Abstract
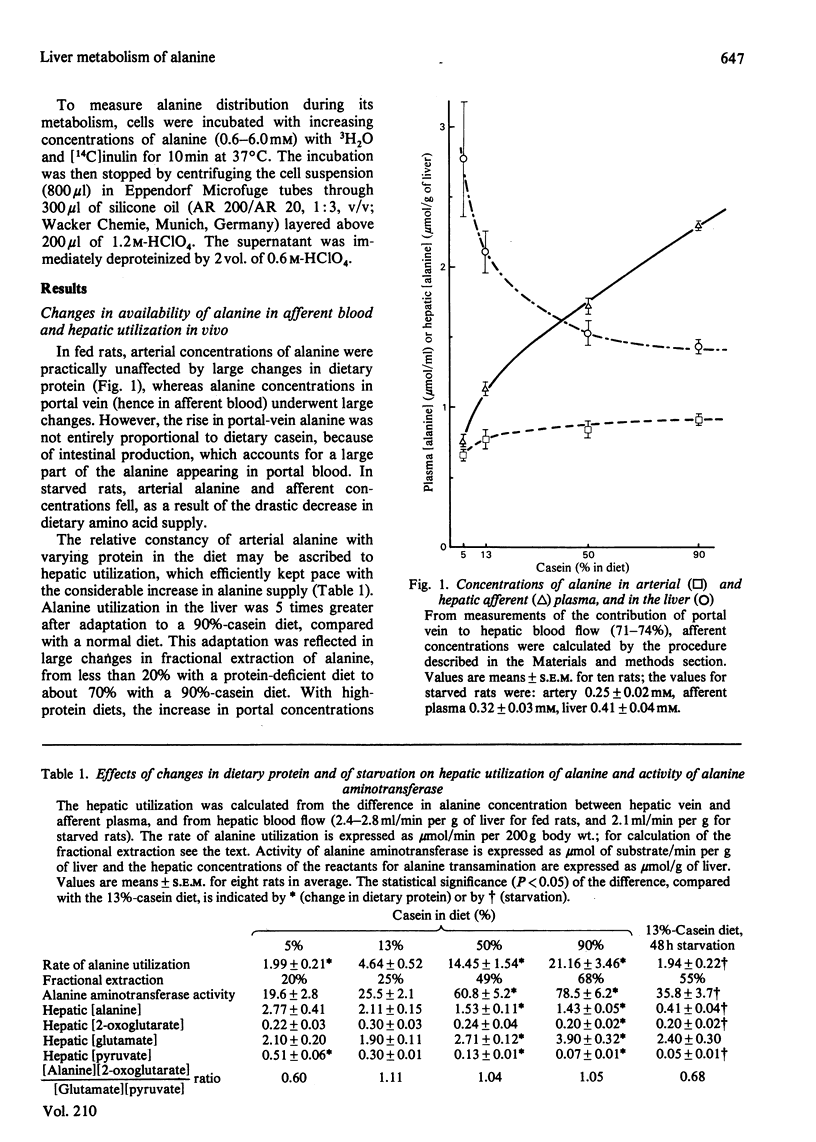
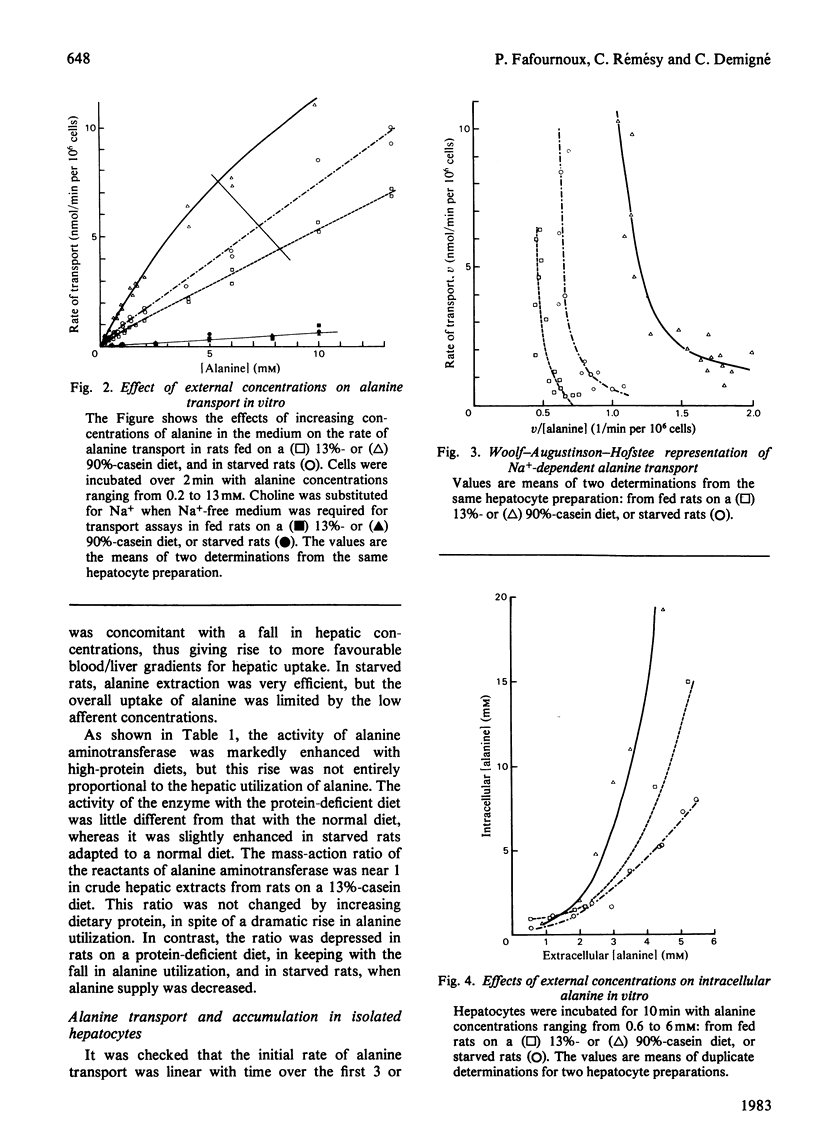
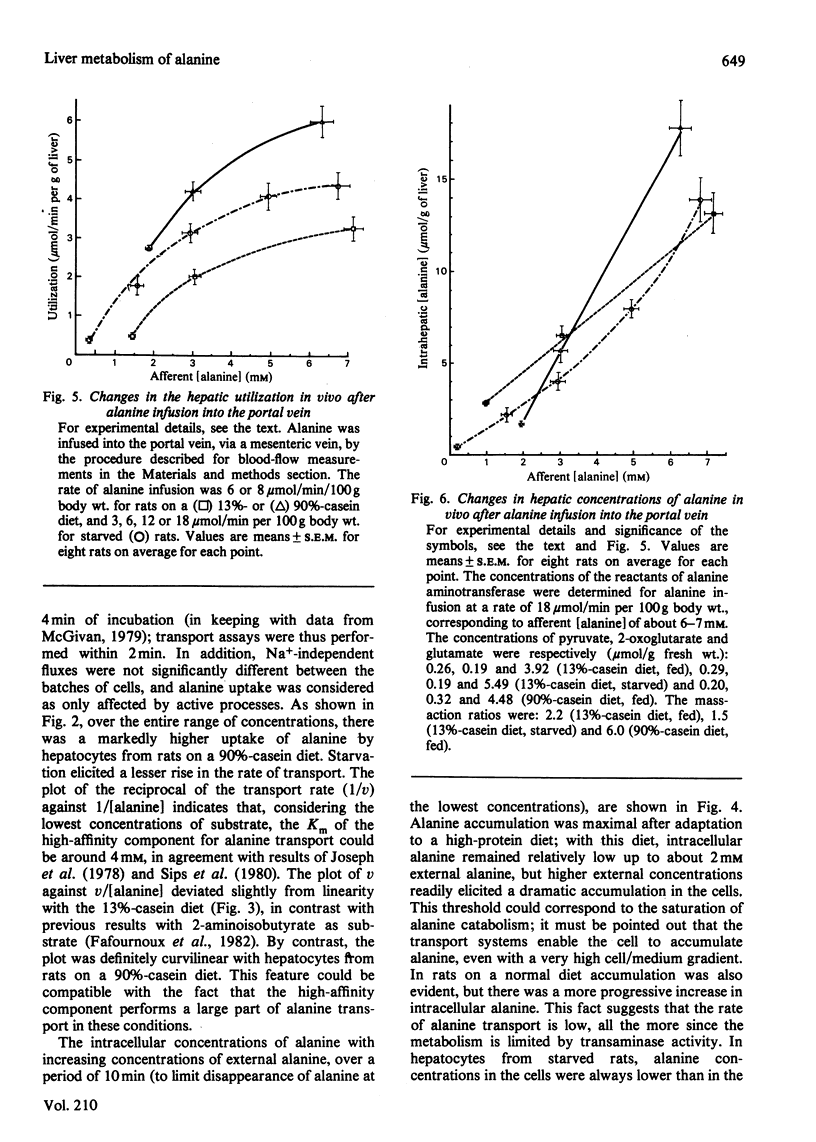
1. Factors governing hepatic utilization of alanine were studied in vivo and in vitro in rats adapted to increasing dietary protein. 2. Hepatic alanine utilization was enhanced 5-fold with a 90%-casein diet, compared with a 13%-casein diet. The increased uptake resulted from enhanced fractional extraction in the presence of high concentrations of alanine in the portal vein. 3. The increase in alanine metabolism on high-protein diets was associated with an increase in alanine aminotransferase and in pyruvate utilization for gluconeogenesis. 4. The emergence of a high-affinity component appeared to be responsible for the enhanced transport of alanine with high-protein diets. 5. High extracellular concentrations after alanine loads resulted in a maximal rate of utilization and of accumulation of alanine by liver cells in vivo and in vitro. Alanine accumulation was particularly active with high-protein diets. 6. In starved rats, alanine transport was also increased, but low concentrations of alanine in afferent blood contributed to make transport limiting for alanine utilization. 7. In fed rats, the rates of transport and catabolism of alanine generally appear to undergo parallel changes; both processes thus play a fundamental role in the control of alanine utilization by the liver.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry M. N., Friend D. S. High-yield preparation of isolated rat liver parenchymal cells: a biochemical and fine structural study. J Cell Biol. 1969 Dec;43(3):506–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canivet B., Fehlmann M., Freychet P. Glucocorticoid and catecholamine stimulation of amino acid transport in rat hepatocytes. Synthesis of a high-affinity component. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1980 Sep;19(3):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(80)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fafournoux P., Rémésy C., Demigné C. Stimulation of amino acid transport into liver cells from rats adapted to a high-protein diet. Biochem J. 1982 Jul 15;206(1):13–18. doi: 10.1042/bj2060013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehlmann M., Le Cam A., Freychet P. Insulin and glucagon stimulation of amino acid transport in isolated rat hepatocytes. Synthesis of a high affinity component of transport. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10431–10437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P. The glucose-alanine cycle. Metabolism. 1973 Feb;22(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90269-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrichs D., Schoner W. Regulation of gluconeogenesis by alanine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 22;343(2):341–355. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groen A. K., Sips H. J., Vervoorn R. C., Tager J. M. Intracellular compartmentation and control of alanine metabolism in rat liver parenchymal cells. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Feb;122(1):87–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05851.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halestrap A. P., Scott R. D., Thomas A. P. Mitochondrial pyruvate transport and its hormonal regulation. Int J Biochem. 1980;11(2):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(80)90241-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensgens H. E., Meijer A. J. Inhibition of urea-cycle activity by high concentrations of alanine. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 15;186(1):1–4. doi: 10.1042/bj1860001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Bradford N. M., McGivan J. D. Characteristics of the transport of alanine, serine and glutamine across the plasma membrane of isolated rat liver cells. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 15;176(3):827–836. doi: 10.1042/bj1760827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilberg M. S., Handlogten M. E., Christensen H. N. Characteristics of system ASC for transport of neutral amino acids in the isolated rat hepatocyte. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3304–3312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A., Freychet P. Glucagon stimulates the A system for neutral amino acid transport in isolated hepatocytes of adult rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 4;72(3):893–901. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80216-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A., Freychet P. Neutral amino acid transport. Characterization of the A and L systems in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):148–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc L., Fréminet A., Bursaux E., Poyart C. Hyperalaninémie au cours de l'hypoxie aiguë chez le lapin anesthésié. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1976 Nov-Dec;12(6):781–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M., Neufeldt N., Park B. N., Berger M., Ruderman N. Alanine metabolism and gluconeogenesis in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1976 Aug;231(2):619–626. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.2.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel H. G. Nutritional and hormonal regulation of pyruvate metabolism in the liver. Am J Physiol. 1979 May;236(5):E501–E507. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.5.E501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGivan J. D. Mechanism of the stimulation of serine and alanine transport into isolated rat liver cells by bicarbonate ions. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 15;182(3):697–705. doi: 10.1042/bj1820697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGivan J. D., Ramsell J. C., Lacey J. H. Stimulation of alanine transport and metabolism by dibutyryl cyclic AMP in the hepatocytes from fed rats. Assessment of transport as a potential rate-limiting step for alanine metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 22;644(2):295–304. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90387-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. A., Aoki T. T., Cahill G. F., Jr Effect of alanine and glycine on glucagon secretion in postabsorptive and fasting obese man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Mar;40(3):418–425. doi: 10.1210/jcem-40-3-418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rémésey C., Demigné C., Aufrère J. Inter-organ relationships between glucose, lactate and amino acids in rats fed on high-carbohydrate or high-protein diets. Biochem J. 1978 Feb 15;170(2):321–329. doi: 10.1042/bj1700321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rémésy C., Demigné C. Impaired lactate utilization in livers of rats fed high protein-diets. J Nutr. 1982 Jan;112(1):60–69. doi: 10.1093/jn/112.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWICK R. W., BARNSTEIN P. L., STANGE J. L. THE METABOLISM OF MITOCHONDRIAL PROTEINS. I. DISTRIBUTION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF THE ISOZYMES OF ALANINE AMINOTRANSFERASE IN RAT LIVER. J Biol Chem. 1965 Aug;240:3334–3340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sips H. J., Groen A. K., Tager J. M. Plasma-membrane transport of alanine is rate-limiting for its metabolism in rat-liver parenchymal cells. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 6;119(2):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80269-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannemacher R. W., Jr, Beall F. A., Canonico P. G., Dinterman R. E., Hadick C. L., Neufeld H. A. Glucose and alanine metabolism during bacterial infections in rats and rhesus monkeys. Metabolism. 1980 Mar;29(3):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Aikawa T., Matsutaka H., Okuda T., Ishikawa E. Interorganal relationships of amino acid metabolism in fed rats. Am J Physiol. 1974 Jun;226(6):1428–1433. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.6.1428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


