Abstract
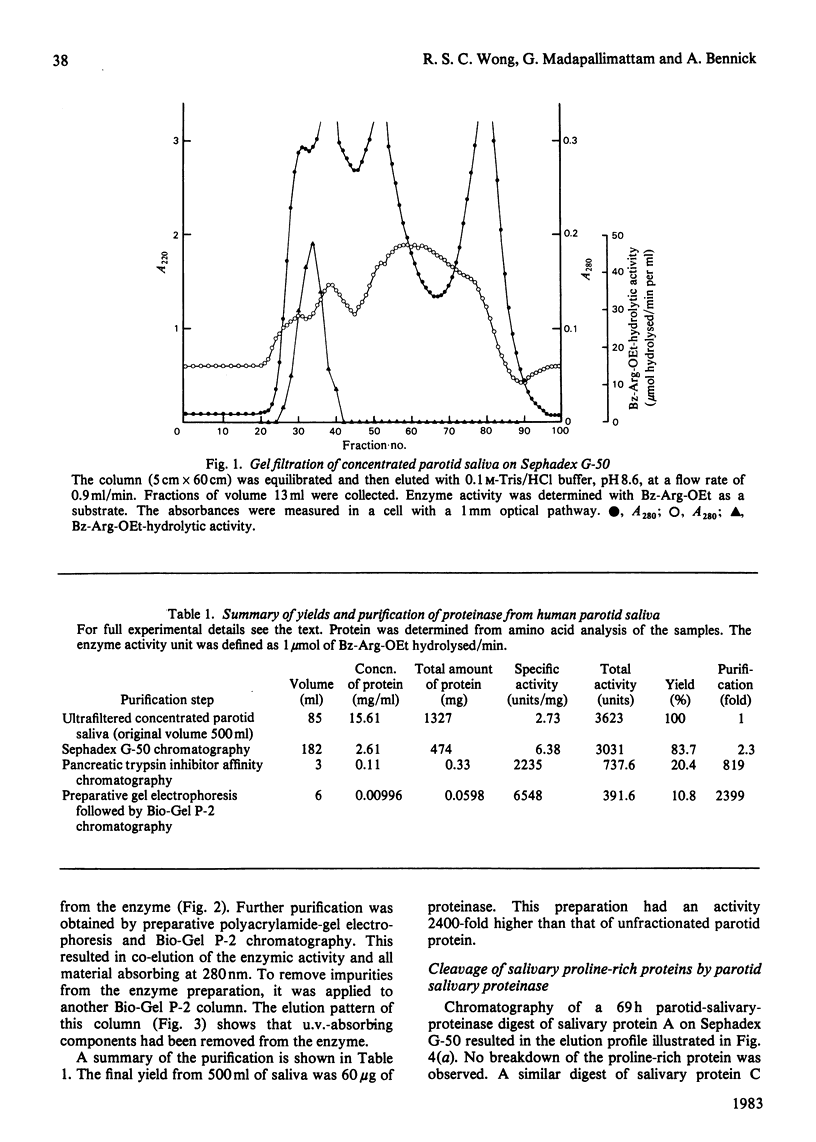
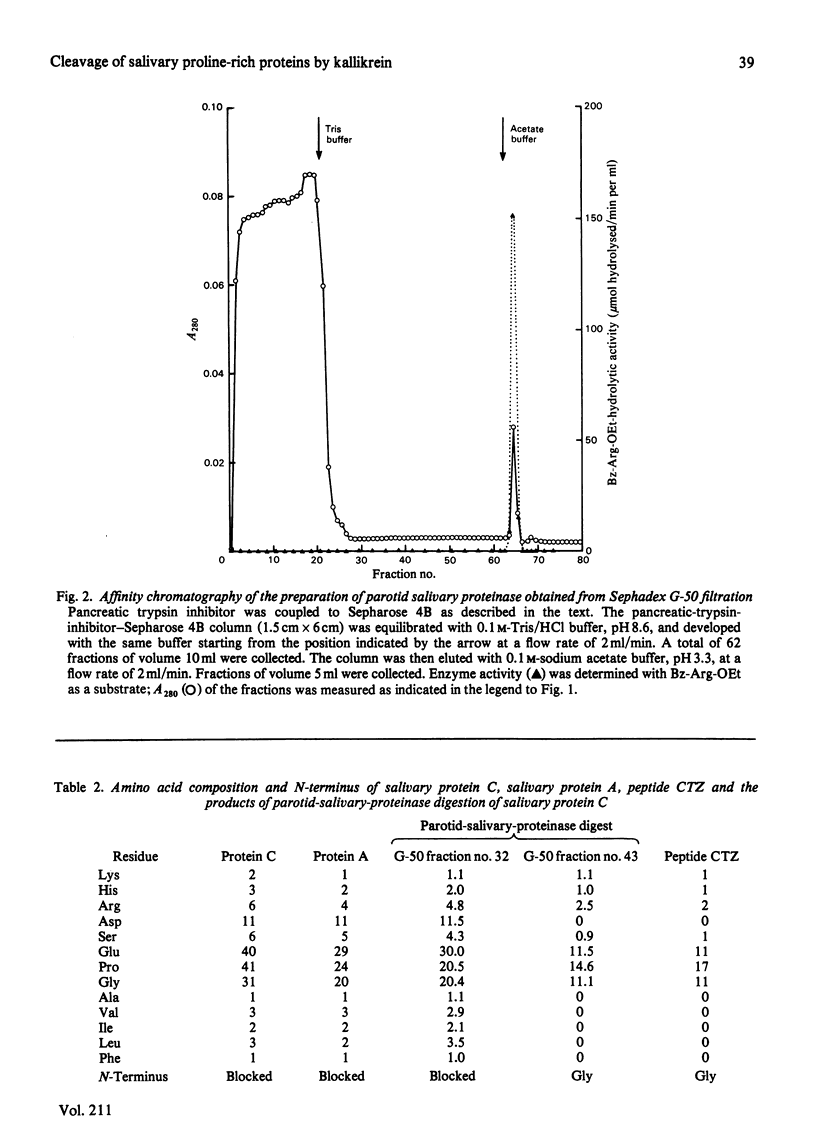
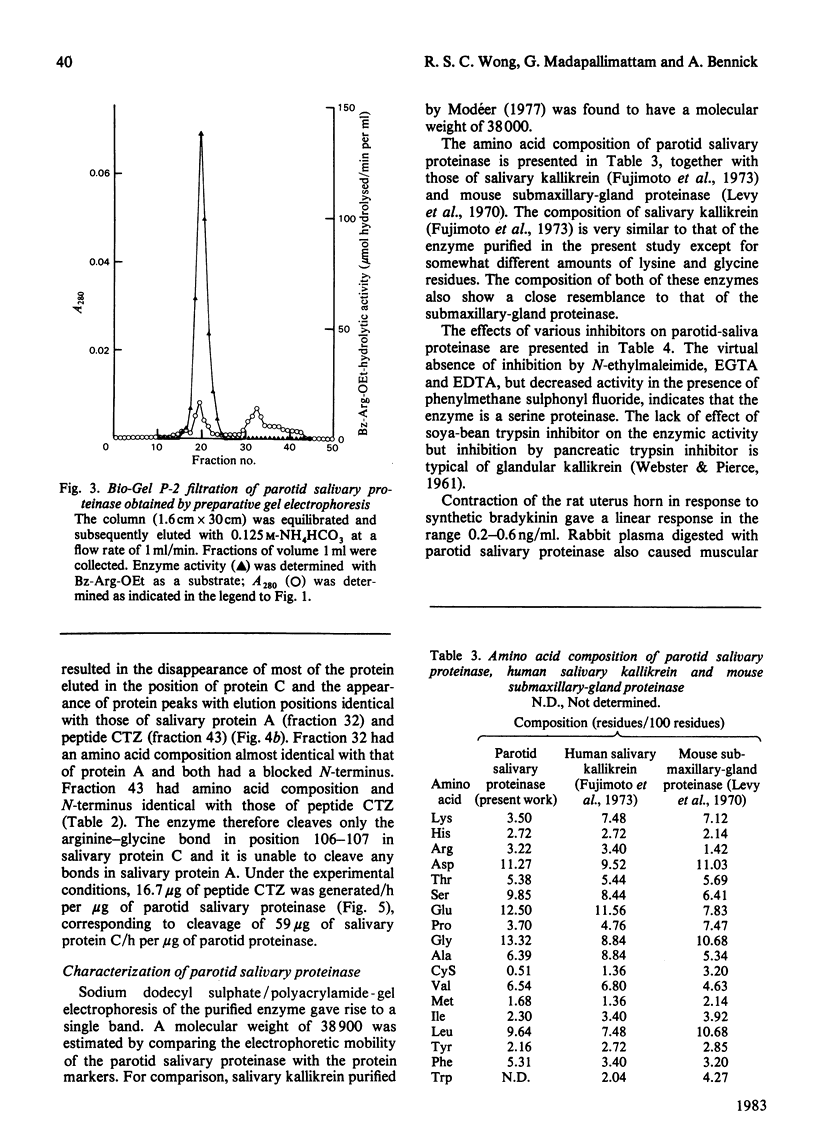
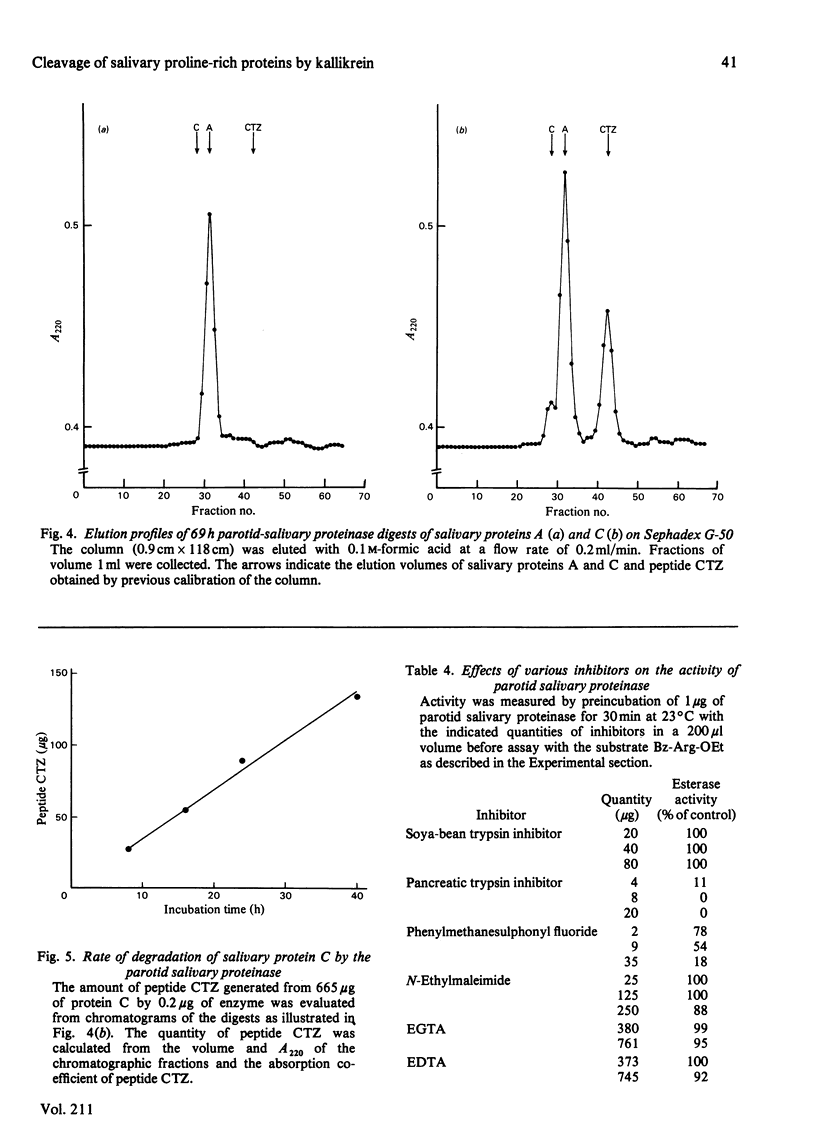
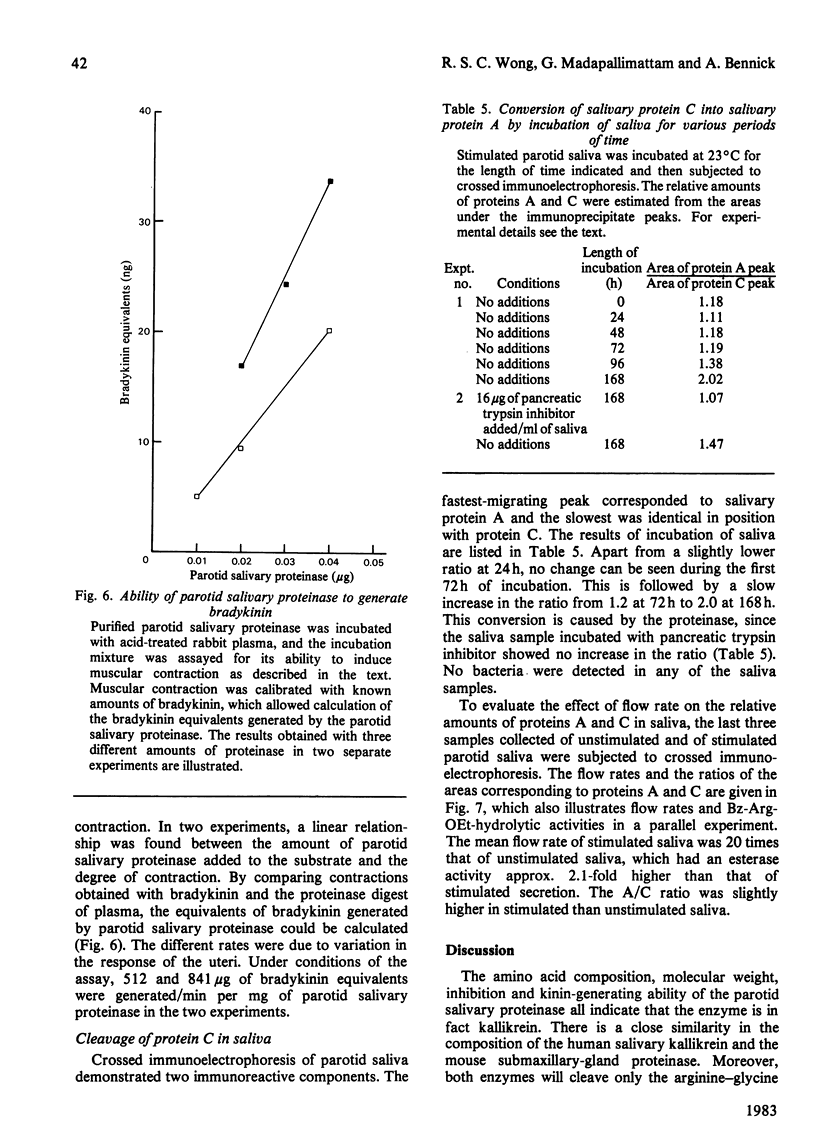
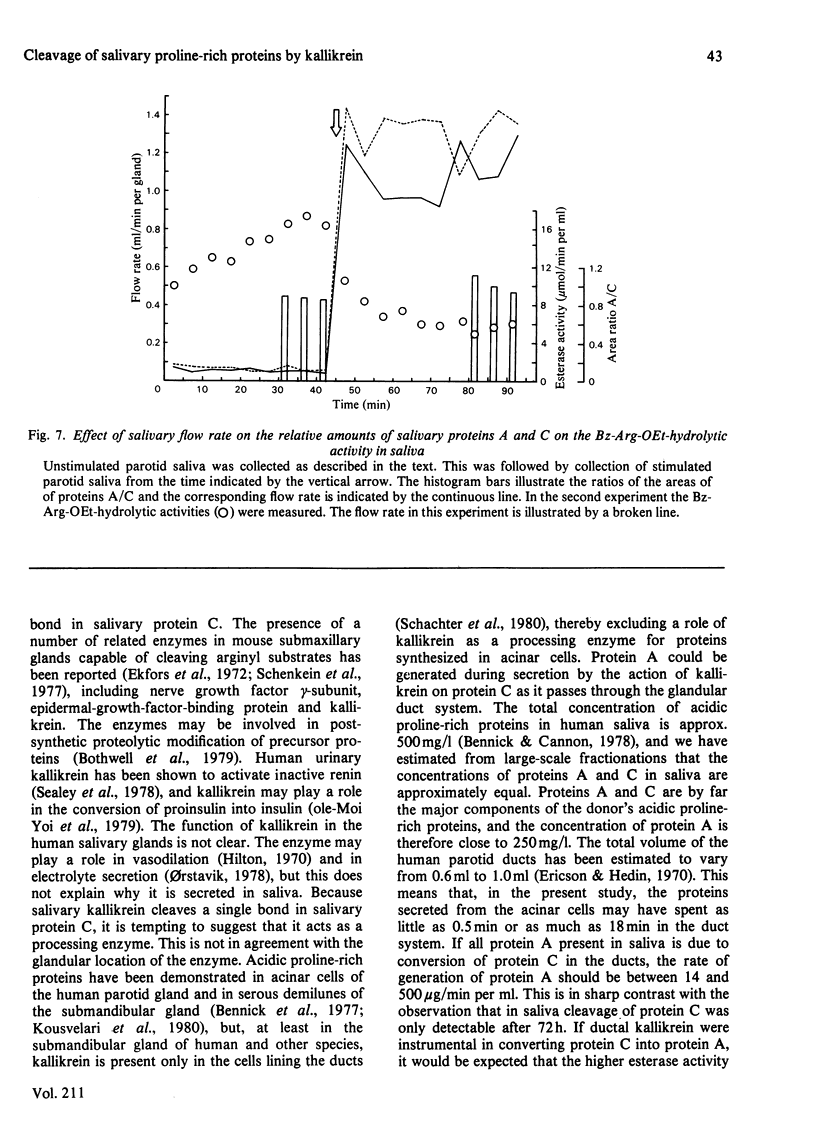
An enzyme was purified from human parotid saliva that can cleave a single arginine-glycine peptide bond between residues 106 and 107 in human salivary proline-rich protein C, hereby giving rise to another proline-rich protein A, which is also found in saliva. The enzyme was purified 2400-fold. It cleaved salivary protein C at the rate of 59 micrograms of protein/h per microgram of enzyme and had amino acid composition, molecular weight and inhibition characteristics similar to those reported for human salivary kallikrein. Confirmation that the enzyme was kallikrein was demonstrated by its kinin-generating ability. Histochemical evidence indicates that a post-synthetic cleavage of protein C by kallikrein would have to take place during passage of saliva through the secretory ducts. In secreted saliva, cleavage of salivary protein C can only be observed after 72 h incubation. In addition, there is no effect of salivary flow rate on the relative amounts of proteins A and C in saliva. On the basis of the experimental observations, it is proposed that in vivo it is unlikely that kallikrein secreted from ductal cells plays a significant role in converting protein C into protein A.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ardlie N. G., Packham M. A., Mustard J. F. Adenosine diphosphate-induced platelet aggregation in suspensions of washed rabbit platelets. Br J Haematol. 1970 Jul;19(1):7–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennick A., Cannon M. Quantitative study of the interaction of salivary acidic proline-rich proteins with hydroxyapatite. Caries Res. 1978;12(3):159–169. doi: 10.1159/000260326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennick A. Chemical and physical characteristics of a phosphoprotein from human parotid saliva. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;145(3):557–567. doi: 10.1042/bj1450557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennick A. Chemical and physical characterization of a phosphoprotein, Protein C, from human saliva and comparison with a related protein A. Biochem J. 1977 May 1;163(2):229–239. doi: 10.1042/bj1630229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennick A., Connell G. E. Purification and partial characterization of four proteins from human parotid saliva. Biochem J. 1971 Jul;123(3):455–464. doi: 10.1042/bj1230455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell M. A., Wilson W. H., Shooter E. M. The relationship between glandular kallikrein and growth factor-processing proteases of mouse submaxillary gland. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7287–7294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekfors T. O., Malmiharju T., Hopsu-Havu V. K. Isolation of six trypsin-like esteropeptidases from the mouse submandibular gland. Enzymologia. 1972 Sep 30;43(3):151–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson S., Hedin M. A clinical roentgenologic method of calculating the volume of the parotid gland. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1970 Apr;29(4):536–543. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(70)90463-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson D. B., Fort A., Elliott A. L., Potts A. J. Circadian rhythms in human parotid saliva flow rate and composition. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Sep;18(9):1155–1173. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90089-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto Y., Moriya H., Moriwaki C. Studies on human salivary kallikrein. I. Isolation of human salivary kallikrein. J Biochem. 1973 Aug;74(2):239–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMEL B. C. A modified spectrophotometric determination of chymotrypsin, trypsin, and thrombin. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Dec;37:1393–1399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isemura S., Saitoh E., Sanada K. The amino acid sequence of a salivary proline-rich peptide, P-C, and its relation to a salivary proline-rich phosphoprotein, protein C. J Biochem. 1980 Apr;87(4):1071–1077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn R. C., Friedman R. D., Merritt A. D. Human salivary proline-rich (Pr) proteins: a posttranslational derivation of the phenotypes. Biochem Genet. 1979 Dec;17(11-12):1061–1077. doi: 10.1007/BF00504345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kousvelari E. E., Baratz R. S., Burke B., Oppenheim F. G. Immunochemical identification and determination of proline-rich proteins in salivary secretions, enamel pellicle, and glandular tissue specimens. J Dent Res. 1980 Aug;59(8):1430–1438. doi: 10.1177/00220345800590081201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. P., Baxter H. J., Guillemette J. G., Lawford H. G., Lewis P. N. Structural studies on yeast nucleosomes. Can J Biochem. 1982 Mar;60(3):379–388. doi: 10.1139/o82-045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modéer Characterization of kallikrein from human saliva isolated by use of affinity chromatography. Acta Odontol Scand. 1977;35(1):31–39. doi: 10.3109/00016357709055988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Poon M. C., Takeuchi Y. The kinin-system of human plasma. I. Isolation of a low molecular weight activator of prekallikrein. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1971;40(1):89–112. doi: 10.1159/000230397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orstavik T. B. The distribution and secretion of kallikrein in some exocrine organs of the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 Dec;104(4):431–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parikh I., March S., Cuatercasas P. Topics in the methodology of substitution reactions with agarose. Methods Enzymol. 1974;34:77–102. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(74)34009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percy M. E., Buchwald B. M. A manual method of sequential Edman degradation followed by dansylation for the determination of protein sequences. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jan;45(1):60–67. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWERT G. W., TAKENAKA Y. A spectrophotometric determination of trypsin and chymotrypsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Apr;16(4):570–575. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90280-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter M., Peret M. W., Moriwaki C., Rodrigues J. A. Localization of kallikrein in submandibular gland of cat, guinea pig, dog, and man by the immunoperoxidase method. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Dec;28(12):1295–1300. doi: 10.1177/28.12.7014710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkein I., Levy M., Franklin E. C., Frangione B. Proteolytic enzymes from the mouse submaxillary gland. Specificity restricted to arginine residues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jul;182(1):64–70. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey J. E., Atlas S. A., Laragh J. H., Oza N. B., Ryan J. W. Human urinary kallikrein converts inactive to active renin and is a possible physiological activator of renin. Nature. 1978 Sep 14;275(5676):144–145. doi: 10.1038/275144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBSTER M. E., PIERCE J. V. Action of the kallikreins on synthetic ester substrates. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 May;107:186–191. doi: 10.3181/00379727-107-26575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. S., Bennick A. The primary structure of a salivary calcium-binding proline-rich phosphoprotein (protein C), a possible precursor of a related salivary protein A. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5943–5948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. S., Hofmann T., Bennick A. The complete primary structure of a proline-rich phosphoprotein from human saliva. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4800–4808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoi O. O., Seldin D. C., Spragg J., Pinkus G. S., Austen K. F. Sequential cleavage of proinsulin by human pancreatic kallikrein and a human pancreatic kininase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3612–3616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


