Abstract
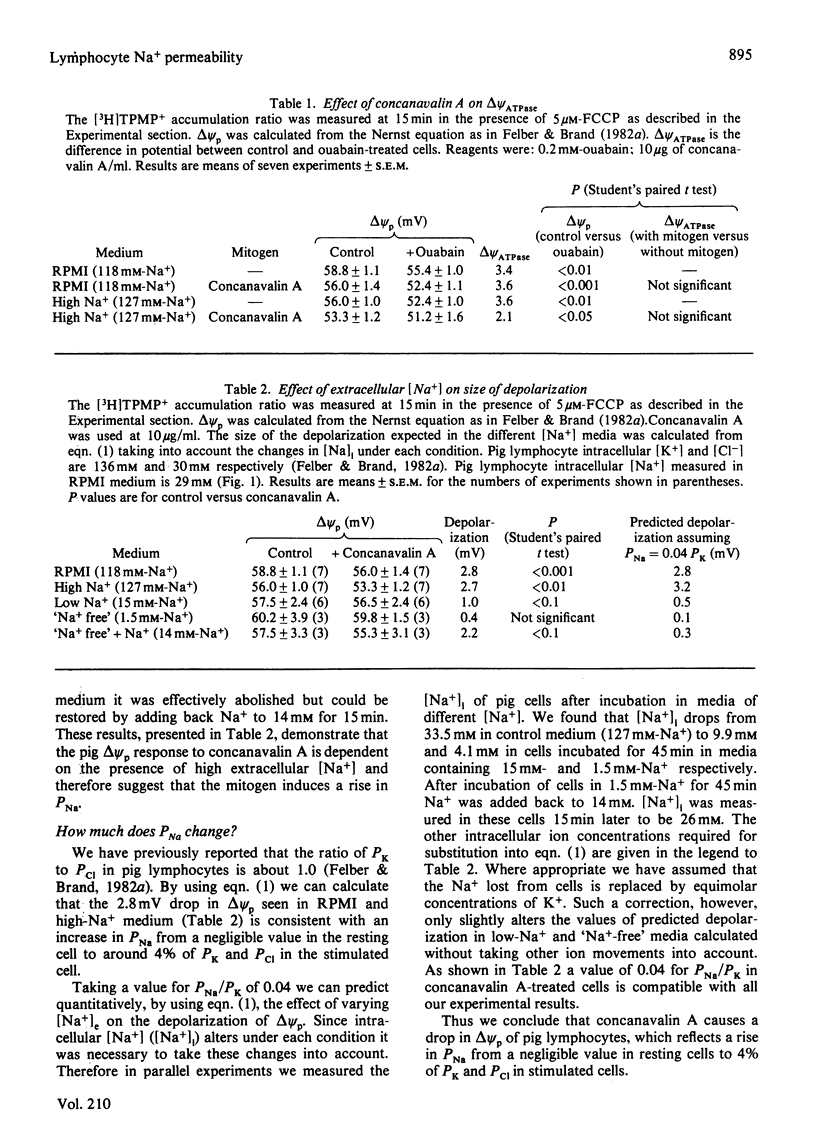
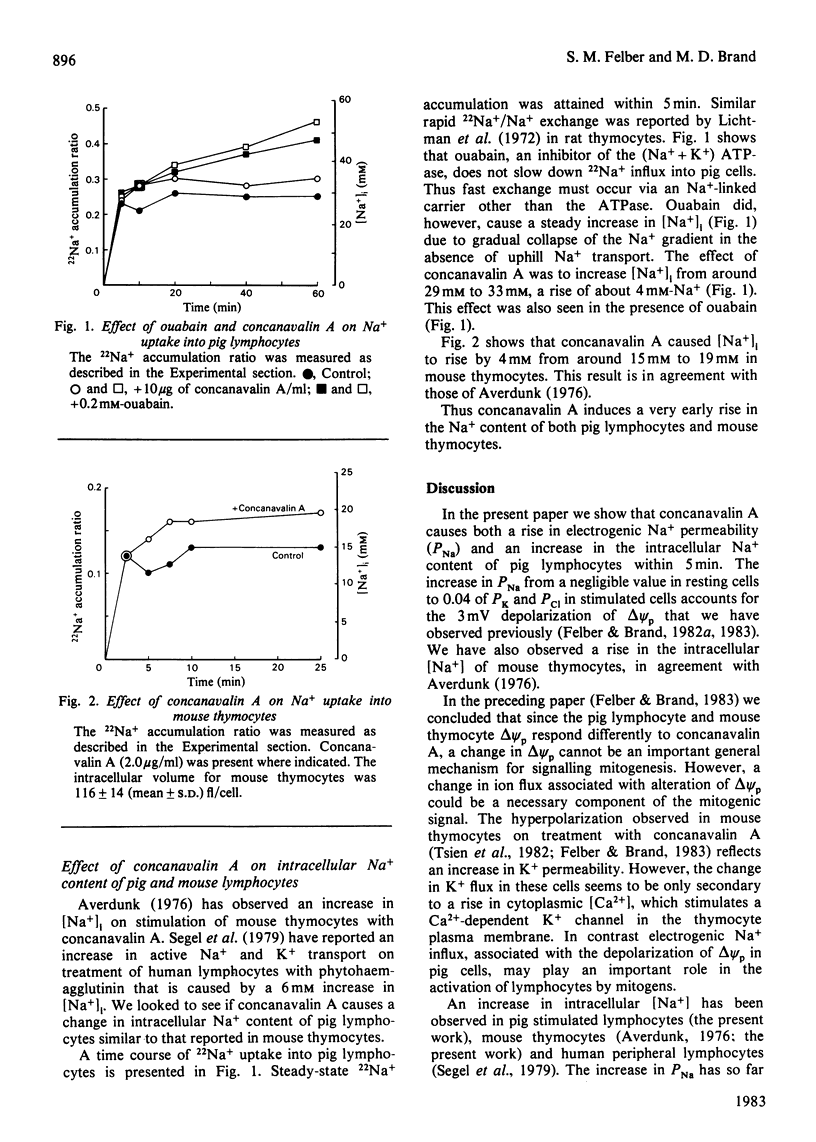
1. The 3mV depolarization of pig lymphocytes observed within 2 1/2 min of treatment with concanavalin A [Felber & Brand (1983) Biochem. J. 210, 885-891] is dependent on the presence of high extracellular [Na+]. 2. The concanavalin A-induced changes in membrane potential at high and low extracellular [Na+] are quantitatively explained by an increase in the electrogenic permeability coefficient for Na+ (PNa). This rises from a negligible value in resting cells to around 4% of the permeability coefficient for K+ or Cl- in stimulated cells. 3. Concanavalin A induces a 4mM increase in the Na+ content of pig lymphocytes. This increase in intracellular [Na+] is not due solely to stimulation of electrogenic Na+ influx resulting from the rise in PNa. 4. Thus concanavalin A stimulates both an electrogenic pathway for Na+ influx, resulting in a small depolarization of the plasma membrane, and a non-electrogenic Na+ influx pathway, resulting in a rise in intracellular [Na+].
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Averdunk R. Early changes of 'leak flux' and the cation content of lymphocytes by concanavalin A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 3;70(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91114-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers E. L., de Armendi J. Membrane potential, action potential and activation potential of eggs of the sea urchin, Lytechinus variegatus. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Aug;122(1):203–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90575-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch C., Price M. A., Johansson C. A sodium requirement for mitogen-induced proliferation in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Dec;136(2):359–369. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber S. M., Brand M. D. Early plasma-membrane-potential changes during stimulation of lymphocytes by concanavalin A. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 15;210(3):885–891. doi: 10.1042/bj2100885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber S. M., Brand M. D. Factors determining the plasma-membrane potential of lymphocytes. Biochem J. 1982 May 15;204(2):577–585. doi: 10.1042/bj2040577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korchak H. M., Weissmann G. Stimulus-response coupling in the human neutrophil. Transmembrane potential and the role of extracellular Na+. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 2;601(1):180–194. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90523-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman M. A., Jackson A. H., Peck W. A. Lymphocyte monovalent cation metabolism: cell volume, cation content and cation transport. J Cell Physiol. 1972 Dec;80(3):383–396. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040800309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Mendoza S. Monovalent ion fluxes and the control of cell proliferation in cultured fibroblasts. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;339:175–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb15977.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segel G. B., Simon W., Lichtman M. A. Regulation of sodium and potassium transport in phytohemagglutinin-stimulated human blood lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1979 Sep;64(3):834–841. doi: 10.1172/JCI109531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro H. M., Natale P. J., Kamentsky L. A. Estimation of membrane potentials of individual lymphocytes by flow cytometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5728–5730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. T-cell mitogens cause early changes in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ and membrane potential in lymphocytes. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):68–71. doi: 10.1038/295068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


