Abstract
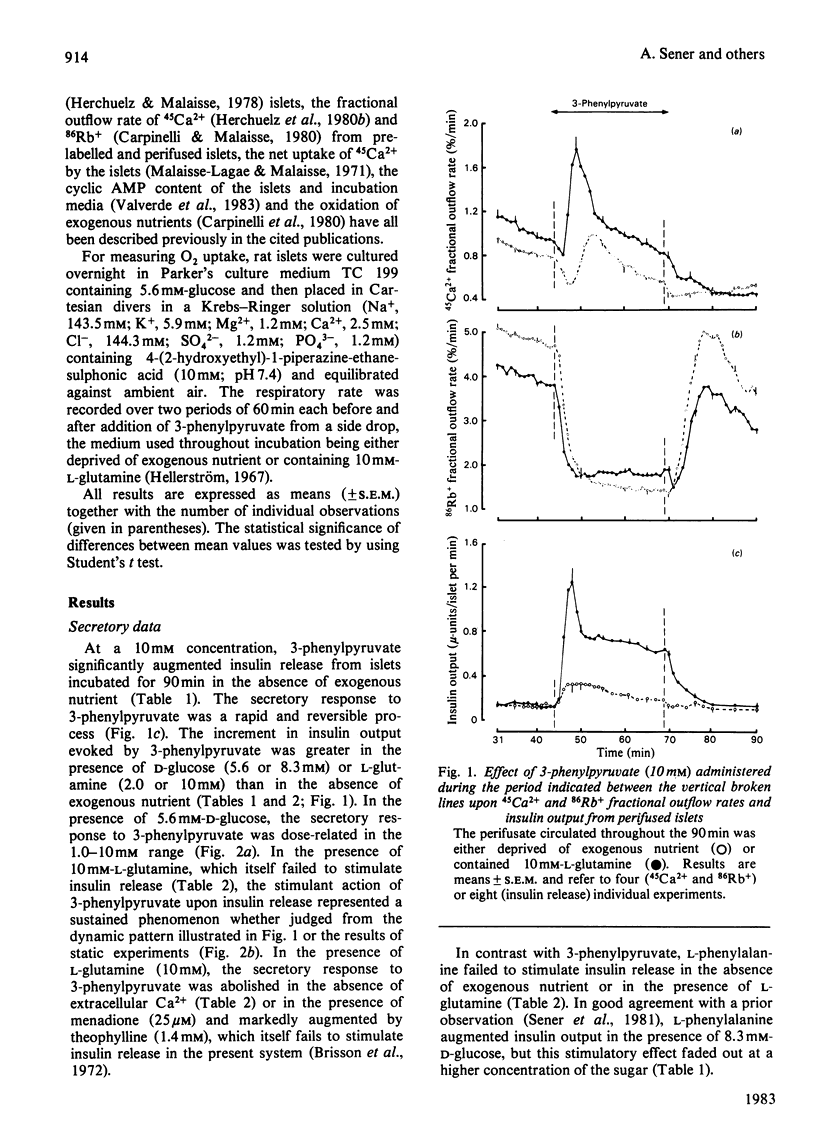
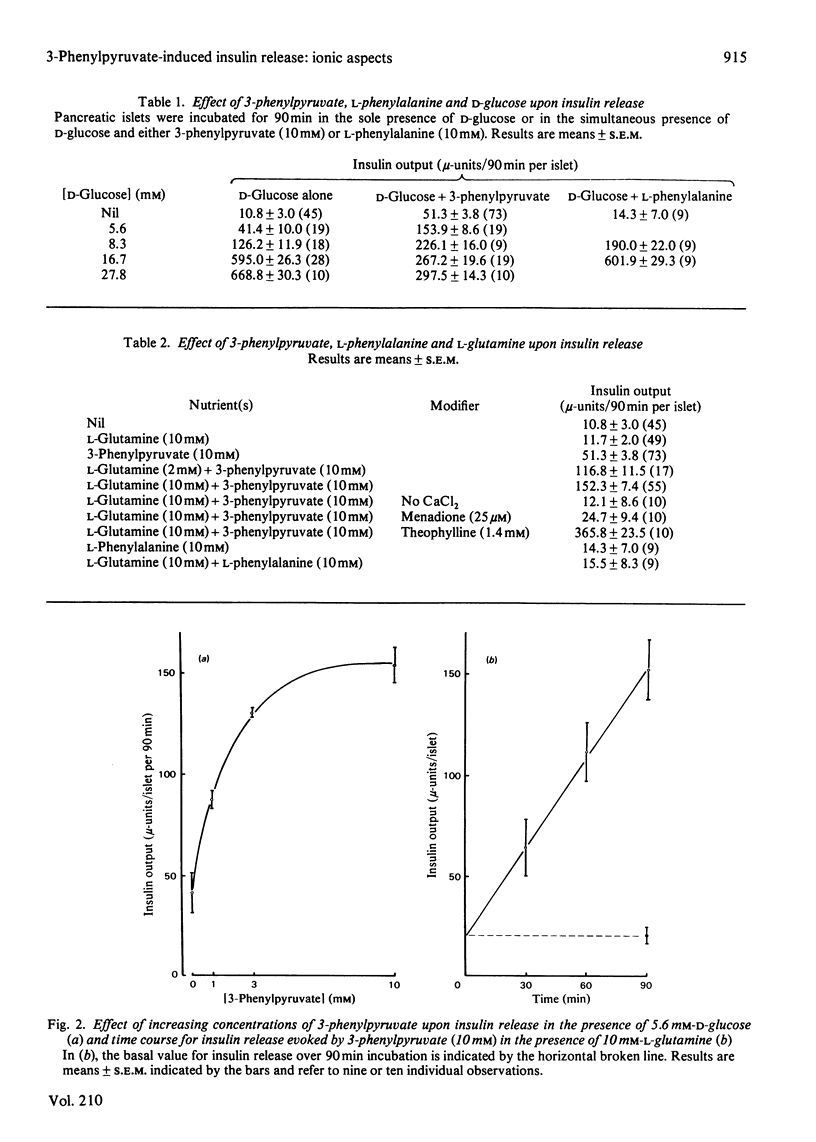
1. 3-Phenylpyruvate caused a dose-related stimulation of insulin release from rat pancreatic islets deprived of exogenous nutrient or incubated in the presence of 5.6 or 8.3 mM-D-glucose. 2. 3-Phenylpyruvate inhibited insulin release evoked by high concentrations of D-glucose (16.7 or 27.8 mM) or 4-methyl-2-oxopentanoate (10.0 mM). This inhibitory effect appeared to be attributable to impairment of 2-oxo-acid transport into the mitochondria, with resulting inhibition of D-glucose, pyruvate or 4-methyl-2-oxopentanoate oxidation. 3. 3-Phenylpyruvate failed to affect the oxidation of, and secretory response to, L-leucine, and did not augment insulin release evoked by a non-metabolized analogue of the latter amino acid. 4. L-Glutamine augmented 3-phenylpyruvate-induced insulin release. The release of insulin evoked by the combination of 3-phenylpyruvate and L-glutamine represented a sustained phenomenon, abolished in the absence of extracellular Ca2+ or the presence of menadione and potentiated by theophylline. 5. Whether in the presence or in the absence of L-glutamine, the secretory response to 3-phenylpyruvate coincided with an increase in O2 uptake, a decrease in K+ conductance, a stimulation of both Ca2+ inflow and 45Ca2+ net uptake and an increase in cyclic AMP content. 6. It is concluded that the release of insulin induced by 3-phenylpyruvate displays features classically encountered when the B-cell is stimulated by nutrient secretagogues, and is indeed attributable to an increase in nutrient catabolism.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boschero A. C., Malaisse W. J. Stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XXIX. Regulation of 86Rb+ efflux from perfused islets. Am J Physiol. 1979 Feb;236(2):E139–E146. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.2.E139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brisson G. R., Malaisse-Lagae F., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. VII. A proposed site of action for adenosine-3',5'-cyclic monophosphate. J Clin Invest. 1972 Feb;51(2):232–241. doi: 10.1172/JCI106808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpinelli A. R., Malaisse W. J. Regulation of 86Rb outflow from pancreatic islets: the dual effect of nutrient secretagogues. J Physiol. 1981 Jun;315:143–156. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpinelli A. R., Sener A., Herchuelz A., Malaisse W. J. Stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. Effect of intracellular acidification upon calcium efflux from islet cells. Metabolism. 1980 Jun;29(6):540–545. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpinelli A., Malaisse W. J. Regulation of 86Rb+ outflow from pancreatic islets. I. Reciprocal changes in the response to glucose, tetraethylammonium and quinine. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1980 Feb;17(2):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(80)90122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halestrap A. P., Brand M. D., Denton R. M. Inhibition of mitochondrial pyruvate transport by phenylpyruvate and alpha-ketoisocaproate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 10;367(1):102–108. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90140-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Meissner H. P. Effects of amino acids on membrane potential and 86Rb+ fluxes in pancreatic beta-cells. Am J Physiol. 1981 Mar;240(3):E245–E252. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.3.E245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herchuelz A., Couturier E., Malaisse W. J. Regulation of calcium fluxes in pancreatic islets: glucose-induced calcium-calcium exchange. Am J Physiol. 1980 Feb;238(2):E96–103. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.2.E96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herchuelz A., Malaisse W. J. Regulation of calcium fluxes in pancreatic islets: dissociation between calcium and insulin release. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:409–424. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herchuelz A., Malaisse W. J. Regulation of calcium fluxes in pancreatic islets: two calcium movements' dissociated response to glucose. Am J Physiol. 1980 Feb;238(2):E87–E95. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.2.E87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herchuelz A., Sener A., Malaisse W. J. Regulation of calcium fluxes in rat pancreatic islets: calcium extrusion by sodium-calcium countertransport. J Membr Biol. 1980 Nov 15;57(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01868981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C., Sener A., Herchuelz A., Atwater I., Kawazu S., Boschero A. C., Somers G., Devis G., Malaisse W. J. Similarities in the stimulus-secretion coupling mechanisms of glucose- and 2-keto acid-induced insulin release. Endocrinology. 1980 Jan;106(1):203–219. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-1-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Kostianovsky M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967 Jan;16(1):35–39. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrun P., Malaisse W. J., Herchuelz A. Paradoxical activation by glucose of quinine-sensitive potassium channels in the pancreatic B-cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jul 16;107(1):350–356. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91711-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenzen S., Panten U. Effects of pyruvate, L-lactate, and 3-phenylpyruvate on function of ob/ob mouse pancreatic islets: insulin secretion in relation to 45Ca2+ uptake and metabolism. Biochem Med. 1981 Jun;25(3):366–372. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(81)90095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse-Lagae F., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. 3. Uptake of 45 calcium by isolated islets of Langerhans. Endocrinology. 1971 Jan;88(1):72–80. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-1-72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse-Lagae F., Sener A., Garcia-Morales P., Valverde I., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of amino acid-induced insulin release. Influence of a nonmetabolized analog of leucine on the metabolism of glutamine in pancreatic islets. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3754–3758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Brisson G., Malaisse-Lagae F. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. I. Interaction of epinephrine and alkaline earth cations. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Dec;76(6):895–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Hutton J. C., Carpinelli A. R., Herchuelz A., Sener A. The stimulus-secretion coupling of amino acid-induced insulin release: metabolism and cationic effects of leucine. Diabetes. 1980 Jun;29(6):431–437. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.6.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Hutton J. C., Kawazu S., Sener A. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. Metabolic effects of menadione in isolated islets. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 1;87(1):121–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Malaisse-Lagae F., Sener A. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release: effect of aminooxyacetate upon nutrient-stimulated insulin secretion. Endocrinology. 1982 Aug;111(2):392–397. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-2-392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Sener A., Carpinelli A. R., Anjaneyulu K., Lebrun P., Herchuelz A., Christophe J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XLVI. Physiological role of L-glutamine as a fuel for pancreatic islets. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1980 Nov;20(2):171–189. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(80)90080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Sener A., Malaisse-Lagae F., Welsh M., Matthews D. E., Bier D. M., Hellerström C. The stimulus-secretion coupling of amino acid-induced insulin release. Metabolic response of pancreatic islets of L-glutamine and L-leucine. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8731–8737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Sener A., Malaisse-Legae F., Hutton J. C., Christophe J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of amino acid-induced insulin release. Metabolic interaction of L-glutamine and 2-ketoisocaproate in pancreatic islets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 18;677(1):39–49. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Sener A., Welsh M., Malaisse-Lagae F., Hellerström C., Christophe J. Mechanism of 3-phenylpyruvate-induced insulin release. Metabolic aspects. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 15;210(3):921–927. doi: 10.1042/bj2100921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panten U., Langer J. Mechanism of 3-phenylpyruvate-induced insulin release from isolated pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 15;198(2):353–356. doi: 10.1042/bj1980353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sener A., Malaisse W. J. Stimulation of insulin release by L-glutamine. Mol Cell Biochem. 1980 Dec 16;33(3):157–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00225288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sener A., Somers G., Devis G., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of amino acid-induced insulin release. Biosynthetic and secretory responses of rat pancreatic islet to L-leucine and L-glutamine. Diabetologia. 1981 Aug;21(2):135–142. doi: 10.1007/BF00251281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


