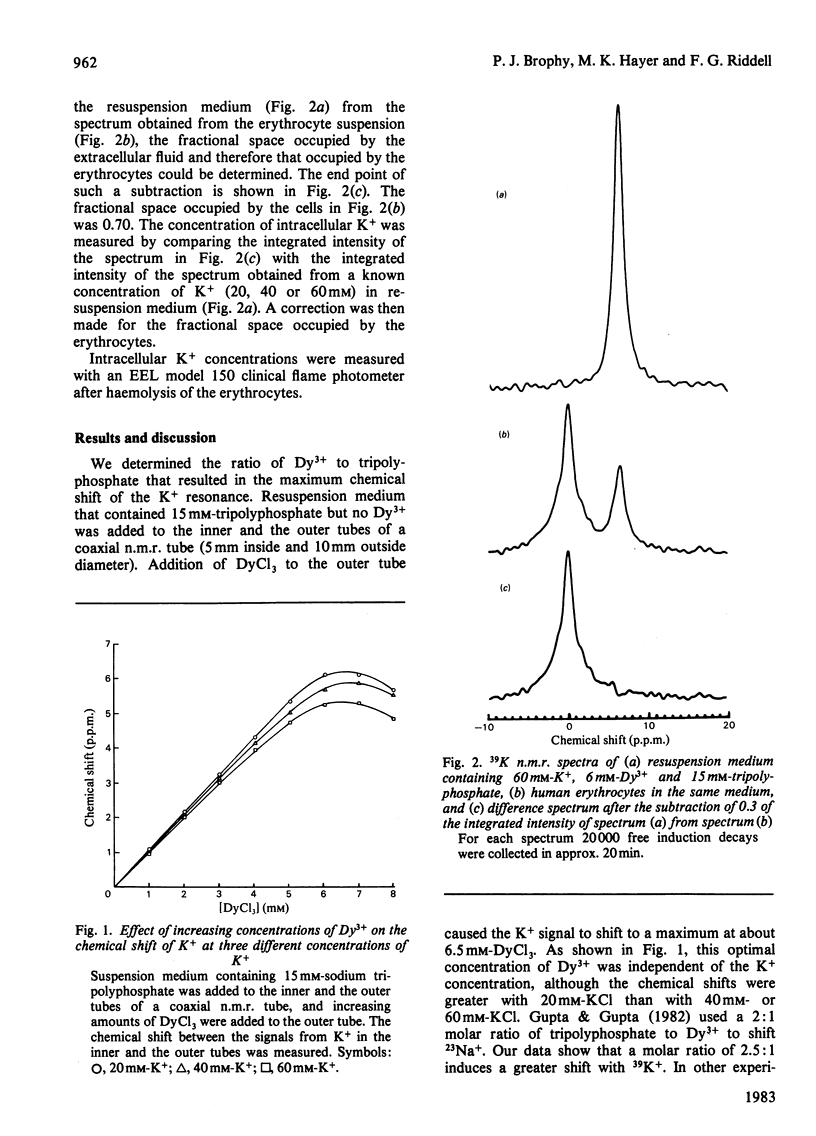
Abstract
39K n.m.r. was used to detect and quantify K+ within human erythrocytes. A shift reagent consisting of an anionic complex of dysprosium(III) with sodium tripolyphosphate permitted a distinction to be made between K+ inside and outside erythrocytes. Intracellular K+ concentrations determined by this method were similar to values obtained by flame photometry.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Pike M. M., Simon S. R., Balschi J. A., Springer C. S., Jr High-resolution NMR studies of transmembrane cation transport: use of an aqueous shift reagent for 23Na. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):810–814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


