Abstract
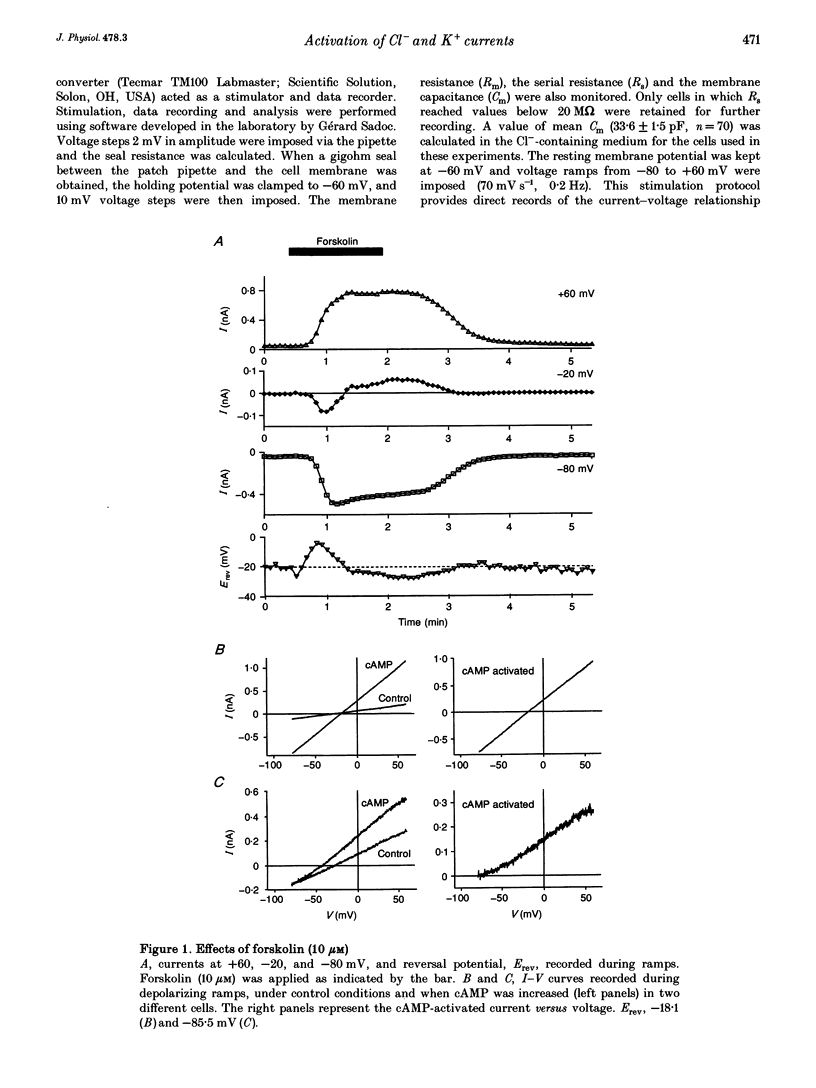
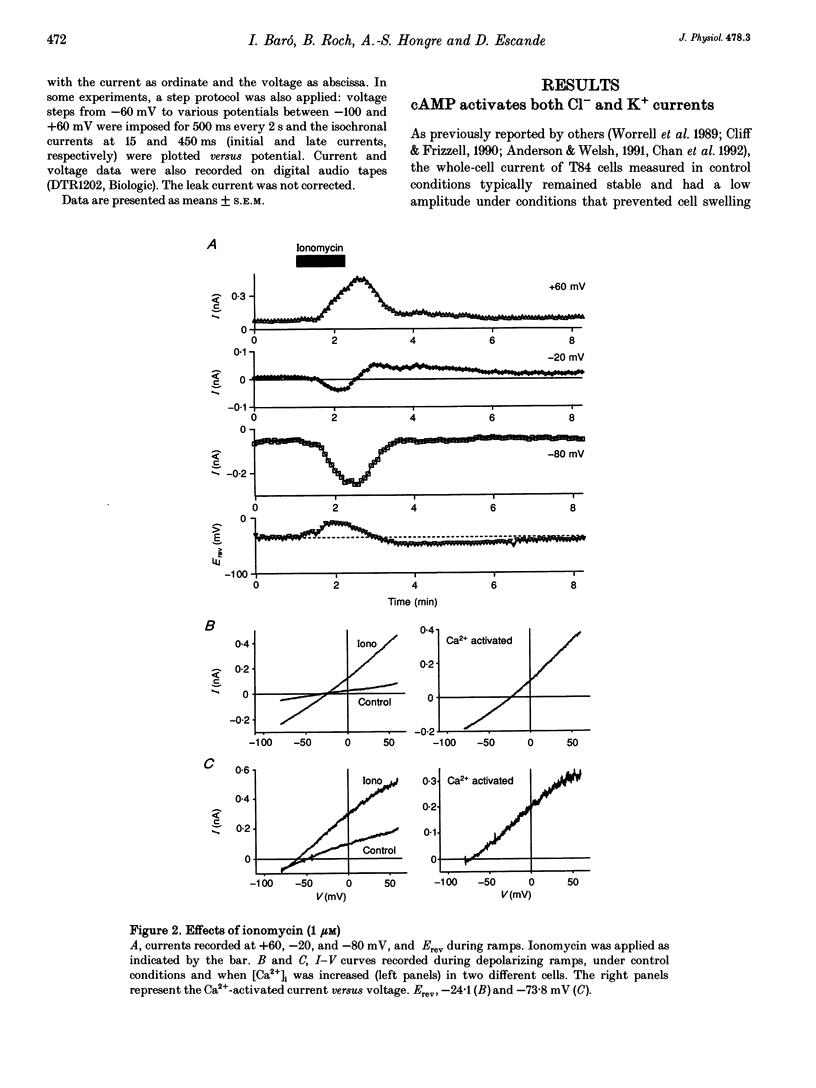
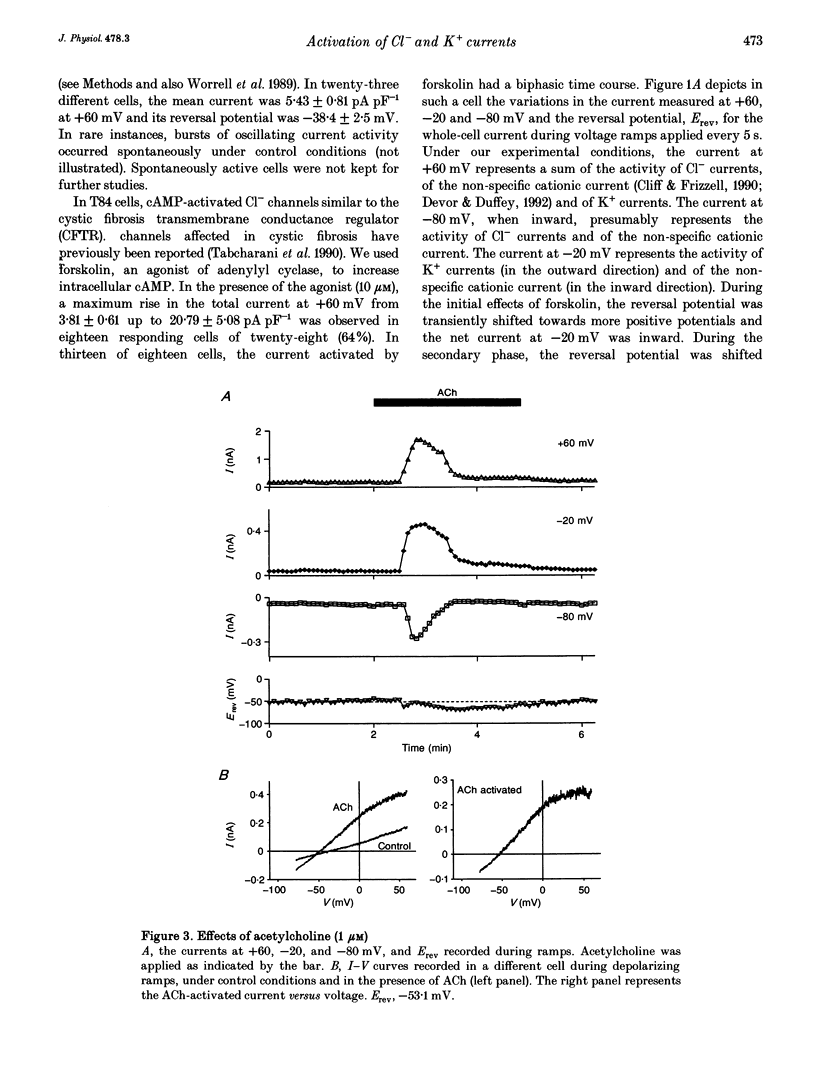
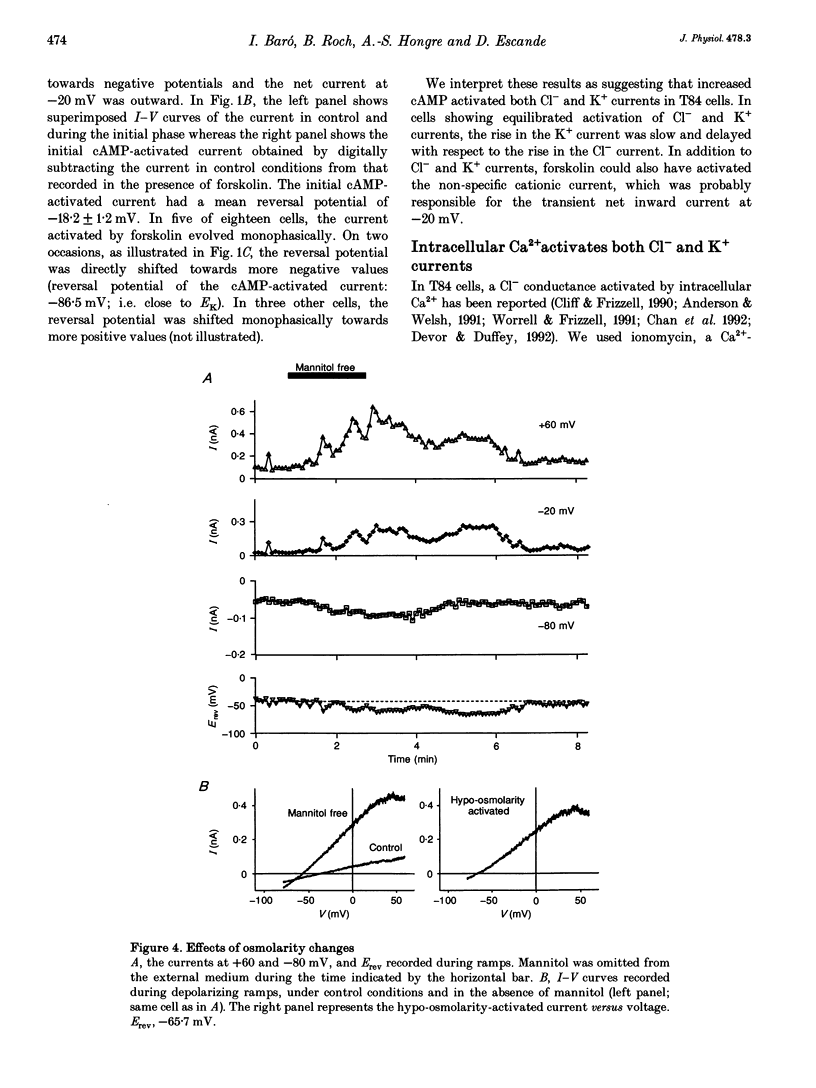
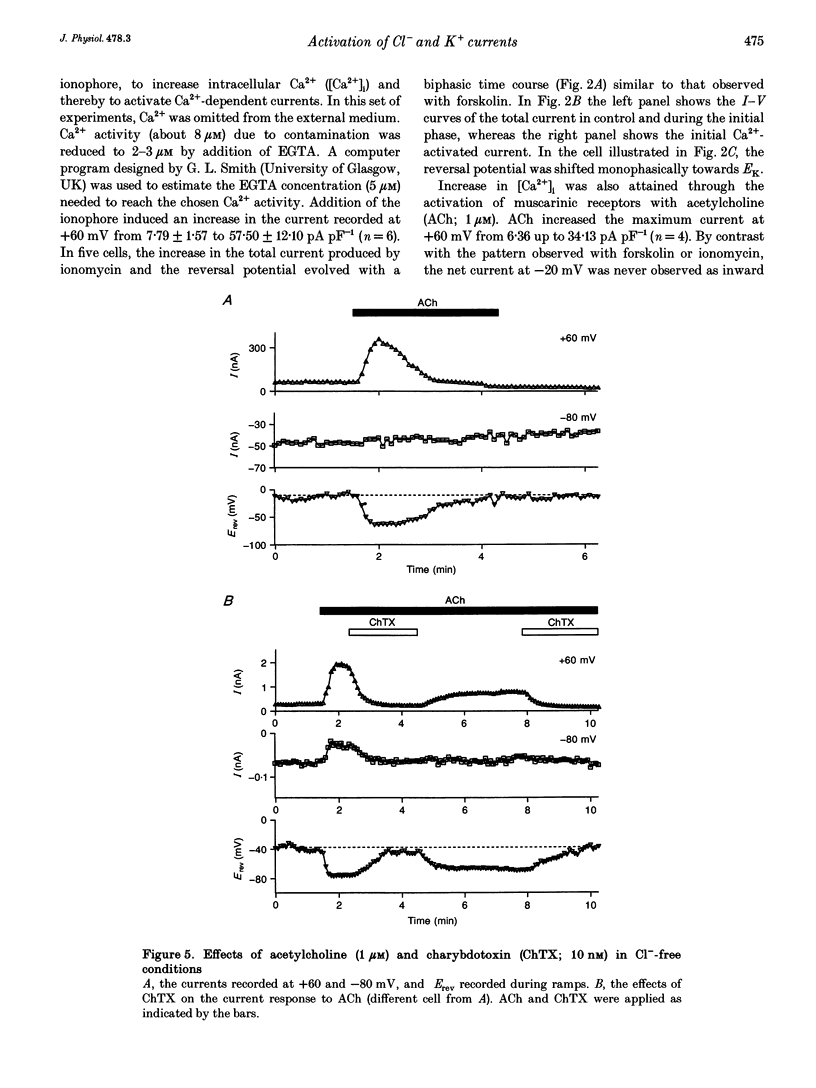
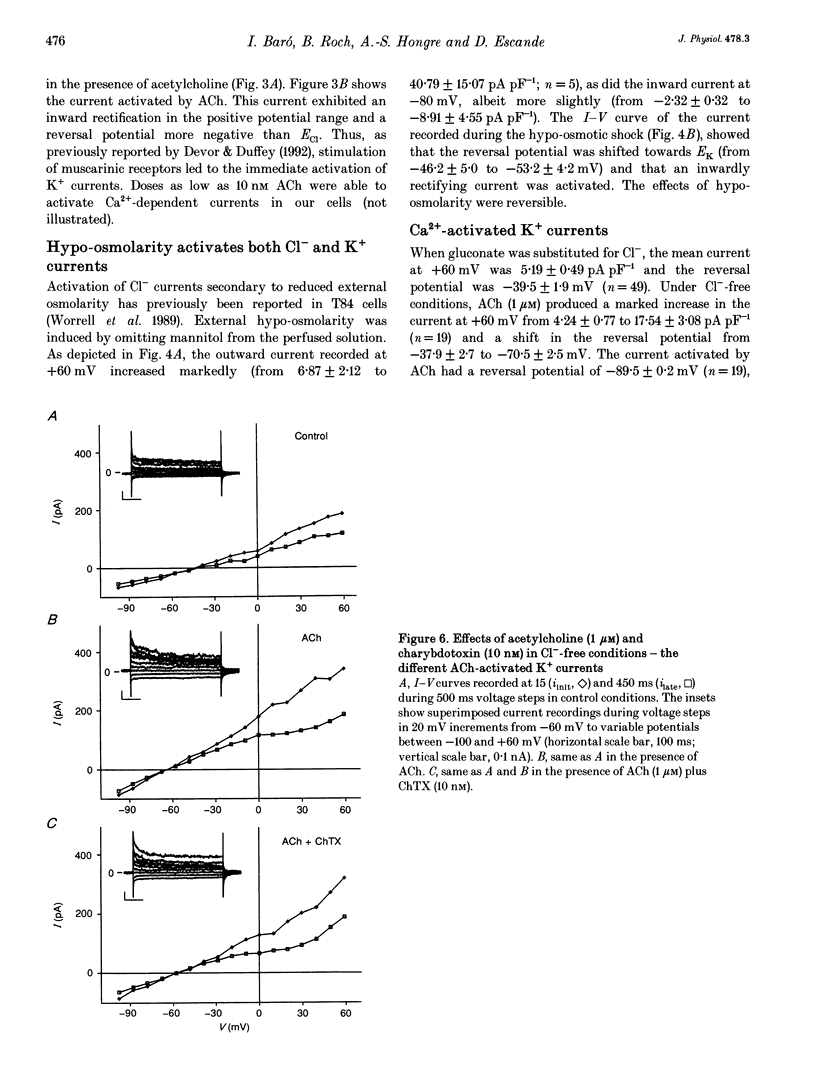
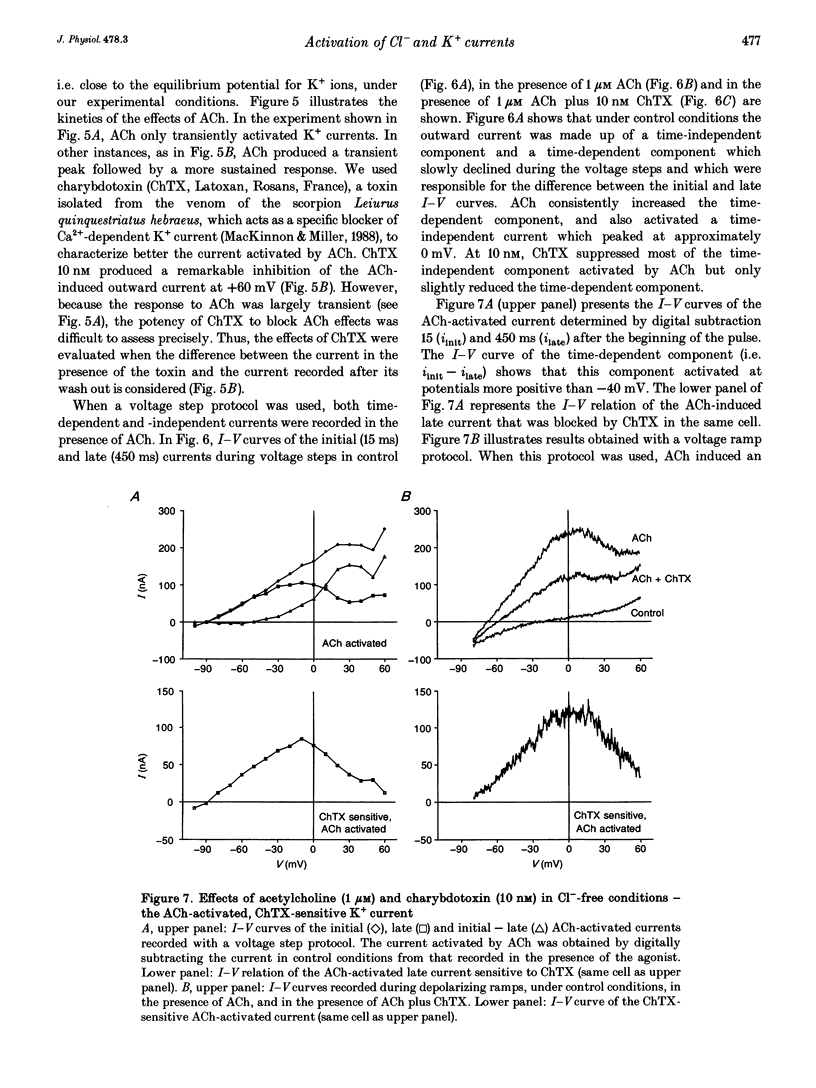
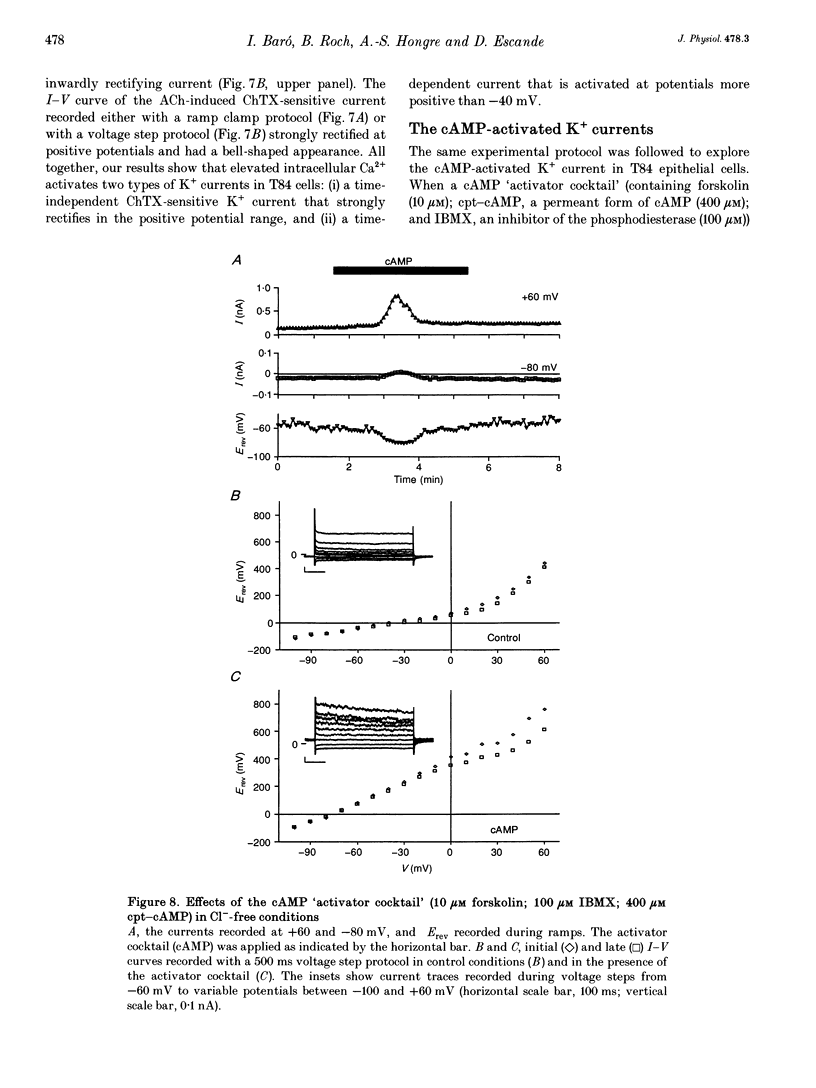
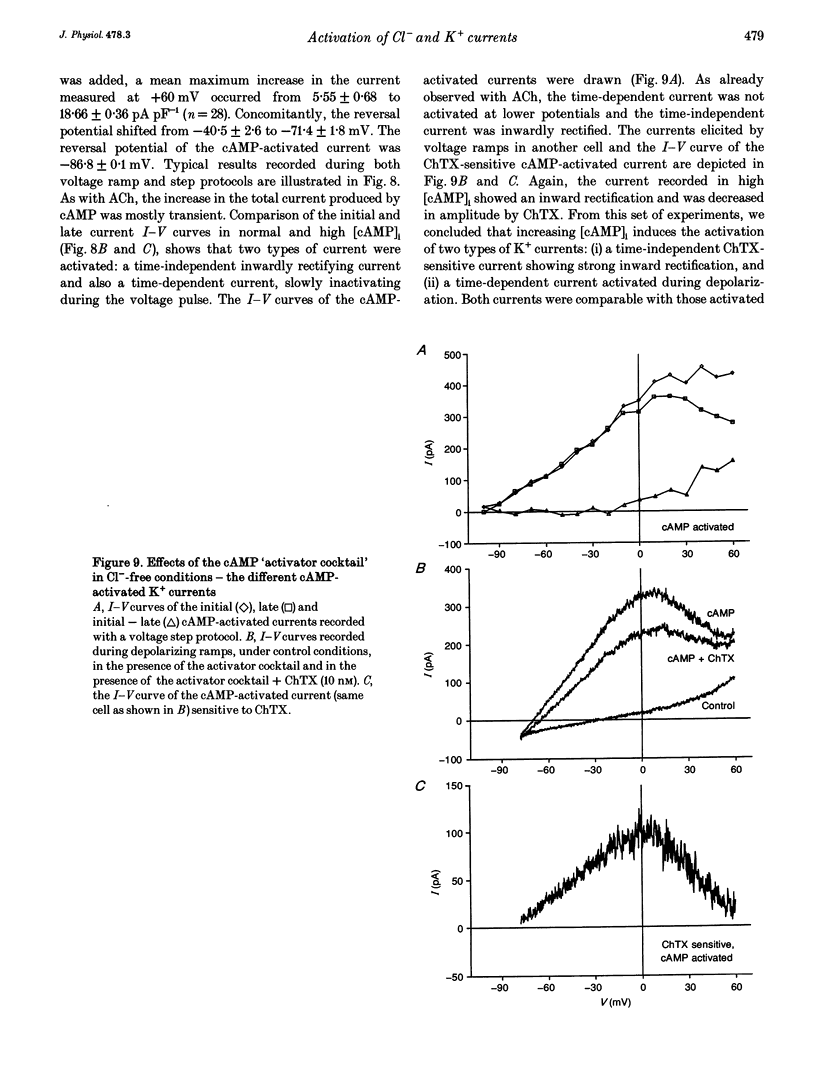
1. Whole-cell currents were investigated in the model salt-secreting epithelium, human T84 cell line, by means of the perforated patch-clamp technique. In the control extracellular medium containing Cl-, depolarizing voltage ramps evoked current responses which peaked at 5.43 +/- 0.81 pA pF-1 at +60 mV and had a reversal potential (Erev) of -38.4 +/- 2.5 mV (n = 23). 2. Activation of the cAMP pathway with forskolin increased the current at +60 mV from 3.81 +/- 0.61 to 20.79 +/- 5.08 pA pF-1 (n = 18). In thirteen cells, Erev was initially shifted towards positive potentials (Erev of the cAMP-activated initial current was -18.2 +/- 1.2 mV) and subsequently shifted towards more negative potentials, consistent with the activation of both Cl- and K+ currents during cAMP stimulation. 3. Increasing the intracellular Ca2+ concentration, [Ca2+]i, with ionomycin (1 microM) or with acetylcholine (1 microM), increased the current at +60 mV from 7.79 +/- 1.57 to 57.50 +/- 12.10 pA pF-1 (n = 6) and from 6.36 to 34.13 pA pF-1 (n = 4), respectively. With both agonists, Erev was shifted either towards the reversal potential for potassium, EK, or towards the reversal potential for chloride, ECl, depending on the cell. 4. In the absence of chloride ions (gluconate substituted), stimulation of the Ca2+ pathway activated a time-independent outward current of large amplitude. This current exhibited inward rectification at positive voltages, reverted at -89.5 +/- 0.2 mV and was markedly reduced by charybdotoxin (10 nM), a specific blocker of Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels. When a voltage step protocol was used, increased [Ca2+]i also activated an outward current at potentials more positive than -40 mV which slowly relaxed during depolarizing steps. 5. The activation of both (i) a time-dependent inwardly rectifying charybdotoxin-sensitive K+ current, and (ii) a time-dependent slowly inactivating current was also produced by cAMP stimulation. 6. We concluded that (i) in the T84 epithelial cells, both Cl- and K+ currents are concomitantly increased by secretagogue stimulation, and (ii) two different types of K+ conductances are activated by either the cAMP or the intracellular Ca2+ secreting pathways.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. P., Welsh M. J. Calcium and cAMP activate different chloride channels in the apical membrane of normal and cystic fibrosis epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6003–6007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bear C. E. A nonselective cation channel in rat liver cells is activated by membrane stretch. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 1):C421–C428. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.3.C421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan H. C., Kaetzel M. A., Nelson D. J., Hazarika P., Dedman J. R. Antibody against a cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-derived synthetic peptide inhibits anion currents in human colonic cell line T84. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8411–8416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase H. S., Jr, Wong S. M. Isoproterenol and cyclic AMP increase intracellular free [Ca] in MDCK cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 2):F374–F384. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.3.F374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cliff W. H., Frizzell R. A. Separate Cl- conductances activated by cAMP and Ca2+ in Cl(-)-secreting epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4956–4960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devor D. C., Duffey M. E. Carbachol induces K+, Cl-, and nonselective cation conductances in T84 cells: a perforated patch-clamp study. Am J Physiol. 1992 Oct;263(4 Pt 1):C780–C787. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.4.C780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devor D. C., Simasko S. M., Duffey M. E. Carbachol induces oscillations of membrane potassium conductance in a colonic cell line, T84. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 1):C318–C326. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.2.C318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., Cohn J., Beuerlein G. Multiple calcium-mediated effector mechanisms regulate chloride secretory responses in T84-cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 1):C1224–C1230. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.6.C1224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., Pandol S. J. Mechanism of chloride secretion induced by carbachol in a colonic epithelial cell line. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):348–354. doi: 10.1172/JCI112311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Shapiro A. B., Rao M. C., Layden T. J. In vivo evidence of altered chloride but not potassium secretion in cystic fibrosis rectal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1991 Oct;101(4):1012–1019. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90728-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. A., Greenwell J. R., Garton A. J., Argent B. E. Regulation of maxi-K+ channels on pancreatic duct cells by cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation. J Membr Biol. 1990 May;115(3):203–215. doi: 10.1007/BF01868636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggino S. E., Suarez-Isla B. A., Guggino W. B., Sacktor B. Forskolin and antidiuretic hormone stimulate a Ca2+-activated K+ channel in cultured kidney cells. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 2):F448–F455. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.249.3.F448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halm D. R., Frizzell R. A. Anion permeation in an apical membrane chloride channel of a secretory epithelial cell. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Mar;99(3):339–366. doi: 10.1085/jgp.99.3.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazama A., Okada Y. Ca2+ sensitivity of volume-regulatory K+ and Cl- channels in cultured human epithelial cells. J Physiol. 1988 Aug;402:687–702. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Marty A. Muscarinic activation of ionic currents measured by a new whole-cell recording method. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Aug;92(2):145–159. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorissen M., Vereecke J., Carmeliet E., Van den Berghe H., Cassiman J. J. Identification of a voltage- and calcium-dependent non-selective cation channel in cultured adult and fetal human nasal epithelial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Feb;415(5):617–623. doi: 10.1007/BF02583515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kachintorn U., Vongkovit P., Vajanaphanich M., Dinh S., Barrett K. E., Dharmsathaphorn K. Dual effects of a phorbol ester on calcium-dependent chloride secretion by T84 epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jan;262(1 Pt 1):C15–C22. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.1.C15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunzelmann K., Pavenstädt H., Beck C., Unal O., Emmrich P., Arndt H. J., Greger R. Characterization of potassium channels in respiratory cells. I. General properties. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Jul;414(3):291–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00584629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M., Nairn A. C., Guggino S. E. cGMP-dependent protein kinase regulation of a chloride channel in T84 cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 1):C1304–C1312. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.5.C1304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Miller C. Mechanism of charybdotoxin block of the high-conductance, Ca2+-activated K+ channel. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Mar;91(3):335–349. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.3.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel K. G., Dharmsathaphorn K., McRoberts J. A. Characterization of a cyclic AMP-activated Cl-transport pathway in the apical membrane of a human colonic epithelial cell line. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):704–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel K. G., McRoberts J. A., Beuerlein G., Foster E. S., Dharmsathaphorn K. Ba2+ inhibition of VIP- and A23187-stimulated Cl- secretion by T84 cell monolayers. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 1):C486–C494. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.3.C486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann J. D., Bhalla R. C., Welsh M. J. Release of intracellular calcium by two different second messengers in airway epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 1):L116–L124. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.2.L116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann J. D., Welsh M. J. Regulation of Cl- and K+ channels in airway epithelium. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:115–135. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.000555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwan G. T., Brown C. D., Hirst B. H., Simmons N. L. Hypo-osmolar stimulation of transepithelial Cl- secretion in cultured human T84 intestinal epithelial layers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jun 10;1135(2):180–183. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90135-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRoberts J. A., Beuerlein G., Dharmsathaphorn K. Cyclic AMP and Ca2+-activated K+ transport in a human colonic epithelial cell line. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14163–14172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitschke R., Leipziger J., Greger R. Intracellular Ca2+ transients in HT29 cells induced by hypotonic cell swelling. Pflugers Arch. 1993 May;423(3-4):274–279. doi: 10.1007/BF00374406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinton P. M. Cystic fibrosis: a disease in electrolyte transport. FASEB J. 1990 Jul;4(10):2709–2717. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.10.2197151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reenstra W. W. Inhibition of cAMP- and Ca-dependent Cl- secretion by phorbol esters: inhibition of basolateral K+ channels. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jan;264(1 Pt 1):C161–C168. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.1.C161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorofsky S. R., Field M., Fozzard H. A. Mechanism of Cl secretion in canine trachea: changes in intracellular chloride activity with secretion. J Membr Biol. 1984;81(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF01868804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabcharani J. A., Low W., Elie D., Hanrahan J. W. Low-conductance chloride channel activated by cAMP in the epithelial cell line T84. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 17;270(1-2):157–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81257-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venglarik C. J., Bridges R. J., Frizzell R. A. A simple assay for agonist-regulated Cl and K conductances in salt-secreting epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 1):C358–C364. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.2.C358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. A., Cozens A. L., Schulman H., Gruenert D. C., Stryer L., Gardner P. Activation of chloride channels in normal and cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells by multifunctional calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):793–796. doi: 10.1038/349793a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. I., Barrett K. E., Huott P. A., Beuerlein G., Kagnoff M. F., Dharmsathaphorn K. Immune-related intestinal Cl- secretion. I. Effect of histamine on the T84 cell line. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jan;254(1 Pt 1):C53–C62. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.1.C53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J., Liedtke C. M. Chloride and potassium channels in cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):467–470. doi: 10.1038/322467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weymer A., Huott P., Liu W., McRoberts J. A., Dharmsathaphorn K. Chloride secretory mechanism induced by prostaglandin E1 in a colonic epithelial cell line. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1828–1836. doi: 10.1172/JCI112175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. M., DeBell M. C., Chase H. S., Jr Cell swelling increases intracellular free [Ca] in cultured toad bladder cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 2):F292–F296. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.2.F292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worrell R. T., Butt A. G., Cliff W. H., Frizzell R. A. A volume-sensitive chloride conductance in human colonic cell line T84. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 1):C1111–C1119. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.6.C1111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worrell R. T., Frizzell R. A. CaMKII mediates stimulation of chloride conductance by calcium in T84 cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Apr;260(4 Pt 1):C877–C882. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.4.C877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


