Abstract
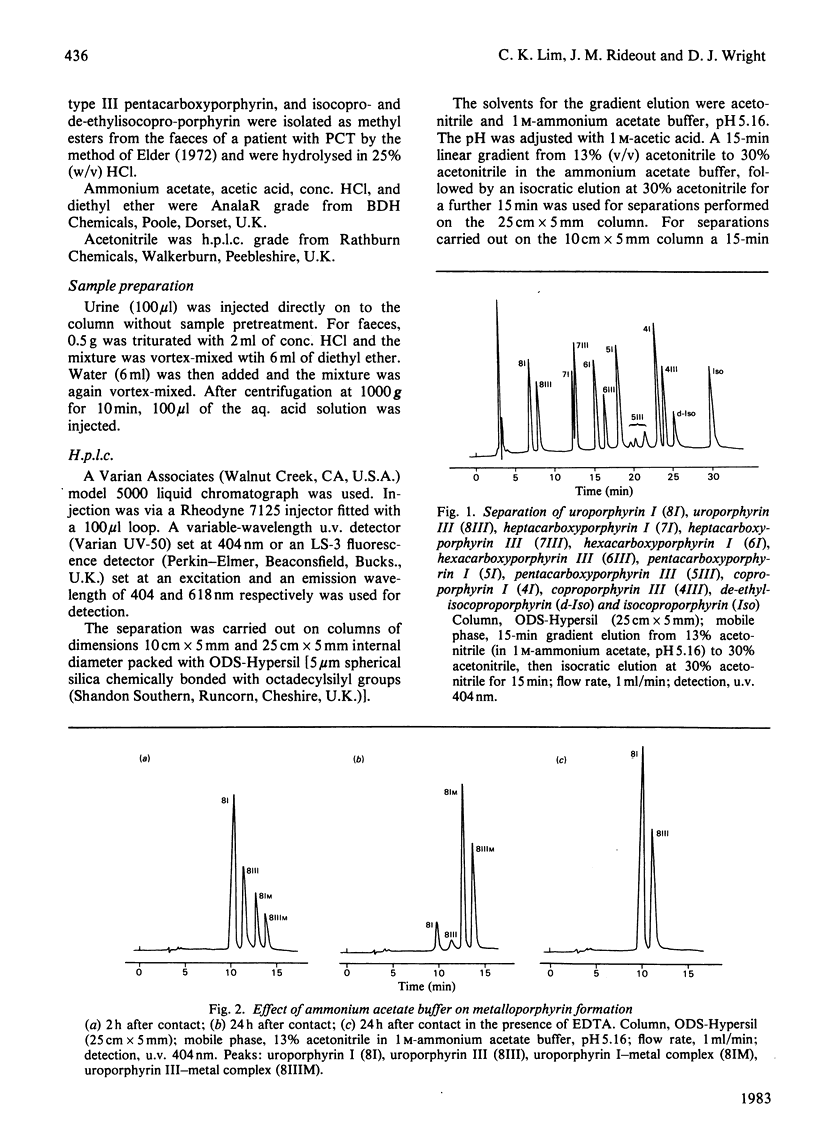
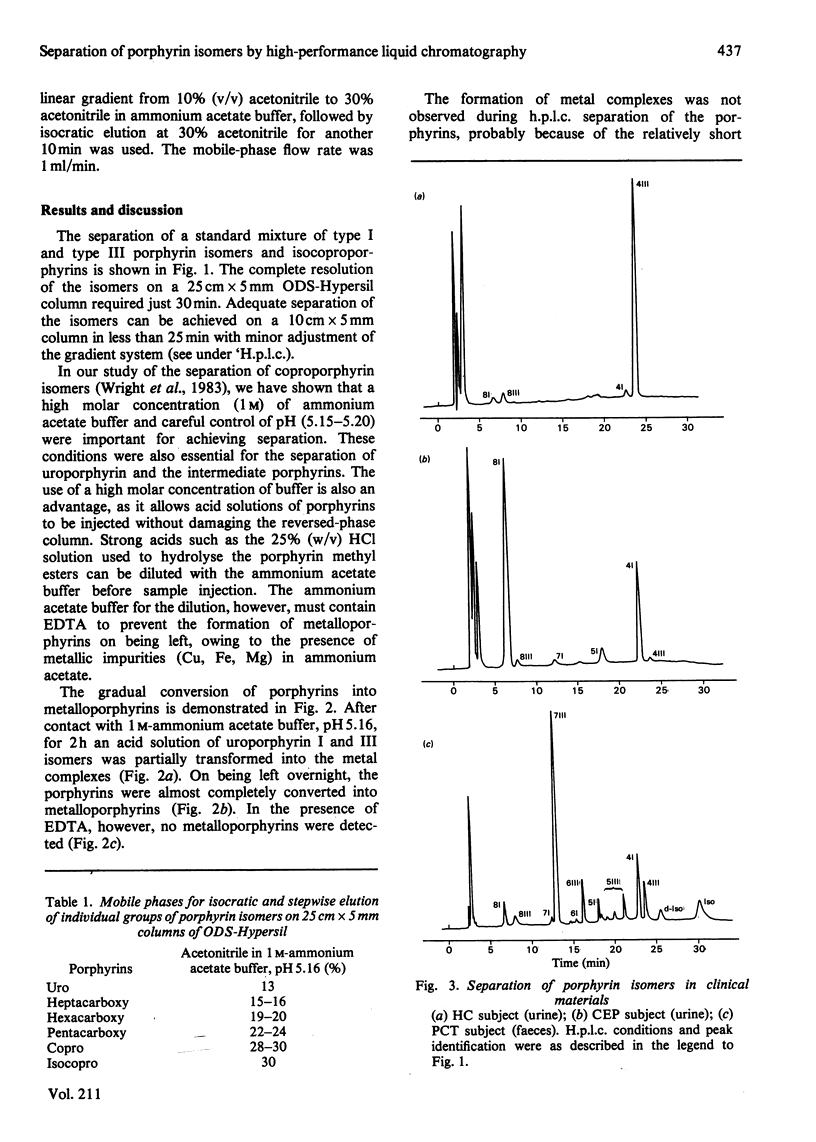
A reversed-phase gradient elution system is described for the simultaneous separation of the type I and type III isomers of 8-, 7-, 6-, 5- and 4-carboxylated porphyrins and isocoproporphyrins. The method, adaptable for isocratic and stepwise separation of individual groups of isomers, is also suitable for preparative isolation of pure porphyrins. The analyses of porphyrin isomers in the urine and faeces of porphyric patients are examples of applications.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Ezzer J., Rimington C., Shani M., Seligsohn U., Sheba C., Szeinberg A. Abnormal excretion of the isomers of urinary coproporphyrin by patients with Dubin-Johnson syndrome in Israel. Clin Sci. 1971 Jan;40(1):17–30. doi: 10.1042/cs0400017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORNFORD P. A., BENSON A. A qualitative and quantitative study of the separation of uroporphyrin octamethyl esters I and III by dioxan chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1963 Feb;10:141–157. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)92287-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder G. H. Differentiation of porphyria cutanea tarda symptomatica from other types of porphyria by measurement of isocoproporphyrin in faeces. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Aug;28(8):601–607. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.8.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder G. H., Evans J. O. A radiochemical method for the measurement of coproporphyrinogen oxidase and the utilization of substrates other than coproporphyrinogen III by the enzyme from rat liver. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 1;169(1):205–214. doi: 10.1042/bj1690205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder G. H. Identification of a group of tetracarboxylate porphyrins, containing one acetate and three propionate -substituents, in faeces from patients with symptomatic cutaneous hepatic porphyria and from rats with porphyria due to hexachlorobenzene. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(4):877–891. doi: 10.1042/bj1260877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. H., Sancovich H. A., Ferramola A. M., Evans N., Games D. E., Matlin S. A., Elder G. H., Smith S. G. Macrocyclic intermediates in the biosynthesis of porphyrins. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Feb 5;273(924):191–206. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1976.0009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskelo P., Mustajoki P. Altered coproporhyrin-isomer excretion in patients with the Dubin-Johnson syndrome. Int J Biochem. 1980;12(5-6):975–978. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(80)90195-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schermuly E., Doss M. Separation of the coprophorphyrin isomers I and III by thin-layer chromatography. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem. 1975 Jul;13(7):299–304. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1975.13.7.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. G., Rao K. R., Jackson A. H. The prophyrins of normal human urine, with a comparison of the excretion pattern in porphyria cutanea tarda. Int J Biochem. 1980;12(5-6):1081–1084. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(80)90216-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolkoff A. W., Wolpert E., Pascasio F. N., Arias I. M. Rotor's syndrome. A distinct inheritable pathophysiologic entity. Am J Med. 1976 Feb;60(2):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90426-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. J., Rideout J. M., Lim C. K. High-performance liquid chromatography of coproporphyrin isomers. Biochem J. 1983 Feb 1;209(2):553–555. doi: 10.1042/bj2090553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


