Abstract
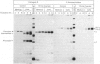
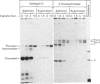
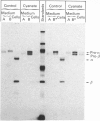
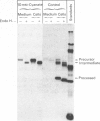
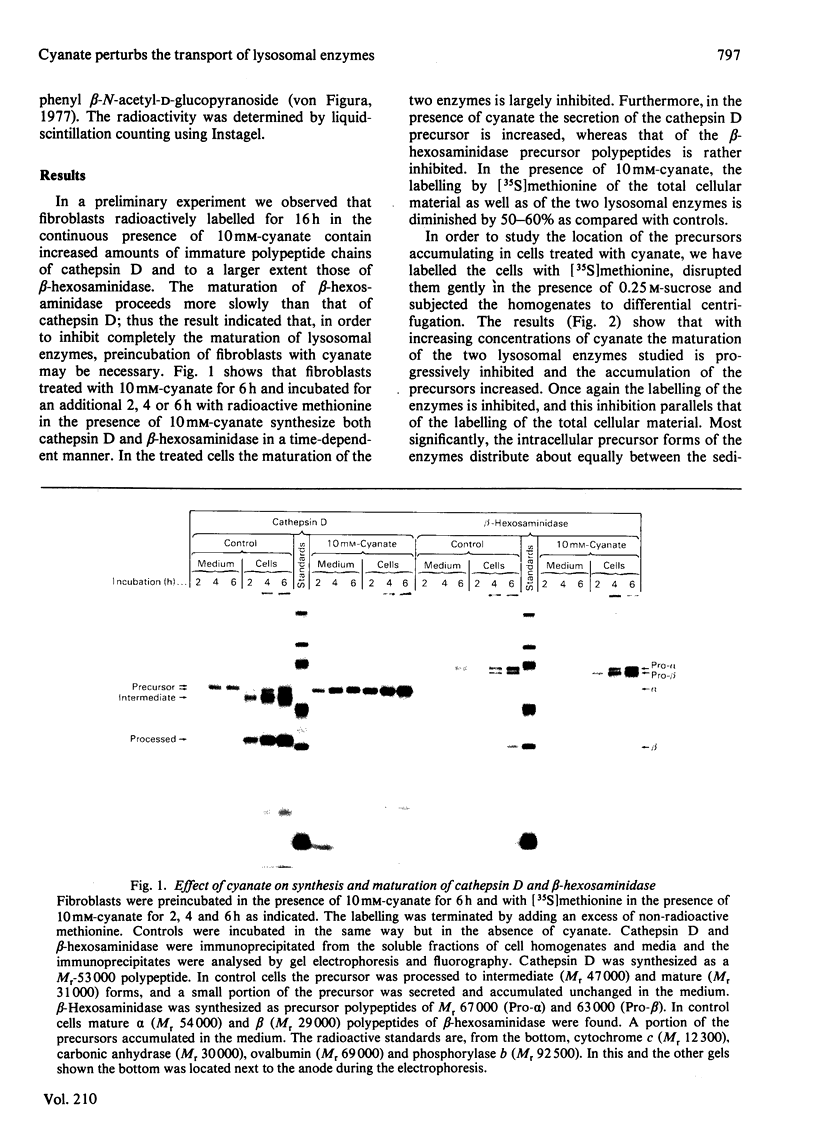
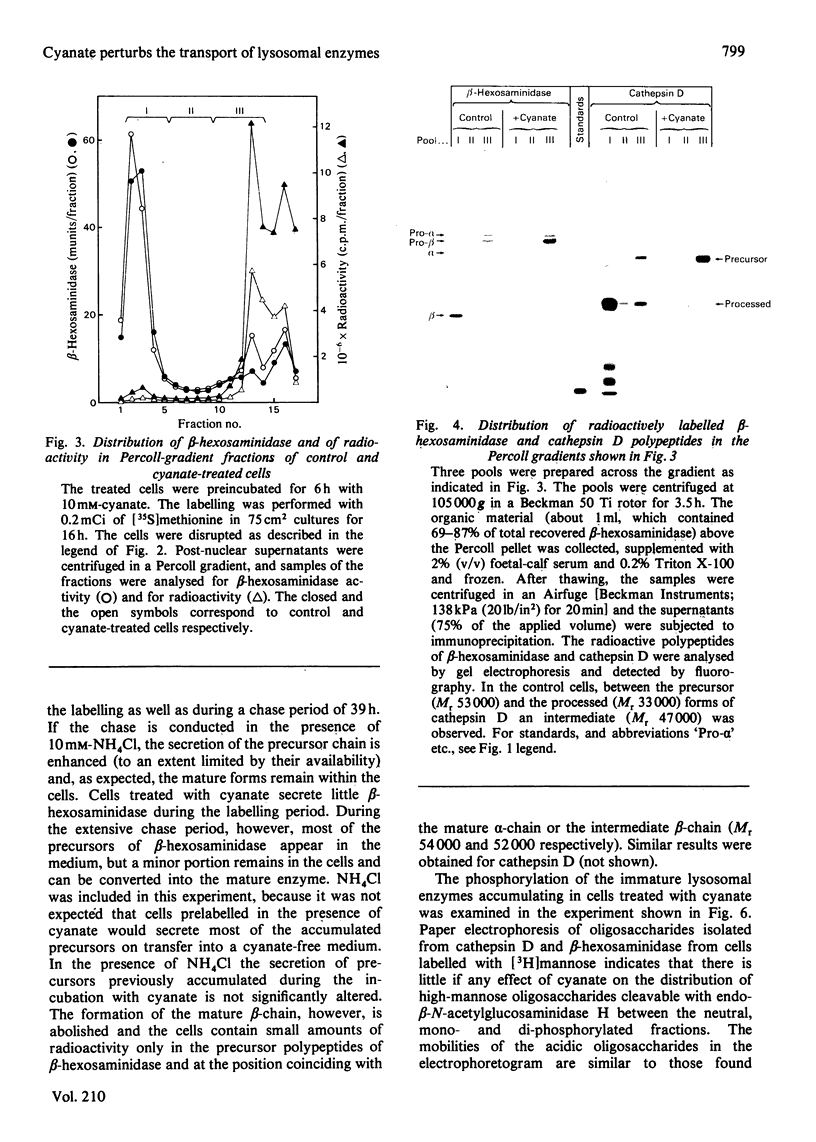
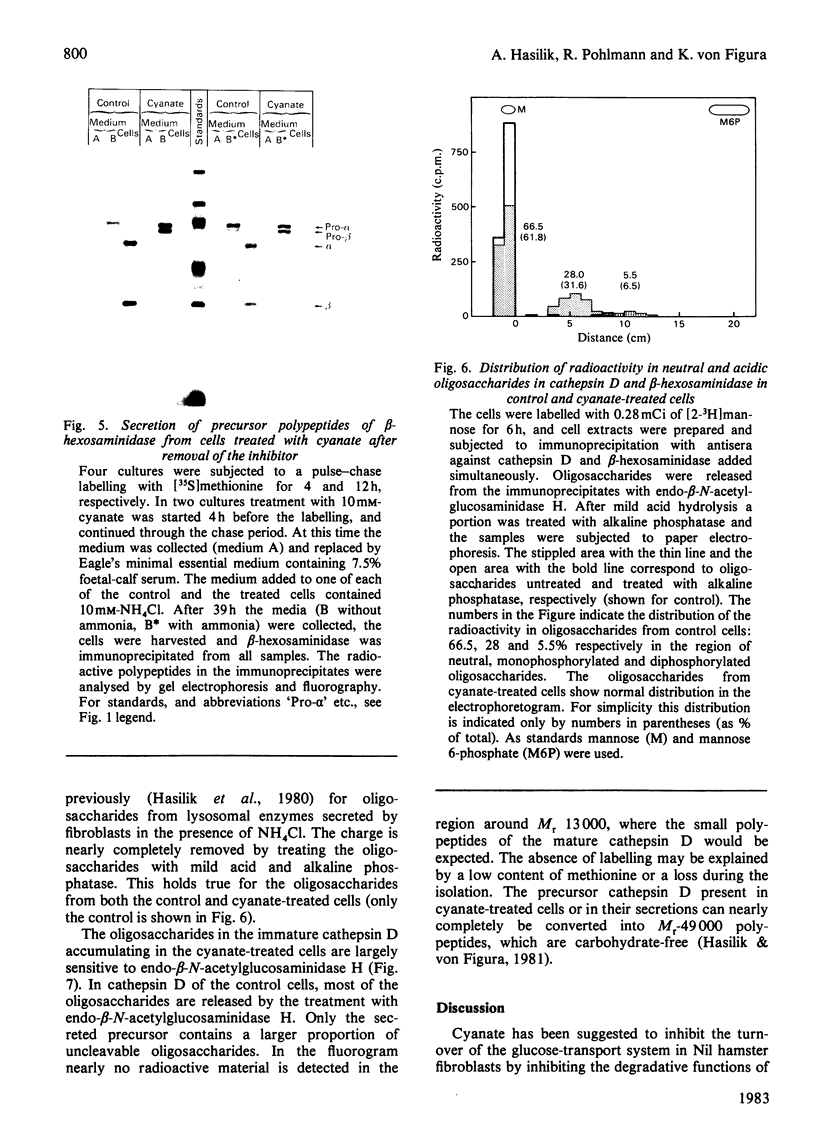
In cultured human fibroblasts, maturation of the lysosomal enzymes beta-hexosaminidase and cathepsin D is inhibited by 10 mM-potassium cyanate. In cells treated with cyanate the two enzymes accumulate in precursor forms. The location of the accumulated precursor is probably non-lysosomal; in fractionation experiments the precursors separate from the bulk of the beta-hexosaminidase activity. The secretion of the precursor of cathepsin D, but not that of beta-hexosaminidase precursor, is enhanced in the presence of cyanate. The secreted cathepsin D, as well as that remaining within the cells, contains mostly high-mannose oligosaccharides cleavable with endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H. After removal of cyanate, the accumulated precursor forms of the lysosomal enzymes are largely released from the pretreated cells. It is concluded that cyanate interferes with the maturation of lysosomal-enzyme precursors by perturbing their intracellular transport. Most probably cyanate affects certain functions of the Golgi apparatus.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bainton D. F., Farquhar M. G. Segregation and packaging of granule enzymes in eosinophilic leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1970 Apr;45(1):54–73. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentfeld-Barker M. E., Bainton D. F. Identification of primary lysosomes in human megakaryocytes and platelets. Blood. 1982 Mar;59(3):472–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christopher C. W., Morgan R. A. Are lysosomes involved in hexose transport regulation? Turnover of hexose carriers and the activity of thiol cathepsins are arrested by cyanate and ammonia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4416–4420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisch A., Neufeld E. F. Limited proteolysis of the beta-hexosaminidase precursor in a cell-free system. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8242–8246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. E., Kornfeld S. The phosphorylation of beta-glucuronidase oligosaccharides in mouse P388D1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):13060–13067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasilik A., Neufeld E. F. Biosynthesis of lysosomal enzymes in fibroblasts. Synthesis as precursors of higher molecular weight. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4937–4945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasilik A., Von Figura K. Oligosaccharides in lysosomal enzymes. Distribution of high-mannose and complex oligosaccharides in cathepsin D and beta-hexosaminidase. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Dec;121(1):125–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06440.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novikoff A. B. The endoplasmic reticulum: a cytochemist's view (a review). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2781–2787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remacle J. A., Houbion A., Houben A. Subcellular fractionation of WI-38 fibroblasts. Comparison between young and old cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 5;630(1):57–70. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90137-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rome L. H., Garvin A. J., Allietta M. M., Neufeld E. F. Two species of lysosomal organelles in cultured human fibroblasts. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90302-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M. The Golgi complex: crossroads for vesicular traffic. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1980;22:227–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varki A., Kornfeld S. Identification of a rat liver alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyl phosphodiesterase capable of removing "blocking" alpha-N-acetylglucosamine residues from phosphorylated high mannose oligosaccharides of lysosomal enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8398–8401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waheed A., Pohlmann R., Hasilik A., von Figura K. Subcellular location of two enzymes involved in the synthesis of phosphorylated recognition markers in lysosomal enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4150–4152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Figura K. Human alpha-N-acetylglucosaminidase. 1. Purification and properties. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Nov 1;80(2):523–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]