Abstract
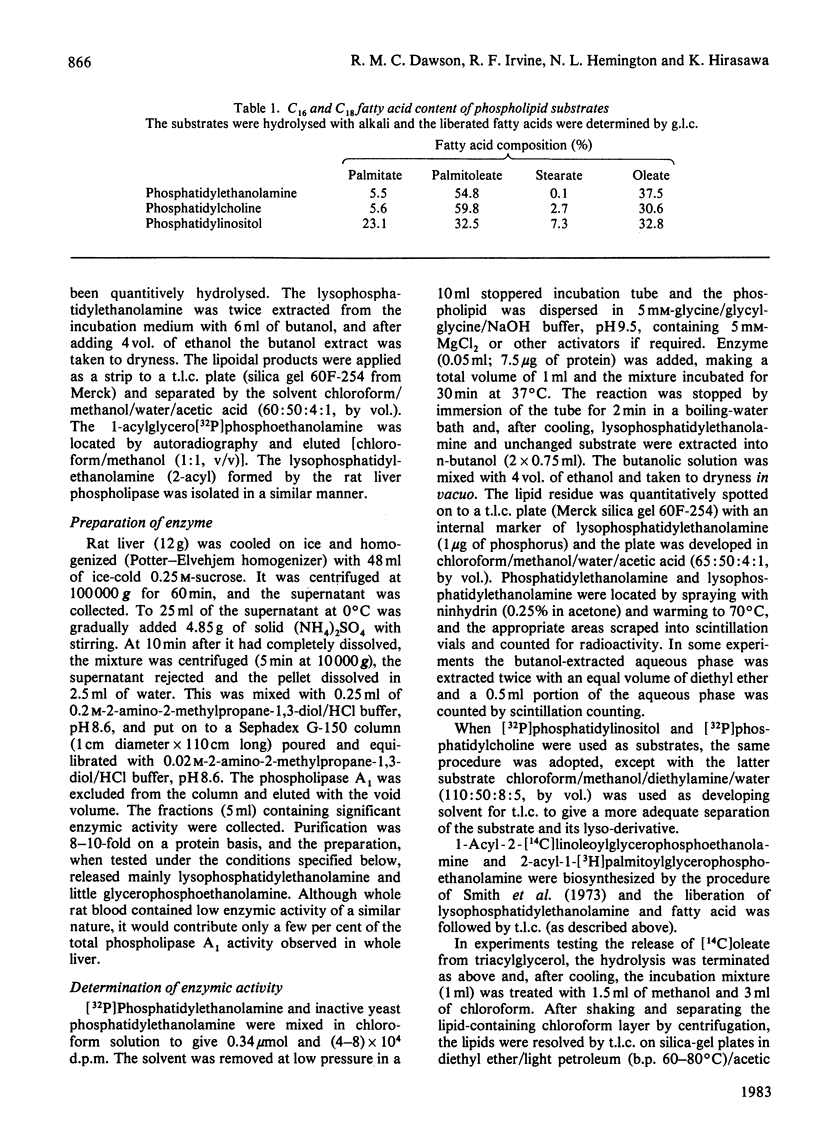
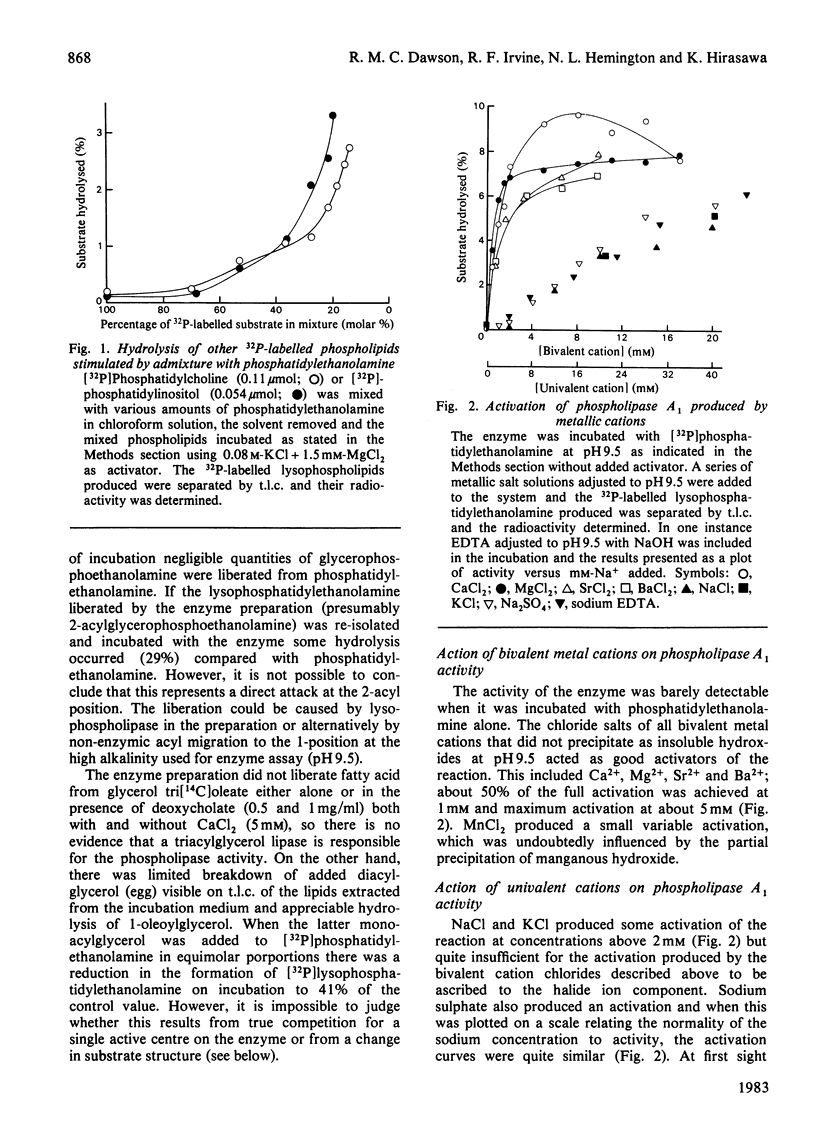
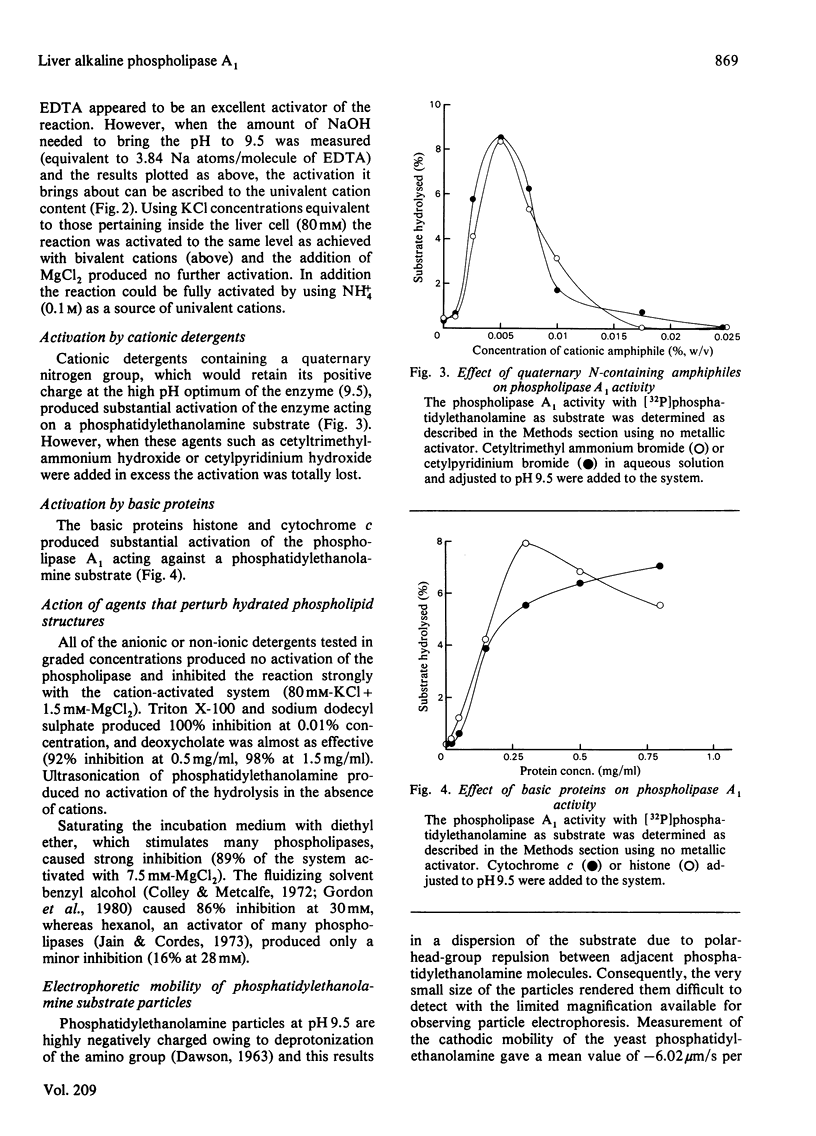
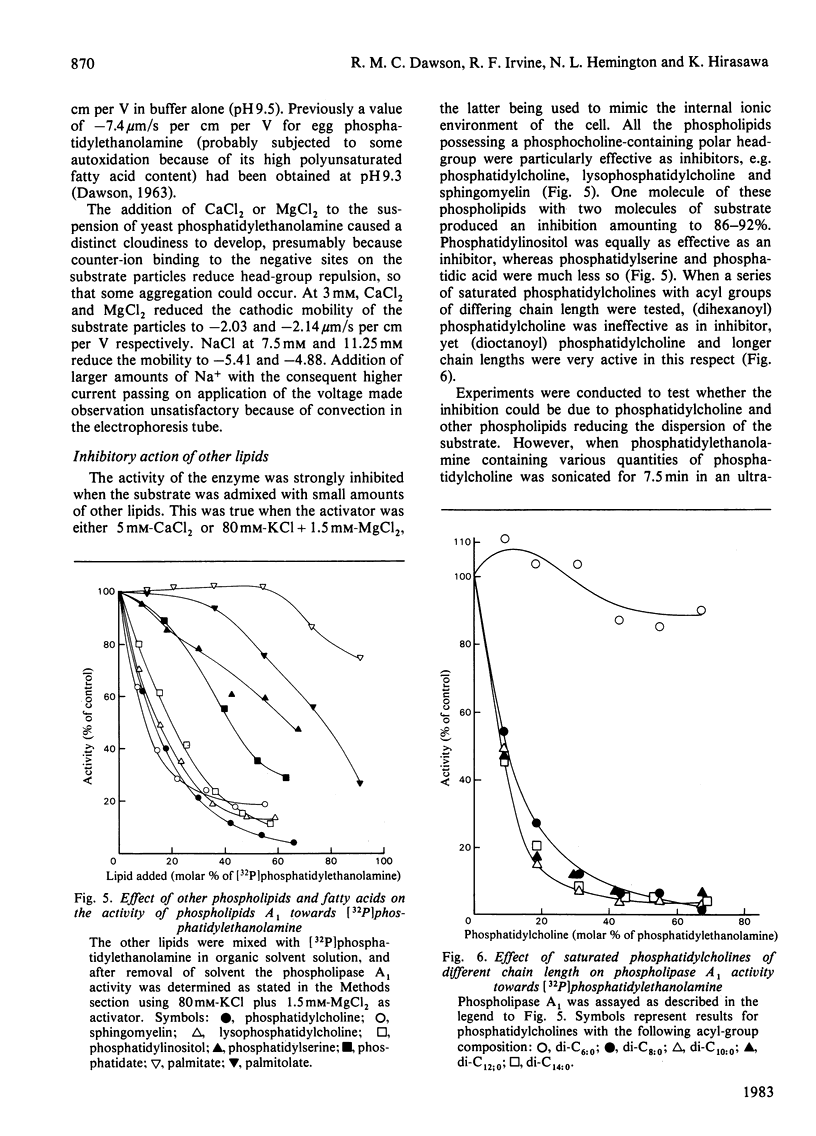
1. Rat liver cytosol contains a heat-sensitive phospholipase A1 active against phosphatidylethanolamine, 1-acylglycerophosphoethanolamine and, to a very much lesser extent, phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylinositol. 2. Activity towards a pure phosphatidylethanolamine substrate is invoked by the presence of water-soluble cations that do not precipitate at the pH optimum of the enzyme (9.5). In this activation bivalent cations, e.g. Mg2+, Ca2+, Mn2+, Sr2+ and Ba2+, are effective at much lower concentrations (2.5-5 mM) than univalent cations K+, Na+ and NH4+ (100 mM). 3. In the absence of such cations the enzyme can be activated by cationic amphiphiles containing quaternary nitrogen or by basic proteins. 4. It is concluded that these agents activate the enzyme by reducing the negative zeta potential on the substrate at the high pH optimum (9.5) and allow interaction with the enzyme whose isoelectric point is at 7.15. 5. The activated enzyme is markedly inhibited by mixing the phosphatidylethanolamine substrate with many other phospholipids that exist in cell membranes, e.g. phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylinositol. On the other hand, both phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylinositol can be hydrolysed much more readily if they are mixed with an excess of phosphatidylethanolamine. 6. Such results on the inhibition and substrate specificity of the enzyme, coupled with birefringence measurements, allow the tentative conclusion that phospholipid substrates are only attacked when they exist in a hexagonal or non-bilayer structure and not in the bilayer (lamellar) form.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANGHAM A. D., DAWSON R. M. The relation between the activity of a lecithinase and the electrophoretic charge of the substrate. Biochem J. 1959 Jul;72:486–492. doi: 10.1042/bj0720486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley C. M., Metcalfe J. C. The localisation of small molecules in lipid bilayers. FEBS Lett. 1972 Aug 15;24(3):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80364-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullis P. R., De Kruijff B. Polymorphic phase behaviour of lipid mixtures as detected by 31P NMR. Evidence that cholesterol may destabilize bilayer structure in membrane systems containing phosphatidylethanolamine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 21;507(2):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90417-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullis P. R., de Kruijff B. The polymorphic phase behaviour of phosphatidylethanolamines of natural and synthetic origin. A 31P NMR study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 19;513(1):31–42. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90109-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. ON THE MECHANISM OF ACTION OF PHOSPHOLIPASE A. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:414–423. doi: 10.1042/bj0880414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Hemington N. L., Miller N. G., Bangham A. D. On the question of an electrokinetic requirement for phospholipase C action. J Membr Biol. 1976 Oct 20;29(1-2):179–184. doi: 10.1007/BF01868958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Hemington N., Irvine R. F. The inhibition and activation of Ca2+-dependent phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase by phospholipids and blood plasma. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Nov;112(1):33–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Irvine R. F., Hemington N., Hirasawa K. The stimulation of the brain alkaline phospholipase A1 attacking phosphatidylethanolamine by various salts and metal chelators. Neurochem Res. 1982 Sep;7(9):1149–1161. doi: 10.1007/BF00964892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty F. J., Rowe C. E. The intracellular location of a Ca2+-stimulated phospholipase A1 in rat brain. Brain Res. 1980 Sep 15;197(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90438-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon L. M., Sauerheber R. D., Esgate J. A., Dipple I., Marchmont R. J., Houslay M. D. The increase in bilayer fluidity of rat liver plasma membranes achieved by the local anesthetic benzyl alcohol affects the activity of intrinsic membrane enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4519–4527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins J. A., Evans W. H. Transverse organization of phospholipids across the bilayer of plasma-membrane subfractions of rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 15;174(2):563–567. doi: 10.1042/bj1740563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui S. W., Stewart T. P., Yeagle P. L., Albert A. D. Bilayer to non-bilayer transition in mixtures of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine: implications for membrane properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Apr 1;207(2):227–240. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Hemington N., Dawson R. M. The hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol by lysosomal enzymes of rat liver and brain. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 15;176(2):475–484. doi: 10.1042/bj1760475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain M. K., Cordes E. H. Phospholipases. I. Effect of n-alkanols on the rate of enzymatic hydrolysis of egg phosphatidylcholine. J Membr Biol. 1973 Dec 31;14(2):101–118. doi: 10.1007/BF01868072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayar R., Schmid S. L., Hope M. J., Cullis P. R. Structural preferences of phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidylinositol-phosphatidylethanolamine model membranes. Influence of Ca2+ and Mg2+. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 21;688(1):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90592-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noordam P. C., van Echteld C. J., de Kruijff B., Verkleij A. J., de Gier J. Barrier characteristics of membrane model systems containing unsaturated phosphatidylethanolamines. Chem Phys Lipids. 1980 Oct;27(3):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(80)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooke J. A., Webster G. R. Phospholipase A in human brain: A1-type at alkaline pH. J Neurochem. 1976 Aug;27(2):613–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb12291.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Silver M. J., Webster G. R. Phospholipase A-1 of human blood platelets. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;131(3):615–618. doi: 10.1042/bj1310615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Matsumoto M. Acid phospholipase A1 requiring phospholipids or Triton X-100 in the cytosol of cultured cells. J Biochem. 1978 Dec;84(6):1411–1422. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waite M., van Deenen L. L. Hydrolysis of phospholipids and glycerides by rat-liver preparations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 6;137(3):498–517. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


