Abstract
1. This study was designed to determine whether cutaneous receptors in the hand exert reflex effects on fusimotor neurones innervating relaxed muscles. Recordings were made from fifty-four muscle spindle afferents in the radial nerve while the arm was held relaxed in a supporting frame. Cutaneous afferents were activated by trains of stimuli at non-noxious levels to the superficial radial nerve or to the palmar surface of the fingers. 2. For the population of muscle spindle afferents, the mean discharge rate was 7.1 +/- 6.4 Hz (range 0-24 Hz). Thirty-three per cent had no background discharge, and this occurred significantly more often in finger extensors than wrist extensors. 3. Trains of cutaneous stimuli produced no change in the discharge rates of the majority of spindle endings irrespective of whether the spindle afferent had a background discharge or was given one by muscle stretch. However, with two of forty afferents, the stimuli produced an increase in discharge at latencies of 135 and 155 ms. 4. With a further fourteen muscle spindle endings, the dynamic responses to stretch were measured 100-400 ms after the trains of cutaneous stimuli. For four spindle afferents there was a statistically significant change in the dynamic response to stretch occurring at conditioned-stretch intervals of 100-200 ms. For two afferents the dynamic response decreased by 17 and 26% and for two others it increased by about 24 and 37%. 5. While these results support the view that the level of background fusimotor drive is low in the relaxed state, they suggest that there is some dynamic fusimotor drive to completely relaxed muscles operating on the human hand, and that this drive can be altered reflexly by cutaneous afferent inputs from the hand.
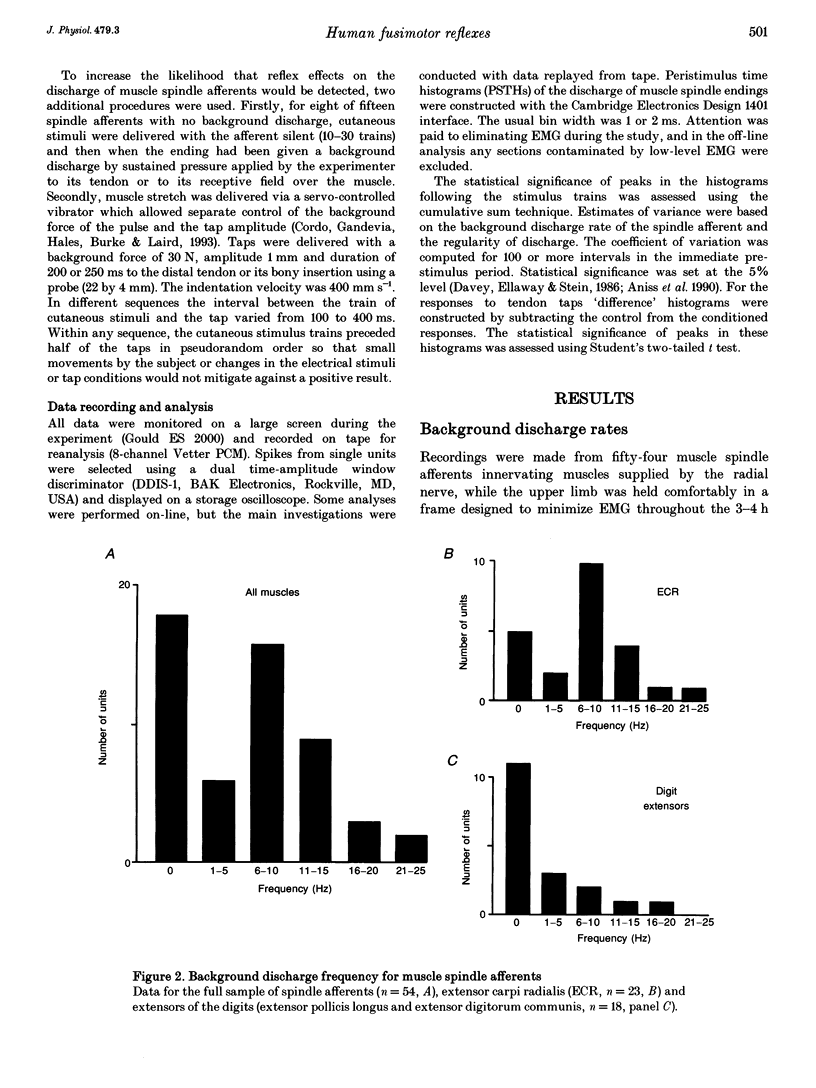
Full text
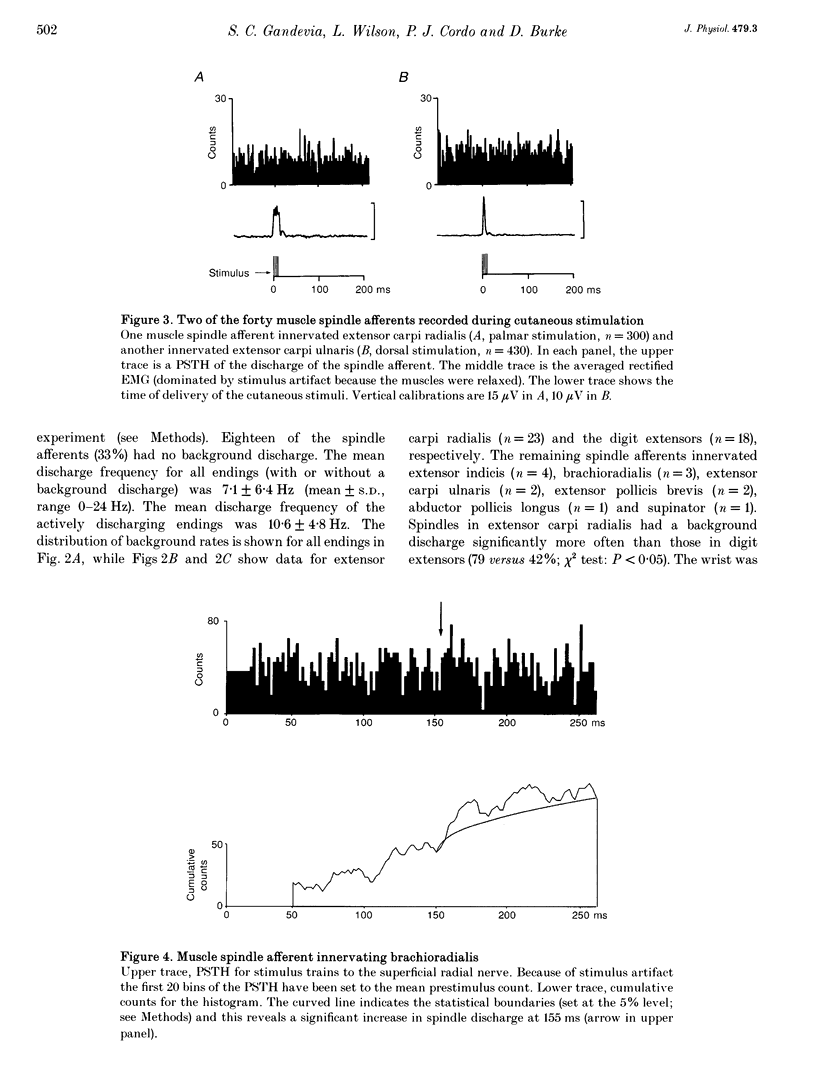
PDF



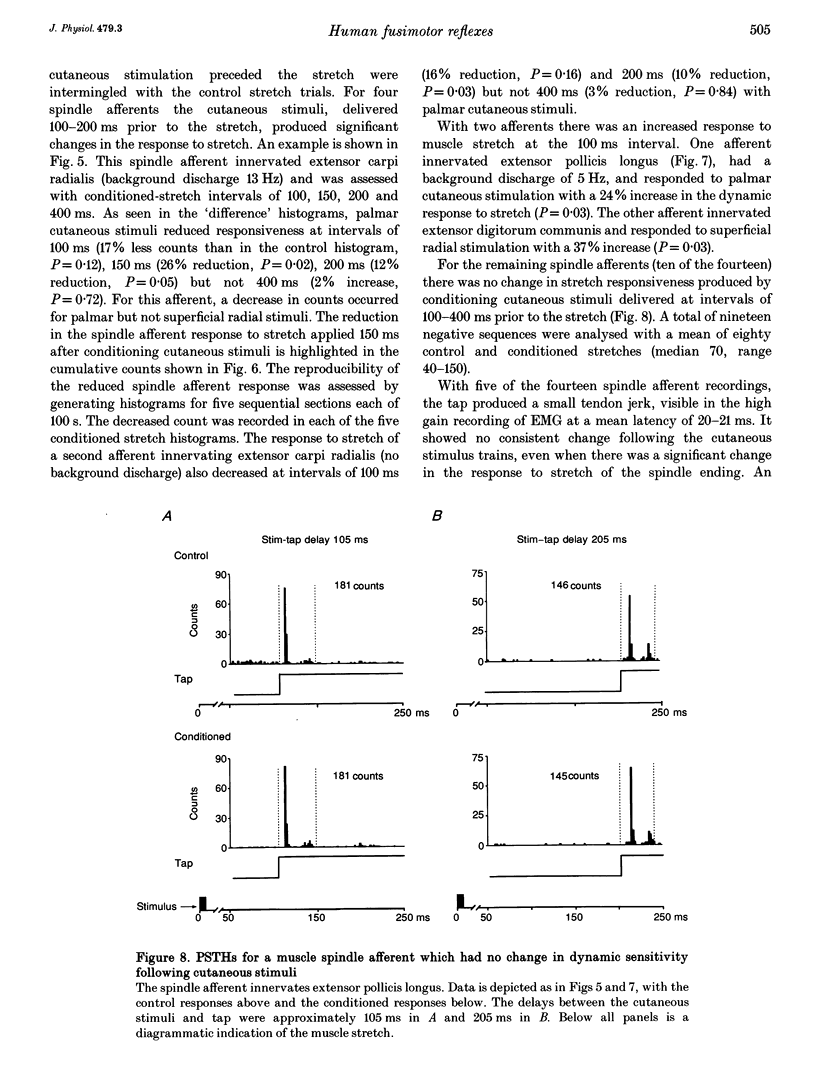



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aniss A. M., Diener H. C., Hore J., Burke D., Gandevia S. C. Reflex activation of muscle spindles in human pretibial muscles during standing. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Aug;64(2):671–679. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.64.2.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aniss A. M., Gandevia S. C., Burke D. Reflex changes in muscle spindle discharge during a voluntary contraction. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Mar;59(3):908–921. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.59.3.908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelberg B., Johansson H., Kalistratov G. The influence of group II muscle afferents and low threshold skin afferents on dynamic fusimotor neurones to the triceps surae of the cat. Brain Res. 1977 Aug 19;132(1):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90713-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessou P., Laporte Y., Pagés B. A method of analysing the responses of spindle primary endings to fusimotor stimulation. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):37–45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Aniss A. M., Gandevia S. C. In-parallel and in-series behavior of human muscle spindle endings. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Aug;58(2):417–426. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.58.2.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Gracies J. M., Mazevet D., Meunier S., Pierrot-Deseilligny E. Convergence of descending and various peripheral inputs onto common propriospinal-like neurones in man. J Physiol. 1992 Apr;449:655–671. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. The activity of human muscle spindle endings in normal motor behavior. Int Rev Physiol. 1981;25:91–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caccia M. R., McComas A. J., Upton A. R., Blogg T. Cutaneous reflexes in small muscles of the hand. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1973 Dec;36(6):960–977. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.36.6.960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheney P. D., Preston J. B. Classification of fusimotor fibers in the primate. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Jan;39(1):9–19. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordo P., Gandevia S. C., Hales J. P., Burke D., Laird G. Force and displacement-controlled tendon vibration in humans. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1993 Feb;89(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0168-5597(93)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey N. J., Ellaway P. H. Facilitation of individual gamma-motoneurones by the discharge of single slowly adapting type 1 mechanoreceptors in cats. J Physiol. 1989 Apr;411:97–114. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey N. J., Ellaway P. H., Stein R. B. Statistical limits for detecting change in the cumulative sum derivative of the peristimulus time histogram. J Neurosci Methods. 1986 Aug;17(2-3):153–166. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(86)90068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmedt J. E., Cheron G. Central somatosensory conduction in man: neural generators and interpeak latencies of the far-field components recorded from neck and right or left scalp and earlobes. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1980 Dec;50(5-6):382–403. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(80)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELDRED E., HAGBARTH K. E. Facilitation and inhibition of gamma efferents by stimulation of certain skin areas. J Neurophysiol. 1954 Jan;17(1):59–65. doi: 10.1152/jn.1954.17.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell W. R., Gandevia S. C., McCloskey D. I. The role of joint receptors in human kinaesthesia when intramuscular receptors cannot contribute. J Physiol. 1987 May;386:63–71. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., Kilbreath S. L. Accuracy of weight estimation for weights lifted by proximal and distal muscles of the human upper limb. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:299–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., Macefield G., Burke D., McKenzie D. K. Voluntary activation of human motor axons in the absence of muscle afferent feedback. The control of the deafferented hand. Brain. 1990 Oct;113(Pt 5):1563–1581. doi: 10.1093/brain/113.5.1563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., Macefield V. G., Bigland-Ritchie B., Gorman R. B., Burke D. Motoneuronal output and gradation of effort in attempts to contract acutely paralysed leg muscles in man. J Physiol. 1993 Nov;471:411–427. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., McCloskey D. I. Effects of related sensory inputs on motor performances in man studied through changes in perceived heaviness. J Physiol. 1977 Nov;272(3):653–672. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., Miller S., Aniss A. M., Burke D. Reflex influences on muscle spindle activity in relaxed human leg muscles. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Jul;56(1):159–170. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.56.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnett R., Stephens J. A. Changes in the recruitment threshold of motor units produced by cutaneous stimulation in man. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:463–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillner S. Supraspinal and segmental control of static and dynamic gamma-motoneurones in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1969;327:1–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C., PAINTAL A. S. Spinal reflex regulation of fusimotor neurones. J Physiol. 1958 Sep 23;143(2):195–212. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C. The reflex activity of mammalian small-nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1951 Dec 28;115(4):456–469. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenner J. R., Stephens J. A. Cutaneous reflex responses and their central nervous pathways studied in man. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:405–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson R. S., Westling G. Roles of glabrous skin receptors and sensorimotor memory in automatic control of precision grip when lifting rougher or more slippery objects. Exp Brain Res. 1984;56(3):550–564. doi: 10.1007/BF00237997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbreath S. L., Gandevia S. C. Independent digit control: failure to partition perceived heaviness of weights lifted by digits of the human hand. J Physiol. 1991 Oct;442:585–599. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maertens de Noordhout A., Rothwell J. C., Day B. L., Dressler D., Nakashima K., Thompson P. D., Marsden C. D. Effect of digital nerve stimuli on responses to electrical or magnetic stimulation of the human brain. J Physiol. 1992 Feb;447:535–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmgren K., Pierrot-Deseilligny E. Inhibition of neurones transmitting non-monosynaptic Ia excitation to human wrist flexor motoneurones. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:765–783. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Rothwell J. C., Traub M. M. Effect of thumb anaesthesia on weight perception, muscle activity and the stretch reflex in man. J Physiol. 1979 Sep;294:303–315. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon B., Burke D. Identification of muscle spindle afferents during in vivo recordings in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1980 May;48(5):606–608. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(80)90297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J., Pierrot-Deseilligny E. Pattern of cutaneous inhibition of the propriospinal-like excitation to human upper limb motoneurones. J Physiol. 1991 Mar;434:169–182. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordh E., Hulliger M., Vallbo A. B. The variability of inter-spike intervals of human spindle afferents in relaxed muscles. Brain Res. 1983 Jul 18;271(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91367-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribot E., Roll J. P., Vedel J. P. Efferent discharges recorded from single skeletomotor and fusimotor fibres in man. J Physiol. 1986 Jun;375:251–268. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbo A. B. Afferent discharge from human muscle spindles in non-contracting muscles. Steady state impulse frequency as a function of joint angle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Feb;90(2):303–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbo A. B., Hagbarth K. E., Torebjörk H. E., Wallin B. G. Somatosensory, proprioceptive, and sympathetic activity in human peripheral nerves. Physiol Rev. 1979 Oct;59(4):919–957. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.4.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



