and by gel filtration. Thromb Res. 1976 Dec;9(6):575–583. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber A. J., Käser-Glanzmann R., Jakábová M., Lüscher E. F. Characterization of a chondroitin 4 -sulfate proteoglycan carrier for heparin neutralizing activity (platelet factor 4 ) released from human blood platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 29;286(2):312–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock P. E., Luscombe M., Marshall S. E., Pepper D. S., Holbrook J. J. The multiple complexes formed by the interaction of platelet factor 4 with heparin. Biochem J. 1980 Dec 1;191(3):769–776. doi: 10.1042/bj1910769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casu B., Oreste P., Torri G., Zoppetti G., Choay J., Lormeau J. C., Petitou M., Sinäy P. The structure of heparin oligosaccharide fragments with high anti-(factor Xa) activity containing the minimal antithrombin III-binding sequence. Chemical and 13C nuclear-magnetic-resonance studies. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 1;197(3):599–609. doi: 10.1042/bj1970599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith M. J. Kinetic analysis of the heparin-enhanced antithrombin III/thrombin reaction. Reaction rate enhancement by heparin-thrombin association. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):12044–12049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handin R. I., Cohen H. J. Purification and binding properties of human platelet factor four. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4273–4282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmer E., Kurachi K., Söderström G. The molecular-weight dependence of the rate-enhancing effect of heparin on the inhibition of thrombin, factor Xa, factor IXa, factor XIa, factor XIIa and kallikrein by antithrombin. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 1;193(2):395–400. doi: 10.1042/bj1930395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmer E., Lindahl U., Bäckström G., Thunberg L., Sandberg H., Söderström G., Anderson L. O. Anticoagulant activities and effects on platelets of a heparin fragment with high affinity for antithrombin. Thromb Res. 1980 Jun 15;18(6):861–869. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90208-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hök M., Björk I., Hopwood J., Lindahl U. Anticoagulant activity of heparin: separation of high-activity and low-activity heparin species by affinity chromatography on immobilized antithrombin. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jul 1;66(1):90–93. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80592-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAQUES L. B., MONKHOUSE F. C., STEWART M. A method for the determination of heparin in blood. J Physiol. 1949 Aug;109(1-2):41–48. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan R. E., Oosta G. M., Gardner W. T., Rosenberg R. D. The binding of low molecular weight heparin to hemostatic enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10073–10080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURENT T. C. Studies on fractionated heparin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Feb;92:224–231. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90341-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam L. H., Silbert J. E., Rosenberg R. D. The separation of active and inactive forms of heparin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 22;69(2):570–577. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90558-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. A., Macgregor I. R., Michalski R., Kakkar V. V. Anticoagulant activities of four unfractionated and fractionated heparins. Thromb Res. 1978 Feb;12(2):257–271. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90297-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent T. C., Tengblad A., Thunberg L., Hök M., Lindahl U. The molecular-weight-dependence of the anti-coagulant activity of heparin. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):691–701. doi: 10.1042/bj1750691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl U., Bäckström G., Hök M., Thunberg L., Fransson L. A., Linker A. Structure of the antithrombin-binding site in heparin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3198–3202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl U., Bäckström G., Thunberg L., Leder I. G. Evidence for a 3-O-sulfated D-glucosamine residue in the antithrombin-binding sequence of heparin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6551–6555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luscombe M., Marshall S., Pepper D. S., Holbrook J. J. The transfer of platelet factor 4 from its proteoglycan carrier to natural and synthetic polymers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 18;678(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor I. R., Lane D. A., Kakkar V. V. Evidence for a plasma inhibitor of the heparin accelerated inhibition of factor Xa by antithrombin III. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Sep 3;586(3):584–593. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor I. R., Lane D. A., Kakkar V. V. The anti-heparin properties of human low-density lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 21;617(3):472–479. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(80)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machovich R., Blaskó G., Pálos L. A. Action of heparin on thrombin-antithrombin reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 30;379(1):193–200. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S., Pepper D. S., Cash J. D. Platelet antiheparin activity. The isolation and characterisation of platelet factor 4 released from thrombin-aggregated washed human platelets and its dissociation into subunits and the isolation of membrane-bound antiheparin activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 27;379(2):370–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewiarowski S., Rucinski B., James P., Lindahl U. Platelet antiheparin proteins and antithrombin III interact with different binding sites on heparin molecule. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 1;102(1):75–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80931-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosta G. M., Gardner W. T., Beeler D. L., Rosenberg R. D. Multiple functional domains of the heparin molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):829–833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piepkorn M. W. Dansyl (5-dimethylaminonaphthalene-1-sulphonyl)-heparin binds antithrombin III and platelet factor 4 at separate sites. Biochem J. 1981 May 15;196(2):649–651. doi: 10.1042/bj1960649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D., Damus P. S. The purification and mechanism of action of human antithrombin-heparin cofactor. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6490–6505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. F. The heparin-thrombin complex in the mechanism of thrombin inactivation by heparin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 11;77(1):111–117. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teien A. N., Lie M. Evaluation of an amidolytic heparin assay method: increased sensitivity by adding purified antithrombin III. Thromb Res. 1977 Mar;10(3):399–410. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90150-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thunberg L., Bäckström G., Grundberg H., Riesenfeld J., Lindahl U. The molecular size of the antithrombin-binding sequence in heparin. FEBS Lett. 1980 Aug 11;117(1):203–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80945-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thunberg L., Bäckström G., Lindahl U. Further characterization of the antithrombin-binding sequence in heparin. Carbohydr Res. 1982 Mar 1;100:393–410. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)81050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thunberg L., Lindahl U., Tengblad A., Laurent T. C., Jackson C. M. On the molecular-weight-dependence of the anticoagulant activity of heparin. Biochem J. 1979 Jul 1;181(1):241–243. doi: 10.1042/bj1810241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


