Abstract
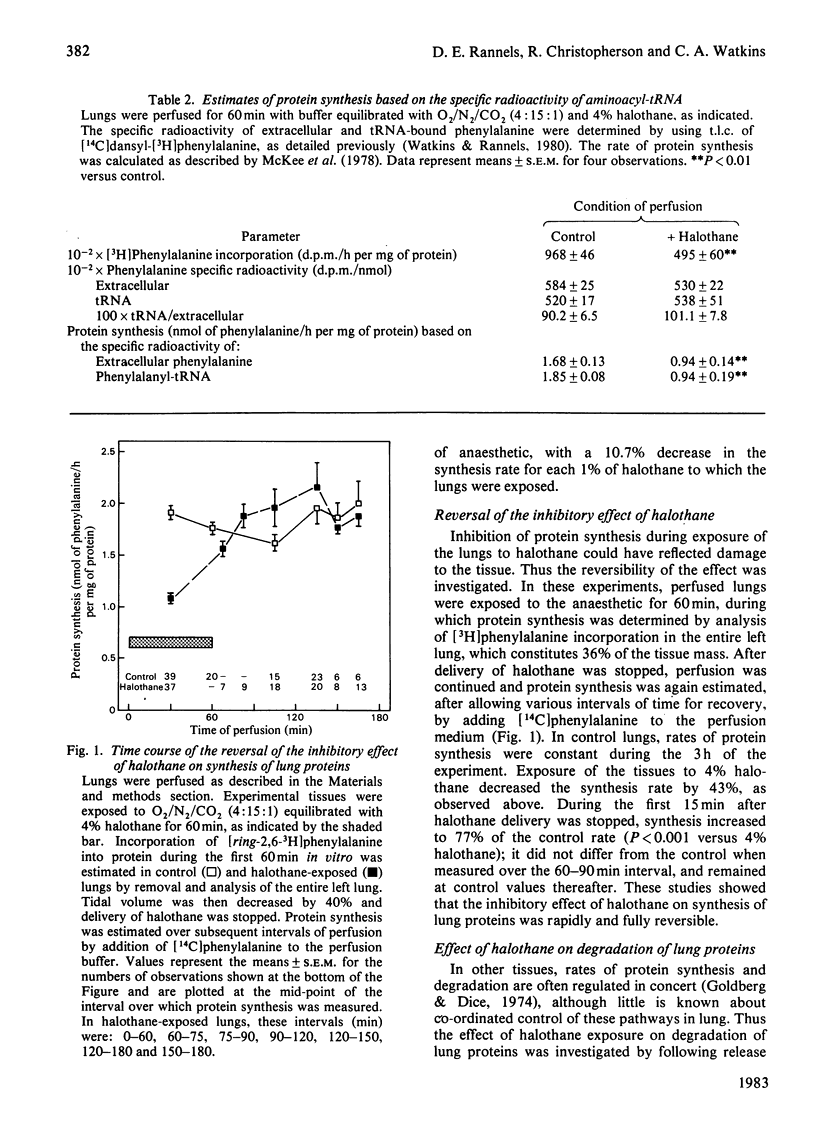
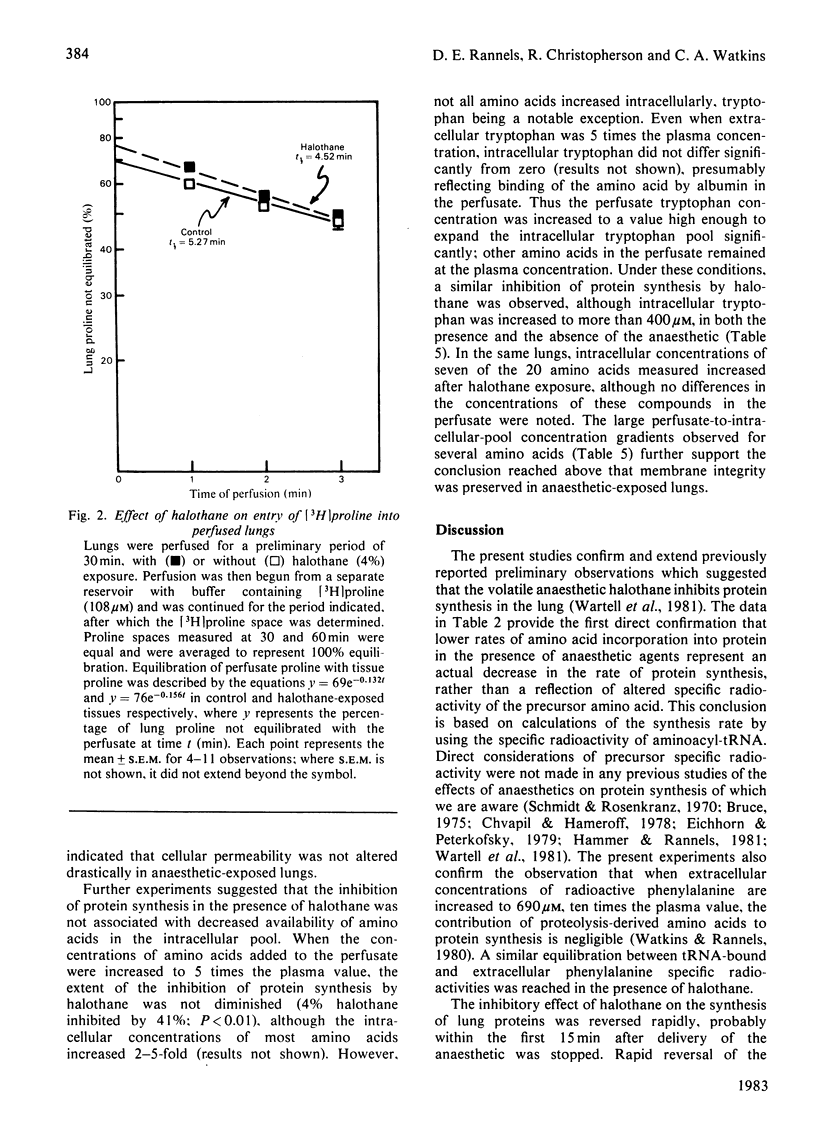
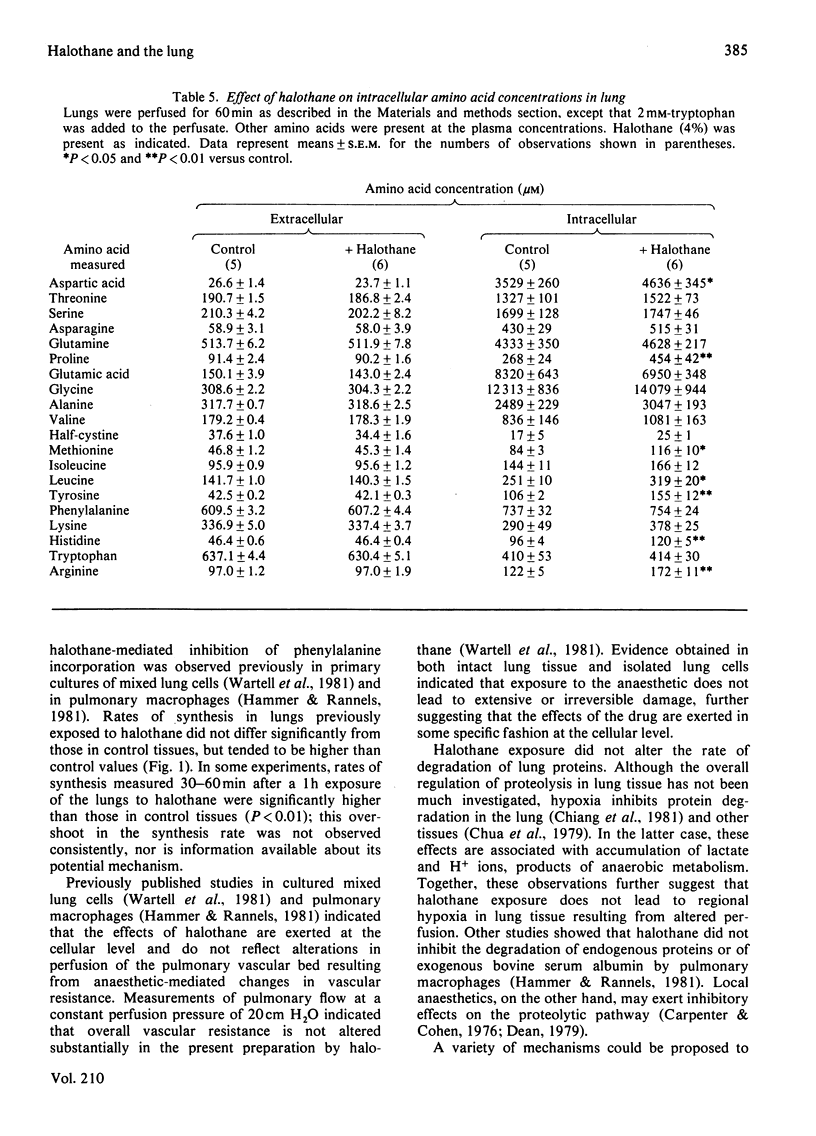
Alterations in the synthesis and degradation of proteins were investigated in intact lungs exposed to the volatile anaesthetic halothane. In rat lungs perfused in situ with Krebs-Henseleit bicarbonate buffer containing 4.5% (w/v) bovine serum albumin, 5.6 mM-glucose, plasma concentrations of 19 amino acids and 690 microM-[U-14C]-phenylalanine and equilibrated with O2/N2/CO2 (4:15:1), protein synthesis, calculated based on the specific radioactivity of aminoacyl-tRNA, was inhibited by halothane. The anaesthetic did not affect degradation of lung proteins. The inhibition of protein synthesis was rapid in onset, dose-dependent, and quickly reversible. It did not appear to be associated with overall energy depletion, with non-specific changes in cellular permeability, or with decreased availability of amino acids as substrates for protein synthesis.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altura B. T., Turlapaty P. D., Altura B. M. Pentobarbital sodium inhibits calcium uptake in vascular smooth muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 25;595(2):309–312. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakhle Y. S., Block A. J. Effects of halothane on pulmonary inactivation of noradrenaline and prostaglandin E2 in anaesthetized dogs. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Jan;50(1):87–90. doi: 10.1042/cs0500087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biebuyck J. F., Lund P. Effects of halothane and other anesthetic agents on the concentrations of rat liver metabolites in vivo. Mol Pharmacol. 1974 May;10(3):474–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biebuyck J. F., Lund P., Krebs H. A. The effects of halothane (2-bromo-2-chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane) on glycolysis and biosynthetic processes of the isolated perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(3):711–720. doi: 10.1042/bj1280711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biebuyck J. F., Lund P., Krebs H. A. The protective effect of oleate on metabolic changes produced by halothane in rat liver. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(3):721–723. doi: 10.1042/bj1280721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce D. L. Halothane inhibition of rna and protein synthesis of PHA-treated human lymphocytes. Anesthesiology. 1975 Jan;42(1):11–14. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197501000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. 125I-labeled human epidermal growth factor. Binding, internalization, and degradation in human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1976 Oct;71(1):159–171. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang M. J., Kishi F., Whitney P., Massaro D. Proteolysis in the rat lung: hypoxia and evidence for an inhibitor of proteolysis. Am J Physiol. 1981 Aug;241(2):E101–E107. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.241.2.E101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua B., Kao R. L., Rannels D. E., Morgan H. E. Inhibition of protein degradation by anoxia and ischemia in perfused rat hearts. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6617–6623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. J. Effect of anesthetics on mitochondrial function. Anesthesiology. 1973 Aug;39(2):153–164. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197308000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean R. T. Macrophage protein turnover. Evidence for lysosomal participation in basal proteolysis. Biochem J. 1979 May 15;180(2):339–345. doi: 10.1042/bj1800339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich J. W., Duffield R. Effects of the calcium antagonist verapamil on in vitro synthesis of skeletal collagen and noncollagen protein. Endocrinology. 1979 Nov;105(5):1168–1172. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-5-1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichhorn J. H., Peterkofsky B. Local anesthetic-induced inhibition of collagen secretion in cultured cells under conditions where microtubules are not depolymerized by these agents. J Cell Biol. 1979 Apr;81(1):26–42. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyring H., Woodbury J. W., D'Arrigo J. S. A molecular mechanism of general anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 1973 May;38(5):415–424. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197305000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gacad G., Dickie K., Massaro D. Protein synthesis in lung: influence of starvation on amino acid incorporation into protein. J Appl Physiol. 1972 Sep;33(3):381–384. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1972.33.3.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., Dice J. F. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):835–869. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.004155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallén B., Johansson G. Inhalation anesthetics and cytochrome P-450-dependent reactions in rat liver microsomes. Anesthesiology. 1975 Jul;43(1):34–40. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197507000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson L. S., Korner A. Influence of amino acid supply on ribosomes and protein synthesis of perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1969 Mar;111(5):703–712. doi: 10.1042/bj1110703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameyama T., Etlinger J. D. Calcium-dependent regulation of protein synthesis and degradation in muscle. Nature. 1979 May 24;279(5711):344–346. doi: 10.1038/279344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee E. E., Cheung J. Y., Rannels D. E., Morgan H. E. Measurement of the rate of protein synthesis and compartmentation of heart phenylalanine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1030–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLain G. E., Sipes I. G., Brown B. R., Jr An animal model of halothane hepatotoxicity: roles of enzyme induction and hypoxia. Anesthesiology. 1979 Oct;51(4):321–326. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197910000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahrwold M. L., Cohen P. J. Additive effect of nitrous oxide and halothane on mitochondrial function. Anesthesiology. 1973 Nov;39(5):534–536. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197311000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito H., Gillis C. N. Effects of halothane and nitrous oxide on removal of norepinephrine from the pulmonary circulation. Anesthesiology. 1973 Dec;39(6):575–580. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197312000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayler W. G., Szeto J. Effect of sodium pentobarbital on calcium in mammalian heart muscle. Am J Physiol. 1972 Feb;222(2):339–344. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.2.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price H. L. Calcium reverses myocardial depression caused by halothane: site of action. Anesthesiology. 1974 Dec;41(6):576–579. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197412000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rannels D. E., Kao R., Morgan H. E. Effect of insulin on protein turnover in heart muscle. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1694–1701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rannels D. E., Roake G. M., Watkins C. A. Additive effects of pentobarbital and halothane to inhibit synthesis of lung proteins. Anesthesiology. 1982 Aug;57(2):87–93. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198208000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rannels D. E., Wartell S. A., Watkins C. A. The measurement of protein synthesis in biological systems. Life Sci. 1982 May 17;30(20):1679–1690. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90300-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W. T., Jr, Daggy B. P., Cardell R. R., Jr Hepatic necrosis caused by halothane and hypoxia in phenobarbital-treated rats. Anesthesiology. 1979 Oct;51(4):327–333. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197910000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roufa D., Wu F. S., Martonosi A. N. The effect of Ca2+ ionophores upon the synthesis of proteins in cultured skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 5;674(2):225–237. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90380-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. M., Rosenkranz H. S. Antimicrobial activity of local anesthetics: lidocaine and procaine. J Infect Dis. 1970 Jun;121(6):597–607. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.6.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turlapaty P. D., Altura B. T., Altura B. M. Ethanol reduces Ca2+ concentrations in arterial and venous smooth muscle. Experientia. 1979 May 15;35(5):639–640. doi: 10.1007/BF01960370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartell S. A., Christopherson R., Watkins C. A., Rannels D. E. Inhibition of synthesis of lung proteins by halothane. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 May;19(3):520–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins C. A., Rannels D. E. In situ perfusion of rat lungs: stability and effects of oxygen tension. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Aug;47(2):325–329. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.47.2.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins C. A., Rannels D. E. Measurement of protein synthesis in rat lungs perfused in situ. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 15;188(1):269–278. doi: 10.1042/bj1880269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins C. A., Wartell S. A., Rannels D. E. Effect of halothane on metabolism of 5-hydroxytryptamine by rat lungs perfused in situ. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 15;210(1):157–166. doi: 10.1042/bj2100157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woźniak M. The cumulative effect of halothane and steroids on mitochondrial respiration. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(24):2959–2961. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunner W. H., Bell J., Munro H. N. The effect of feeding with a tryptophan-free amino acid mixture on rat-liver polysomes and ribosomal ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):417–428. doi: 10.1042/bj1010417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


