Abstract
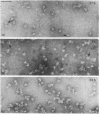
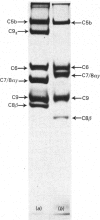
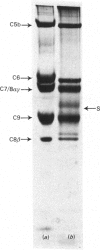
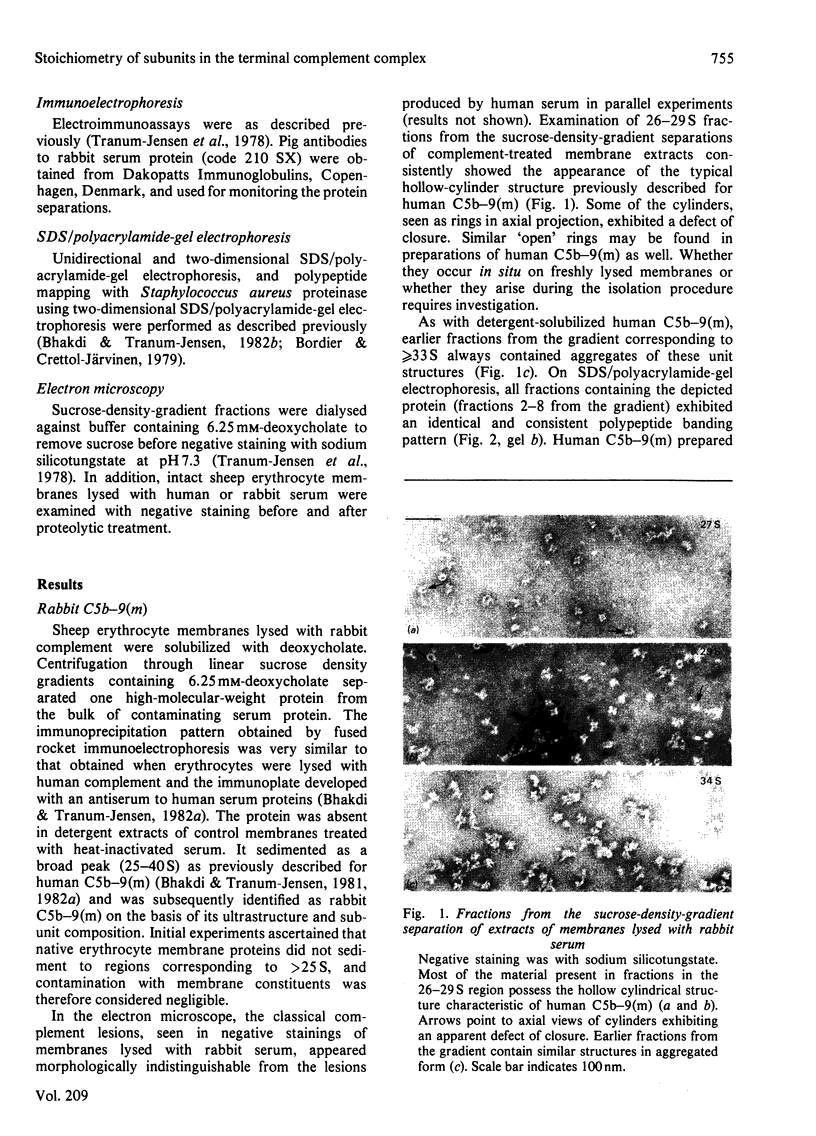
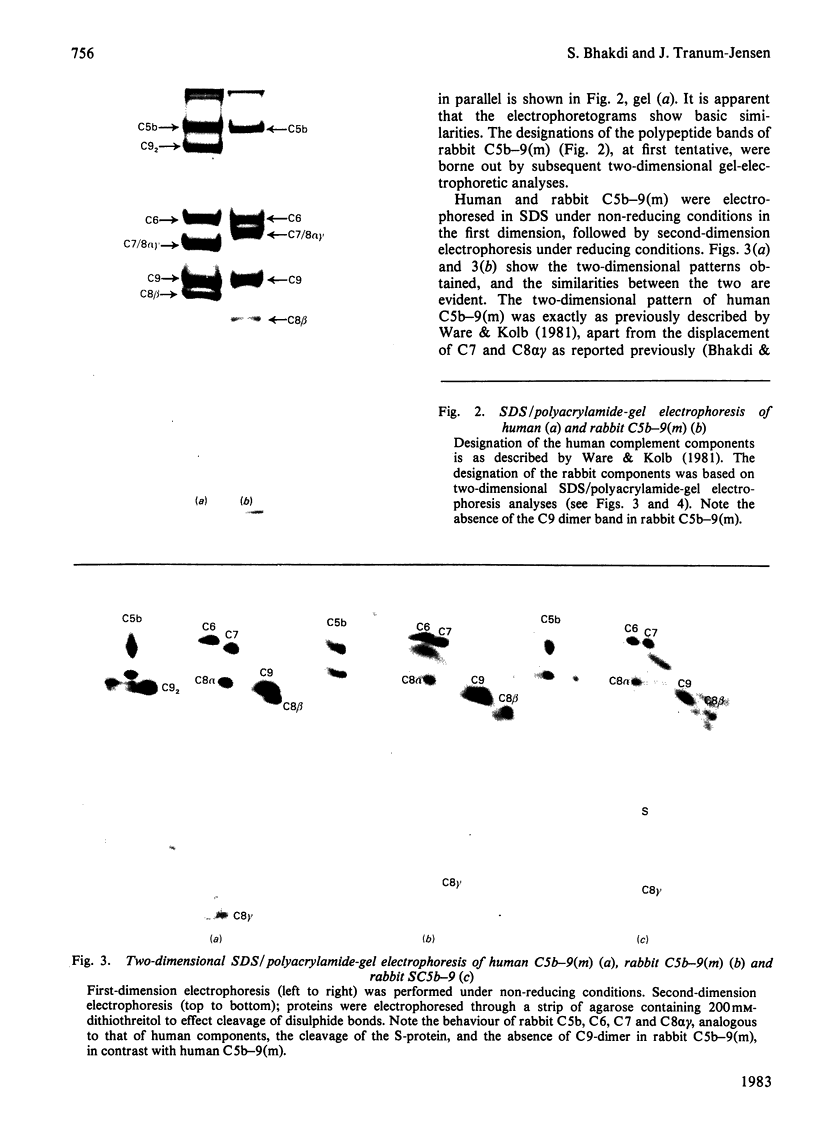
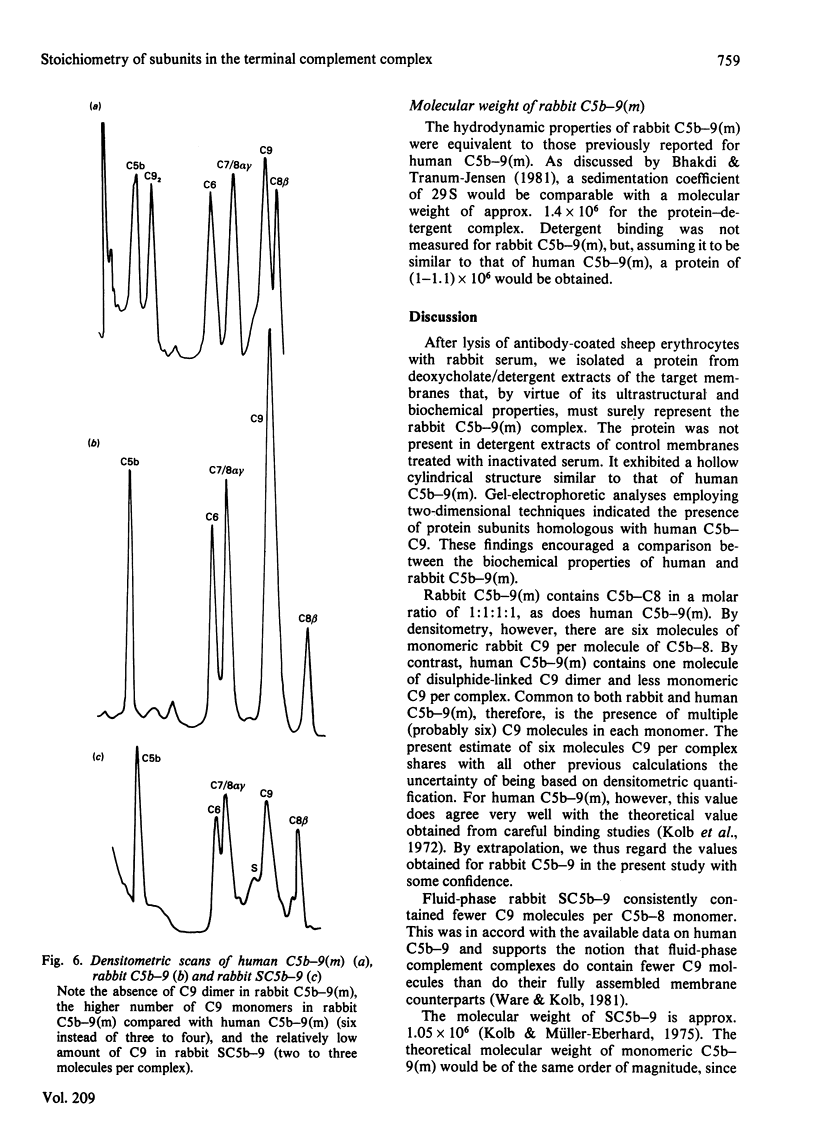
The terminal membrane C5b-9(m) and fluid-phase SC5b-9 complexes of rabbit complement were isolated from target sheep erythrocyte membranes and from inulin-activated rabbit serum respectively. In the electron microscope, rabbit C5b-9(m) was observed as a hollow protein cylinder, a structure identical with that of human C5b-9(m). Monodispersed rabbit C5b-9(m) exhibited an apparent sedimentation coefficient of 29 S in deoxycholate-containing sucrose density gradients, corresponding to a composite protein-detergent molecular-weight of approx. 1.4 X 10(6). Protein subunits corresponding to human C5b-C9 were found on sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. By densitometry, there were consistently six molecules of monomeric C9 present for each monomeric C5b-8 complex. Fluid-phase rabbit SC5b-9 was a hydrophilic 23 S ma macromolecule that differed in subunit composition from its membrane counterpart in that it contained S-protein and only two to three molecules of C9 per monomer complex. The data are in accord with the previous report on human C5b-9 that C5b-9(m) contains more C9 molecules than SC5b-9 [Ware & Kolb (1981) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 6426-6430]. They corroborate the previous molecular-weight estimate of approx. 10(6) for C5b-9(m) and thus support the concept that the fully assembled, unit lesion of complement is a C5b-9 monomer [Bhakdi & Tranum-Jensen (1981) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 1818-1822]. They also show that C9 dimer formation is not required for assembly of the rabbit C5b-9(m) protein cylinder, or for expression of its membrane-damaging function.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhakdi S., Bhakdi-Lehnen B., Bjerrum O. J., Tranum-Jensen J. Difference in antigenic reactivity and ultrastructure between fluid-phase C5b-9 and the C5b-9 membrane attack complex of human complement. FEBS Lett. 1979 Mar 1;99(1):15–19. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80238-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Ey P., Bhakdi-Lehnen B. Isolation of the terminal complement complex from target sheep erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 6;419(3):445–457. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Evidence for a two-domain structure of the terminal membrane C5b-9 complex of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5872–5876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Hydrophilic-amphiphilic transition of the terminal SC5b-8 complement complex through tryptic modification: biochemical and ultrastructural studies. Mol Immunol. 1982 Sep;19(9):1167–1177. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90327-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Molecular nature of the complement lesion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5655–5659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Molecular weight of the membrane C5b-9 complex of human complement: characterization of the terminal complex as a C5b-9 monomer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1818–1822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Terminal membrane C5b-9 complex of human complement: transition from an amphiphilic to a hydrophilic state through binding of the S protein from serum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):755–759. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesecker G., Podack E. R., Halverson C. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. C5b-9 dimer: isolation from complement lysed cells and ultrastructural identification with complement-dependent membrane lesions. J Exp Med. 1979 Feb 1;149(2):448–458. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.2.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C., Crettol-Järvinen A. Peptide mapping of heterogeneous protein samples. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2565–2567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle M. D., Borsos T. Studies on the terminal stages of immune hemolysis. V. Evidence that not all complement-produced transmembrane channels are equal. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):71–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle M. D., Gee A. P., Borsos T. Studies on the terminal stages of immune hemolysis. VI. Osmotic blockers of differing Stokes' radii detect complement-induced transmembrane channels of differing size. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):77–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giavedoni E. B., Chow Y. M., Dalmasso A. P. The functional size of the primary complement lesion in resealed erythrocyte membrane ghosts. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):240–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Haxby J. A., Arroyave C. M., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular analysis of the membrane attack mechanism of complement. J Exp Med. 1972 Mar 1;135(3):549–566. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Muller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement. Isolation and subunit composition of the C5b-9 complex. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):724–735. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Mode of action of human C9: adsorption of multiple C9 molecules to cell-bound C8. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):479–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement. Verification of a stable C5-9 complex in free solution. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):438–451. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Thompson R. A. Reactive lysis: the complement-mediated lysis of unsensitized cells. II. The characterization of activated reactor as C56 and the participation of C8 and C9. J Exp Med. 1970 Apr 1;131(4):643–657. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.4.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Thompson R. A. Reactive lysis: the complement-mediated lysis of unsensitized cells. II. The characterization of activated reactor as C56 and the participation of C8 and C9. J Exp Med. 1970 Apr 1;131(4):643–657. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.4.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. M. Mechanism of cytolysis by complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2954–2958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels D. W., Abramovitz A. S., Hammer C. H., Mayer M. M. Increased ion permeability of planar lipid bilayer membranes after treatment with the C5b-9 cytolytic attack mechanism of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2852–2856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Biesecker G., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Membrane attack complex of complement: generation of high-affinity phospholipid binding sites by fusion of five hydrophilic plasma proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):897–901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Esser A. F., Biesecker G., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Membrane attack complex of complement: a structural analysis of its assembly. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):301–313. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Membrane attack complex of complement. Evidence for its dimeric structure based on hybrid formation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3145–3148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Tschoop J., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular organization of C9 within the membrane attack complex of complement. Induction of circular C9 polymerization by the C5b-8 assembly. J Exp Med. 1982 Jul 1;156(1):268–282. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.1.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. J., Lauf P. K. Steady-state analysis of tracer exchange across the C5b-9 complement lesion in a biological membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5669–5673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C., Reynolds J. A. Characterization of membrane proteins in detergent solutions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 26;457(2):133–170. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tranum-Jensen J., Bhakdi S., Bhakdi-Lehnen B., Bjerrum O. J., Speth V. Complement lysis: the ultrastructure and orientation of the C5b-9 complex on target sheep erythrocyte membranes. Scand J Immunol. 1978;7(1):45–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Podack E. R. Formation of transmembrane tubules by spontaneous polymerization of the hydrophilic complement protein C9. Nature. 1982 Aug 5;298(5874):534–538. doi: 10.1038/298534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware C. F., Kolb W. P. Assembly of the functional membrane attack complex of human complement: formation of disulfide-linked C9 dimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6426–6430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware C. F., Wetsel R. A., Kolb W. P. Physicochemical characterization of fluid phase (SC5b-9) and membrane derived (MC5b-9) attack complexes of human complement purified by immunoadsorbent affinity chromatography or selective detergent extraction. Mol Immunol. 1981 Jun;18(6):521–531. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(81)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Kawashima T., Migita S. Glutathione-catalyzed disulfide-linking of C9 in the membrane attack complex of complement. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8573–8576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]