Abstract
The binding of NADH and NAD+ by cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase was studied by various direct and indirect methods. At pH 7.0 at 25 degrees C there appears to be approx. 1 binding site for both nucleotides per 200 000 daltons of protein, although the NAD+-binding results are rather uncertain. Estimates of the dissociation constants of the E . NADH and E . NAD+ complexes under the stated conditions are also presented. Preparations of enzyme are sometimes found to contain significant amounts of very tightly bound NAD+ and NADH. The implications of these findings are discussed.
Full text
PDF


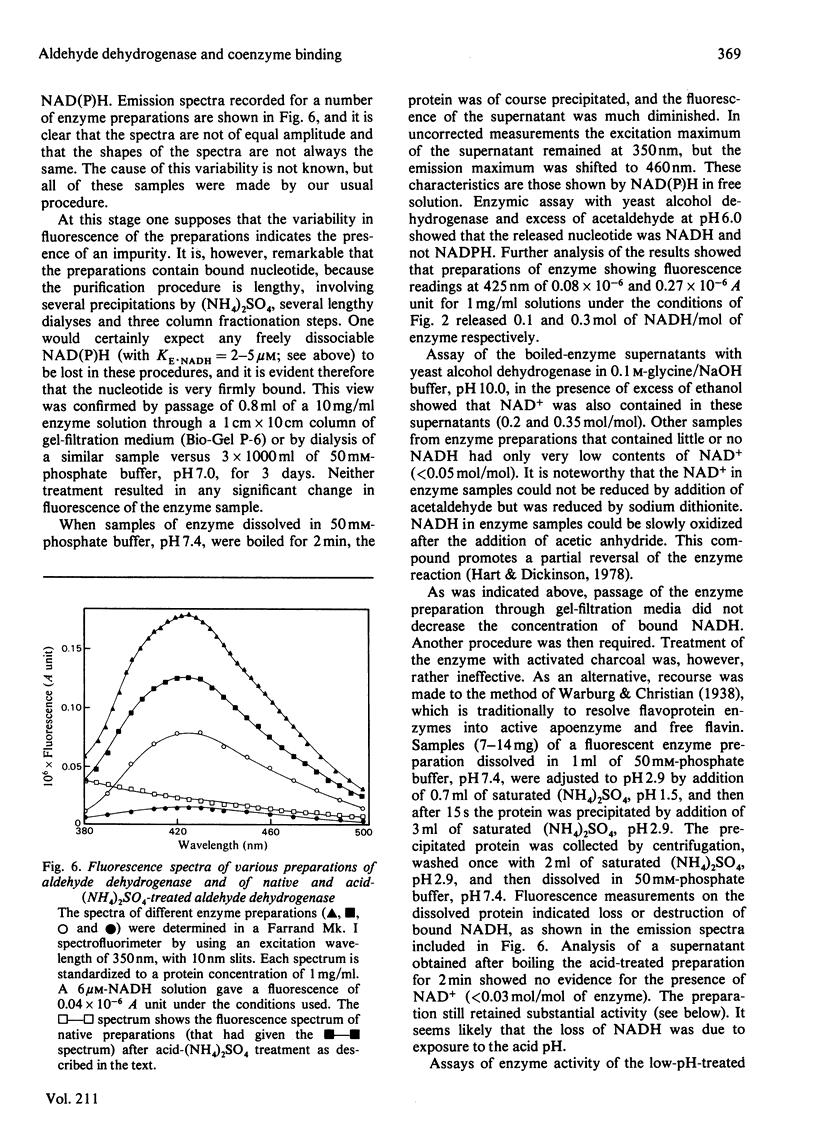
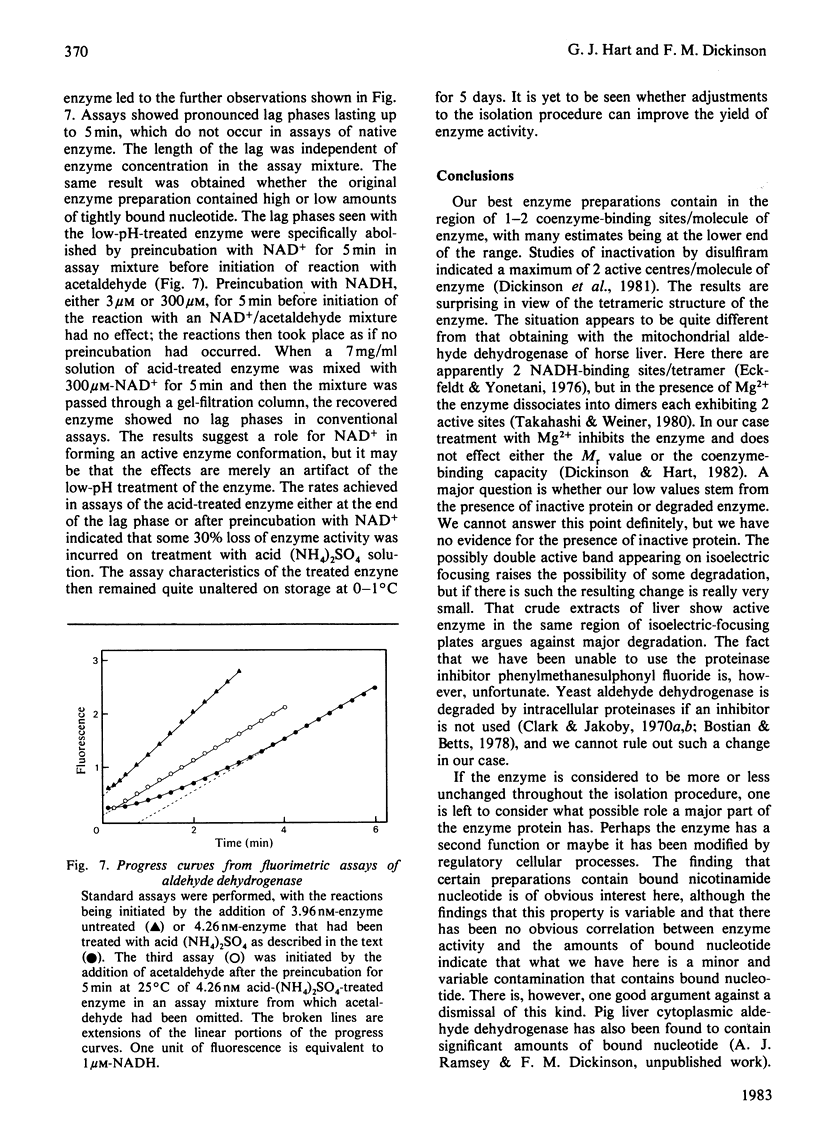

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnew K. E., Bennett A. F., Crow K. E., Greenway R. M., Blackwell L. F., Buckley P. D. A reinvestigation of the purity, isoelectric points and some kinetic properties of the aldehyde dehydrogenases from sheep liver. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep;119(1):79–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05579.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostian K. A., Betts G. F. Rapid purification and properties of potassium-activated aldehyde dehydrogenase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 1;173(3):773–786. doi: 10.1042/bj1730773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. F., Jakoby W. B. Yeast aldehyde dehydrogenase. 3. Preparation of three homogeneous species. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 25;245(22):6065–6071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. F., Jakoby W. B. Yeast aldehyde dehydrogenase. IV. Dissociation and reassociation of native and hybrid forms. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 25;245(22):6072–6077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow K. E., Kitson T. M., MacGibbon A. K., Batt R. D. Intracellular localisation and properties of aldehyde dehydrogenases from sheep liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 20;350(1):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALZIEL K. Kinetic studies of liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1962 Aug;84:244–254. doi: 10.1042/bj0840244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALZIEL K. Some observations on the preparation and properties of dihydronicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide. Biochem J. 1962 Aug;84:240–244. doi: 10.1042/bj0840240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALZIEL K. The purification of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and kinetic effects of nucleotide impurities. J Biol Chem. 1963 Apr;238:1538–1543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson F. M., Hart G. J. Effects of Mg2+, Ca2+ and Mn2+ on sheep liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1982 Aug 1;205(2):443–448. doi: 10.1042/bj2050443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson F. M., Hart G. J., Kitson T. M. The use of pH-gradient ion-exchange chromatography to separate sheep liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase from mitochondrial enzyme contamination, and observations on the interaction between the pure cytoplasmic enzyme and disulfiram. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 1;199(3):573–579. doi: 10.1042/bj1990573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckfeldt J. H., Yonetani T. Kinetics and mechanism of the F1 isozyme of horse liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Mar;173(1):273–281. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90260-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. I., Weiner H. Horse liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. I. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jan 10;247(1):260–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield N. J., Pietruszko R. Two aldehyde dehydrogenases from human liver. Isolation via affinity chromatography and characterization of the isozymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jul 8;483(1):35–45. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMEL J. P., DREYER W. J. Measurement of protein-binding phenomena by gel filtration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Oct 8;63:530–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. J., Dickinson F. M. Kinetic properties of highly purified preparations of sheep liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1982 Jun 1;203(3):617–627. doi: 10.1042/bj2030617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. J., Dickinson F. M. Partial reversal of the acetaldehyde and butyraldehyde oxidation reactions catalysed by aldehyde dehydrogenases from sheep liver. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):753–756. doi: 10.1042/bj1750753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. J., Dickinson F. M. Some properties of aldehyde dehydrogenase from sheep liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1977 May 1;163(2):261–267. doi: 10.1042/bj1630261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian R., Duncan S. The action of progesterone and diethylstilboestrol on the dehydrogenase and esterase activities of a purified aldehyde dehydrogenase from rabbit liver. Biochem J. 1977 Jan 1;161(1):123–130. doi: 10.1042/bj1610123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGibbon A. K., Blackwell L. F., Buckley P. D. Kinetics of sheep-liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jul 1;77(1):93–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11645.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGibbon A. K., Blackwell L. F., Buckley P. D. Pre-steady-state kinetic studies on cytoplasmic sheep liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 1;167(2):469–477. doi: 10.1042/bj1670469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGibbon A. K., Haylock S. J., Buckley P. D., Blackwell L. F. Kinetic studies on the esterase activity of cytoplasmic sheep liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1978 Jun 1;171(3):533–538. doi: 10.1042/bj1710533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGibbon A. K., Motion R. L., Crow K. E., Buckley P. D., Blackwell L. F. Purification and properties of sheep-liver aldehyde dehydrogenases. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun 1;96(3):585–595. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13073.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman C. R., Jakoby W. B. Yeast aldehyde dehydrogenase. I. Purification and crystallization. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 10;242(21):5019–5023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson R. A., Holbrook J. J. Equilibrium binding of nicotinamide nucleotides to lactate dehydrogenases. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;131(4):719–728. doi: 10.1042/bj1310719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Weiner H., Hu J. H. Increase in the stoichiometry of the functioning active sites of horse liver aldehyde dehydrogenase in the presence of magnesium ions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Dec;205(2):571–578. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Weiner H. Magnesium stimulation of catalytic activity of horse liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Changes in molecular weight and catalytic sites. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8206–8209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallari R. C., Pietruszko R. Kinetic mechanism of the human cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase E1. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Nov;212(1):9–19. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90338-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]